ViT模型学习
Vision Transformer(ViT)简介
ViT则是自然语言处理和计算机视觉两个领域的融合结晶。在不依赖卷积操作的情况下,依然可以在图像分类任务上达到很好的效果。
模型特点
ViT模型主要应用于图像分类领域。因此,其模型结构相较于传统的Transformer有以下几个特点:
- 数据集的原图像被划分为多个patch(图像块)后,将二维patch(不考虑channel)转换为一维向量,再加上类别向量与位置向量作为模型输入。
- 模型主体的Block结构是基于Transformer的Encoder结构,但是调整了Normalization的位置,其中,最主要的结构依然是Multi-head Attention结构。
- 模型在Blocks堆叠后接全连接层,接受类别向量的输出作为输入并用于分类。通常情况下,我们将最后的全连接层称为Head,Transformer Encoder部分为backbone。
构建模型
Multi-Head Attention
- 多头注意力可以实现并行加速,且可以保持参数量
from mindspore import nn, ops
class Attention(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self,
dim: int,
num_heads: int = 8,
keep_prob: float = 1.0,
attention_keep_prob: float = 1.0):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = ms.Tensor(head_dim ** -0.5)
self.qkv = nn.Dense(dim, dim * 3)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(p=1.0-attention_keep_prob)
self.out = nn.Dense(dim, dim)
self.out_drop = nn.Dropout(p=1.0-keep_prob)
self.attn_matmul_v = ops.BatchMatMul()
self.q_matmul_k = ops.BatchMatMul(transpose_b=True)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(axis=-1)
def construct(self, x):
"""Attention construct."""
b, n, c = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x)
qkv = ops.reshape(qkv, (b, n, 3, self.num_heads, c // self.num_heads))
qkv = ops.transpose(qkv, (2, 0, 3, 1, 4))
q, k, v = ops.unstack(qkv, axis=0)
attn = self.q_matmul_k(q, k)
attn = ops.mul(attn, self.scale)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
out = self.attn_matmul_v(attn, v)
out = ops.transpose(out, (0, 2, 1, 3))
out = ops.reshape(out, (b, n, c))
out = self.out(out)
out = self.out_drop(out)
return out
TransformerEncoder
class TransformerEncoder(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self,
dim: int,
num_layers: int,
num_heads: int,
mlp_dim: int,
keep_prob: float = 1.,
attention_keep_prob: float = 1.0,
drop_path_keep_prob: float = 1.0,
activation: nn.Cell = nn.GELU,
norm: nn.Cell = nn.LayerNorm):
super(TransformerEncoder, self).__init__()
layers = []
for _ in range(num_layers):
normalization1 = norm((dim,))
normalization2 = norm((dim,))
attention = Attention(dim=dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
keep_prob=keep_prob,
attention_keep_prob=attention_keep_prob)
feedforward = FeedForward(in_features=dim,
hidden_features=mlp_dim,
activation=activation,
keep_prob=keep_prob)
layers.append(
nn.SequentialCell([
ResidualCell(nn.SequentialCell([normalization1, attention])),
ResidualCell(nn.SequentialCell([normalization2, feedforward]))
])
)
self.layers = nn.SequentialCell(layers)
def construct(self, x):
"""Transformer construct."""
return self.layers(x)
pos_embedding
class PatchEmbedding(nn.Cell):
MIN_NUM_PATCHES = 4
def __init__(self,
image_size: int = 224,
patch_size: int = 16,
embed_dim: int = 768,
input_channels: int = 3):
super(PatchEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.image_size = image_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size, has_bias=True)
def construct(self, x):
"""Path Embedding construct."""
x = self.conv(x)
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x = ops.reshape(x, (b, c, h * w))
x = ops.transpose(x, (0, 2, 1))
return x
Vit部分实现
from mindspore.common.initializer import Normal
from mindspore.common.initializer import initializer
from mindspore import Parameter
def init(init_type, shape, dtype, name, requires_grad):
"""Init."""
initial = initializer(init_type, shape, dtype).init_data()
return Parameter(initial, name=name, requires_grad=requires_grad)
class ViT(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self,
image_size: int = 224,
input_channels: int = 3,
patch_size: int = 16,
embed_dim: int = 768,
num_layers: int = 12,
num_heads: int = 12,
mlp_dim: int = 3072,
keep_prob: float = 1.0,
attention_keep_prob: float = 1.0,
drop_path_keep_prob: float = 1.0,
activation: nn.Cell = nn.GELU,
norm: Optional[nn.Cell] = nn.LayerNorm,
pool: str = 'cls') -> None:
super(ViT, self).__init__()
self.patch_embedding = PatchEmbedding(image_size=image_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
input_channels=input_channels)
num_patches = self.patch_embedding.num_patches
self.cls_token = init(init_type=Normal(sigma=1.0),
shape=(1, 1, embed_dim),
dtype=ms.float32,
name='cls',
requires_grad=True)
self.pos_embedding = init(init_type=Normal(sigma=1.0),
shape=(1, num_patches + 1, embed_dim),
dtype=ms.float32,
name='pos_embedding',
requires_grad=True)
self.pool = pool
self.pos_dropout = nn.Dropout(p=1.0-keep_prob)
self.norm = norm((embed_dim,))
self.transformer = TransformerEncoder(dim=embed_dim,
num_layers=num_layers,
num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_dim=mlp_dim,
keep_prob=keep_prob,
attention_keep_prob=attention_keep_prob,
drop_path_keep_prob=drop_path_keep_prob,
activation=activation,
norm=norm)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=1.0-keep_prob)
self.dense = nn.Dense(embed_dim, num_classes)
def construct(self, x):
"""ViT construct."""
x = self.patch_embedding(x)
cls_tokens = ops.tile(self.cls_token.astype(x.dtype), (x.shape[0], 1, 1))
x = ops.concat((cls_tokens, x), axis=1)
x += self.pos_embedding
x = self.pos_dropout(x)
x = self.transformer(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = x[:, 0]
if self.training:
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.dense(x)
return x
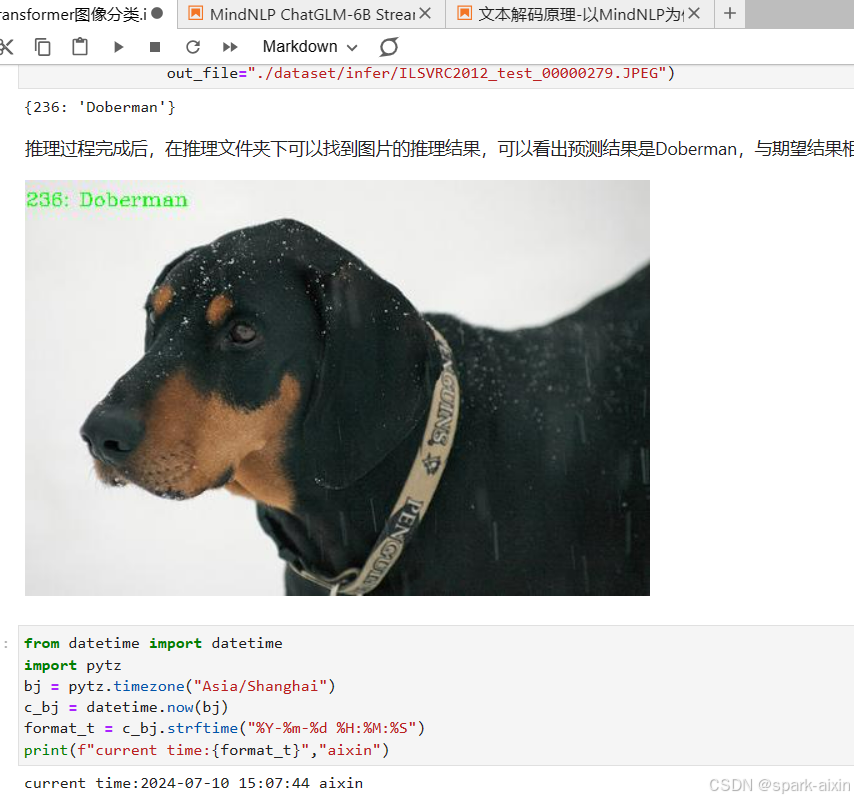
推理结果
此章节学习到此结束,感谢昇思平台。