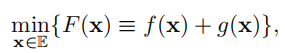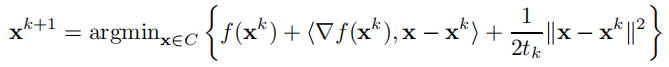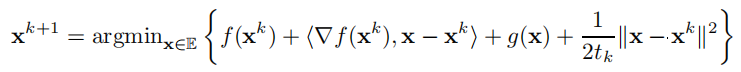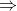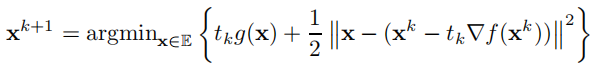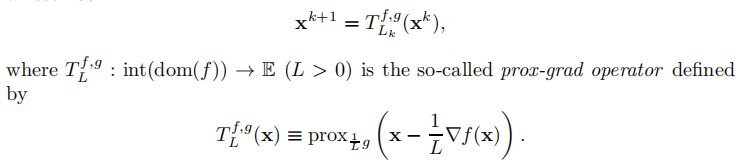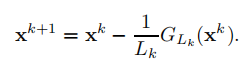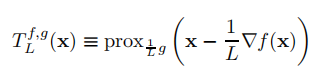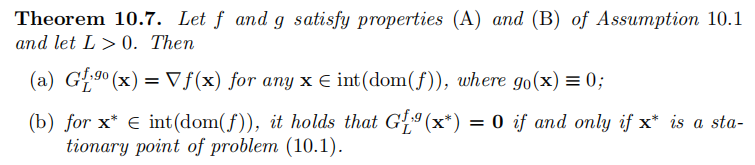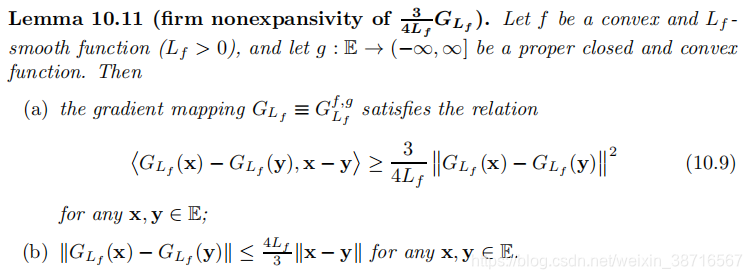参考文献:first-order methods in optimization: Amir Beck
Underlying Space:Euclidean norm
1 The Composite Model
本章主要考虑的复合函数模型及假设如下:
2 The Proximal Gradient Method
考虑以下问题(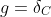
投影梯度方法:
等价于
回到更一般的复合函数问题,有:
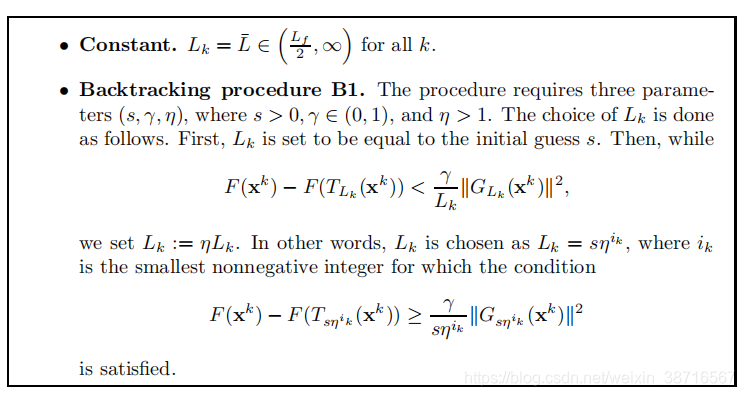
这里的步长是取定的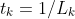
下面我们非凸和凸两种情况讨论这种算法的收敛性:
3 Analysis of the Proximal Gradient Method—The Nonconvex Case
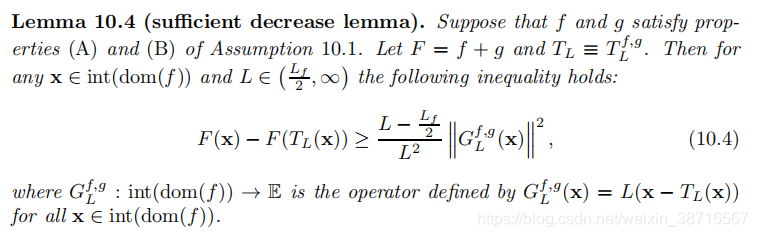
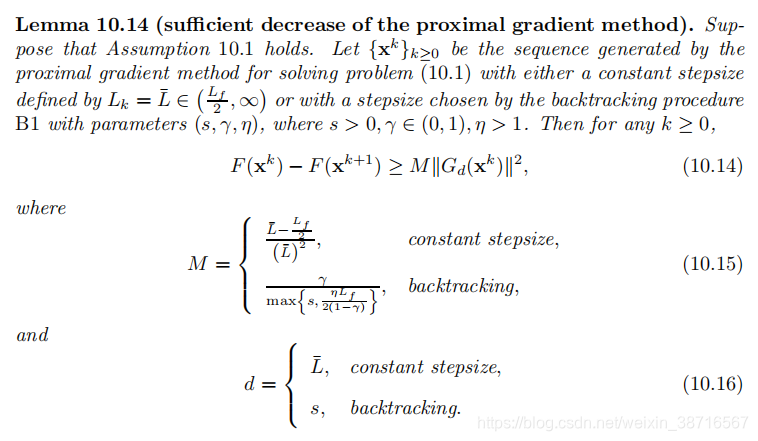
3.1 Sufficient Decrease
讨论非凸情形下的充分下降性:
易证。
3.2 The Gradient Mapping
其中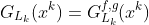
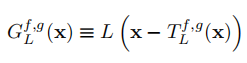
很容易得到该式。 此时若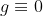

我们把G看作一个度量,实际上同原始的梯度相同,一开始都是<0,但到达稳定点时,等于0。
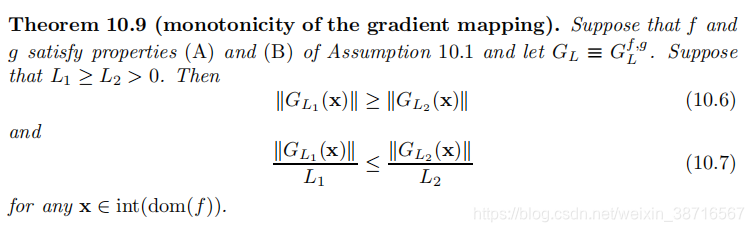
探索G的性质,实际上10.7也属于G的性质:
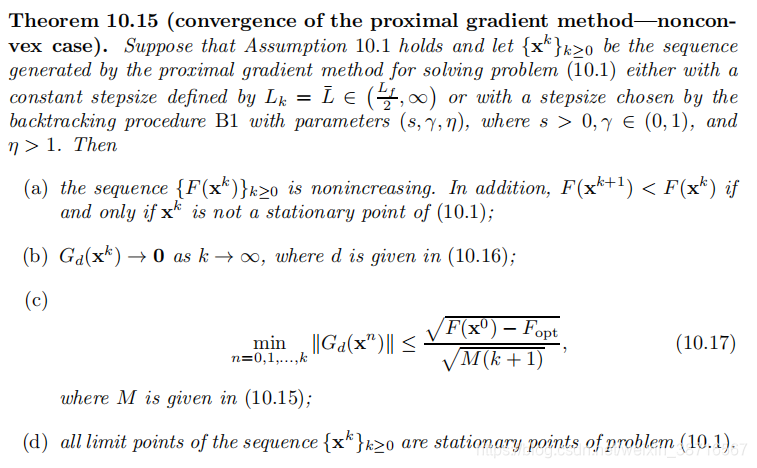
3.3 Convergence of the Proximal Gradient Method—The Nonconvex Case
步长选取:
4 Analysis of the Proximal Gradient Method—The Convex Case