EAST结构分析+pytorch源码实现
文章目录
友情提示
友情提示不针对第三方,为了给读者更好的体验
一. U-Net的前车之鉴
在介绍EAST网络之前我们先介绍一下前面的几个网络,看看这个EAST网络怎么来的?为什么来的?
当然这里的介绍仅仅是引出EAST而不是详细的讲解其他网络,有需要的读者可以去看看这三个优秀网络。
1.1 FCN网络结构
FCN网络,在之前FCN从原理到代码的理解已经详细分析了,有需要的可以去看看,顺便跑一跑代码。
- 网络的由来
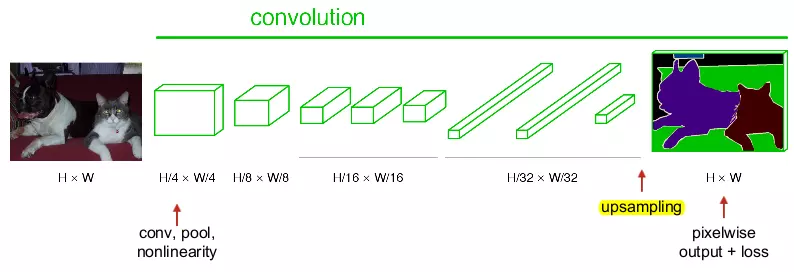
不管是识别(传统机器学习、CNN)还是检测(SSD、YOLO等),都只是基于大块的特征进行的,检测之后都是以长方形去表示检测结果,由于这是其算法内部回归的结果导致,而且feature map经过卷积一直减小,如果强行进行
256X256到512X512的插值,那么结果可以想象,边界非常不好。
那么如何实现图1-1所示的结果呢?把每个像素都进行分割?
- 网络的成果
FCN给出的方法是使用反卷积进行上采样操作,使得经过CNN之后减小的图能够恢复大小。
当然作者还提出一个好方法,不同的feature map进行组合,使得感受野进行扩充。
注释:笔者认为使用反卷积有两个作用,其一是使得计算LOSS比较方便,标签和结果可以直接进行计算。其二是可以进行参数的学习,更为智能化。
1.2 U-NET网络
U-net网络之前没怎么看过,现在也仅仅是大概看了论文和相关资料,内部实现不是很了解。
- 网络的由来
FCN完全可以做到基于像素点的分割,为什么还要这个U-net网络啊?
FCN网络检测的效果还可以,但是其边缘的处理就特别的差。虽然说多个层进行合并,但是合并的内容杂乱无章,导致最后的信息没有完全得到。总的来说
FCN分割的效果不够,精度也不够。
- 网络的成果
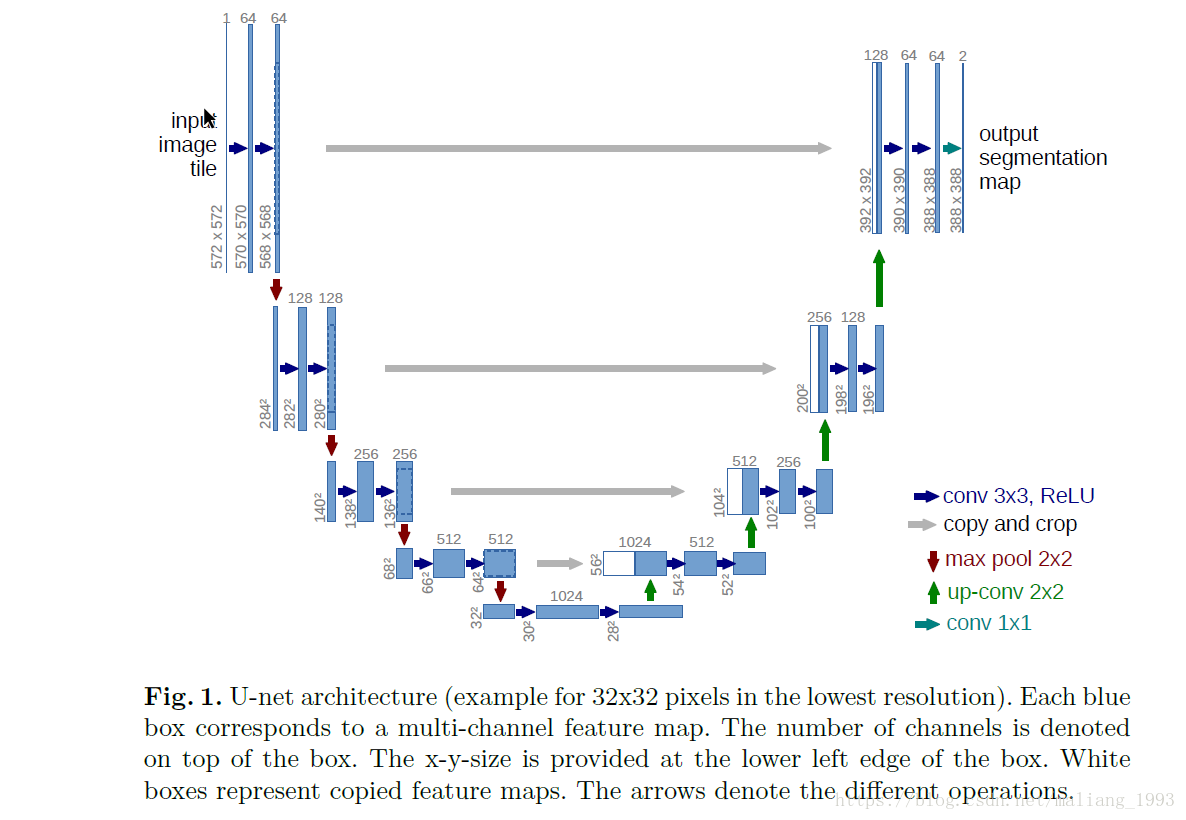
U-net提出了对称的网络结构,使得网络参数的学习效果更好(为什么对称网络学习更好,这个理解不透,如果是结果再放大一倍使得不对称不也一样吗?感觉还是网络结构设计的好,而不是对称)不同feature map合并的方式更加优化,使得在边缘分割(细节)上更加优秀。
网络架构清晰明了,分割效果也很好,现在医学图像分割领域还能看见身影。
1.3 CTPN网络
刚开始准备使用CTPN进行文本的检测,所以看了一些相关资料,致命缺点是不能检测带角度文字和网络比较复杂。
- 网络的由来
文本检测和其他检测却别很大,比如用SSD检测文本就比较困难(边缘检测不好),如何针对文本进行检测?
- 网络的成果
CTPN网络有很多创造的想法–>>目标分割小块,然后一一进行检测,针对文本分割成
height>width的方式,使得检测的边缘更为精确。使用
BiLSTM对小块进行连接,针对文本之间的相关性。
CTPN想法具有创造性,但是太过复杂。
- 首先样本的制作麻烦
- 每个小框进行回归,框的大小自己定义
- 边缘特意进行偏移处理
- 使用RNN进行连接
检测水平效果还是不错的,但是对于倾斜的文本就不行了。
为什么不加一个angle进行回归?
本就很复杂的网络,如果再给每个小box加一个angle参数会更复杂,当然是可以实施的。
二. EAST结构分析
2.1 结构简述
EAST原名为: An Efficient and Accurate Scene Text Detector
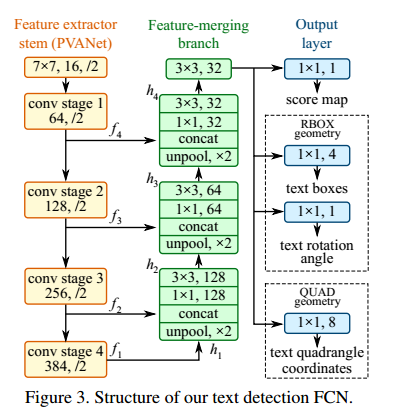
结构:检测层(PVANet) + 合并层 + 输出层
下图图2-2是检测效果,任意角度的文本都可以检测到。
**注意:**EAST只是一个检测网络,如需识别害的使用CRNN等识别网络进行后续操作。
具体网络在2-2节进行详细介绍=====>>>
2.2 结构详解
- 整体结构
EAST根据他的名字,我们知道就是高效的文本检测方法。
上面我们介绍了CTPN网络,其标签制作很麻烦,结构很复杂(分割成小方框然后回归还要RNN进行合并)
看下图图2-3,只要进行类似FCN的结构,计算LOSS就可以进行训练。测试的时候走过网络,运行NMS就可以得出结果。太简单了是不是?
- 特征提取层
特征的提取可以任意网络(VGG、RES-NET等检测网络),本文以VGG为基础进行特征提取。这个比较简单,看一下源码就可以清楚,见第四章源码分析
- 特征合并层
在合并层中,首先在定义特征提取层的时候把需要的输出给保留下来,通过forward函数把结构进行输出。之后再合并层调用即可
如下代码定义,其中合并的过程再下面介绍
#提取VGG模型训练参数
class extractor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, pretrained):
super(extractor, self).__init__()
vgg16_bn = VGG(make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=True))
if pretrained:
vgg16_bn.load_state_dict(torch.load('./pths/vgg16_bn-6c64b313.pth'))
self.features = vgg16_bn.features
def forward(self, x):
out = []
for m in self.features:
x = m(x)
#提取maxpool层为后续合并
if isinstance(m, nn.MaxPool2d):
out.append(x)
return out[1:]
- 特征合并层
合并特征提取层的输出,具体的定义如下代码所示,代码部分已经注释.
其中x中存放的是特征提取层的四个输出
def forward(self, x):
y = F.interpolate(x[3], scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
y = torch.cat((y, x[2]), 1)
y = self.relu1(self.bn1(self.conv1(y)))
y = self.relu2(self.bn2(self.conv2(y)))
y = F.interpolate(y, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
y = torch.cat((y, x[1]), 1)
y = self.relu3(self.bn3(self.conv3(y)))
y = self.relu4(self.bn4(self.conv4(y)))
y = F.interpolate(y, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
y = torch.cat((y, x[0]), 1)
y = self.relu5(self.bn5(self.conv5(y)))
y = self.relu6(self.bn6(self.conv6(y)))
y = self.relu7(self.bn7(self.conv7(y)))
return y
- 输出层
输出层包括三个部分,这里以RBOX为例子,发现网上都没有QUAN为例子的?
首先QUAN的计算是为了防止透视变换的存在,正常情况下不存在这些问题,正常的斜框可以解决。
因为QUAN的计算没啥好处,前者已经完全可以解决正常的检测问题,后者回归四个点相对来说较为困难(如果文本变化较大就更困难,所以SSD和YOLO无法检测文本的原因)。
如果想得到特殊的文本,基本考虑别的网络了(比如弯曲文字的检测)
def forward(self, x):
score = self.sigmoid1(self.conv1(x))
loc = self.sigmoid2(self.conv2(x)) * self.scope
angle = (self.sigmoid3(self.conv3(x)) - 0.5) * math.pi
geo = torch.cat((loc, angle), 1)
return score, geo
三. EAST细节分析
3.1 标签制作
注意:这里是重点和难点!!!
文章说要把标签向里缩进0.3
笔者认为这样做的目的是提取到更为准确的信息,不论是人工标注的好与不好,我们按照
0.3缩小之后提取的特征都是全部的文本信息。但是这样做也会丢失一些边缘信息,如果按照上述的推断,那么SSD或YOLO都可以这样设计标签了。
作者肯定是经过测试的,有好处有坏处吧!
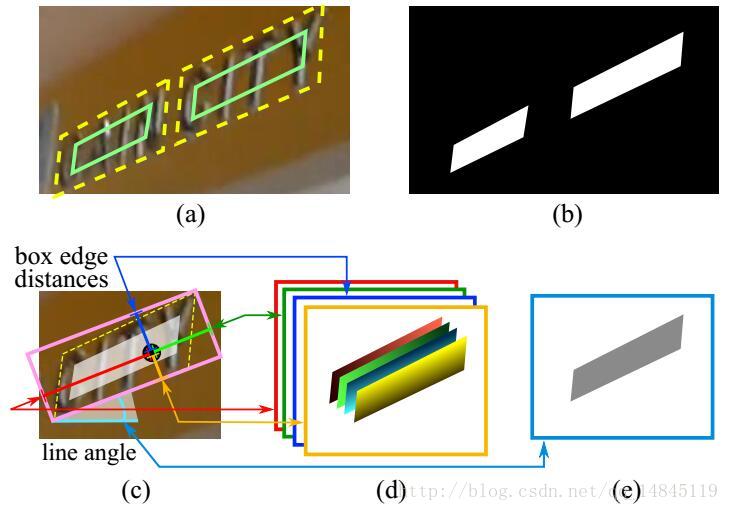
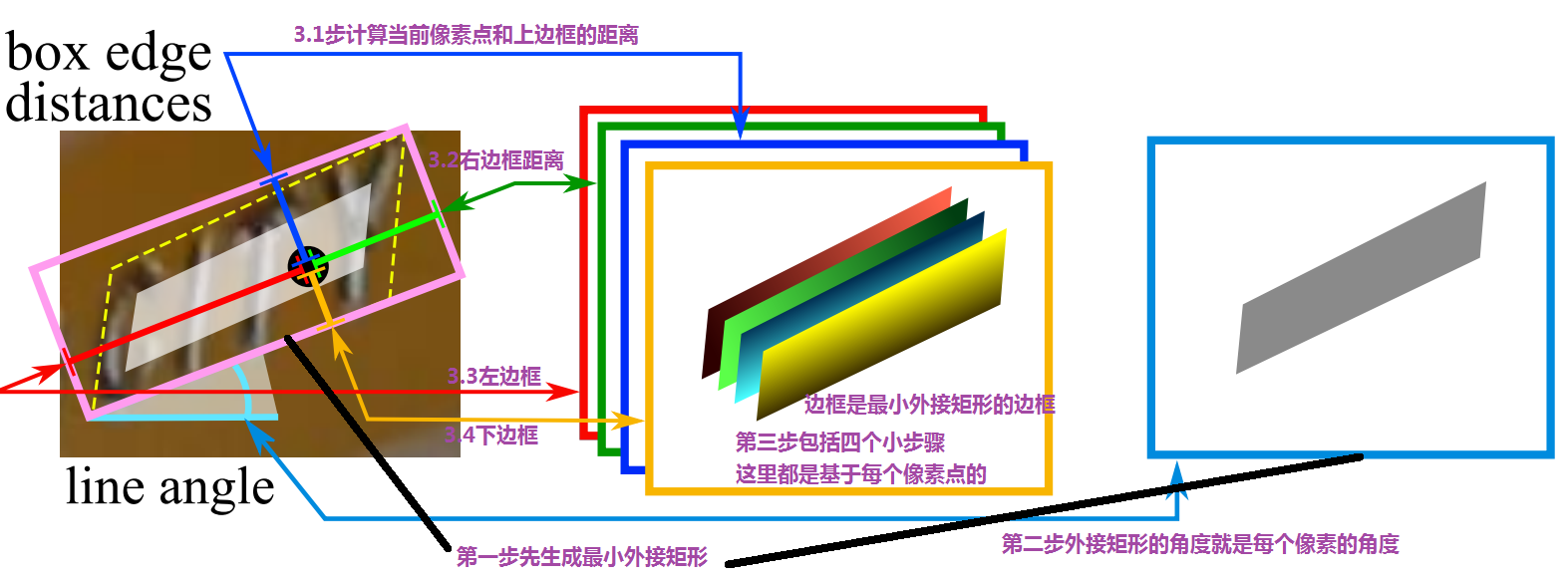
标签格式为:5个geometry(4个location+1个angle) + 1个score ==6 × N × M
其中(b)为score图 ,(d)为四个location图, (e)为angle图
上图可能看的不清楚,下面以手绘图进行说明:
上图可能看不清楚,下面再用文字大概说一下吧!
- 先进行0.3缩放,这个时候的图就是score
- 以没缩放的图像为基准,画最小外接矩形,这个外接矩形的角度就是angle。这个大小是缩放的的图大小。感觉直接以score图做角度也一样的。
- score图的每个像素点到最小外接矩形的距离为四个location图。
3.2 LOSS计算
LOSS计算就比较简单的,直接回归location、angle、score即可。
def forward(self, gt_score, pred_score, gt_geo, pred_geo, ignored_map):
#图像中不存在目标直接返回0
if torch.sum(gt_score) < 1:
return torch.sum(pred_score + pred_geo) * 0
#score loss 采用Dice方式计算,没有采用log熵计算,为了防止样本不均衡问题
classify_loss = get_dice_loss(gt_score, pred_score*(1-ignored_map))
#geo loss采用Iou方式计算(计算每个像素点的loss)
iou_loss_map, angle_loss_map = get_geo_loss(gt_geo, pred_geo)
#计算一整张图的loss,angle_loss_map*gt_score去除不是目标点的像素(感觉这句话应该放在前面减少计算量,放在这里没有减少计算loss的计算量)
angle_loss = torch.sum(angle_loss_map*gt_score) / torch.sum(gt_score)
iou_loss = torch.sum(iou_loss_map*gt_score) / torch.sum(gt_score)
geo_loss = self.weight_angle * angle_loss + iou_loss#这里的权重设置为1
print('classify loss is {:.8f}, angle loss is {:.8f}, iou loss is {:.8f}'.format(classify_loss, angle_loss, iou_loss))
return geo_loss + classify_loss
**注意:**这里score的LOSS使用Dice方式,因为普通的交叉熵无法解决样本不均衡问题!!!
3.3 NMS计算
NMS使用的是locality NMS,也就是为了针对EAST而提出来的。
首先我们先来看看这个LANMS的原理和过程:
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
def intersection(g, p):
#取g,p中的几何体信息组成多边形
g = Polygon(g[:8].reshape((4, 2)))
p = Polygon(p[:8].reshape((4, 2)))
# 判断g,p是否为有效的多边形几何体
if not g.is_valid or not p.is_valid:
return 0
# 取两个几何体的交集和并集
inter = Polygon(g).intersection(Polygon(p)).area
union = g.area + p.area - inter
if union == 0:
return 0
else:
return inter/union
def weighted_merge(g, p):
# 取g,p两个几何体的加权(权重根据对应的检测得分计算得到)
g[:8] = (g[8] * g[:8] + p[8] * p[:8])/(g[8] + p[8])
#合并后的几何体的得分为两个几何体得分的总和
g[8] = (g[8] + p[8])
return g
def standard_nms(S, thres):
#标准NMS
order = np.argsort(S[:, 8])[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
ovr = np.array([intersection(S[i], S[t]) for t in order[1:]])
inds = np.where(ovr <= thres)[0]
order = order[inds+1]
return S[keep]
def nms_locality(polys, thres=0.3):
'''
locality aware nms of EAST
:param polys: a N*9 numpy array. first 8 coordinates, then prob
:return: boxes after nms
'''
S = [] #合并后的几何体集合
p = None #合并后的几何体
for g in polys:
if p is not None and intersection(g, p) > thres: #若两个几何体的相交面积大于指定的阈值,则进行合并
p = weighted_merge(g, p)
else: #反之,则保留当前的几何体
if p is not None:
S.append(p)
p = g
if p is not None:
S.append(p)
if len(S) == 0:
return np.array([])
return standard_nms(np.array(S), thres)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 343,350,448,135,474,143,369,359
print(Polygon(np.array([[343, 350], [448, 135],
[474, 143], [369, 359]])).area)
别看那么多代码,讲的很玄乎,其实很简单:
- 遍历每个预测的框,然后按照交集大于某个值
K就合并相邻的两个框。 - 合并完之后就按照正常NMS消除不合理的框就行了。
注意: 为什么相邻的框合并?
- 因为每个像素预测一个框(不明白就自己去看上面LOSS计算),一个目标的几百上千个框基本都是重合的(如果预测的准的话),所以说相邻的框直接进行合并就行了。
- 其实竖直和横向都合并一次最好,反正原理一样的。
四. Pytorch源码分析
源码就不进行分析了,上面已经说得非常明白了,基本每个难点和重点都说到了。
有一点小bug,现进行说明:
- 训练的时候出现孔样本跑死
SampleNum = 3400 #定义样本数量,应对空标签的文本bug,临时处理方案
class custom_dataset(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, img_path, gt_path, scale=0.25, length=512):
super(custom_dataset, self).__init__()
self.img_files = [os.path.join(img_path, img_file) for img_file in sorted(os.listdir(img_path))]
self.gt_files = [os.path.join(gt_path, gt_file) for gt_file in sorted(os.listdir(gt_path))]
self.scale = scale
self.length = length
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_files)
def __getitem__(self, index):
with open(self.gt_files[index], 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
while(len(lines)<1):
index = int(SampleNum*np.random.rand())
with open(self.gt_files[index], 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
vertices, labels = extract_vertices(lines)
img = Image.open(self.img_files[index])
img, vertices = adjust_height(img, vertices)
img, vertices = rotate_img(img, vertices)
img, vertices = crop_img(img, vertices, labels, self.length,index)
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ColorJitter(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.25), \
transforms.ToTensor(), \
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5,0.5,0.5),std=(0.5,0.5,0.5))])
score_map, geo_map, ignored_map = get_score_geo(img, vertices, labels, self.scale, self.length)
return transform(img), score_map, geo_map, ignored_map
- 测试的时候读取PIL会出现RGBA情况
img_path = './013.jpg'
model_path = './pths/model_epoch_225.pth'
res_img = './res.bmp'
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = np.array(img)[:,:,:3]
img = Image.fromarray(img)
- 后续工作
- 这个代码感觉有点问题,训练速度很慢,猜测是数据处理部分。
- 原版EAST每个点都进行回归,太浪费时间了,后续参考AdvanceEAST进行修改,同时加个人理解优化
- 网络太大了,只适合服务器或者PC上跑,当前网络已经修改到15MB,感觉还是有点大。
- 后续还要加识别部分,困难重重。。。。。。
这里的代码都是github上的,笔者只是搬运工而已!!!
五. 第一次更新内容
- 2019-6-30更新
之前提到这个工程的代码有几个缺陷,在这里进行详细的解决
- 训练速度很慢
这是由于源代码的数据处理部分编写有问题导致,随机crop中对于边界问题处理
以下给出解决方案,具体修改请读者对比源代码即可:
def crop_img(img, vertices, labels, length, index):
'''crop img patches to obtain batch and augment
Input:
img : PIL Image
vertices : vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>
labels : 1->valid, 0->ignore, <numpy.ndarray, (n,)>
length : length of cropped image region
Output:
region : cropped image region
new_vertices: new vertices in cropped region
'''
try:
h, w = img.height, img.width
# confirm the shortest side of image >= length
if h >= w and w < length:
img = img.resize((length, int(h * length / w)), Image.BILINEAR)
elif h < w and h < length:
img = img.resize((int(w * length / h), length), Image.BILINEAR)
ratio_w = img.width / w
ratio_h = img.height / h
assert(ratio_w >= 1 and ratio_h >= 1)
new_vertices = np.zeros(vertices.shape)
if vertices.size > 0:
new_vertices[:,[0,2,4,6]] = vertices[:,[0,2,4,6]] * ratio_w
new_vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] = vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] * ratio_h
#find four limitate point by vertices
vertice_x = [np.min(new_vertices[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]]), np.max(new_vertices[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]])]
vertice_y = [np.min(new_vertices[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]]), np.max(new_vertices[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]])]
# find random position
remain_w = [0,img.width - length]
remain_h = [0,img.height - length]
if vertice_x[1]>length:
remain_w[0] = vertice_x[1] - length
if vertice_x[0]<remain_w[1]:
remain_w[1] = vertice_x[0]
if vertice_y[1]>length:
remain_h[0] = vertice_y[1] - length
if vertice_y[0]<remain_h[1]:
remain_h[1] = vertice_y[0]
start_w = int(np.random.rand() * (remain_w[1]-remain_w[0]))+remain_w[0]
start_h = int(np.random.rand() * (remain_h[1]-remain_h[0]))+remain_h[0]
box = (start_w, start_h, start_w + length, start_h + length)
region = img.crop(box)
if new_vertices.size == 0:
return region, new_vertices
new_vertices[:,[0,2,4,6]] -= start_w
new_vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] -= start_h
except IndexError:
print("\n crop_img function index error!!!\n,imge is %d"%(index))
else:
pass
return region, new_vertices
- LOSS刚开始收敛下降,到后面就呈现抖动(像过拟合现象),检测效果角度很差
由于Angle Loss角度计算错误导致,请读者阅读作者原文进行对比
def find_min_rect_angle(vertices):
'''find the best angle to rotate poly and obtain min rectangle
Input:
vertices: vertices of text region <numpy.ndarray, (8,)>
Output:
the best angle <radian measure>
'''
angle_interval = 1
angle_list = list(range(-90, 90, angle_interval))
area_list = []
for theta in angle_list:
rotated = rotate_vertices(vertices, theta / 180 * math.pi)
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 = rotated
temp_area = (max(x1, x2, x3, x4) - min(x1, x2, x3, x4)) * \
(max(y1, y2, y3, y4) - min(y1, y2, y3, y4))
area_list.append(temp_area)
sorted_area_index = sorted(list(range(len(area_list))), key=lambda k : area_list[k])
min_error = float('inf')
best_index = -1
rank_num = 10
# find the best angle with correct orientation
for index in sorted_area_index[:rank_num]:
rotated = rotate_vertices(vertices, angle_list[index] / 180 * math.pi)
temp_error = cal_error(rotated)
if temp_error < min_error:
min_error = temp_error
best_index = index
if angle_list[best_index]>0:
return (angle_list[best_index] - 90) / 180 * math.pi
return (angle_list[best_index]+90) / 180 * math.pi
- 修改网络从50MB到15MB,对于小样本训练效果很好
这里比较简单,直接修改VGG和U-NET网络feature map即可
cfg = [32, 32, 'M', 64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M']
#合并不同的feature map
class merge(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(merge, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 1)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu3 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=1)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu4 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 1)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.relu5 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=1)
self.bn6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.relu6 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=1)
self.bn7 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.relu7 = nn.ReLU()
#初始化网络参数
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
- 小的字体检测很好,大的字体检测不到(部分检测不到)情况
这里是模仿AdvanceEAST的方法进行训练,先在小图像进行训练,然后迁移到大图像即可。
意思就是先将图像缩小到254254训练得到modeul_254.pth
然后在将图像resize到384384,网络参数使用modeul_254.pth,训练得到modeul_384.pth
。。。一次进行512或者更大的图像即可
- 针对图像训练和检测的慢(相对于其他检测网络)
这里需要根据原理来说了,是因为全部的像素都需要预测和计算loss,可以看看AdvanceEAST的网络进行处理即可
- 修改网络说明
训练样本3000
测试样本100
检测精度85%,IOU准确度80%
5个epoch收敛结束(这些都是这里测试的)
两块1080TI,训练时间10分钟左右
五. 参考文献
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.03155.pdf
- https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/9776611.html
- LANMS源码
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_14845119/article/details/78986449
- http://campar.in.tum.de/pub/milletari2016Vnet/milletari2016Vnet.pdf
- https://blog.csdn.net/liuxiaoheng1992/article/details/82870923
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37504120
- https://blog.csdn.net/attitude_yu/article/details/80724187
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/6e35829a38de
- https://blog.csdn.net/wangdongwei0/article/details/84576044
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41783077/article/details/83789743#commentsedit
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_14845119/article/details/80787753
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/50126479
- 写博客太费时间了,基本花了五天左右,参考文献不整理了
- 部分参考资料找不到出处了,如有侵权很抱歉,请告知删除!