leetcode 部分题解(python)
215. Kth Largest Element in an Array
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/#/description
思路_第k大的数
利用快速排序的思想;从数组S中随机找出一个元素X,把数组分为两部分Sa和Sb。Sa中的元素大于等于X,Sb中元素小于X。这时有两种情况:
1. Sa中元素的个数小于k,则Sb中的第k-|Sa|个元素即为第k大数;
2. Sa中元素的个数大于等于k,则返回Sa中的第k大数。时间复杂度近似为O(n)
class Solution(object):
def findKthLargest(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
if len(nums)==1:
return nums[0]
target = nums[0]
i,j = 0,len(nums)-1
while i<j:
while i<j and nums[j]>=target:
j -= 1
nums[i] = nums[j]
while i<j and nums[i]<=target:
i += 1
nums[j] = nums[i]
nums[i] = target
right = len(nums)-j
# print(right)
if right==k:
return nums[j]
elif right>k:
return self.findKthLargest(nums[j+1:],k)
else:
print(j)
return self.findKthLargest(nums[:j],k-right)57. Insert Interval
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-interval/?tab=Description
思路_链表insert
代码:
def insert(self, intervals, newInterval):
"""
:type intervals: List[Interval]
:type newInterval: Interval
:rtype: List[Interval]
"""
ans =[]
if len(intervals)==0:
ans.append(newInterval)
return ans
pos = 0
for inte in intervals:
if inte.start>newInterval.end:
ans.append(inte)
elif inte.end<newInterval.start:
ans.append(inte)
pos+=1
else:
newInterval.start = min(newInterval.start,inte.start)
newInterval.end = max(newInterval.end,inte.end)
ans.insert(pos,newInterval)
return ans56. Merge Intervals
题目链接:http://write.blog.csdn.net/mdeditor#!postId=53885139
lambda排序
参考网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zuoyuan/p/3782028.html
通过 operator 模块提供的函数还可以实现多重排序的功能。比如,先按 grade 排序再按 age 排序:
sorted(student_tuples, key=itemgetter(1,2))
[(‘john’, ‘A’, 15), (‘dave’, ‘B’, 10), (‘jane’, ‘B’, 12)]sorted(student_objects, key=attrgetter(‘grade’, ‘age’))
[(‘john’, ‘A’, 15), (‘dave’, ‘B’, 10), (‘jane’, ‘B’, 12)]
28. Implement strStr()
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-strstr/?tab=Description
思路:查找子串
在一个序列中找到子串并且返回下标索引位置
代码:
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
"""
:type haystack: str
:type needle: str
:rtype: int
"""
if haystack==None or needle==None:
return -1
hlen = len(haystack)
nlen = len(needle)
for i in range(0,hlen-nlen+1):
j = 0
while j<nlen:
if needle[j]==haystack[j+i]:
j+=1
else:
break
if j==nlen:
return i
return -11. Two Sum
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/?tab=Description
思路:哈希
在一个序列里面找到两个数使得和为目标值,并且返回两个数的下标
代码:
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
def twoSum(self, num, target):
dict = {}
for i in range(len(num)):
x = num[i]
if target-x in dict:
return (dict[target-x]+1, i+1)
dict[x] = i92. Reverse Linked List II
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/?tab=Description
思路_子链表翻转烧脑
代码:
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head==None or head.next==None or m==n:
return head
L = ListNode(0)
L.next = head
cur = L
for i in range(m-1):
cur = cur.next
p = cur.next
for i in range(n-m):
tem = cur.next
cur.next = p.next
p.next = p.next.next
cur.next.next = tem
return L.next279. Perfect Squares
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/perfect-squares/?tab=Description
题意:计算当前数字最少可以由多少个平方数相加得到
思路_动态规划
维护一个数组d[n],d[i]表示数字i最少可以由多少个平方数相加得到,初始化d[0]=0,其余为max,动态更新方程可表示为:d[i+j*j] = max(d[i+j*j],d[i]+1)
代码:
def numSquares(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
d = [100]*(n+1)
d[0] = 0
d[1] = 1
for i in range(0,n+1):
for j in range(0,n):
if i+j*j<=n:
d[i+j*j] = min(d[i+j*j],d[i]+1)
else:
break
return d[n]————
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/?tab=Description
题意:找到根节点到叶节点的所有路径组成的数字,求和之
思路_二叉树-DFS
代码同:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/?tab=Description
257. Binary Tree Paths
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/?tab=Description
题意:输出根节点到叶节点的所有路径
思路_二叉树-DFS
代码:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[str]
"""
self.ans = []
if root==None:
return self.ans
def dfs(root,path):
if root.left==None and root.right==None:
self.ans.append(path)
if root.left:
dfs(root.left,path+"->"+str(root.left.val))
if root.right:
dfs(root.right,path+"->"+str(root.right.val))
dfs(root,str(root.val))
return self.ans110. Balanced Binary Tree
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/?tab=Description
题意:验证是否是二叉平衡树(任意节点的两个子树高度差最多为1)
思路_二叉树深度
代码:
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if root == None:
return True
if abs((self.depth(root.left)-self.depth(root.right)))>1:
return False
else:
return self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)
def depth(self, r):
if r==None:
return 0
else:
return max(self.depth(r.left), self.depth(r.right))+124. Swap Nodes in Pairs
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/?tab=Description
题意:交换链表里面相邻的两个节点,空间恒定
思路链表递归
代码:
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head==None or head.next==None:
return head
nex = head.next
tem = nex.next
nex.next = head
head.next = self.swapPairs(tem)
return nex342. Power of Four
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/power-of-four/?tab=Solutions
题意:判断一个数是否是4的幂
思路_二进制
The basic idea is from power of 2, We can use “n&(n-1) == 0” to determine if n is power of 2. For power of 4, the additional restriction is that in binary form, the only “1” should always located at the odd position. For example, 4^0 = 1, 4^1 = 100, 4^2 = 10000. So we can use “num & 0x55555555==num” to check if “1” is located at the odd position.
代码:
return (num > 0) && ((num & (num - 1)) == 0) && ((num & 0x55555555) == num)416. Partition Equal Subset Sum
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/
题意:验证一个数组是否存在两个子集,使得两个子集的和相等。
思路:_01背包问题
参照背包的博文
代码:
class Solution(object):
def canPartition(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
n = len(nums)
sum_num = sum(nums)
if sum_num%2!=0:
return False
# print(sum_num)
result = [[0]*sum_num for i in range(n+1)]
for i in range(1,n+1):
for j in range(nums[i-1],int(sum_num/2)+1):
result[i][j] = max([result[i-1][j],result[i-1][j-nums[i-1]]+nums[i-1]])
if result[n][int(sum_num/2)]==sum_num/2:
return True
else:
return False334. Increasing Triplet Subsequence
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/increasing-triplet-subsequence/
题意:在一个无序的序列中找到一个长度为3的递增子序列。
思路: if_elif_else
我特么已经蠢到这种题都不会了,维护一个最小数a和次小数b,遍历到第三个数c满足c>b 返回Ture
代码:
class Solution(object):
def increasingTriplet(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
if len(nums)<3:
return False
max_num = max(nums)
c1 = max_num
c2 = max_num
for i in nums:
if i <= c1:
c1 = i
elif i<=c2:
c2 = i
else:
return True
return FalseBinary Tree Level Order Traversal II
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/
思路queue层次遍历
题意,就是层次遍历,不过是从bottom to up
代码:
class Solution(object):
def levelOrderBottom(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if root==None:
return []
results = []
queue = [root]
while queue:
cur_li = []
for i in range(0,len(queue)):
cur = queue.pop(0)
cur_li.append(cur.val)
if cur.left!=None:
queue.append(cur.left)
if cur.right!=None:
queue.append(cur.right)
results.append(cur_li)
return [results[i] for i in range(len(results)-1,-1,-1)]Search a 2D Matrix II
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/
思路_面试题
题意:给一个n*m的矩阵,每一行,每一列都从小到大的排列,然后查找target这个数是否存在矩阵中。
脑子不灵活,对每一行二分查找,时间复杂度也要nlogn,,,面试题怎么会这么做呢?(我简直蠢到家)
从右上角开始, 比较target 和 matrix[i][j]的值. 如果小于target, 则该行不可能有此数, 所以i++; 如果大于target, 则该列不可能有此数, 所以j–. 遇到边界则表明该矩阵不含target.
代码:
class Solution(object):
def searchMatrix(self, matrix, target):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:type target: int
:rtype: bool
"""
n = len(matrix)
if n==0:
return False
m = len(matrix[0])-1
if m==-1:
return False
i = 0
while m>=0 and i<n:
if matrix[i][m]>target:
m -= 1
elif matrix[i][m]<target:
i +=1
else:
return True
return False53. Maximum Subarray
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
思路_经典的DP问题:
题意:给定一个序列,要找到和最大的那个子序列,并且返回该子序列之和。
维护两个列表,local[i]即包含当前元素的局部最大和值,DP求local[i]时,local[i] = max(local[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i]) ;
全局最优值globa[i] = max(globa[i-1],local[i]),即先找到包含当前值的局部最优值local[i],当前的全局最优值globa[i]即为不包含当前值的全局最优与当前局部最优的最大值。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def maxSubArray(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
local = [0]*len(nums)
globa = [0]*len(nums)
local[0] = nums[0]
globa[0] = nums[0]
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
local[i] = max(local[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i])
globa[i] = max(globa[i-1],local[i])
return max(local[-1],globa[-1])235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
思路二叉搜索树递归:
题意:求二叉搜索树(!)任意两个节点的最低共有祖先。
对于二叉搜索树,公共祖先的值一定大于等于较小的节点,小于等于较大的节点。换言之,在遍历树的时候,如果当前结点大于两个节点,则结果在当前结点的左子树里,如果当前结点小于两个节点,则结果在当前节点的右子树里。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if root==None:
return None
if root.val>p.val and root.val>q.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
if root.val<p.val and root.val<q.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
return root202. Happy Number
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/happy-number/
思路_智力题:
给定一个数,判断这个数是不是happy number;即循环的做每一位的平方和,直到最后得到1这个数。
基本方法就是维护一个列表,每次出现一个新的数,则加到列表里面,如果当前这个已经存在列表中了则返回false; 如果不存在列表中则添加,若得到1则返回true。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
resulst = [n]
while 1:
s = 0
n = resulst[-1]
while n:
cur = n%10
n /=10
s += cur**2
if s in resulst and s!=1:
return False
elif s not in resulst and s!=1:
resulst.append(s)
else:
return TrueSum of Two Integers
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-two-integers/
题目翻译:
计算两个整数a和b的和,但是不能使用运算符加号和减号。
比如:给定a=1,b=2,返回3。
思路_(位操作):
既然不能使用加法和减法,那么就用位操作。下面以计算5+4的例子说明如何用位操作实现加法:
1. 用二进制表示两个加数,a=5=0101,b=4=0100;
2. 用and(&)操作得到所有位上的进位carry=0100;
3. 用xor(^)操作找到a和b不同的位,赋值给a,a=0001;
4. 将进位carry左移一位,赋值给b,b=1000;
5. 循环直到进位carry为0,此时得到a=1001,即最后的sum。
上面思路还算正常,然而对于Python就有点麻烦了。因为Python的整数不是固定的32位,所以需要做一些特殊的处理,具体见代码吧。
代码里的将一个数对0x100000000取模(注意:Python的取模运算结果恒为非负数),是希望该数的二进制表示从第32位开始到更高的位都同是0(最低位是第0位),以在0-31位上模拟一个32位的int。
class Solution(object):
def getSum(self, a, b):
"""
:type a: int
:type b: int
:rtype: int
"""
while b != 0:
carry = a & b
a = (a ^ b) % 0x100000000
b = (carry << 1) % 0x100000000
return a if a <= 0x7FFFFFFF else a | (~0x100000000+1)
Roman to Integer
题目链接:https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/roman-to-integer/
思路:
罗马数字是最古老的数字表示方式,比阿拉伯数组早2000多年,起源于罗马
罗马数字有如下符号:
基本字符IVXLCDM对应阿拉伯数字1510501005001000
计数规则:
1. 相同的数字连写,所表示的数等于这些数字相加得到的数,例如:III = 3
2. 小的数字在大的数字右边,所表示的数等于这些数字相加得到的数,例如:VIII = 8
3. 小的数字,限于(I、X和C)在大的数字左边,所表示的数等于大数减去小数所得的数,例如:IV = 4
4. 正常使用时,连续的数字重复不得超过三次
5. 在一个数的上面画横线,表示这个数扩大1000倍(本题只考虑3999以内的数,所以用不到这条规则)
其次,罗马数字转阿拉伯数字规则(仅限于3999以内):
从前向后遍历罗马数字,如果某个数比前一个数小,则加上该数。反之,减去前一个数的两倍然后加上该数
House Robber III
题目连接:https://leetcode.com/problems/house-robber-iii/
思路_(DP):
动态规划,因为当前的计算需要依赖之前的结果,那么我们对于某一个节点a,如果其左子节点b存在,我们通过递归调用函数,算出不包含左子节点b返回的值,同理,如果右子节点c存在,算出不包含右子节点c返回的值,那么此节点的最大值可能有两种情况,一种是该节点a值加上不包含左子节点b和右子节点c的返回值之和,另一种是左右子节点返回值之和而不包含当期节点值,
class Solution(object):
def rob(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
def dsf(root):
if not root:
return [0,0]
leftr = dsf(root.left)
rightr = dsf(root.right)
nocurr = leftr[1]+rightr[1]
cur = leftr[0]+rightr[0] + root.val
maxval = max(cur,nocurr)
return [nocurr,maxval]
return dsf(root)[1]
Serialize and Deserialize BST
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-bst/#
思路_(序列化、queue_BFS):
序列化就是将一个数据结构或物体转化为一个位序列,可以存进一个文件或者内存缓冲器中,然后通过网络连接在相同的或者另一个电脑环境中被还原,还原的过程叫做去序列化。
层序遍历的非递归解法:借助queue来做,本质是BFS算法
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
"""Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
if not root:
return '{}'
val = root.val
index = 0
queue = [root]
while index <len(queue):
if queue[index] is not None:
queue.append(queue[index].left)
queue.append(queue[index].right)
index +=1
while queue[-1] is None:
queue.pop()
re = ''
for i in range(0,len(queue)-1):
if queue[i] is not None:
re += str(queue[i].val) + ','
else:
re +='#,'
re='{'+re+str(queue[-1].val)+'}'
return re
def deserialize(self, data):
"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
data = data.strip('\n')
if data == '{}':
return None
vals = data[1:-1].split(',')
root = TreeNode(int(vals[0]))
queue = [root]
isLeftChild = True
index = 0
for val in vals[1:]:
if val is not '#':
node = TreeNode(int(val))
if isLeftChild:
queue[index].left = node
else:
queue[index].right = node
queue.append(node)
if not isLeftChild:
index += 1
isLeftChild = not isLeftChild
return root459. Repeated Substring Pattern
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/repeated-substring-pattern/
思路_(KMP_next数组):
题意:给定一个非空字符串,判断它是否可以通过自身的子串重复若干次构成。你可以假设字符串只包含小写英文字母,并且长度不会超过10000
记字符串长度为size,利用KMP算法求next数组,记next数组的最后一个元素为p
若p > 0 并且 size % (size - p) == 0,返回True
code:
class Solution(object):
def repeatedSubstringPattern(self, str):
"""
:type str: str
:rtype: bool
"""
k=-1
j=0
next = [0]*(len(str)+1)
next[0]=-1
while (j<len(str)):
if k==-1 or str[j]==str[k]:
j+=1
k+=1
next[j]=k
else:
k = next[k]
l = next[-1]
return len(str)%(len(str)-l)==0 and l>0关于next数组很多代码里面求解的是当前字符的前面所有字符的最长前后匹配子串;该解题部分求取了当前位字符的最长匹配子串,只需要将next数组右移一位即可。关于next数组的具体求法参考:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7041827
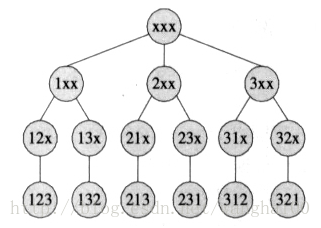
46. Permutations
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
思路_(递归全排列):
可以将这个排列问题画成图形表示,即排列枚举树,比如下图为{1,2,3}的排列枚举树,此树和我们这里介绍的算法完全一致;
不断将每个元素放作第一个元素,然后将这个元素作为前缀,并将其余元素继续全排列(递归调用即可)
代码:
class Solution(object):
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
re = []
def perm(num,k,l):
if k==l:
re.append(list(num))
else:
for i in range(k,l):
num[i],num[k]=num[k],num[i]
perm(num,k+1,l)
num[i],num[k]=num[k],num[i]
perm(nums,0,len(nums))
return re405. Convert a Number to Hexadecimal
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-a-number-to-hexadecimal/
思路_(进制数转化):
将数字转化为16进制字符串,负数采用补码表示。
只需要将负数转换为无符号短整型即可,即负数本身+100000000000000000000000000000000(0x100000000
)
代码:
class Solution(object):
def toHex(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: str
"""
ans = []
hexs = '0123456789abcdef'
if num < 0: num += 0x100000000
while num:
ans.append(hexs[num % 16])
num /= 16
t=''
for i in range(len(ans)-1,-1,-1):
t+=str(ans[i])
return t if ans else '0'96. Unique Binary Search Trees
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/
思路_(DP):
n个点中每个点都可以作为root,当 i 作为root时,小于 i 的点都只能放在其左子树中,大于 i 的点只能放在右子树中,此时只需求出左、右子树各有多少种,二者相乘即为以 i 作为root时BST的总数。
利用动态规划的思想,维护数组results, results[i]表示含有i个数的BST总数
代码:
class Solution(object):
def numTrees(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
results = [0]*(n+1)
results[0]=1
results[1]=1
for i in range(2,n+1):
for j in range(0,i):
results[i] += results[j]*results[i-j-1]
return results[n]153. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array/
思路_(二分查找):
大概题意就是说当前的序列是一个有序的序列从某个节点打乱后的结果,比如[3,4,5,1,2] 要从这个序列中找到最小值。
看了别人的解题思路以后才懂了,利用二分查找(logn)
(1) A[mid] < A[end]:A[mid : end] sorted => min不在A[mid+1 : end]中
搜索A[start : mid]
(2) A[mid] > A[end]:A[start : mid] sorted且又因为该情况下A[end]
class Solution(object):
def findMin(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
start, end = 0, len(nums)-1
target = nums[end]
while start<end:
mid = (start+end)/2
if nums[mid]<target:
end = mid
else:
start = mid+1
return min(nums[start],nums[end])70. Climbing Stairs
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs/
思路_(DP):
题意:给定一个有n个台阶的梯子,每次可以走1步或者2步,问一共有多少种走法,典型的动态规划问题,当前阶梯数n的路径数量=n-1阶梯数的路径数量+n-1阶梯数的路径数量
代码:
class Solution(object):
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n==1:
return 1
results = [0]*(n+1)
results[1] = 1
results[0] = 1
for i in range(2,n+1):
results[i] = results[i-1]+results[i-2]
return results[n]Binary Tree Right Side View
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
思路:(queue层次遍历):
题意:人站在树的右边,从右往左看,能看到的从上往下的序列。
做完这道题感觉智商被限制,debug了半天,对queue使用不熟练。
层次遍历,每次先左右的节点入栈,遍历每一层的时候把最右边的节点值保存即可。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def rightSideView(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
results = []
if root==None:
return []
queue = [root]
while queue:
for r in range(0,len(queue)):
cur = queue.pop(0)
if r==0:
results.append(cur.val)
if cur.right!=None:
queue.append(cur.right)
if cur.left!=None:
queue.append(cur.left)
return results21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
思路_链表
链表合并没啥难度上代码:
class Solution(object):
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if l1==None:
return l2
if l2==None:
return l1
L = ListNode(0)
R = L
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val<l2.val:
L.next = l1
L = L.next
l1 = l1.next
else:
L.next = l2
L = L.next
l2 = l2.next
if l1==None:
L.next = l2
else:
L.next = l1
return R.nextSpiral Matrix II
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/
思路_螺旋矩阵生成
题意:给定一个数,将1·n^2以螺旋结构的形式填充到矩阵中。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def generateMatrix(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
a = [[0]*n for x in range(n)]
colbegin,colend,rowbegin,rowend = 0,n,0,n
num = 1
while colbegin<colend and rowbegin<rowend:
if num<=n**2:
for i in range(colbegin,colend):
a[rowbegin][i] = num
num += 1
rowbegin += 1
if num<=n**2:
for i in range(rowbegin,rowend):
a[i][colend-1] = num
num += 1
colend -= 1
if num<=n**2:
for i in range(colend-1,colbegin-1,-1):
a[rowend-1][i] = num
num += 1
rowend -= 1
if num<=n**2:
for i in range(rowend-1,rowbegin-1,-1):
a[i][colbegin] = num
num += 1
colbegin += 1
return a