这篇文章是基于Android ConstraintLayout完全解析和性能分析(章节一)基础上对属性的深入详解,如果之前对Android ConstraintLayout不了解或者不会使用的,请查看章节一的内容。若是有一定的了解,想深入对ConstraintLayout属性的了解及性能的分析,请直接阅读本章节内容。
一、ConstraintLayout属性讲解
先简单了解一下我们使用ConstraintLayout要用到的一些基本方位属性,如下表所示:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf | 把A的left side放在B的left side(左边对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf | 把A的left side放在B的right side(左边相对右边对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf | 把A的right side放在B的left side(右边相对左边对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf | 把A的right side放在B的right side(右边对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf | 把A的top side放在B的top side(顶部对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf | 把A的top side放在B的bottom side(顶部相对底部对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf | 把A的bottom side放在B的top side(底部相对顶部对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf | 把A的bottom side放在B的bottom side(底部对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf | 把A的start position放在B的end position(起始位置相对结束位置对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf | 把A的start position放在B的start position(起始位置对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf | 把A的end position放在B的start position(结束位置相对起始位置对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf | 把A的end position放在B的end position(结束位置对齐) |
| app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf | 把A的bottom side放在B的top side(基准线对齐) |
注意:属性的命名空间是app
一看这么多属性,估计整个人都不健康了,那让我们先看一个简单的例子吧:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
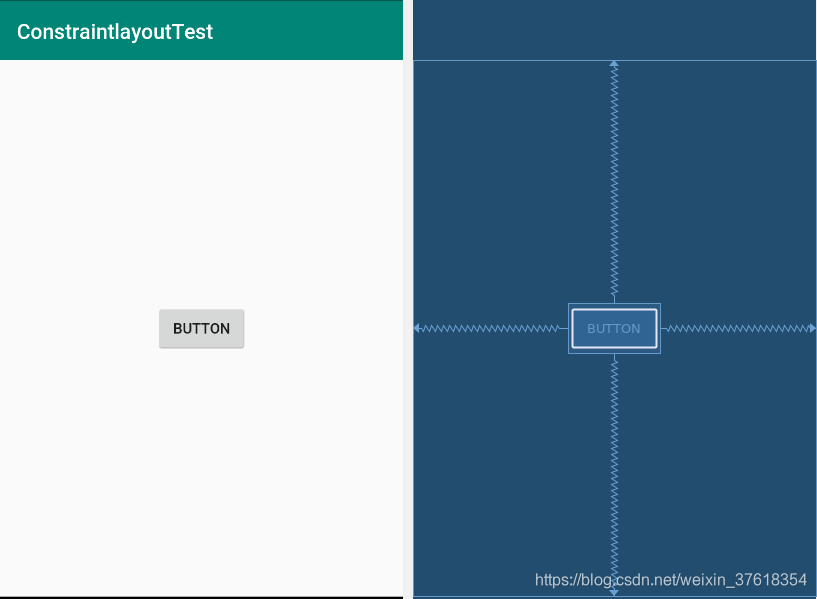
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
通过以上的这段布局,既可以完成下图所展示的布局。
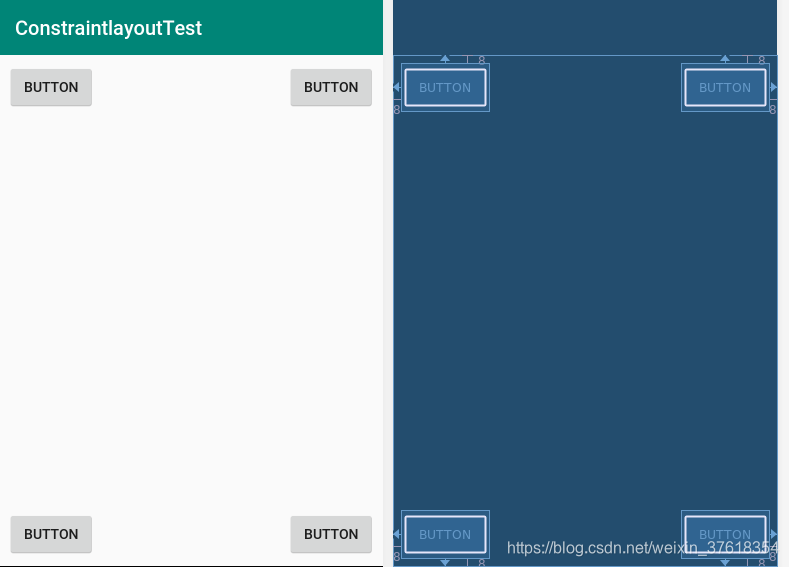
让一个控件在屏幕居中是不是特别简单,那让我们在看一个不同方位的控件展示,代码如下:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
展示效果如下图:
有没有感脚这些属性特别像RelativeLayout中的android:layout_alignParentXXX,没错,是特别像,但是作用会有略微不同。
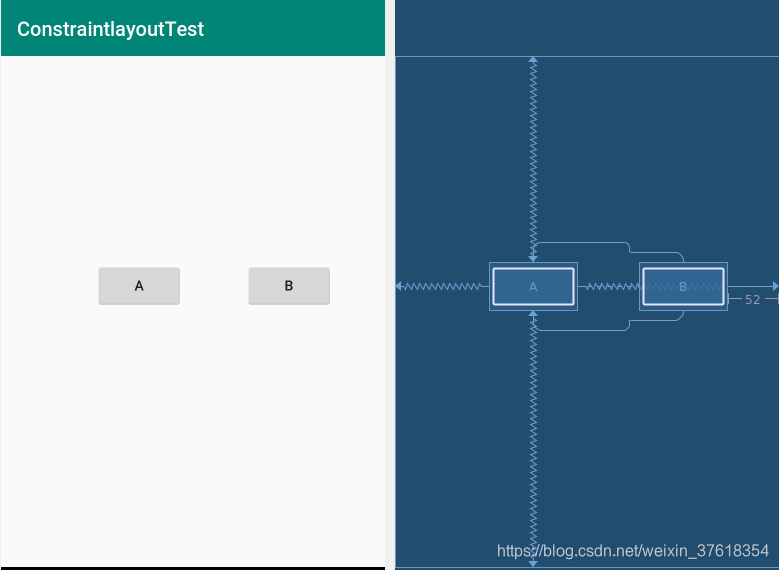
上面讲述了让控件相对于屏幕位置展示的效果,那如果想根据控件和控件之间的相对位置进行摆放的话,那么可以参考如下的使用方式进行处理:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.317"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.444" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="52dp"
android:layout_marginRight="52dp"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/button2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/button2"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.0" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
布局的代码页很简单,就是把A控件作为参照位置,然后再根据A的位置来定位B控件的相对位置。
那么通过上面的例子,你会发现,RelativeLayout的相对位置的操作,ConstraintLayout也能轻易实现。需要说明的是:这些属性的值既可以是parent,也可以是某个View的id
二、偏斜(Bias)
在使用LinearLayout的时候,我们通常会使用Gravity来将水平或者垂直排列的控件按照权重的分配进行排列。而在ConstraintLayout中,它提供了bias属性来对控件进行权重的分配。
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.25"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
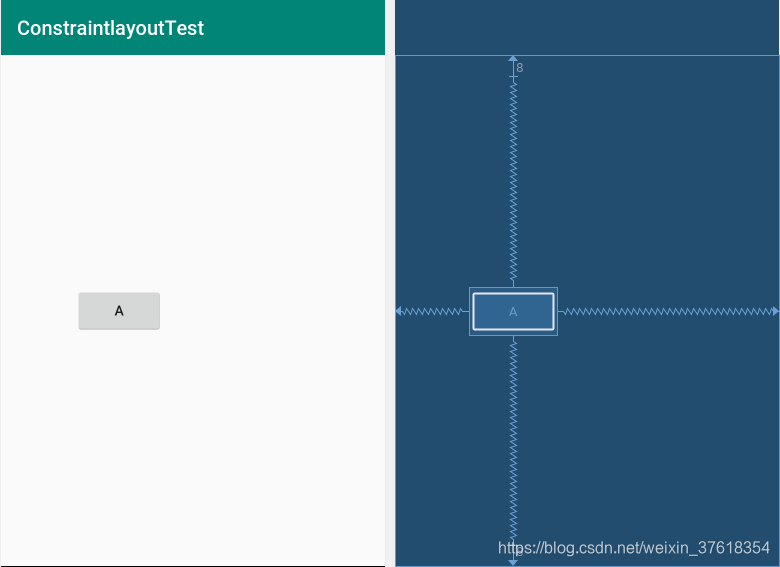
以上代码我们可以简单的看出,当一个控件被约束在屏幕的左侧,又被约束在屏幕的右侧,结果这个控件显示在了中间的位置,为什么? (1) 当使用了bias属性并设置了0.25的偏移量之后,我们发现控件在水平方向上向左偏移了屏幕宽度的1/4距离 (2) 如果我们把偏移值改成0.75,我们可以看到控件在水平方向上向右偏移了1/4的距离。
效果图如下:
那么有的同学可能就会有疑问了,既然横向可以设置屏幕的占比,那纵向是不是也有相应的属性呢,恭喜你答对了,是有的。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias | 水平方向偏移系数 |
| app:layout_constraintVertical_bias | 垂直方向偏移系数 |
需要注意的是,它的取值区间为:0~1
三、GONE不是真的GONE
我们在使用RelativeLayout开发时,经常会碰到这么一种逻辑,当某个数据为空的时候,该数据所绑定的控件则GONE掉。那么这样会出现这样的问题,例如有三个控件A、B、C垂直排列,B在A的下方,C在B的下方,那B隐藏(GONE)掉了之后,由于C对于A并没有依赖关系,所以会导致页面错误。这个问题ConstraintLayout给出了很好的解决方案。当在ConstraintLayout中,若一个控件隐藏(GONE)之后,它会变成一个点,因此对于把该控件作为参考控件的其它控件依然具有约束作用。
当这个控件隐藏之后,我们还可以参照这个隐藏的控件对其他控件设置边距的属性。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_goneMarginLeft | 隐藏控件左边距 |
| app:layout_goneMarginRight | 隐藏控件右边距 |
| app:layout_goneMarginTop | 隐藏控件顶部边距 |
| app:layout_goneMarginBottom | 隐藏控件底部边距 |
| app:layout_goneMarginStart | 隐藏控件起始边距 |
| app:layout_goneMarginEnd | 隐藏控件结束边距 |
四、宽高比
1、View的宽高比
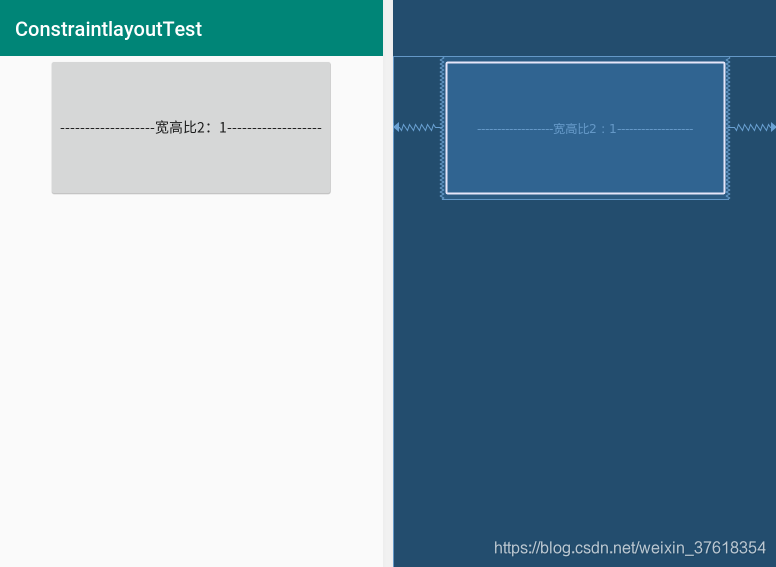
在ConstraintLayout中,还可以将宽定义成高的一个比例或者高定义成宽的比例。首先,需要先将宽或者高设置为0dp(即MATCH_CONSTRAINT),既要适应约束条件。然后通过layout_constraintDimensionRatio属性设置一个比例即可。这个比例可以是“浮点数”,表示宽度和高度之间的比例;也可以是“宽度:高度”形式的比例。比如:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="-------------------宽高比2:1-------------------"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="2:1"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
这里将按钮的高度设置为宽度的一半了。如下图所示:
如果宽和高都设置为0dp(即MATCH_CONSTRAINT),那么layout_constraintDimensionRatio的值需要先加一个"W,宽度:高度"或者"H,宽度:高度"来表示约束宽度或者高度,代码如下:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="h,10:6"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
效果图如下:
这例子是说,首先宽度将满足父布局的约束,然后将安装10:6的比例设置高度。
2、View百分比宽高
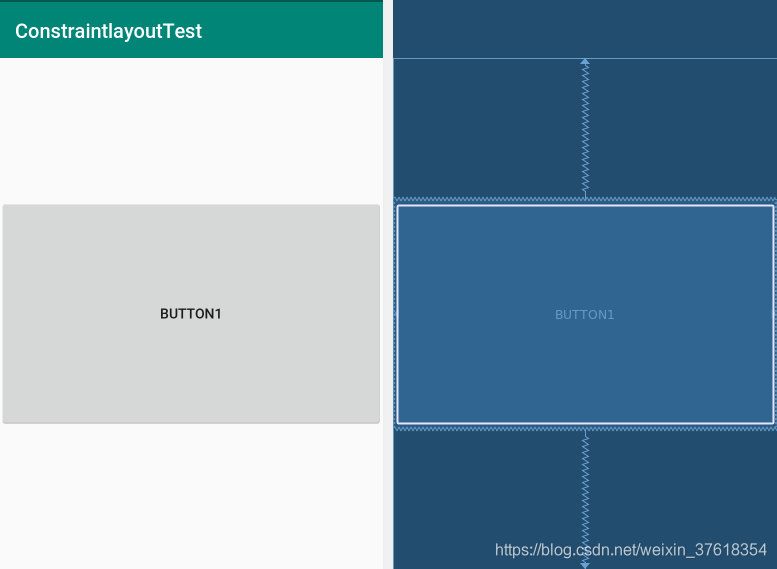
ConstraintLayout还能使用百分比来设置view的宽高,要使用百分比宽度或高度需要设置成0dp(即MATCH_CONSTRAINT)。
然后设置如下属性即可:
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="percent" //设置宽为百分比
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent="0.3" //0到1之间的值
或
app:layout_constraintHeight_default="percent" //设置高为百分比
app:layout_constraintHeight_percent="0.3" //0到1之间的值
其中layout_constraintHeight_default或者layout_constraintWidth_default的属性有三种类型:percent、spread、wrap,默认的为percent。
例子代码如下:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent="0.3"
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="percent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
效果图如下:
五、复杂布局的福星-Chain属性
Chain链时一种特殊的约束让多个chain链链接的Views能够平分剩余空间位置,在Android传统布局特征里面最相似的应该是LinearLayout中的权重比weight,但Chains链能做到的远远不止权重比weight的功能。如果要实现一个控件之间的链结构,我们可以将这些控件之间建立起互相的约束关系,并在这些关系的基础上选择创建水平方向的链还是垂直方向的链。
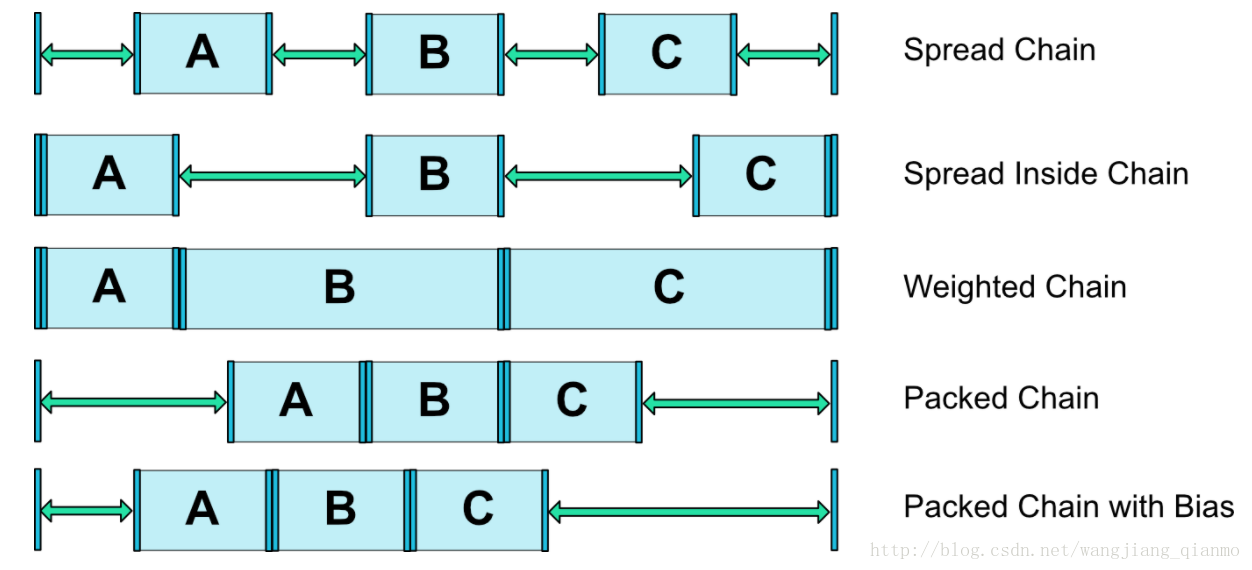
官方提供了一共有5种样式的链:
我们可以通过下面的方式设置:
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread|spread_inside|packed"
或者
app:layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle="spread|spread_inside|packed"
在这里需要注意的是:在Chain的第一个组件上设置chainStyle,切记 切记
1、属性参数和值
对于Chian属性的种类来说,一共两种:水平方向(Horizontal)和垂直方向(Vertical)
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle | 水平方向上的Chain |
| app:layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle | 垂直方向上的Chain |
对于Chain属性的模式来说,一共三种:展开(spread)、内部展开(spread_inside)、包裹(packed)
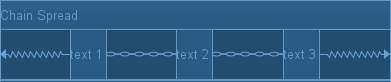
2. Spread链模式
spread模式会会把空间平均分配开来,每个View占有各自的平分空间,它是Chain属性的默认模式。
在该模式下,在设置View的宽度和高度为非0dp时,展示效果如下:
当使用了这个模式的时候,我们还可以配合weight属性设置spread的权重,在设置权重的时候,我们需要将控件的width或者height设置成0dp,并设置layout_constraintHorizontal_weight或者layout_constraintVertical_weight的值:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_constraintVertical_weight | 垂直方向的控件权重 |
| app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight | 水平方向的控件权重 |
通过权重的设置,如图:
3. Spread Inside链模式
spread inside模式是在Spread的基础上,把两边最边缘的两个View到外向父组件边缘的距离去除,然后让剩余的Views在剩余的空间内部平分空间。
在该模式下,在设置View的宽度和高度为非0dp时,展示效果如下:
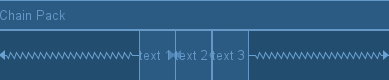
4、Packed链模式
packed模式很直观,它将所有Views聚拢在一起,控件和控件之间不留间隙,并将聚拢之后的Views居中显示。
在该模式下,在设置View的宽度和高度为非0dp时,展示效果如下:
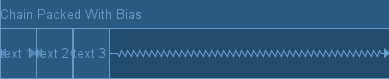
当我们使用了Packed模式了之后,我们还可以通过bias参数对聚拢在一起的Views进行位置的调整。
5、XML中设置Chain示例
设置Chain属性需要保证两个条件:
- 定义chain链的约束条件
- 在Chain的第一个组件上设置chainStyle。
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button16"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button17"
app:layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="39dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button17"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button18"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button16"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="39dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button18"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button17"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="39dp" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
6、GuideLine的使用
GuideLine只是用在ConstraintLayout布局里面的一个工具类,用于辅助布局,类似于辅助线,可以设置android:orientation属性来确定是横向还是纵向。
重要的是Guideline是不会显示到界面上的,默认是GONE的。
| 方向 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| android:orientation | 方向 |
创建了GuideLine之后,我们可以设置参考线的初始位置:
| 权重属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| app:layout_constraintGuide_begin | 以View的起始位置为参照物,水平或垂直方向上边界(dp) |
| app:layout_constraintGuide_end | 以View的结束位置为参照物,水平或垂直方向上边界(dp) |
| app:layout_constraintGuide_percent | 水平或垂直方向上的百分比(float ratio 0.0f - 1.0f) |
至此,整个ConstraintLayout的属性已讲解完毕,下面的章节我们讲分析ConstraintLayout在Android中的性能表现。让ConstraintLayout在Android中飞起来吧,Android ConstraintLayout性能分析