目录
统计出现次数top n的字符串
题目:第一道要求在输入一系列url字符串和n,要求统计各个字符串的出现次数,根据n输出数量top n的字符串。
思路:用hashmap保存每个字符串的出现次数,每次输入一个字符串,判断该字符串是否在hashmap中,没有就插入value为1key为该字符串的值,存在则更新value+1。在输入一个整数之后,从当前的统计数据map中获取所有数据add到一个优先级队列,按照次数大的优先排列,poll出n个数据即为top n数据。这里使用优先级队列是因为它内部使用堆的数据结构,查找最值效率比较高,每次poll最值出队列后会自动调整堆,保证队头数据是最值。
解决方案:
public class calculatetopn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Map<String, Integer> urlStatistic = new HashMap<>();
PriorityQueue<UrlCount> currentTopNQ = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<UrlCount>() {
@Override
public int compare(UrlCount o1, UrlCount o2) {
int com = o2.count - o1.count;
if (com == 0){
return o1.url.compareTo(o2.url);
}
return com;
}
});
while (sc.hasNext()) {
String lineValue = sc.nextLine();
if (lineValue.equals("")){
continue;
}
if ((lineValue.length() == 1 && lineValue.charAt(0) > '0' && lineValue.charAt(0) <= '9') || lineValue.equals("10")){// is number
int countN = Integer.parseInt(lineValue);
// output top n
// collect all url count
currentTopNQ.clear();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : urlStatistic.entrySet()) {
UrlCount urlCount = new UrlCount(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
currentTopNQ.add(urlCount);
}
// output n
String needToPrint = "";
for (int i = 0; i < countN; i++){
needToPrint = needToPrint + currentTopNQ.poll().url;
if(i != countN - 1){
needToPrint = needToPrint + ',';
}
}
System.out.println(needToPrint);
} else {// is url
int value;
if (urlStatistic.containsKey(lineValue)){
value = urlStatistic.get(lineValue);
value += 1;
urlStatistic.put(lineValue, value);
} else {
value = 1;
urlStatistic.put(lineValue, value);
}
}
}
}
private static class UrlCount{
public String url;
public int count;
public UrlCount(String url, int count){
this.url = url;
this.count = count;
}
}
}求最后一个有效字符下标
题目:要求在输入两个字符串S和L之后,判断S是否是L的有效序列并输入最后还一个有效字符在L中出现的位置。这里的有效序列定义为S中的每个字符在L中都存在,并且顺序一致,例如“ace”是“abcde”的有效序列,“aec”不是“abcde”的有效序列,但是ae是最长的有效序列,e是最后一个有效字符。
思路:从子串开始遍历,用找子串当前字符去顺序查找并匹配母串中的字符,匹配到了则子串和母串下标都+1,此时记录匹配到的下标为最后一个有效序列的下标;如果匹配失败一次,则母串下标+1,继续匹配,当子串或母串下标超出长度则停止,输入记录的最后有序字符下标。
解决方案:
public class findsubstr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String childString = sc.nextLine();
String motherString = sc.nextLine();
int childLength = childString.length();
int motherLength = motherString.length();
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int lastMatch = -1;
while (i < childLength && j < motherLength) {// to match{
if (childString.charAt(i) == motherString.charAt(j)) {// match current char in child string
lastMatch = j;
i++;
j++;
} else {
// not match, then move to next char of the mother string
j++;
}
}
System.out.println(lastMatch);
}
}复杂链表的复制
题目:输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针random指向一个随机节点),请对此链表进行深拷贝,并返回拷贝后的头结点。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)。 下图是一个含有5个结点的复杂链表。图中实线箭头表示next指针,虚线箭头表示random指针。为简单起见,指向null的指针没有画出。
思路:分三步走。第一步,在原链表上复制每一个节点的副本,作为此节点的next节点,如原来的A->B变为A->A'->B->B';第二步,根据旧节点的random指针,给新节点的random指针赋值,因为第一步的操作,所以新节点的random指针就为旧节点的random指针的next节点(如果random指针不为null的话,为null就都为null);第三步,对当前链表进行拆分,根据新旧节点交替的特点,拆分旧节点链表和新节点链表。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args){
RandomListNode node1 = new RandomListNode(1);
RandomListNode node2 = new RandomListNode(2);
RandomListNode node3 = new RandomListNode(3);
RandomListNode node4 = new RandomListNode(4);
RandomListNode node5 = new RandomListNode(5);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
node1.random = node3;
node2.random = node5;
node4.random = node2;
RandomListNode copyNode = Clone(node1);
printListNode(node1);
printListNode(copyNode);
}
public static RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null){
return null;
}
// copy a replicate, for every node, copy a replicate to the next
RandomListNode tmpHead = pHead;
while (tmpHead != null) {
RandomListNode currentCopyNode = new RandomListNode(tmpHead.label);
RandomListNode nextNode = tmpHead.next;
tmpHead.next = currentCopyNode;
currentCopyNode.next = nextNode;
tmpHead = nextNode;
}
// according to the old list's random pointer, assign the random pointer of the new list
// point to the head node again
RandomListNode preNode = pHead;
// if it is the new node
while (preNode != null){
RandomListNode currentNewNode = preNode.next; // this is the new node
// assign the random pointer
if (preNode.random == null){
currentNewNode.random = null;
} else {
currentNewNode.random = preNode.random.next;
}
preNode = currentNewNode.next;
}
// extract the new node list
tmpHead = pHead;
RandomListNode newNodeHead = null;
RandomListNode newLastNode = null;
RandomListNode preTmpHead = null;
while (tmpHead != null){
RandomListNode currentNewNode = tmpHead.next; // this is the new node
if (newLastNode == null){ // it is the first new node
newLastNode = currentNewNode;
newNodeHead = currentNewNode;
} else {
newLastNode.next = currentNewNode;
newLastNode = currentNewNode;
}
if (preTmpHead != null){ // not first time
preTmpHead.next = tmpHead;
}
preTmpHead = tmpHead; // change the last old node
tmpHead = currentNewNode.next; // change to the next old node
}
preTmpHead.next = null;
return newNodeHead;
}
public static void printListNode(RandomListNode listNode){
while (listNode != null){
System.out.println(listNode);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
}删除链表中重复的结点
题目:在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表 1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
数据范围:链表长度满足 0≤n≤1000 ,链表中的值满足 1≤val≤1000
进阶:空间复杂度 O(n)\O(n) ,时间复杂度 O(n) \O(n)
例如输入{1,2,3,3,4,4,5}时,对应的输出为{1,2,5}
思路:遍历原链表,遇到重复的节点,需要删除,这里我用的方式是直接忽略重复节点,记录最后一个非重复的节点,一旦遍历到非重复的节点,就接在最后一个非重复节点的后面,直到结束。这里有挺多边界条件,例如只包含一个节点的,或者是只包含两个重复节点的,这些分支情况都需要保证覆盖到。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args){
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode listNode6 = new ListNode(6);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
listNode5.next = listNode6;
printListNode(listNode5);
ListNode afterDelete = deleteDuplication(listNode5);
System.out.println("after deleting");
printListNode(afterDelete);
}
public static void printListNode(ListNode listNode){
while (listNode != null){
System.out.println(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
public static ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null){
return null;
}
ListNode tmpHead = pHead;
ListNode afterDeleteNewHead = null;
ListNode lastNotDuplicate = null;
ListNode preNode = null;
boolean currentFoundDuplicate = false;
while(tmpHead != null){
if (preNode != null){
if (preNode.val != tmpHead.val){
if (!currentFoundDuplicate){
if (lastNotDuplicate != null){
lastNotDuplicate.next = preNode;
} else {
afterDeleteNewHead = preNode;
}
lastNotDuplicate = preNode;
}
currentFoundDuplicate = false;
} else {
currentFoundDuplicate = true;
}
}
preNode = tmpHead;
tmpHead = tmpHead.next;
}
if (lastNotDuplicate != null){
if (currentFoundDuplicate){
lastNotDuplicate.next = null;
} else {
lastNotDuplicate.next = preNode;
}
} else {
if (!currentFoundDuplicate) {
afterDeleteNewHead = preNode;
}
}
return afterDeleteNewHead;
}
}删除链表的节点
题目:
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。返回删除后的链表的头节点。
1.此题对比原题有改动
2.题目保证链表中节点的值互不相同
3.该题只会输出返回的链表和结果做对比,所以若使用 C 或 C++ 语言,你不需要 free 或 delete 被删除的节点
数据范围:
0<=链表节点值<=10000
0<=链表长度<=10000
思路:对原链表进行遍历,记录前一个节点为preNode,比较当前节点的值是否跟目标值相同,相同就删除当前节点,preNode的next指针指向下一个节点即可。因为题目保证链表中的节点的值互不相同,所以只要找到目标节点就可以退出遍历循环。
解决方案:
public class Sulution {
public static void main(String[] args){
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode listNode6 = new ListNode(6);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
listNode5.next = listNode6;
printListNode(listNode6);
ListNode afterDelete = deleteNode(null, 6);
System.out.println("after deleting");
printListNode(afterDelete);
}
public static ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
// write code here
if (head == null){
return null;
}
if (head.val == val){
return head.next;
}
ListNode tmpHead = head.next;
ListNode preNode = head;
while (tmpHead != null){
if (tmpHead.val == val){
// delete current node
preNode.next = tmpHead.next;
break;
}
preNode = tmpHead;
tmpHead = tmpHead.next;
}
return head;
}
public static void printListNode(ListNode listNode){
while (listNode != null){
System.out.println(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
}二叉树的深度
题目:
输入一棵二叉树,求该树的深度。从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度,根节点的深度视为 1 。
数据范围:节点的数量满足 0 \le n \le 1000≤n≤100 ,节点上的值满足 0 \le val \le 1000≤val≤100
进阶:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1) ,时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)。
思路:运用递归的思路,根节点为root的树的深度,为它的左子树深度和右子树深度的最大值+1。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args){
}
public static int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(TreeDepth(root.left), TreeDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}二叉搜索树的第k个节点
题目:
给定一棵结点数为n 二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第 k 小的TreeNode结点值。
1.返回第k小的节点值即可
2.不能查找的情况,如二叉树为空,则返回-1,或者k大于n等等,也返回-1
3.保证n个节点的值不一样
数据范围: 0 \le n \le10000≤n≤1000,0 \le k \le10000≤k≤1000,树上每个结点的值满足0 \le val \le 10000≤val≤1000
进阶:空间复杂度 O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)
思路:因为空间复杂度为O(n),也就是可以使用辅助空间,所以先中旭遍历该树,这样就能按升序访问节点,遍历过程中将节点存入一个Vector数组,遍历结束后取下标为k - 1的元素值即可。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(1);
printTree(node);
int n1 = KthNode(null, 1);
System.out.println(n1);
}
public static int KthNode (TreeNode proot, int k) {
// write code here
Vector<Integer> treeList = new Vector<>();
if (proot == null || k == 0) {return -1;}
collecttree(proot, treeList);
if (k <= treeList.size()){
return treeList.get(k - 1);
}
return -1;
}
private static void collecttree(TreeNode pRoot, Vector<Integer> targetArray){
if (pRoot.left != null){
collecttree(pRoot.left, targetArray);
}
// collect parant node
targetArray.add(pRoot.val);
if (pRoot.right != null){
collecttree(pRoot.right, targetArray);
}
}
private static void printTree(TreeNode pRoot){
if (pRoot.left != null){
printTree(pRoot.left);
}
// collect parant node
System.out.println(pRoot.val);
if (pRoot.right != null){
printTree(pRoot.right);
}
}
}二叉树的镜像
题目:
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
数据范围:二叉树的节点数 0 \le n \le 10000≤n≤1000 , 二叉树每个节点的值 0\le val \le 10000≤val≤1000
要求: 空间复杂度 O(n) 。本题也有原地操作,即空间复杂度 O(1) 的解法,时间复杂度 O(n)。
思路:运用递归的思想,一颗跟节点为root的树的镜像二叉树为左子树的镜像二叉树和右子树的镜像二叉树交换位置后的树,递归到左节点和右节点是null或者是叶子节点时,交换左右节点。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(tmp);
return root;
}
}
判断是不是平衡二叉树
题目:输入一棵节点数为 n 二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。在这里,我们只需要考虑其平衡性,不需要考虑其是不是排序二叉树。平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree),具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
思路:根据平衡二叉树的定义,利用递归的思想,根据左右两个子树的高度差绝对值不超过一并且左右两个子树都是一颗平衡二叉树,判断以当前节点为根节点的树是否是平衡二叉树。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){return true;}
if (Math.abs(treeDepth(root.left) - treeDepth(root.right)) <= 1 && IsBalanced_Solution(root.left) && IsBalanced_Solution(root.right)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
private int treeDepth(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(treeDepth(root.left), treeDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}二叉搜索树与双向链表
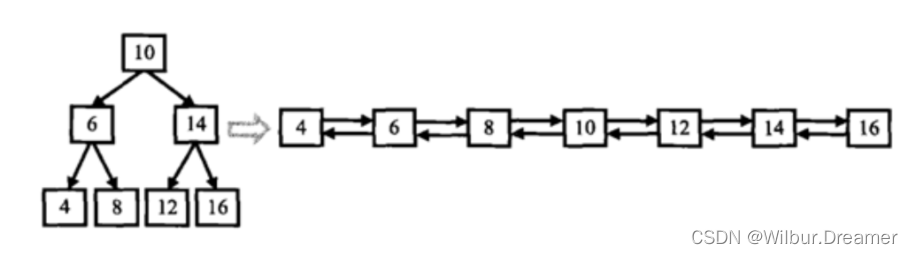
题目:
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。如下图所示
思路:将树节点的left指针看做是链表的前驱指针,right指针看做是链表的后驱指针,需要用递归将节点的左子树和右子树也转换成双向链表,左子树在转换成双向链表后要返回其最右节点指针且与父节点重新相连接,右子树则相反,在转换成双向链表后返回其最左节点指针,且与父节点重新相连接。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode(8);
TreeNode node10 = new TreeNode(10);
TreeNode node12 = new TreeNode(12);
TreeNode node14 = new TreeNode(14);
TreeNode node16 = new TreeNode(16);
node10.left = node6;
node10.right = node14;
node6.left = node4;
node6.right = node8;
node14.left = node12;
node14.right = node16;
TreeNode result = Convert(null);
// System.out.println(result.val);
}
public static TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
TreeNode convertResult = convertLeft(pRootOfTree);
// find the end node
if (convertResult == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode tmpNode = convertResult;
while (tmpNode.left != null){
tmpNode = tmpNode.left;
}
return tmpNode;
}
private static TreeNode convertLeft(TreeNode childNode){ // return largest node
if (childNode == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode leftAfterConvert = convertLeft(childNode.left);
if (leftAfterConvert != null) {
leftAfterConvert.right = childNode;
}
childNode.left = leftAfterConvert;
TreeNode rightAfterConvert = convertRight(childNode.right);
childNode.right = rightAfterConvert;
if (rightAfterConvert != null){
rightAfterConvert.left = childNode;
}
if (rightAfterConvert != null){return rightAfterConvert;}
return childNode;
}
private static TreeNode convertRight(TreeNode childNode){ // return smallest node
if (childNode == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode leftAfterConvert = convertLeft(childNode.left);
if (leftAfterConvert != null) {
leftAfterConvert.right = childNode;
}
childNode.left = leftAfterConvert;
TreeNode rightAfterConvert = convertRight(childNode.right);
childNode.right = rightAfterConvert;
if (rightAfterConvert != null){
rightAfterConvert.left = childNode;
}
if (leftAfterConvert != null) {return leftAfterConvert;}
return childNode;
}
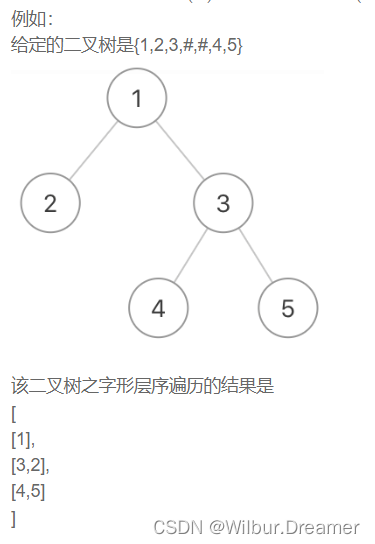
}按之字形顺序打印二叉树
题目:
给定一个二叉树,返回该二叉树的之字形层序遍历,(第一层从左向右,下一层从右向左,一直这样交替)
数据范围:0 0≤n≤1500,树上每个节点的val满足 |val| <= 1500
要求:空间复杂度:O(n),时间复杂度:O(n)
思路:第一层为从左到右打印根节点,记录每一层打印的节点列表,后面每一层从尾到头遍历上一层打印的节点,交替着更换左右节点的优先顺序,例如第二层是右节点优先打印,第三层是左节点优先打印...循环直到当前新打印的节点列表为空。可以使用递归,但是发现使用递归程序运行时间会稍微长一些,所以尽量不使用递归。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode n1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode n2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode n3 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode n4 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode n5 = new TreeNode(5);
n1.left = n2;
n1.right = n3;
n3.left = n4;
n3.right = n5;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result;
result = Print(n1);
printArrayist(result);
}
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> zTreeResult = new ArrayList<>();
if (pRoot == null) {
return zTreeResult;
}
ArrayList<Integer> lastLayerValue = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> lastTreeNodeList = new ArrayList<>();
lastLayerValue.add(pRoot.val);
lastTreeNodeList.add(pRoot);
zTreeResult.add(lastLayerValue);
boolean bRightFirst = true;
while (true) {
int lastLayerLength = lastTreeNodeList.size();
ArrayList<Integer> nextLayer = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> nextTreeNodeList = new ArrayList<>();
if (bRightFirst){
for (int i = lastLayerLength - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right.val);
}
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left.val);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = lastLayerLength - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left.val);
}
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right.val);
}
}
}
if (!nextLayer.isEmpty()){
zTreeResult.add(nextLayer);
lastTreeNodeList = nextTreeNodeList;
} else{
break;
}
bRightFirst = !bRightFirst;
}
return zTreeResult;
}
// recursion;
private static void collectZTree(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> zTreeResult, ArrayList<TreeNode> lastTreeNodeList, boolean bRightFirst){
int arrayLength = zTreeResult.size();
if (arrayLength == 0) {
return ;
}
int lastLayerLength = lastTreeNodeList.size();
ArrayList<Integer> nextLayer = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> nextTreeNodeList = new ArrayList<>();
if (bRightFirst){
for (int i = lastLayerLength - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right.val);
}
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left.val);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = lastLayerLength - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).left.val);
}
if (lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right != null){
nextTreeNodeList.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right);
nextLayer.add(lastTreeNodeList.get(i).right.val);
}
}
}
if (!nextLayer.isEmpty()){
zTreeResult.add(nextLayer);
lastTreeNodeList.clear();
lastTreeNodeList.addAll(nextTreeNodeList);
collectZTree(zTreeResult, lastTreeNodeList, !bRightFirst);
}
}
private static void printArrayist(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result){
for (ArrayList<Integer> arr: result
) {
for (Integer value: arr
) {
System.out.print(value);
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
1.对于该题的最近的公共祖先定义:对于有根树T的两个节点p、q,最近公共祖先LCA(T,p,q)表示一个节点x,满足x是p和q的祖先且x的深度尽可能大。在这里,一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先.
2.二叉搜索树是若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值
3.所有节点的值都是唯一的。
4.p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
思路:一开始觉得难度好像不只是简单的程度,然后注意到了这是一颗搜索树,所以就有了思路。同时进行搜索这两个数的过程,两个数可能会匹配当前节点,或者两个数分别往左子树和右子树继续查找匹配,这两种情况最近公共祖先都是当前节点;而如果是两个数都往左子树搜索,则递归左子树,进行同样的判断,反之递归右子树进行同样的操作。
解决方案:
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
// write code here
if (root.val == p || root.val == q){
return root.val;
}
if ((p < root.val && q > root.val) || (q < root.val && p > root.val)){
return root.val;
}
if (q < root.val){ // all to left
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
}
// all to right
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
}树的子结构
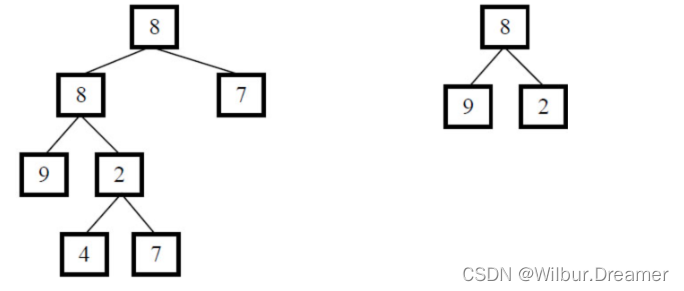
题目:
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
假如给定A为{8,8,7,9,2,#,#,#,#,4,7},B为{8,9,2},2个树的结构如下,可以看出B是A的子结构
思路:时间复杂度为O(n^2)的解法是在双循环中遍历两棵树,先遍历较高的树,对于较高的树中的每个节点N都进行与矮树的匹配,匹配的方式就是递归矮树的同时一边遍历N以及比较,如果完全匹配,则说明矮树是高树的一个子结构,如果不能完全匹配则继续外层高树的递归遍历。
解决方案:
public static boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null || root2 == null) { // current node
return false;
}
if (ifMatch(root1, root2)){
return true;
}
// left search
return HasSubtree(root1.left, root2) || HasSubtree(root1.right, root2);
}
private static boolean ifMatch(TreeNode longTree, TreeNode shortTree){ // 一边遍历一边比较值
if (shortTree != null) {
if (longTree == null || longTree.val != shortTree.val){
return false; // not match , do not need to deep search any more
}
// deep search and match
return ifMatch(longTree.left, shortTree.left) && ifMatch(longTree.right, shortTree.right);
}
return true;
}根据先序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
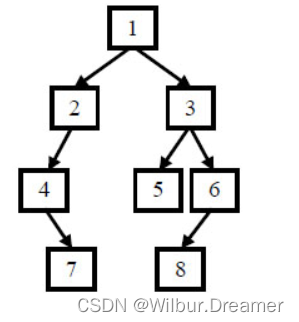
题目:
给定节点数为 n 的二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历结果,请重建出该二叉树并返回它的头结点。
例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建出如下图所示。
思路:由于先序遍历顺序为中左右,中序遍历为左中右,那么可以确定先序遍历序列的首节点为根节点,再查找中序遍历序列此节点的位置,其以左为这个父节点的左节点树序列,其以右为这个父节点的右节点树序列,然后,因为先序遍历序列父节点后面是左节点树,从中序遍历序列中得到它的数量,从而能够得到左节点树和右节点树的先序遍历序列,分别对左节点树和右节点树递归上面的操作,返回的第一个节点与上面父节点连接,递归至遍历序列为空停止。
解决方案:
public static TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre, int [] vin) {
return findFirst(pre, vin, 0, pre.length - 1, 0, vin.length - 1);
}
private static TreeNode findFirst(int[] pre, int[] vin, int preBegin, int preEnd, int vinBegin, int vinEnd) {
if (preEnd - preBegin < 0){
return null;
}
TreeNode firstNode = new TreeNode(pre[preBegin]);
int middleIndex = 0;
for (middleIndex = vinBegin ; middleIndex <= vinEnd; middleIndex++){
if (vin[middleIndex] == pre[preBegin]){
break;
}
}
firstNode.left = findFirst(pre, vin, preBegin + 1, preBegin + middleIndex - vinBegin, vinBegin, middleIndex - 1);
firstNode.right = findFirst(pre, vin, preBegin + middleIndex - vinBegin + 1, preEnd,middleIndex + 1, vinEnd);
return firstNode;
}从上往下打印二叉树
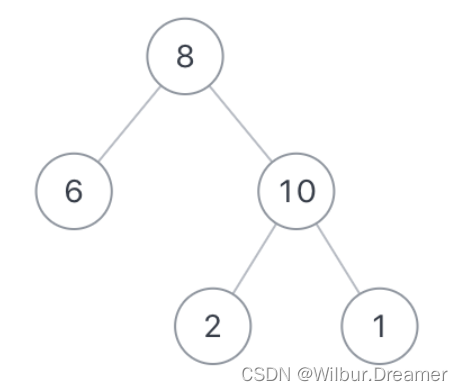
题目:不分行从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。例如输入{8,6,10,#,#,2,1},如以下图中的示例二叉树,则依次打印8,6,10,2,1(空节点不打印,跳过),请你将打印的结果存放到一个数组里面,返回。
思路:这道题是简单的,首先将根节点压入队列,循环并每次从队列取队头元素出来,如果左节点和右节点不为空,则依次打印其左节点和右节点,并将其入队,然后队头元素出队,处理下一个队头元素,直到队列为空循环停止。
解决方案:
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> resultlist = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return resultlist;
}
resultlist.add(root.val);
Queue<TreeNode> treeNodes = new LinkedList<>();
treeNodes.add(root);
while (!treeNodes.isEmpty()){
TreeNode currentNodeToPrint = treeNodes.peek();
if (currentNodeToPrint.left != null){
resultlist.add(currentNodeToPrint.left.val);
treeNodes.add(currentNodeToPrint.left);
}
if (currentNodeToPrint.right != null){
resultlist.add(currentNodeToPrint.right.val);
treeNodes.add(currentNodeToPrint.right);
}
treeNodes.poll();
}
return resultlist;
}对称的二叉树
题目:给定一棵二叉树,判断其是否是自身的镜像(即:是否对称)
例如: 下面这棵二叉树是对称的
思路:这是很简单的一道题,花了我将近一小时,果然状态不佳的时候不能刷题。一开始以为按“左中右”顺序遍历左子树得到序列1,然后按“右中左”顺序遍历右子树得到序列2,最后比较序列1和2的值是否完全匹配,这样忽略了树1233#2#的情况,也就是不仅顺序要一致,两边匹配的节点左右顺序要相反的,即左节点匹配右节点,右节点匹配左节点;所以还是得在遍历左子树和右子树的同时就一边判断两边遍历到的值是否相等,一旦有不相等的,就判定为不对称,递归即可。
解决方案:
public static boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
if (pRoot == null){
return true;
}
return isSymmetrical(pRoot.left, pRoot.right);
}
private static boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode leftFirst, TreeNode rightFirst) {
if ((leftFirst == null && rightFirst != null) || (rightFirst == null && leftFirst != null)){
return false;
}
if (leftFirst != null){
if (leftFirst.val != rightFirst.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetrical(leftFirst.left, rightFirst.right) && isSymmetrical(leftFirst.right, rightFirst.left);
}
return true;
}把二叉树打印成多行
题目:
给定一个节点数为 n 二叉树,要求从上到下按层打印二叉树的 val 值,同一层结点从左至右输出,每一层输出一行,将输出的结果存放到一个二维数组中返回。
例如:
给定的二叉树是{1,2,3,#,#,4,5}
该二叉树多行打印层序遍历的结果是
[
[1],
[2,3],
[4,5]
]
思路:中等难度的一道题,其实很简单。从首行也就是根节点开始打印并收集每一行节点的值,同时存储最后一行的节点到一个数组中,从首到尾遍历该数组节点,如果其左节点和右节点不为空,则依次收集为这一行数据,同时存储其节点到另一个数组,将这个数组作为最后一行节点数组,循环上面的操作和处理,直到最后一行需要打印的节点数为0为止。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> zTreeResult = new ArrayList<>();
if (pRoot == null) {
return zTreeResult;
}
ArrayList<Integer> lastLayerValue = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> lastTreeNodeList = new ArrayList<>();
lastLayerValue.add(pRoot.val);
lastTreeNodeList.add(pRoot);
zTreeResult.add(lastLayerValue);
boolean bRightFirst = true;
while (true) {
ArrayList<Integer> nextLayer = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> nextTreeNodeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (TreeNode treeNode : lastTreeNodeList) {
if (treeNode.left != null) {
nextTreeNodeList.add(treeNode.left);
nextLayer.add(treeNode.left.val);
}
if (treeNode.right != null) {
nextTreeNodeList.add(treeNode.right);
nextLayer.add(treeNode.right.val);
}
}
if (!nextLayer.isEmpty()){
zTreeResult.add(nextLayer);
lastTreeNodeList = nextTreeNodeList;
} else{
break;
}
bRightFirst = !bRightFirst;
}
return zTreeResult;
}
}二叉搜索树的后续遍历序列
题目:输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
数据范围: 节点数量 0 \le n \le 10000≤n≤1000 ,节点上的值满足 1 \le val \le 10^{5}1≤val≤105 ,保证节点上的值各不相同
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n) ,时间时间复杂度 O(n^2)O(n2)
提示:
1.二叉搜索树是指父亲节点大于左子树中的全部节点,但是小于右子树中的全部节点的树。
2.该题我们约定空树不是二叉搜索树
3.后序遍历是指按照 “左子树-右子树-根节点” 的顺序遍历
思路:二叉搜索树的后续遍历序列最后一个节点为父节点,剩余part能够被分成两部分,前面一部分都小于父节点,后面一部门都大于父节点,并且这两部分如果不为空,则也是后续遍历序列,满足同样的规律,所以解决方案为对这个序列进行上述判断以及对分割出的左序列和右序列部分递归判断处理即可。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] sequence = {5,7,6,9,11,10,8};
boolean result = VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if (sequence == null || sequence.length == 0){
return false;
}
return VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);
}
public static boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence, int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex == endIndex){
return true;
}
int parent = sequence[endIndex];
int leftBeginIndex = beginIndex;
int leftEndIndex = -1;
int rightBeginIndex = -1;
int rightEndIndex = -1;
endIndex = endIndex - 1;
while (beginIndex <= endIndex){
if (sequence[beginIndex] < parent){// is left node
leftEndIndex = beginIndex;
} else {
break;
}
beginIndex++;
}
if (beginIndex > endIndex) { // all is left node
return VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence, leftBeginIndex, leftEndIndex);
}
rightBeginIndex = beginIndex;
while (beginIndex <= endIndex){ // this should be the right node part, so every node should be larger then its parent
if (sequence[beginIndex] <= parent){
break;
}
beginIndex++;
}
if (beginIndex > endIndex){ // it satisfy
rightEndIndex = endIndex;
if (leftEndIndex == -1){// left part is empty
return VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence, rightBeginIndex, rightEndIndex);
} else { // left part is not empty, that is to sat the sequence can be split to left part and right part
return VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence, rightBeginIndex, rightEndIndex) && VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence, leftBeginIndex,leftEndIndex);
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
题目:给定一个二叉树root和一个值 sum ,判断是否有从根节点到叶子节点的节点值之和等于 sum 的路径。
1.该题路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶子结点所经过的结点
2.叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点
3.路径只能从父节点到子节点,不能从子节点到父节点
4.总节点数目为n
思路:遍历遍历所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径,在遍历到每个节点时记录当前已经过路径的节点值之和,到达子节点的时候判断路径之和是否满足条件。
解决方案:
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
// write code here
if (root == null){
return false;
}
return hasPathSum(root, 0, sum);
}
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int currentValue, int sum) {
// write code here
if (root == null){
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
if (root.val + currentValue == sum){
return true;
}
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, root.val + currentValue, sum) || hasPathSum(root.right, root.val + currentValue, sum);
}二叉树的下一个结点
题目:给定一个二叉树其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的next指针。下图为一棵有9个节点的二叉树。树中从父节点指向子节点的指针用实线表示,从子节点指向父节点的用虚线表示。
思路:给定中序遍历序列和一个节点,返回遍历过程中的下一个节点 取右子树第一个遍历节点,如果为空,向上找满足next与left双向的中节点,找不到则返回空。
解决方案:
public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) {
if (pNode == null){
return null;
}
if (pNode.right != null){
return findFirst(pNode.right);
}
// right is null, then the next could be its next
TreeLinkNode next = pNode.next;
if (next == null){
return null;
}
int childValue = pNode.val;
while (next != null){
if ((next.right != null) && next.right.val == childValue){ // is right
childValue = next.val;
next = next.next;
} else {
break;
}
}
return next;
}
public TreeLinkNode findFirst(TreeLinkNode root){
if (root.left == null){
return root;
}
return findFirst(root.left);
}二叉树中和为某一值的路径(二)
题目:输入一颗二叉树的根节点root和一个整数expectNumber,找出二叉树中结点值的和为expectNumber的所有路径。
1.该题路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶子结点所经过的结点
2.叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点
3.路径只能从父节点到子节点,不能从子节点到父节点
4.总节点数目为n
如二叉树root为{10,5,12,4,7},expectNumber为22
思路:中序遍历整个树,遍历到每个节点时,将该节点加入当前从根节点到该节点的路径数组,如果是子节点,判断该路径是否满足条件,满足则将其加入结果数组;当遍历完一个节点的左子树和右子树时,从当前路径中删除该节点,进行回溯。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root, int expectNumber) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> currentPath = new ArrayList<>();
findAllPath(root, result, currentPath, 0, expectNumber);
return result;
}
public void findAllPath (TreeNode root, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result, ArrayList<Integer> currentPath, int currentSum, int sum) {
// write code here
if (root == null){
return ;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
if (root.val + currentSum == sum){
//collect
ArrayList<Integer> newResult = new ArrayList<>(currentPath);
newResult.add(root.val);
result.add(newResult);
}
return;
}
currentPath.add(root.val);
findAllPath(root.left, result, currentPath, currentSum + root.val , sum);
findAllPath(root.right, result, currentPath, currentSum + root.val, sum);
currentPath.remove(currentPath.size() - 1);
}
public void findAllPath_0 (TreeNode root, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result, ArrayList<Integer> currentPath, int currentSum, int sum) {
// write code here
if (root == null){
return ;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
if (root.val + currentSum == sum){
//collect
currentPath.add(root.val);
result.add(currentPath);
}
return;
}
currentPath.add(root.val);
ArrayList<Integer> leftCopy = new ArrayList<>(currentPath);
ArrayList<Integer> rightCopy = new ArrayList<>(currentPath);
findAllPath(root.left, result, leftCopy, currentSum + root.val , sum);
findAllPath(root.right, result, rightCopy, currentSum + root.val, sum);
}
}
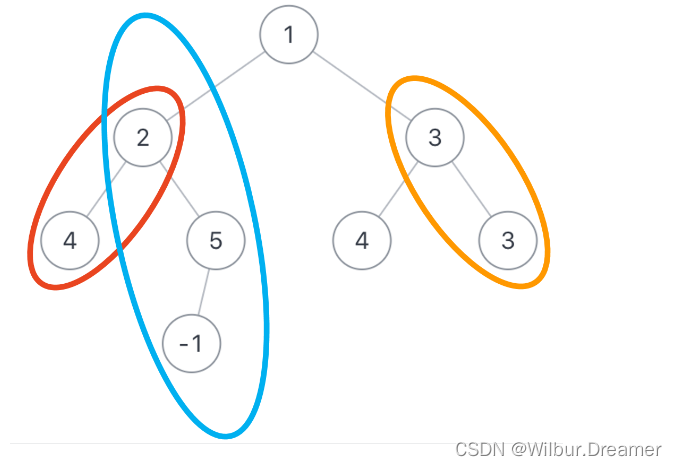
二叉树中和为某一值的路径(三)
题目:给定一个二叉树root和一个整数值 sum ,求该树有多少路径的的节点值之和等于 sum 。
1.该题路径定义不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是一定是从父亲节点往下到孩子节点
2.总节点数目为n
3.保证最后返回的路径个数在整形范围内(即路径个数小于231-1)
数据范围:
0<=n<=10000<=n<=1000
-10^9<=节点值<=10^9−109<=节点值<=109
假如二叉树root为{1,2,3,4,5,4,3,#,#,-1},sum=6,那么总共如下所示,有3条路径符合要求
思路:对整个树进行中序遍历,同时记录从根节点到当前节点的路径,遍历完某个节点,就从当前路径中删除该节点,对于每个节点的当前路径,遍历所有包含该节点的子路径,判断是否满足条件,满足则总计数加一,中序遍历完整个树即可。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
private int count = 0;
public int FindPath (TreeNode root, int sum) {
// write code here
ArrayList<Integer> currentPath = new ArrayList<>();
findAllPath(root, sum, currentPath);
return count;
}
private void findAllPath(TreeNode root, int sum, ArrayList<Integer> currentPath){
if (root == null){
return;
}
currentPath.add(root.val);
count = count + calculate(currentPath, sum);
findAllPath(root.left, sum, currentPath);
findAllPath(root.right, sum, currentPath);
currentPath.remove(currentPath.size() - 1);
}
private int calculate(ArrayList<Integer> currentPath, int sum){
int size = currentPath.size();
int count = 0;
int pathSum = 0;
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--){
pathSum += currentPath.get(i);
if (pathSum == sum){
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}用两个栈实现队列
题目:
用两个栈来实现一个队列,使用n个元素来完成 n 次在队列尾部插入整数(push)和n次在队列头部删除整数(pop)的功能。 队列中的元素为int类型。保证操作合法,即保证pop操作时队列内已有元素。
数据范围: n\le1000n≤1000
要求:存储n个元素的空间复杂度为 O(n)O(n) ,插入与删除的时间复杂度都是 O(1)O(1)
思路:一个栈用来正常push数据,一个栈用来pop数据,当用来pop的栈为空时,从栈1中不断pop数据出来并push进栈2,这样栈2pop的数据就是队列头元素。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.size() == 0) {
while (!stack1.empty()) {
int nextToPop = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(nextToPop);
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}包含min函数的栈
题目:
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的 min 函数,输入操作时保证 pop、top 和 min 函数操作时,栈中一定有元素。
此栈包含的方法有:
push(value):将value压入栈中
pop():弹出栈顶元素
top():获取栈顶元素
min():获取栈中最小元素
数据范围:操作数量满足 0 \le n \le 300 \0≤n≤300 ,输入的元素满足 |val| \le 10000 \∣val∣≤10000
进阶:栈的各个操作的时间复杂度是 O(1)\O(1) ,空间复杂度是 O(n)\O(n)
思路:使用辅助栈存储每一个元素进栈时当前的最小值,每一个元素在进栈时如果比当前最小值小,则进辅助栈,否则压当前最小值进栈,出栈时辅助栈也出栈。min函数返回辅助栈栈顶元素。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
private Stack<Integer> originalStack = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<>();
private int currentMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public void push(int node) {
if (minStack.empty()) {
minStack.push(node);
} else {
minStack.push(Math.min(node, minStack.peek()));
}
originalStack.push(node);
}
public void pop() {
originalStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return originalStack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}数字在升序数组中出现的次数
题目:给定一个长度为 n 的非降序数组和一个非负数整数 k ,要求统计 k 在数组中出现的次数
数据范围:0 \le n \le 1000 , 0 \le k \le 1000≤n≤1000,0≤k≤100,数组中每个元素的值满足 0 \le val \le 1000≤val≤100
要求:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1),时间复杂度 O(logn)O(logn)
思路:先对已排序数组进行二分查找,找到目标值的下标后分别往左和往右顺序找相等的值的个数,返回该值的总数即可。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public int GetNumberOfK(int [] array, int k) {
int targetIndex = findValue(array, k, 0, array.length - 1);
if (targetIndex == -1) {
return 0;
}
int count = 1;
int tmp = targetIndex;
tmp--;
while (tmp > -1) {
if (array[tmp] == k) {
count++;
} else {
break;
}
tmp--;
}
tmp = targetIndex + 1;
while (tmp < array.length) {
if (array[tmp] == k) {
count++;
} else {
break;
}
tmp++;
}
return count;
}
private static int findValue(int[] array, int k, int begin, int end) {
if (end - begin < 0) {
return -1;
}
int middle = (begin + end) / 2;
if (array[middle] == k) {
return middle;
}
if (k < array[middle]) {
return findValue(array, k, begin, middle - 1);
}
return findValue(array, k, middle + 1, end);
}
}翻转句子中的单词
题目:I am a nowcode.翻转为 nowcode. a am I
思路:简单的一道题。按空格分隔句子,然后逆序打印单词,中间用空格分开即可。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "nowcoder. a am I";
System.out.println(ReverseSentence(sentence));
}
public static String ReverseSentence(String str) {
String[] words = str.split(" ");
if (words.length == 0){
return "";
}
StringBuffer reverseWords = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = words.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){
reverseWords.append(words[i]);
if (i != 0){
reverseWords.append(' ');
}
}
return reverseWords.toString();
}
}
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面(二)
题目:输入一个长度为 n 整数数组,数组里面可能含有相同的元素,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前面部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后面部分,对奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不做要求,但是时间复杂度和空间复杂度必须如下要求。
数据范围:0 ≤n≤50000,数组中每个数的值 0 ≤val≤10000
要求:时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)
思路:采用快速排序的思想,将数组元素分成两部分。从后往前遍历,如果是奇数,就与前面奇数部分的后一个元素交换位置,如果是偶数,则继续遍历,直到等于奇数部分的下一个下标。
解决方案:
public int[] reOrderArrayTwo (int[] array) {
// write code here
int lastOddIndex = -1;
int i = array.length - 1;
while (i > lastOddIndex + 1){
if (array[i] % 2 == 0){
i--;
} else {
int tmp = array[i];
lastOddIndex++;
array[i] = array[lastOddIndex];
array[lastOddIndex] = tmp;
}
}
return array;
}连续子数组的最大和
题目:
输入一个长度为n的整型数组array,数组中的一个或连续多个整数组成一个子数组,子数组最小长度为1。求所有子数组的和的最大值。
数据范围:1 <= n <= 2\times10^51<=n<=2×105
-100 <= a[i] <= 100−100<=a[i]<=100
要求:时间复杂度为 O(n)O(n),空间复杂度为 O(n)
进阶:时间复杂度为 O(n)O(n),空间复杂度为 O(1)
思路:最终的具有最大和的连续子数组以某个元素为结尾,那么计算所有dp[i],其表示以元素array[i]结尾的连续子数组最大和,每次计算后更新记录最大值即可。
解决方案:
public static int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
int length = array.length;
int[] maxSum = new int[length];
maxSum[0] = array[0];
int latter_sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++){
latter_sum = latter_sum + array[i];
if (latter_sum >= 0){
maxSum[i] = Math.max(maxSum[i - 1] + latter_sum, array[i]);
} else {
maxSum[i] = Math.max(maxSum[i - 1], array[i]);
}
if (maxSum[i] != maxSum[i - 1]){
latter_sum = 0;
}
}
return maxSum[length - 1];
}*最小的k个数**
题目:
给定一个长度为 n 的可能有重复值的数组,找出其中不去重的最小的 k 个数。例如数组元素是4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1,2,3,4(任意顺序皆可)。
数据范围:0≤k,n≤10000,数组中每个数的大小00≤val≤1000
要求:空间复杂度 O(n),时间复杂度 O(nlogk)
思路:需要用最小堆,先建最小堆,取堆顶元素出来,与最后一个元素交换,堆size减一,调整堆,再取堆顶元素与最后一个元素交换,直到取出k个数为止。使用java api优先级队列。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> inpurtQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
inpurtQueue.add(input[i]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> output = new ArrayList<>();
while (k-- > 0) {
output.add(inpurtQueue.poll());
}
return output;
}
}*数据流中的中位数
题目:如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。我们使用Insert()方法读取数据流,使用GetMedian()方法获取当前读取数据的中位数。
数据范围:数据流中数个数满足 1 ≤n≤1000 ,大小满足 1 ≤val≤1000
进阶: 空间复杂度 O(n) , 时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
思路:因为不断取出数据流,然后从取出的数据流中计算中位数,中位数能够从排序的数列中获取,所以对取出的数据流进行排序,用插入排序的话,每次取出一个元素需要将其插入已经排序序列,复杂度是O(N^2),如果插入时使用二分查找搜索插入的位置,则复杂度是O(log n)。二分查找的话找到元素之后还需要移动元素,复杂度也还是O(n),目前我只有O(n^2)的解法。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
private int[] array = new int[1001];
private int size = 0;
public void Insert(Integer num) {
if (size == 0) {
array[0] = num;
size++;
return;
}
int last = size - 1;
int insertIndex = size;
while (last >= 0) {
if (array[last] > num) {
array[last + 1] = array[last];
last--;
insertIndex--;
} else {
break;
}
}
array[insertIndex] = num;
size++;
}
public Double GetMedian() {
int middle = (size - 1) / 2;
if (size % 2 == 0) { // 偶数
return ((double) array[middle] + (double)array[middle + 1]) / 2;
} else {
return (double)array[middle];
}
}
}
栈的压入、弹出序列
题目:
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
1. 0<=pushV.length == popV.length <=1000
2. -1000<=pushV[i]<=1000
3. pushV 的所有数字均不相同
思路:如果能够按照push序列进栈,按照pop序列出栈,那么就说明该pop序列是该push序列的弹出序列。新建一个栈,按照push序列进栈,进栈后判断顶端元素是否与pop序列头元素相等,相等则一起移除,继续同样的判断直到栈顶元素和pop序列头元素不等,继续按照push序列进栈,如果最后当push序列的元素全部进栈结束后,栈为空且pop序列也为空,则该pop序列是push序列的一个弹出序列,反之则不是。
解决方案:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA, int [] popA) {
Stack<Integer> oneStack = new Stack<>();
int lengthOfPush = pushA.length;
int lengthOfPop = popA.length;
if (lengthOfPop != lengthOfPush) {
return false;
}
int indexOfPop = 0;
for (int i : pushA) {
oneStack.push(i);
while (!oneStack.empty() && oneStack.peek().equals(popA[indexOfPop])) {
oneStack.pop();
indexOfPop++;
}
}
return oneStack.empty() && indexOfPop == lengthOfPop;
}
}跳台阶
题目:
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
数据范围:1 \leq n \leq 401≤n≤40
要求:时间复杂度:O(n)O(n) ,空间复杂度: O(1)O(1)
思路:该题是动态规划分类下的,所以考虑寻找n从小到大的结果之间的关系。我们考虑最后一步如果是跳1级,那么f(n) = f(n-1),如果是跳2级,那么f(n) = f(n-2),实际这两种情况都是满足的,所以f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public int jumpFloor(int target) {
if (target == 1){
return 1;
}
if (target == 2){
return 2;
}
return jumpFloor(target - 1) + jumpFloor(target - 2);
}
}
顺时针打印矩阵
题目:
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵:
[[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8], [9,10,11,12], [13,14,15,16]]
则依次打印出数字
[1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10]
思路:比较简单的一道题。从外到内一圈一圈地打印,按顺序打印上面一行、右边一列、下面一行和左边一列,然后要考虑最后一圈是一行或者一列的情况,全部打印完即可。
解决方案:
package printMatrix;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] array = {{1,2,3,4},{5,6,7,8},{9,10,11,12},{13,14,15,16}};
ArrayList<Integer> result = printMatrix(array);
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
int row = matrix.length;
int column = matrix[0].length;
int rowBegin = 0;
int rowEnd = row - 1;
int colBegin = 0;
int colEnd = column - 1;
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
while ((colEnd - colBegin >= 0 && rowEnd - rowBegin >= 0) ||
(colEnd == colBegin && rowBegin == rowEnd)) {
// 打印上面一行
for (int i = colBegin; i <= colEnd; i++) {
result.add(matrix[rowBegin][i]);
}
//打印右边一列
for (int i = rowBegin + 1; i <= rowEnd; i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][colEnd]);
}
//打印下面一行
if (rowEnd != rowBegin) {
for (int i = colEnd - 1; i >= colBegin; i--) {
result.add(matrix[rowEnd][i]);
}
}
//打印左边一列
if (colBegin != colEnd) {
for (int i = rowEnd - 1; i >= rowBegin + 1; i--) {
result.add(matrix[i][colBegin]);
}
}
rowBegin++;
rowEnd--;
colBegin++;
colEnd--;
}
return result;
}
}
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面(一)
题目:
输入一个长度为 n 整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前面部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后面部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
数据范围:0 \le n \le 50000≤n≤5000,数组中每个数的值 0 \le val \le 100000≤val≤10000
要求:时间复杂度 O(n)O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
进阶:时间复杂度 O(n^2)O(n2),空间复杂度 O(1)O(1)
思路:调整数组元素的位置,使得所有的偶数位于数组的后面部分,并保证**奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
用快排分割两部分的方法会打乱原来顺序。只要遍历两次就行,第一次只取奇数,第二次只取偶数,都放到一个新的数组里。
解决方案:
package reOrderArray;
public class Solution {
public int[] reOrderArray (int[] array) {
// write code here
int length = array.length;
int[] resultArr = new int[length];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
if (array[i] % 2 == 1){
resultArr[index++] = array[i];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){
if (array[i] % 2 == 0){
resultArr[index++] = array[i];
}
}
return resultArr;
}
}
数组中只出现一次的两个数字
题目:
一个整型数组里除了两个数字只出现一次,其他的数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。
数据范围:数组长度 2\le n \le 10002≤n≤1000,数组中每个数的大小 0 < val \le 10000000<val≤1000000
要求:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
提示:输出时按非降序排列。
思路:由于题目要求空间复杂度O(1),想了很久,最后看了一下题解,好像也没有空间复杂度O(1)的解法。于是果断用上hashmap强硬地统计,最后遍历map获取count为1的两个数,完事。
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param array int整型一维数组
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] FindNumsAppearOnce (int[] array) {
// write code here
HashMap<Integer, Integer> valueCount = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (!valueCount.containsKey(array[i])) {
valueCount.put(array[i], 1);
} else {
valueCount.put(array[i], 2);
}
}
int[] arrayResult = new int[2];
int index = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry :
valueCount.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().equals(1)) {
arrayResult[index++] = entry.getKey();
}
}
if (arrayResult[1] < arrayResult[0]) {
// sort
int tmp = arrayResult[1];
arrayResult[1] = arrayResult[0];
arrayResult[0] = tmp;
}
return arrayResult;
}
}不用加减乘除做加法
题目:
写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+、-、*、/四则运算符号。
数据范围:两个数都满足 -10 \le n \le 1000−10≤n≤1000
进阶:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1),时间复杂度 O(1)O(1)
思路:看了一下题解,就是用与运算符计算与结果作为进位,用异或运算符作为加之后的结果,进位左移再异或计算,直到进位为0,返回异或的结果。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public int Add(int num1,int num2) {
int shift = num1 & num2;
int sum = num1 ^ num2;
if (shift == 0){
return sum;
}
shift = shift << 1;
return Add(shift, sum);
}
}跳台阶扩展问题
题目:描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶(n为正整数)总共有多少种跳法。
数据范围:1 \le n \le 201≤n≤20
进阶:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1) , 时间复杂度 O(1)O(1)
思路:根据最后一步跳多少级可以得出根据递推公式,f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) + 。。。。+f(1) + 1,又因为 f(n-1) = f(n-2) + 。。。。+f(1) + 1,所以实际上f(n) =2 f(n-1),代码实现递归计算即可。
解决方案:
package jumpFloorII;
public class Solution {
public int jumpFloorII(int target) {
if (target == 1){
return 1;
}
return jumpFloorII(target - 1) * 2;
}
}
矩阵中的路径
题目:
请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个n乘m的矩阵中是否存在一条包含某长度为len的字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则该路径不能再进入该格子。 例如
[[a,b,c,e],[s,f,c,s],[a,d,e,e]] 矩阵中包含一条字符串"bcced"的路径,但是矩阵中不包含"abcb"路径,因为字符串的第一个字符b占据了矩阵中的第一行第二个格子之后,路径不能再次进入该格子。
数据范围:0≤n,m≤20 ,1\le len \le 25\1≤len≤25
思路:首先遍历整个矩阵,找到和首字符匹配的字符位置,然后深度优先搜索下一个可达的并且当前搜索路径上未访问的位置,判断是否匹配字符串的下一个字符,匹配到了就继续对可达位置深度优先搜索,直到能够匹配最后一个字符,就说明能够找到包含整个字符串的路径,返回true,在这个过程中只要有一个字符没能匹配到,就返回false。回溯的时候需要将当前最近访问过的位置重置为false。
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param matrix char字符型二维数组
* @param word string字符串
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean hasPath (char[][] matrix, String word) {
// write code here
int row = matrix.length;
int column = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[row][column];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++){
if (matrix[i][j] == word.charAt(0)){
isVisited = setToFalse(isVisited, row, column);
isVisited[i][j] = true;
boolean nowMatch = findTheNextChar(matrix, row, column, i, j, isVisited, word, 0);
if (nowMatch){
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean findTheNextChar(char[][] matrix, int row, int column,
int currentRow, int currentCol, boolean[][] isVisited, String word,
int currentMatched) {
if (currentMatched == word.length() - 1){
return true;
}
int[] row_offset = {-1, +1, 0, 0};
int[] col_offset = {0, 0, -1, +1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int next_row = currentRow + row_offset[i];
int next_col = currentCol + col_offset[i];
if (next_row >= 0 && next_row < row && next_col >= 0 && next_col < column && !isVisited[next_row][next_col]){
if (matrix[next_row][next_col] == word.charAt(currentMatched + 1)){
//matched
isVisited[next_row][next_col] = true;
boolean result = findTheNextChar(matrix, row, column, next_row, next_col, isVisited, word, currentMatched + 1);
if (result){
return true;
}
isVisited[next_row][next_col] = false;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean[][] setToFalse(boolean[][] matrix, int row, int column) {
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++){
matrix[i][j] = false;
}
}
return matrix;
}
}数字序列中某一位的数字
题目:数字以 0123456789101112131415... 的格式作为一个字符序列,在这个序列中第 2 位(从下标 0 开始计算)是 2 ,第 10 位是 1 ,第 13 位是 1 ,以此类题,请你输出第 n 位对应的数字。
数据范围: 0≤n≤109
思路:根据数字序列的顺序规律,计算1位数、2位数等分别占位置的区间,1位数占位区间为【0,9】,2位数占位区间为【10,99】,除了1位数序列是10位,后面n位数序列有数字位9*10^(n-1)*n,先计算出n位对应数字所在的区间,再确定所在的数,最后获取该位数。
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param n int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int findNthDigit (int n) {
// write code here
if (n < 10) {
return n;
}
// write code here
long nBit = (long)n;
long count = 1;
int index = 0;
for (index = 0; index < 1000; index++) {
// 1位数的有10 * 1位;2位数的为10-99,总共位数为9 * 10 * 2,推出所有(index + 1)位数总共包含9的index次方+10* (index + 1)
count = count + longPow(10, index) * 9 * (index + 1);
if (count >
nBit) { // (index + 1)位的数排列后总位数超出了n,说明最终n位所在的数正是(index + 1)
break;
}
}
count = count - longPow(10,
index) * 9 * (index + 1); // 得出前index位数组成的序列总位数
nBit = nBit - count; // 让序列从第一个(index + 1)位数开始排起
// 次数序列从第一个(index + 1)位数开始
// 计算是第几个数
long num = nBit / (index + 1);
int left = (int)nBit % (index + 1);
// 计算最终n所在的数
num = longPow(10, index) + num;
System.out.println("num is " + num + " and left is " + left);
if (index == 0) { // 有个坑,如果index为0,num只能从1开始
num -= 1;
}
// 计算具体是哪一位
String s = num + "";
return Integer.parseInt(s.substring(left, left + 1));
}
private long longPow(int value, int pow) {
long result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < pow; i++) {
result *= value;
}
return result;
}
}机器人的运动范围
地上有一个 rows 行和 cols 列的方格。坐标从 [0,0] 到 [rows-1,cols-1] 。一个机器人从坐标 [0,0] 的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 threshold 的格子。 例如,当 threshold 为 18 时,机器人能够进入方格 [35,37] ,因为 3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格 [35,38] ,因为 3+5+3+8 = 19 。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
数据范围: 0≤threshold≤15 ,1 \le rows,cols \le 100 \1≤rows,cols≤100
进阶:空间复杂度 O(nm) \O(nm) ,时间复杂度 O(nm) \O(nm)
思路:题目难度一般,只要用对深度优先搜索算法就能较快的解出。从【0,0】开始遍历下一步可到达的位置,进一步判断其合法性,本题是下标位数之和小于给定阈值。这个过程用递归实现,每次递归之后的计数作为返回值,当再没有可达位置的时候停止递归,返回最终的位置计数。
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
boolean[][] isArrived = new boolean[rows][cols];
int count = 1;
isArrived[0][0] = true;
count = movingCount(isArrived, threshold, 0, 0, rows, cols, count);
return count;
}
public int movingCount(boolean[][] isArrived, int threshold, int curRow,
int curCol, int rows, int cols, Integer count) {
int[] offsetRow = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] offsetCol = {0, 0, -1, 1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextRow = curRow + offsetRow[i];
int nextCol = curCol + offsetCol[i];
if (nextRow >= 0 && nextRow < rows && nextCol >= 0 && nextCol < cols) {
if (!isArrived[nextRow][nextCol] &&
bitSum(nextRow) + bitSum(nextCol) <= threshold) {
count++;
isArrived[nextRow][nextCol] = true;
// 这个位置是可达的,继续遍历递归
count = movingCount(isArrived, threshold, nextRow, nextCol, rows, cols, count);
}
}
}
return count;
}
private int bitSum(int num) {
String numStr = num + "";
int bitSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numStr.length(); i++) {
bitSum += Integer.parseInt(numStr.substring(i, i + 1));
}
return bitSum;
}
}
求两个有序数组的第k小值
题目:从两个从小到大排好序的数组中查找第k小的值;
思路:用归并排序的方法合并这两个有序数组,合并到第k小的值时返回,题目保证k合法,即不超过两个数组的长度之和。走一趟归并排序,从两个有序数组中获取首位较小的值,首位较小的数组下标后移,直到找到第k小的值。这里需要判断边界值,两个数组的首位下标不超过数组长度。这种方法复杂度是O(k)。另一种获取第k小值的方法是将两个数组的数都压入一个优先级队列,生成一个最小堆,从最小堆获取k次队头的值即是第k小的值。第二种算法复杂度是kO(log n)
解决方案:
package kthNum;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 5, 1000};
int[] b = {2, 6, 8, 9};
int result = findK(a, b, 7);
System.out.println(result);
}
private static int findK(int[] a, int[] b, int K) {
// 返回a,b两个数组第K小的值。 这里用归并排序的方法合并这两个有序数组,合并到第k小的值时返回,题目保证k合法,即不超过两个数组的长度之和
int aIndex = 0;
int bIndex = 0;
int countTh = 0;
int currentMin = 0;
int aLength = a.length;
int bLength = b.length;
while (aIndex < aLength && bIndex < bLength){
if (a[aIndex] < b[bIndex]){
currentMin = a[aIndex];
aIndex++;
} else {
currentMin = b[bIndex];
bIndex++;
}
countTh++;
if (countTh == K){
return currentMin;
}
}
if (aIndex >= aLength){
return b[bIndex + K - countTh - 1];
}
return a[aIndex + K - countTh - 1];
/*
这里使用了优先级队列来存储最小值,其本质是最小堆;从这个最小堆取k次最小值得到第k小的值;输入的两个数组不要求有序
PriorityQueue<Integer> minheap = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int j : a) {
minheap.add(j);
}
for (int j : b) {
minheap.add(j);
}
for (int i = 0; i < K - 1; i++){
minheap.poll();
}
return minheap.poll();*/
}
}
数组中的逆序对
题目:在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数P。并将P对1000000007取模的结果输出。 即输出P mod 1000000007。
思路:用归并排序算法对数组进行排序,然后在合并两个有序子数组的时候,如果右边数组的首元素小于左边数组的首元素,则右数组该元素与左数组所有元素组成逆序对,此时逆序对个数增加左数组当前元素个数。
解决方案:
package InversePairs;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,0};
int n = nums.length;
int[] tmp = new int[n];
InversePairs(nums);
System.out.println(count);
}
private static long count = 0;
public static int InversePairs(int [] array) {
int n = array.length;
int[] tmp = new int[n];
mergeSort(array, 0, n - 1, tmp);
return (int)(count % 1000000007);
}
private static void mergeSort(int[] nums, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left == right){//当拆分到数组当中只要一个值的时候,结束递归,递归一定要有结束条件
return;
}
int mid = (left+right)/2; //找到下次要拆分的中间值
mergeSort(nums,left,mid,temp);//记录树左边的
mergeSort(nums,mid+1,right,temp);//记录树右边的
//合并两个区间
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
temp[i] = nums[i];
//temp就是辅助列表,新列表的需要排序的值就是从辅助列表中拿到的
}
int i = left; //给辅助数组里面的值标点
int j = mid +1;
for (int k = left; k <= right ; k++) {//k 就为当前要插入的位置
if (i == mid + 1){
nums[k] = temp[j];
j++;
}else if (j == right+1){
nums[k] = temp[i];
i++;
}
else if (temp[i] <= temp[j]){
nums[k] = temp[i];
i++;
}else {
nums[k] = temp[j];
count += mid - i + 1;
j++;
}
}
}
}
链表内指定区间反转
题目:
将一个节点数为 size 链表 m 位置到 n 位置之间的区间反转,要求时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)。
例如:
给出的链表为 1→2→3→4→5 → 1→2→3→4→5→NULL, m=2,n=4,
返回 1→4→3→2→5→ 1→4→3→2→5→NULL.
数据范围: 链表长度 0<≤10000<size≤1000,00<m≤n≤size,链表中每个节点的值满足 ∣∣≤1000∣val∣≤1000
要求:时间复杂度 O(n) ,空间复杂度 O(n)
进阶:时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)
思路:反转链表的算法是通用的,在前面已经写过,这里因为反转的是链表的中间片段,所以理所当然要通过遍历找到反转片段的起点,找到的时候记录上一个节点F方便后面重新接上,然后往后遍历的同时进行反转,也就是当前节点指针指向前节点,至节点n之后结束,记录结束之后的节点为L,最后就是反转片段的新头节点(如果F为null,,它就是头节点)与前面记录的节点F相接(F不为null),反转片段的新尾部节点next接后面的节点L。时间复杂度为O(log n),由于只需要几个临时变量,所以空间复杂度为O(1)。
解决方案:
package reverseBetween;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5);
node1.next = node2;
// node2.next = node3;
//node3.next = node4;
//node4.next = node5;
ListNode result = reverseBetween(node1, 1, 2);
System.out.println(result.val);
}
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @param m int整型
* @param n int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
public static ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) {
// write code here
//记录几个位置,反转中间一段链表,然后将几个位置接起来
ListNode beforeReverse = null;
ListNode reversedListTail = null;
ListNode preNode = null;
ListNode currentNode = head;
int cursor = 1;
while (cursor <= n){// 小于等于n的节点都要反转
if (cursor < m){// 还不用反转
beforeReverse = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} else if (cursor == m){ //开始需要反转
reversedListTail = currentNode;// 记录反转片段的头节点
preNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} else {// 指向前一个节点
ListNode tmpNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
tmpNode.next = preNode;
preNode = tmpNode;
}
cursor++;
}
if (beforeReverse != null){
beforeReverse.next = preNode;
} else { //也就是首节点是需要反转的
head = preNode;
}
reversedListTail.next = currentNode;
return head;
}
}
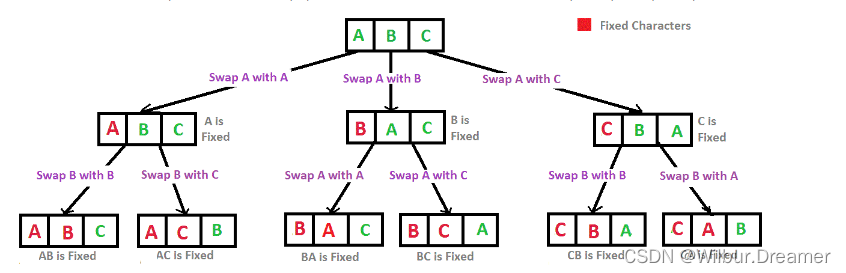
字符串的排列
题目:输入一个长度为 n 字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列,你可以以任意顺序返回这个字符串数组。例如输入字符串ABC,则输出由字符A,B,C所能排列出来的所有字符串ABC,ACB,BAC,BCA,CBA和CAB。
思路:该题目要求算出字符串中字符的所有排列。任意交换两个字符,可以得到新的字符串,比如“AB”交换之后得到“BA”。如下图所示,递归交换生成一棵树,树的子节点就是排列字符串。最后收集排列字符串的时候要用HashSet存储以去重。
解决方案:
package stringSequence;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Solution {
private static final ArrayList<String> allSequences = new ArrayList<>();
private static final HashSet<String> restltStrings = new HashSet<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
String base = "aab";
ArrayList<String> result = Permutation(base);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
allSequences.clear();
restltStrings.clear();
getSequences(str, -1);
allSequences.addAll(restltStrings);
return allSequences;
}
public static void getSequences(String str, int lastFixed) {
int length = str.length();
if (lastFixed == length - 2) {
restltStrings.add(str);
}
lastFixed++;
for (int i = lastFixed; i < length; i++) {
// 从lastFixed开始每一位都跟lastFixed交换得到一个字符
String newSeq = swapString(str, lastFixed, i);
// 对于一个新字符串,递归同样的操作
getSequences(newSeq, lastFixed);
}
}
private static String swapString(String base, int index1, int index2) {
StringBuilder newStr = new StringBuilder();
int n = base.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i == index1) {
newStr.append(base.charAt(index2));
} else if (i == index2) {
newStr.append(base.charAt(index1));
} else {
newStr.append(base.charAt(i));
}
}
return newStr.toString();
}
}
数值的整数次方
题目:实现函数 double Power(double base, int exponent),求base的exponent次方。
注意:
1.保证base和exponent不同时为0。
2.不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题
3.有特殊判题,不用考虑小数点后面0的位数。
思路:根据exponent的绝对值对base进行累积就可以,如果exponent是负数,再除以1。
解决方案:
package Power;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double base = 2.0;
int exponent = -2;
System.out.println(Power(base, exponent));
}
public static double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if (base == 0){
return 0.0;
}
if (exponent == 0){
return 1.0;
}
double result = 1;
if (exponent > 0){
for (int i = 0; i < exponent; i++){
result *= base;
}
} else {
exponent = 0 - exponent;
for (int i = 0; i < exponent; i++){
result *= base;
}
result = 1 / result;
}
return result;
}
}
把字符串转换成整数(atoi)
题目:写一个函数 StrToInt,实现把字符串转换成整数这个功能。不能使用 atoi 或者其他类似的库函数。传入的字符串可能有以下部分组成:
1.若干空格
2.(可选)一个符号字符('+' 或 '-')
3. 数字,字母,符号,空格组成的字符串表达式
4. 若干空格
思路:根据题目要求,先去掉前导空格,然后判断第一个字符是否为+或-从而确定正负,接着判断下一个字符是否为数字,如果不是,则没有有效的整数部分,返回0,如果是,往后遍历找连续的整数数字得到有效的整数部分。收集到有效的整数部分后如果是负数前面再拼接一个-,用Integer.parseInt转换成整数,用捕获异常的方式处理大于最大整数和小于最小整数的情况即可。
解决方案:
package StrToInt;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " -21474836471"; // 2147483647
int num = StrToInt(str);
System.out.println(num);
}
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param s string字符串
* @return int整型
*/
public static int StrToInt (String s) {
// write code here
s = s.trim();
boolean isPositive = true;
int beginFrom = 0;
StringBuilder collectStringNumbers = new StringBuilder();
if (s.startsWith("-")){
isPositive = false;
beginFrom = 1;
collectStringNumbers.append('-');
} else if (s.startsWith("+")){
beginFrom = 1;
}
String maxInt = String.valueOf(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
String minInt = String.valueOf(Integer.MIN_VALUE).substring(1);
int length = s.length();
if (beginFrom == length){
return 0;
}
if (!(s.charAt(beginFrom) >= '0' && s.charAt(beginFrom) <= '9')){
return 0;
}
for (int i = beginFrom; i < length; i++){
if (s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9'){
collectStringNumbers.append(s.charAt(i));
} else {
break;
}
}
String onlyNumbers = collectStringNumbers.toString();
if (onlyNumbers.equals("")){
return 0;
}
int number;
try {
number = Integer.parseInt(onlyNumbers);
} catch (Exception e){
if (isPositive){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
return number;
}
}
最长不含重复字符的子字符串
题目:请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。
数据范围: s.length≤40000 s.length≤40000
思路:对于输入的字符串s,令f(n)为以s[n]结尾的最长子串,由f(n)求f(n + 1)的方法是,判断s[n+1]是否在f(n)字符串中,如果不在则f(n+1)为f(n)后面加一个字符,如果在则求f(n)中s[n+1]的位置右边部分子串然后拼接s[n + 1],并更新最长子串长度的最大值,最大值即所求值。
解决方案:
package lengthOfLongestSubstring;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring("pwwkew"));
}
public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {
// write code here
if (s.equals("")){
return 0;
}
int maxLength = 1;
ArrayList<String> longestSubStringEndWith = new ArrayList<>();
int length = s.length();
longestSubStringEndWith.add(String.valueOf(s.charAt(0)));
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++){
String preLongestSubString = longestSubStringEndWith.get(i - 1);
int indexofCurrrent = preLongestSubString.indexOf(s.charAt(i) + "");
String newlongestSubString = "";
if (indexofCurrrent == -1){ // 不存在,最长子串加当前字符
newlongestSubString = preLongestSubString + s.charAt(i);
} else {
newlongestSubString = preLongestSubString.substring(indexofCurrrent + 1) + s.charAt(i);
}
if (newlongestSubString.length() > maxLength){
maxLength = newlongestSubString.length();
}
longestSubStringEndWith.add(newlongestSubString);
}
return maxLength;
}
}
和为S的连续正数序列
题目:小明很喜欢数学,有一天他在做数学作业时,要求计算出9~16的和,他马上就写出了正确答案是100。但是他并不满足于此,他在想究竟有多少种连续的正数序列的和为100(至少包括两个数)。没多久,他就得到另一组连续正数和为100的序列:18,19,20,21,22。现在把问题交给你,你能不能也很快的找出所有和为S的连续正数序列?
思路:采用滑动窗口的思想,一开始滑动窗口内元素为0,遍历数组,把遍历到的元素放入滑动窗口,并统计当前滑动窗口内所有数值的和,如果等于则滑动窗口内的序列就是满足结果的,如果小于S则继续遍历数组往窗口里加,如果大于S就要去除窗口最左数,窗口左界加1.
解决方案:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
int windowLeft = 1;
int windowRight = 2;
int up = (sum - 1) / 2;
int windowSum = 3;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (windowLeft <= up) {
if (sum == windowSum) {
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = windowLeft; i <= windowRight; i++) {
tmp.add(i);
}
result.add(tmp);
windowSum -= windowLeft;
windowLeft++;
} else if (windowSum < sum) {
windowRight++;
windowSum += windowRight;
} else {
windowSum -= windowLeft;
windowLeft++;
}
}
return result;
}
}滑动窗口的最大值
题目:给定一个长度为 n 的数组 num 和滑动窗口的大小 size ,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值。例如,如果输入数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,他们的最大值分别为{4,4,6,6,6,5}; 针对数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}的滑动窗口有以下6个: {[2,3,4],2,6,2,5,1}, {2,[3,4,2],6,2,5,1}, {2,3,[4,2,6],2,5,1}, {2,3,4,[2,6,2],5,1}, {2,3,4,2,[6,2,5],1}, {2,3,4,2,6,[2,5,1]}。
思路:滑动窗口在滑动的时候会移除和添加数据,也就是在这个动态的变化过程求最大值,所以想到用堆去计算最大值,每次滑动窗口的时候将所有数据放入堆中,然后从堆顶拿最大值。
解决方案:
package maxInWindows;
import huaweiod.calculatetopn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1};
System.out.println(maxInWindows(arr, 3));
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size) {
int length = num.length;
if (size == 0 || size > length){
return new ArrayList<>();
}
ArrayList<Integer> maxValueList = new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxValueHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
int windowLeft = 0;
int windowRight = size - 1;
while (windowRight < length){
maxValueHeap.clear();
for (int i = windowLeft; i <= windowRight; i++){
maxValueHeap.add(num[i]);
}
maxValueList.add(maxValueHeap.poll());
windowRight++;
windowLeft++;
}
return maxValueList;
}
}
孩子们的游戏(圆圈中最后剩下的数)
题目:每年六一儿童节,牛客都会准备一些小礼物和小游戏去看望孤儿院的孩子们。其中,有个游戏是这样的:首先,让 n 个小朋友们围成一个大圈,小朋友们的编号是0~n-1。然后,随机指定一个数 m ,让编号为0的小朋友开始报数。每次喊到 m-1 的那个小朋友要出列唱首歌,然后可以在礼品箱中任意的挑选礼物,并且不再回到圈中,从他的下一个小朋友开始,继续0... m-1报数....这样下去....直到剩下最后一个小朋友,可以不用表演,并且拿到牛客礼品,请你试着想下,哪个小朋友会得到这份礼品呢?
思路:数据结构使用双向链表,因为方便删除数据,第一次删除处于m-1位置的数,下次尝试删除后面+(m-1)位置的数,如果超出此时链表的长度,则需要计算目标位置对链表长度取余的值进行删除,因为链表需要看成是环状的。
解决方案:
package LastRemaining_Solution;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print(LastRemaining_Solution(
10,17));
}
public static int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) {
LinkedList<Integer> numbers = new LinkedList<>();
if (n == 1) {
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
numbers.add(i);
}
int begin = 0;
while (numbers.size() > 1) {
int currentRemove = begin + m - 1;
if (currentRemove > numbers.size() - 1) {
currentRemove = currentRemove % numbers.size();
}
numbers.remove(currentRemove);
begin = currentRemove;
}
return numbers.get(0);
}
}
买卖股票的最大利益
题目:给定一只股票的一段时间内每天的价格,在这段时间内,允许你多次买卖这只股票,求可以获得的最大利益。
思路:买卖股票的时候如果知道接下来股票会涨,那就会提前买入和继续持有,如果股票接下来会跌,那就应该是赶紧卖出,或者是等待买的时机。基于以上逻辑,对当天和第二天的股价进行对比,再根据当前手上是否持有股票,进而判断是买入、卖出还是暂时不操作。
解决方案:
public static int maxProfit(int[] prices){
int length = prices.length;
int profit = 0;
int hasPrice = 0;
boolean bHas = false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
if (i + 1 < length){
if (prices[i] > prices[i+1]){
if (bHas){
profit += prices[i] - hasPrice;
bHas = false;
}
} else if (prices[i] < prices[i+1]){
if (!bHas){
hasPrice = prices[i];
bHas = true;
}
}
} else {
if (bHas){
profit += prices[i] - hasPrice;
}
}
}
return profit;
}逐层打印一棵树
题目:对一个树进行逐层打印节点值,也就是根节点值打印在第一行,其左右两节点打印在第二行,以此类推。
思路:用一个队列存储即将要打印的节点序列,每次从队列头拿出节点进行打印,将当前要打印的节点的左右子节点存入队列,同时每个节点带上所处的层级,当打印的节点层级增加时,打印一个换行符。
解决方案:
public static void printTree(Node root){
Queue<NodeWithLayer> treeNodes = new LinkedList<>();
NodeWithLayer layerNodeRoot = new NodeWithLayer();
layerNodeRoot.node = root;
layerNodeRoot.layer = 0;
treeNodes.add(layerNodeRoot);
int currentLayer = 0;
while (!treeNodes.isEmpty()){
NodeWithLayer currentNode = treeNodes.poll();
if (currentNode.layer > currentLayer){
System.out.print("\n");
}
System.out.print(currentNode.node.value);
System.out.print(' ');
currentLayer = currentNode.layer;
if (currentNode.node.left != null){
NodeWithLayer leftNode = new NodeWithLayer();
leftNode.node = currentNode.node.left;
leftNode.layer = currentLayer + 1;
treeNodes.add(leftNode);
}
if (currentNode.node.right != null) {
NodeWithLayer rightNode = new NodeWithLayer();
rightNode.node = currentNode.node.right;
rightNode.layer = currentLayer + 1;
treeNodes.add(rightNode);
}
}
}
public static class NodeWithLayer{
Node node;
int layer;
}
public static class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
}整数中1出现的次数(从1到n整数中1出现的次数)
题目:输入一个整数 n ,求 1~n 这 n 个整数的十进制表示中 1 出现的次数
例如, 1~13 中包含 1 的数字有 1 、 10 、 11 、 12 、 13 因此共出现 6 次
思路:题目描述很简单也很容易懂,但是解起来却不容易,因为跟一般算法无关,所以只能用数学推导出其中的“奥妙”。题目实际想求1~n的数中,每一位等于1时,其他位能取值的范围累计有多少种,类似“滚轮密码锁”,设置一个最大值,将某一位设为1,其他位有多少种组合的方式?然后对每一位的取值做区别和判断:
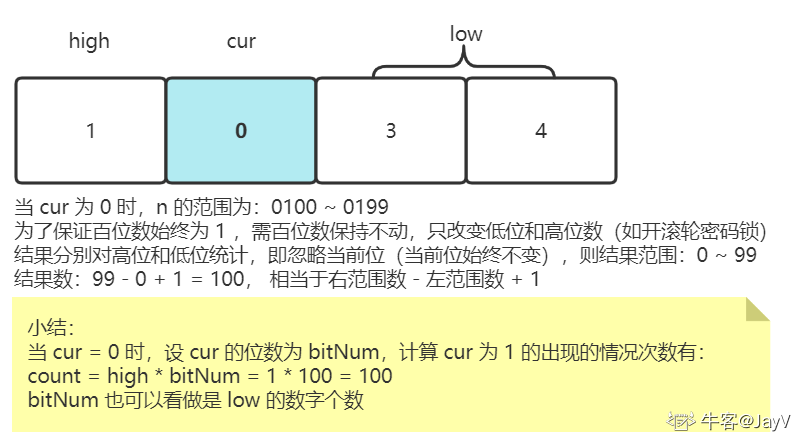
1. cur = 0 :
- 设 n = 1034 的百位数 “0” 为 cur,作为当前位,则 “1” 为 high,作为高位数,“34” 为 low,表示低位数
-
公式解释:
因为 cur 始终不变,而我们只统计出现不同数字情况的数量,因此可忽略不变量,此处可通过刚刚说过的行李箱 “滚动密码锁” 的开锁帮助理解
对高低位分别计算:如上面的 0100-0199,忽略当前位: 0-099,高位 0 忽略,低位 99
而 99 有 0~99 的情况,则有 100 种结果
公式
count = high * bitNum可以这样理解:忽略不变的 cur,相当于 99,count = 高位数的结果 + 低位数的结果,即0 + (99 + 1) = 1 * 100 = 0 + (99 + 1) = (high - 1) * bitNum + (99 + 1),也是计算高位和低位的结果数之和
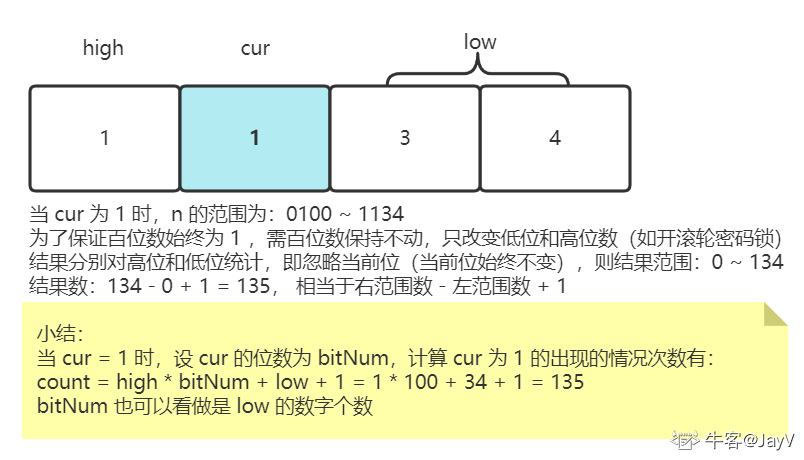
2. 当 cur = 1
- 设 n = 1134 的百位数 “1” 为 cur,作为当前位,则最左边的 “1” 为 high,作为高位数,“34” 为 low,表示低位数
-
公式解释:
因为 cur 始终不变,而我们只统计出现不同数字情况的数量,因此可忽略不变量,此处可通过刚刚说过的行李箱 “滚动密码锁” 的开锁帮助理解
对高低位分别计算:如上面的 0100-1134,忽略当前位: 000 - 134,对于134, 高位为 1,低位为 34
而 134 有 0 ~ 134 的情况,则有 135 种结果
好比使用滚轮密码锁,保持 cur 为 1 不变,不断从 0100 到 1134 改变高位和低位的数字,总共就有 135 种结果
公式
count = high * bitNum + low + 1可以这样理解:忽略不变的 cur,相当于 134,count = 高位数的结果 + 低位数的结果,即134 + 1 = 1 * 100 + 34 + 1 = (1 * 100) + (34 + 1) = (high * bitNum) + (low + 1), 最后的 (low + 1) 表示低位数都为 0 的情况
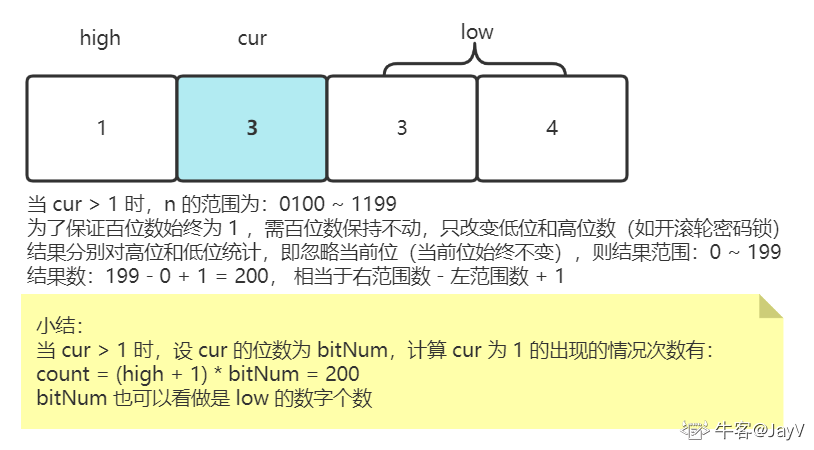
3. 当 cur > 1
- 设 n = 1334 的百位数 “3” 为 cur,作为当前位,则 “3” 为 high,作为高位数,“34” 为 low,表示低位数
-
公式解释:
因为 cur 始终不变,而我们只统计出现不同数字情况的数量,因此可忽略不变量,此处可通过刚刚说过的行李箱 “滚动密码锁” 的开锁帮助理解
对高低位分别计算:如上面的 0100-0199,忽略当前位: 0-099,高位 0 忽略,低位 99
而 99 有 0~99 的情况,则有 100 种结果
公式
count = (high + 1) * bitNum可以这样理解:忽略不变的 cur,相当于 199,count = 高位数的结果 + 低位数的结果,即199 + 1 = (1 + 1) * 100 = (1 * 100) + (99 + 1) = (high * bitNum) + (低位数结果数)
解决方案:
package NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(0));
}
public static int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int base = 1;
int result = 0;
while (base <= n) {
int cur = n / base % 10;
int high = n / base / 10;
int low = n % base;
if (cur > 1) {
result += (high + 1) * base;
} else if (cur == 0) {
result += high * base;
} else {
result += high * base + low + 1;
}
base *= 10;
}
return result;
}
}
数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目:给一个长度为 n 的数组,数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组[1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2]。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。
思路:遍历数组,将每个数值出现次数存入一个hash表中,并判断次数是否超过数组长度的一半,是的话就返回该值。
解决方案:
package MoreThanHalfNum_Solution;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1};
}
public static int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(ArrayList<Integer> array) {
int length = array.size();
Map<Integer, Integer> valueCount = new HashMap<>();
if (length == 1){
return array.get(0);
}
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
if (valueCount.containsKey(array.get(j))) {
int value = valueCount.get(array.get(j)) + 1;
if (value > length / 2) {
return array.get(j);
}
valueCount.put(array.get(j), value);
} else {
valueCount.put(array.get(j), 1);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
把数组排成最小的数
题目:输入一个非负整数数组numbers,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。
例如输入数组[3,32,321],则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为321323。
1.输出结果可能非常大,所以你需要返回一个字符串而不是整数
2.拼接起来的数字可能会有前导 0,最后结果不需要去掉前导 0
思路:对数组的数进行排序,判断两个数大小的方法重载为逐位遍历两个整数并判断位上数的大小,小的排前面,如果其中一个数提前结束了,则假设其位为最高位。看了题解,其实只要比较x + y < y + x即可。
解决方案:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public String PrintMinNumber(int [] numbers) {
Integer[] originalNumbers;
originalNumbers = Arrays.stream(numbers).boxed().toArray(Integer[]::new);
Arrays.sort(originalNumbers, (n1, n2) -> nyCompare(n1, n2));
StringBuilder minNumberResult = new StringBuilder();
for (Integer originalNumber : originalNumbers) {
minNumberResult.append(originalNumber);
}
return minNumberResult.toString();
}
public static int nyCompare(Integer n1, Integer n2) {
int highestBit = (int) String.valueOf(n1).charAt(0);
int index = 0;
String n1Str = String.valueOf(n1);
String n2Str = String.valueOf(n2);
int n1Length = n1Str.length();
int n2Length = n2Str.length();
while (index < n1Length && index < n2Length) {
if (n1Str.charAt(index) < n2Str.charAt(index)) {
return -1; //return n1;
}
if (n1Str.charAt(index) > n2Str.charAt(index)) {
return 1; // return n2;
}
index++;
}
if (index == n1Length && index == n2Length) {
return 0; //return n1;
}
if (index == n1Length) {
while (index < n2Length) {
if (highestBit == n2Str.charAt(index)) {
index++;
} else {
return highestBit - n2Str.charAt(index);
}
}
return 1;
// return highestBit > n2Str.charAt(index) ? n2 : n1;
}
if (index == n2Length) {
while (index < n1Length) {
if (highestBit == n1Str.charAt(index)) {
index++;
} else {
return n1Str.charAt(index) - highestBit;
}
}
return -1;// return highestBit > n1Str.charAt(index) ? n1 : n2;
}
return 1;
}
}还原双倍数组的原数组
题目:将一个数组中的所有整数乘以2得到新值放到原数组中,并和原数组的值一起打断顺序存储,将这样的数组称为一个双倍数组。给定一个双倍数组,求原数组。
思路:遍历双倍数组的元素,通过“摘除”掉每一对成二倍关系的数对,判断最终能否全部成对并记录原数组的值,可以得到原数组,需要一个辅助hashmap存储暂时没能配对的数,配对的时候去hashmap中查找是否有等于其一半或二倍的数,有的话就匹配成功一对,则从hashmap中将该元素的value减1,如果下标为0了,则直接删除,最终判断hashmap是否为空,是的话就是还原原数组成功。
方案:
package original;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,3,4,2,6,8, 9,10};
System.out.println(getOriginal(arr));
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> getOriginal(int[] original){
Map<Integer, Integer> keyCount = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j : original) {
int half = j / 2;
int doubleVal = j * 2;
if (j % 2 == 0 && keyCount.containsKey(half)) {
int curVal = keyCount.get(half);
if (curVal > 1) {
keyCount.put(half, curVal - 1);
} else {
keyCount.remove(half);
}
result.add(half);
} else if (keyCount.containsKey(doubleVal)) {
int curVal = keyCount.get(doubleVal);
if (curVal > 1) {
keyCount.put(doubleVal, curVal - 1);
} else {
keyCount.remove(doubleVal);
}
result.add(j);
} else if (keyCount.containsKey(j)) {
int curValue = keyCount.get(j);
keyCount.put(j, curValue + 1);
} else {
keyCount.put(j, 1);
}
}
if (keyCount.isEmpty()){
return result;
}
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
剪绳子(进阶版)
题目:给你一根长度为 n 的绳子,请把绳子剪成整数长的 m 段( m 、 n 都是整数, n > 1 并且 m > 1 , m <= n ),每段绳子的长度记为 k[1],...,k[m] 。请问 k[1]*k[2]*...*k[m] 可能的最大乘积是多少?例如,当绳子的长度是 8 时,我们把它剪成长度分别为 2、3、3 的三段,此时得到的最大乘积是 18 。由于答案过大,请对 998244353 取模。
思路:这道题涉及到数学推导和快速幂的算法。首先用数学推导的方法推导出当尽量减成相等片段并且等长的片段长度是3的时候各个片段长乘积具有最大值。由于推导过于复杂,这里引用一下
然后用快速幂算法求3^n值。快速幂将指数转成二进制数然后分别计算各个位的权重,遍历所有位,只要位1,就与权重相乘,累加。例如3^5计算的时候,5的二进制数为101,从个位到高位权重分别为3^0,3^1,3^2,所以结果为3^0+3^2。
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param number long长整型
* @return long长整型
*/
public long cutRope (long number) {
// write code here
if (number <= 3) {
return number - 1;
}
if (number % 3 == 0) {
return fastPow(3, number / 3) % 998244353;
}
if (number % 3 == 1) {
return fastPow(3, number / 3 - 1) * 4 % 998244353;
}
return fastPow(3, number / 3) * 2 % 998244353;
}
private static long fastPow(long base, long pow) {
long result = 1;
while (pow >= 1) {
if ((pow & 1) == 1) {
result *= base;
if (result > 998244353) {
result = result % 998244353;
}
}
base *= base;
if (base > 998244353) {
base = base % 998244353;
}
pow = pow >> 1;
}
return result % 998244353;
}
}字符流中第一个不重复的字符
题目:请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符 "go" 时,第一个只出现一次的字符是 "g" 。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符 “google" 时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"l"。
思路:1、需要统计只需要一次的字符;2、需要判断字符是否已出现过 维护一个队列,存储只出现过一次的字符,按照先进先出的特点,队头就是第一个只出现一次的字符。另外需要用hashmap存储字符是否出现过,接收字符的时候判断字符是否出现过,没有才加入队列。
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//Insert one char from stringstream
private static Queue<Character> charAppearOncelist = new LinkedList<>();
private static Map<Character, Boolean> hasFound = new HashMap<>();
public void Insert(char ch)
{
charAppearOncelist.remove(ch);
if (!hasFound.containsKey(ch)){
charAppearOncelist.add(ch);
}
hasFound.put(ch, true);
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
public char FirstAppearingOnce()
{
if (charAppearOncelist.isEmpty()){return '#';}
return charAppearOncelist.peek();
}
}
坐标移动
题目:开发一个坐标计算工具, A表示向左移动,D表示向右移动,W表示向上移动,S表示向下移动。从(0,0)点开始移动,从输入字符串里面读取一些坐标,并将最终输入结果输出到输出文件里面。
思路:也就是要根据一组坐标系中的移动指令计算出最后的坐标。解题过程需要根据输入得到一系列移动指令,如A19表示向左移动19个单位,并对指令左合法性判断,然后计算移动之后的坐标,经过一系列计算之后可以得到终点坐标值。
解决方案:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
private static List<Character> directions = new ArrayList<>();
static {
directions.add('A');
directions.add('D');
directions.add('W');
directions.add('S');
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String inputData = in.nextLine();
String[] motions = inputData.split(";");
AtomicInteger horizon = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger vertical = new AtomicInteger();
int length = motions.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
String motion = motions[i];
if (!isValid(motion)) {
continue;
}
char direction = motion.charAt(0);
int number = Integer.parseInt(motion.substring(1));
switch (direction) {
case 'A': //left
horizon.addAndGet(-number);
break;
case 'W': // up
vertical.addAndGet(number);
break;
case 'S': // down
vertical.addAndGet(-number);
break;
case 'D': // right
horizon.addAndGet(number);
break;
};
}
System.out.print(horizon);
System.out.print(",");
System.out.print(vertical);
}
private static boolean isValid(String motion) {
if (motion.length() <= 0 || motion.length() > 3) {
return false;
}
char first = motion.charAt(0);
if (!directions.contains(first)) {
return false;
}
String numberPart = motion.substring(1);
int number = 0;
try {
number = Integer.parseInt(numberPart);
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return number >= 0 && number <= 99;
}
}删除字符串中出现次数最少的字符
题目:实现删除字符串中出现次数最少的字符,若出现次数最少的字符有多个,则把出现次数最少的字符都删除。输出删除这些单词后的字符串,字符串中其它字符保持原来的顺序。
数据范围:输入的字符串长度满足 1≤�≤20 1≤n≤20 ,保证输入的字符串中仅出现小写字母。
解决思路: 1、遍历字符串,统计各个字符出现的次数,存到哈希表中;2、遍历哈希表,找到最小value值; 3、再遍历哈希表,找到拥有该value的所有key 4、从字符串中删除所有上一步找到的key,剩下的字符收集到一个stringbuilder中
解决方案:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNext()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
String input = in.nextLine();
System.out.println(removeLeastFrequentChar(input));
}
}
public static String removeLeastFrequentChar(String str) {
if (str == null || str.isEmpty()) {
return str;
}
Map<Character, Integer> charCount = new HashMap<>();
List<Character> leastFrequentChars = new ArrayList<>();
// 计算每个字符的出现次数
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
charCount.put(c, charCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
// 找到最小出现次数
int minValue = Collections.min(charCount.values());
// 并找出出现次数最少的所有字符
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
if (charCount.get(c) == minValue) {
leastFrequentChars.add(c);
}
}
// 如果存在多个出现次数最少的字符,都删除
for (char c : leastFrequentChars) {
str = str.replace(c + "", "");
}
return str;
}简单错误记录
题目:这是牛客网华为机试系列的一道题,要求在给出一些字符串数据之后,输出统计好的最后8个记录。
思路:这就是一个统计某些数据出现的次数,只是在这个过程中增加了若干需求,比如文件名长度如果超过16,则取后16位,还有只输出最后8个记录。文件名和代码行数都一致的话被认为是同一个记录,那就遍历已存储的记录,有相同的则记录数=1,没有则增加一条新的记录数据。因为最后要获取后8条记录,所以选择用普通数组存储而不用哈希表。
解决方案:
import java.util.Scanner;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Record[] records = new Record[105];
int lastRecordIndex = -1;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNext()) {
String line = in.nextLine();
if (line.equals("")) {
break;
}
String[] recordInfo = line.split(" ");
String fileName = getFileName(recordInfo[0]);
String lineNumber = recordInfo[1];
if (lastRecordIndex == -1) {
Record newRecord = new Record(fileName, lineNumber, 1);
records[++lastRecordIndex] = newRecord;
} else {
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i <= lastRecordIndex; i++) {
if (fileName.equals(records[i].getFileName()) &&
lineNumber.equals(records[i].getLineNumber())) {
records[i].existCount++;
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
Record newRecord = new Record(fileName, lineNumber, 1);
records[++lastRecordIndex] = newRecord;
}
}
}
int beginIndex = 0;
if (lastRecordIndex > 7) {
beginIndex = lastRecordIndex - 7;
}
while (beginIndex <= lastRecordIndex) {
System.out.println(records[beginIndex].getFileName() + ' ' +
records[beginIndex].getLineNumber() + ' ' +
records[beginIndex].getExistCount());
beginIndex++;
}
}
public static String getFileName(String filePath) {
String fileName = filePath.substring(filePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1);
if (fileName.length() > 16) {
fileName = fileName.substring(fileName.length() - 16);
}
return fileName;
}
private static class Record {
private String fileName;
private String lineNumber;
private int existCount = 0;
public Record(String fileName, String lineNumber, int existCount) {
this.fileName = fileName;
this.lineNumber = lineNumber;
this.existCount = existCount;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
public void setFileName(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
public String getLineNumber() {
return lineNumber;
}
public void setLineNumber(String lineNumber) {
this.lineNumber = lineNumber;
}
public int getExistCount() {
return existCount;
}
public void setExistCount(int existCount) {
this.existCount = existCount;
}
}
}字符串加解密
题目:这是牛客网华为机试系列的一道题,要求根据具体加解密逻辑实现代码。
解题思路:加解密过程涉及字母大小写变换和数字加减,注意字母大小变换可以通过字母的阿斯克码计算而得就可以。
解决方案:
import java.util.Scanner;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNext()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
String toEncrypt = in.nextLine();
String toDecrypt = in.nextLine();
System.out.println(encrypt(toEncrypt));
System.out.println(decrypt(toDecrypt));
}
}
private static String encrypt(String content) {
int length = content.length();
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = content.charAt(i);
if (c == 'Z') {
result.append('a');
} else if (c == 'z') {
result.append('A');
} else if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'y') {
result.append((char) (c + 1 - 32));
} else if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Y') {
result.append((char)(c + 1 + 32));
} else if (c >= '0' && c < '9') {
result.append((char) (c + 1));
} else if (c == '9') {
result.append('0');
} else {
result.append(c);
}
}
return result.toString();
}
private static String decrypt(String content) {
int length = content.length();
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = content.charAt(i);
if (c == 'a') {
result.append('Z');
} else if (c == 'A') {
result.append('z');
} else if (c >= 'b' && c <= 'z') {
result.append((char) (c - 1 - 32));
} else if (c >= 'B' && c <= 'Z') {
result.append((char)(c - 1 + 32));
} else if (c >= '1' && c <= '9') {
result.append((char) (c - 1));
} else if (c == '0') {
result.append('9');
} else {
result.append(c);
}
}
return result.toString();
}
}字符串查找
题目:来自华为机试的题目,输入第一个字符串包含若干个字符和空格、tab,输入第二个字符串,输出第二个字符串能够在第一个字符串中匹配到的次数。
思路:先对第一个字符串做去空格、tab处理,然后从其第一个字符位置开始,向后截取到和弟二个字符串长度相等的部分,比对他们的内容,相等则匹配数加1,然后继续从第二个字符开始往后截取,直到最后截取到末尾的字符为止。
解决方案:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNext()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
String mainString = in.nextLine();
String childStr = in.nextLine();
mainString = mainString.replaceAll(" ", "");
mainString = mainString.replaceAll("\t", "");
int length = mainString.length();
int childStrLen= childStr.length();
int matchCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length - childStrLen + 1; i++){
if (childStr.equals(mainString.substring(i, i + childStrLen))){
matchCount++;
}
}
System.out.println(matchCount);
}
}矩阵路径查找
题目:已知一个5*5矩阵,其中每个元素值不一样,再输入六个整数元素,判断这六个整数是否在矩阵中相邻,也就是它们任何一个都至少和另一个相邻。矩阵如下:
1 2 3 4 5
11 12 13 14 15
21 22 23 24 25
31 32 33 34 35
41 42 43 44 45
输入如: 1 2 3 4 5 15 结果是相邻的6个数 输出 1 不是相邻的输出0
解决方案;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNext()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[46];
Map<Integer, Integer> toSearchNumbers = new HashMap<>();
String numStr = in.nextLine();
String[] numbers = numStr.split(" ");
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (numbers.length != 6){
System.out.println(0);
} else {
for (String number : numbers) {
toSearchNumbers.put(Integer.valueOf(number), 1);
}
if (isValid(Integer.parseInt(numbers[0]))){
queue.add(Integer.valueOf(numbers[0]));
// 开始广度优先搜索
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int currentArrived = queue.poll();
isVisited[currentArrived] = true;
// 计算下一步可达,分别往四个方向走,上下左右
int toUp = currentArrived - 10;
int toDown = currentArrived + 10;
int toRight = currentArrived + 1;
int toLeft = currentArrived - 1;
if (isValid(toUp) && !isVisited[toUp] && toSearchNumbers.containsKey(toUp)){
queue.add(toUp);
isVisited[toUp] = true;
}
if (isValid(toDown) && !isVisited[toDown] && toSearchNumbers.containsKey(toDown)){
queue.add(toDown);
isVisited[toDown] = true;
}
if (isValid(toRight) && !isVisited[toRight] && toSearchNumbers.containsKey(toRight)){
queue.add(toRight);
isVisited[toRight] = true;
}
if (isValid(toLeft) && !isVisited[toLeft] && toSearchNumbers.containsKey(toLeft)){
queue.add(toLeft);
isVisited[toLeft] = true;
}
}
// 最后遍历到结束,判断输入的序列是否都被遍历到
AtomicInteger notFoundCount = new AtomicInteger();
toSearchNumbers.keySet().forEach(key -> {
if (!isVisited[key]){
notFoundCount.getAndIncrement();
}
});
if (notFoundCount.get() > 0){ //存在没有访问到的
System.out.println(0);
} else {
System.out.println(1);
}
} else {
System.out.println(0);
}
}
}
}
private static boolean isValid(int value){
return value >= 1 && value <= 45;
}
}