参考:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchunming033/category_3193659.html
(一)Pytest简介
pytest是python的一种单元测试框架,与python自带的unittest测试框架类似,但是比unittest框架使用起来更简洁,效率更高。根据pytest的官方网站介绍,它具有如下特点:
- 非常容易上手,入门简单,文档丰富,文档中有很多实例可以参考
- 能够支持简单的单元测试和复杂的功能测试
- 支持参数化
- 执行测试过程中可以将某些测试跳过,或者对某些预期失败的case标记成失败
- 支持重复执行失败的case
- 支持运行由nose, unittest编写的测试case
- 具有很多第三方插件,并且可以自定义扩展
- 方便的和持续集成工具集成
(二)pytest框架的使用
1. 编写的class和方法必须遵循以下规则
- 测试文件以test_开头(以_test结尾也可以)
- 测试类以Test开头(不能小写test开头),并且不能带有 __init__ 方法
- 测试函数以test_开头
- 断言使用基本的assert即可
2.用例代码
import pytest
#1.规定:
# 测试文件以test_开头(以_test结尾也可以)
# 测试类以Test开头,并且不能带有 init 方法
# 测试函数以test_开头
# 断言使用基本的assert即可
#2.执行模块命令:
# pytest 模块名称 例如:pytest test_123.py
#3.生成测试报告
# pytest --html=report.html
#4.运行模式
# 模式1:直接运行test_hello.py文件中的所有cases: pytest test_hello.py
#模式2:运行test_hello.py文件中的TestClassOne这个class下的两个cases: pytest test_hello.py::TestClassOne
# 模式3:运行test_hello.py文件中的TestClassTwo这个class下的test_one: pytest test_hello.py::TestClassTwo::test_one
class TestClassOne(object):
def test_one(self):
x = "this"
assert 't'in x
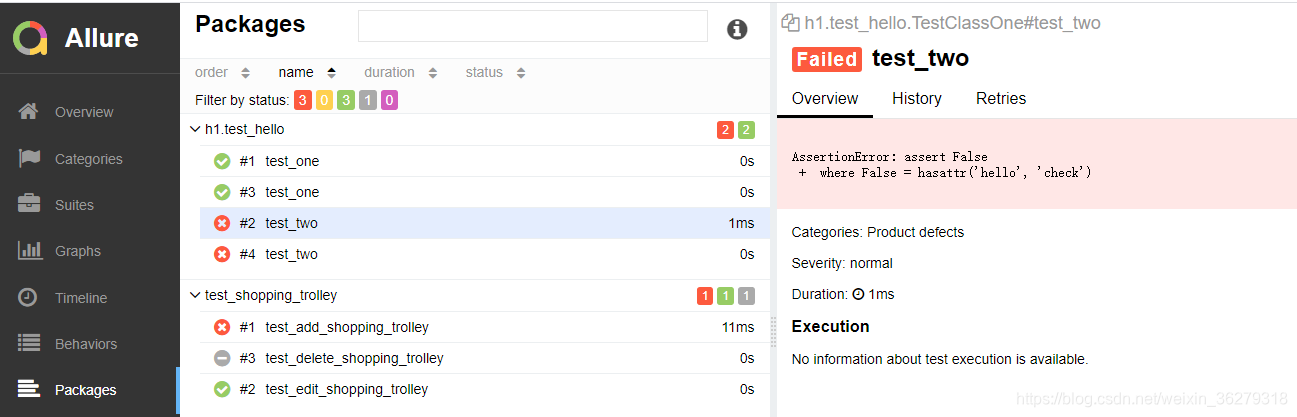
def test_two(self):
x = "hello"
assert hasattr(x, 'check')
class TestClassTwo(object):
def test_one(self):
x = "iphone"
assert 'p'in x
def test_two(self):
x = "apple"
assert hasattr(x, 'check')
3.用例运行总结为以下三种运行模式
- 模式1:直接运行test_hello.py文件中的所有cases: pytest test_hello.py
- 模式2:运行test_hello.py文件中的TestClassOne这个class下的两个cases: pytest test_hello.py::TestClassOne
- 模式3:运行test_hello.py文件中的TestClassTwo这个class下的test_one: pytest test_hello.py::TestClassTwo::test_on
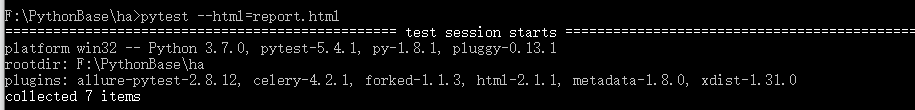
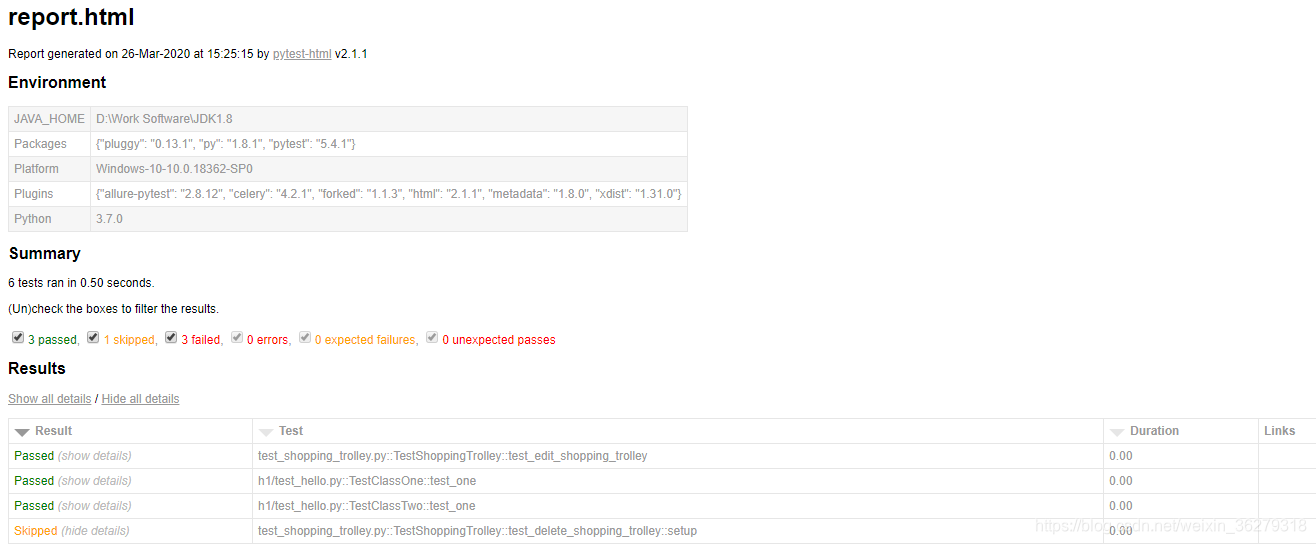
4.生成测试报告
pytest --html=report.html执行以上命令在项目report.html文件,现在我们用浏览器打开report.html看一下
(三) Pytest+Allure环境的搭建
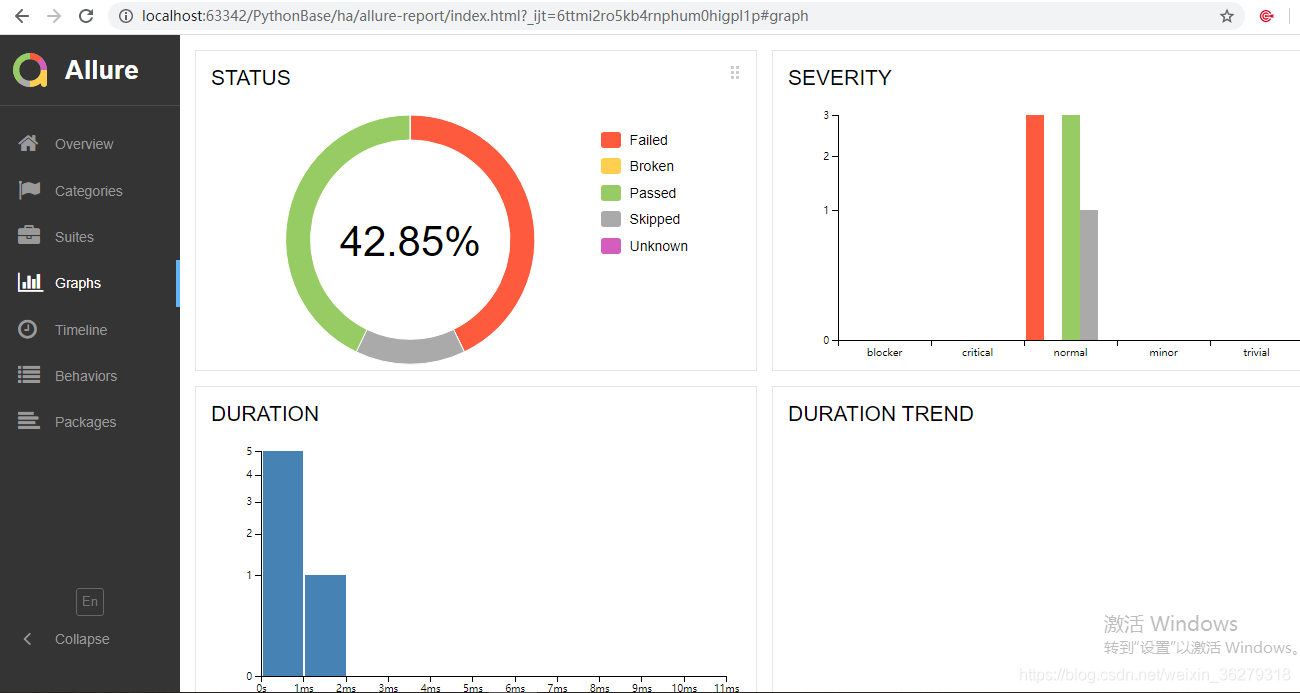
现在我们想要用例执行完成后,使用可视化界面展示用例的执行情况,方便查看测试报告,我们要使用到可是化工具allure
环境代建步骤:
1.安装JDK1.8,并配置环境变量:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
3.解压好allure,把allure配置环境变量,例如D:\Program Files\allure-2.7.0\bin配置在系统环境变量中
4.验证环境变量是否配置成功:allure --version
5.安装pytest,命令:pip install pytest
完成以上步骤,现在我们验证一下用例执行完成,allure是否可以展示用例的执行情况
测试代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import pytest
import allure
# allure generate --clean report 生成测试报告
@allure.feature('购物车功能') # 用feature说明产品需求,可以理解为JIRA中的Epic
class TestShoppingTrolley(object):
@allure.story('加入购物车') # 用story说明用户场景,可以理解为JIRA中的Story
def test_add_shopping_trolley(self):
login('刘春明', '密码') # 步骤1,调用“step函数”
with allure.step("浏览商品"): # 步骤2,step的参数将会打印到测试报告中
allure.attach('笔记本', '商品1') # attach可以打印一些附加信息
allure.attach('手机', '商品2')
with allure.step("点击商品"): # 步骤3
pass
with allure.step("校验结果"): # 步骤4
allure.attach('添加购物车成功', '期望结果')
allure.attach('添加购物车失败', '实际结果')
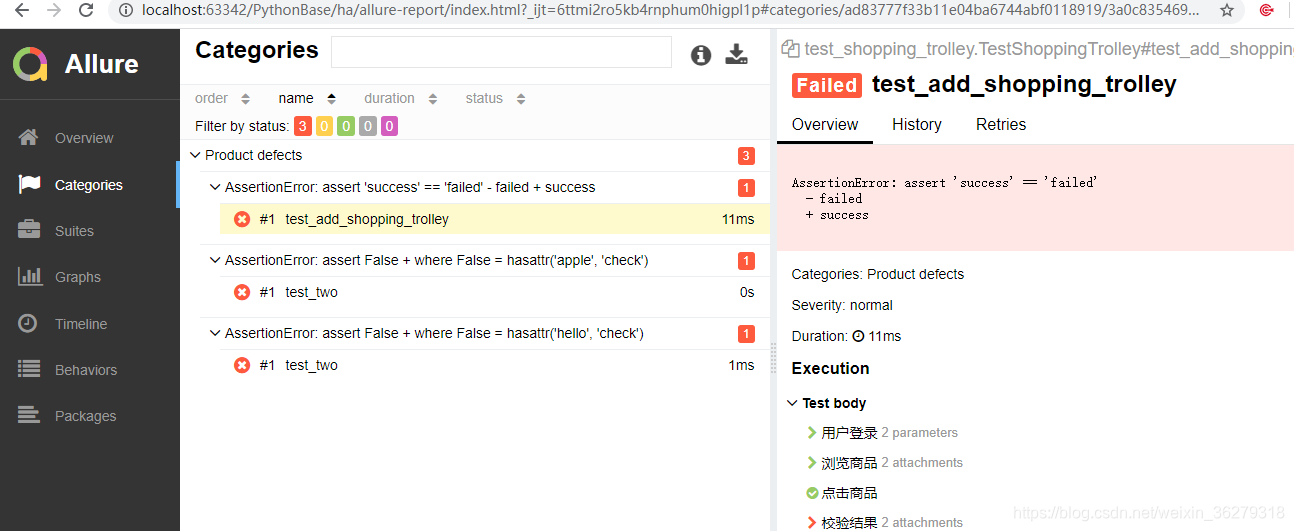
assert 'success' == 'failed'
@allure.story('修改购物车')
def test_edit_shopping_trolley(self):
pass
@pytest.mark.skipif(reason='本次不执行')
@allure.story('删除购物车中商品')
def test_delete_shopping_trolley(self):
pass
@allure.step('用户登录') # 将函数作为一个步骤,调用此函数时,报告中输出这个步骤,我把这样的函数叫“step函数”
def login(user, pwd):
print(user, pwd)
上面使用了Allure的几个特性:
- @allure.feature # 用于描述被测试产品需求
- @allure.story # 用于描述feature的用户场景,即测试需求
- with allure.step # 用于描述测试步骤,将会输出到报告中
- allure.attach # 用于向测试报告中输入一些附加的信息,通常是一些测试数据,截图等
- @pytest.allure.step # 用于将一些通用的函数作为测试步骤输出到报告,调用此函数的地方会向报告中输出步骤
生成测试报告需要执行命令:
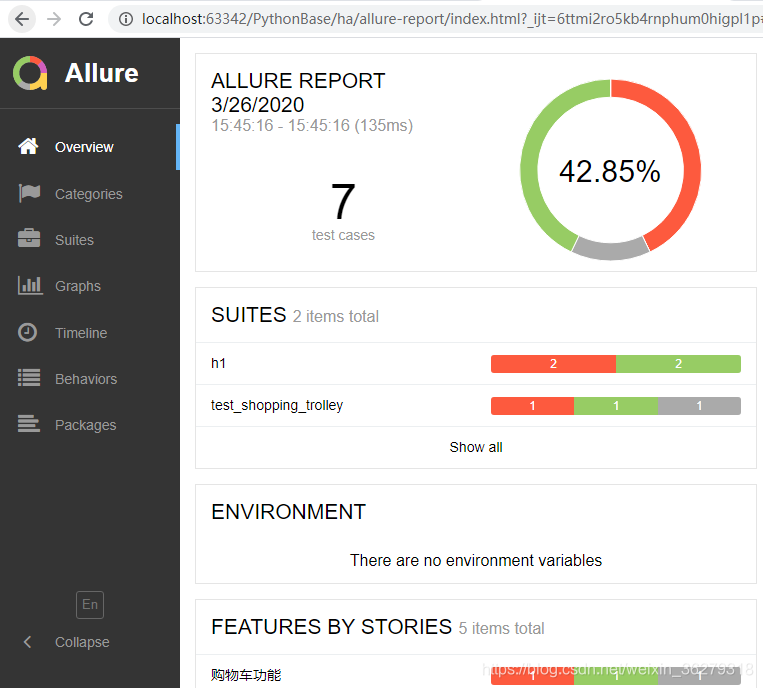
首先执行pytest -s --alluredir=report命令,生成的文件是json格式,怎么办?
执行命令:allure generate --clean report 另外生成一个allure-report文件夹,用浏览器打开index.html即可