管道的聚合
管道在Unix和Linux中一般用于将当前命令的输出结果作为下一个命令的参数。
MongoDB的聚合管道将MongoDB文档在一个管道处理完毕后将结果传递给下一个管道处理。管道操作是可以重复的。
表达式:处理输入文档并输出。表达式是无状态的,只能用于计算当前聚合管道的文档,不能处理其它的文档。
这里我们介绍一下聚合框架中常用的几个操作:
- $project:修改输入文档的结构。可以用来重命名、增加或删除域,也可以用于创建计算结果以及嵌套文档。
- match:用于过滤数据,只输出符合条件的文档。match使用MongoDB的标准查询操作。
- $limit:用来限制MongoDB聚合管道返回的文档数。
- $skip:在聚合管道中跳过指定数量的文档,并返回余下的文档。
- $unwind:将文档中的某一个数组类型字段拆分成多条,每条包含数组中的一个值。
- $group:将集合中的文档分组,可用于统计结果。
- $sort:将输入文档排序后输出。
- $geoNear:输出接近某一地理位置的有序文档。
1、$project实例
db.mycol.aggregate({$project:{name : 1, score : 1}})
这样的话结果中就只还有_id,name和score三个字段了,默认情况下_id字段是被包含的,如果要想不包含_id话可以这样:
db.mycol.aggregate({$project:{_id : 0, name : 1, score : 1}})
2、$match实例
m a t c h 用于获取分数大于 30 小于并且小于 100 的记录,然后将符合条件的记录送到下一阶段 match用于获取分数大于30小于并且小于100的记录,然后将符合条件的记录送到下一阶段 match用于获取分数大于30小于并且小于100的记录,然后将符合条件的记录送到下一阶段group管道操作符进行处理
db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …atch :{score: {gt: 30, KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 8: lt: 100}̲}},{group:{_id:'KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: sex',count:{sum:1}}}])
Aggregation-聚合查询和mysql sql语句对应
Aggregation:
- 参数说明:sql(Operators)
where ( m a t c h ) 、 g r o u p b y ( match) 、group by ( match)、groupby(group) 、having( m a t c h ) 、 s e l e c t ( match)、select( match)、select(project)、order by( s o r t ) 、 l i m i t ( sort)、limit( sort)、limit(limit) sum( s u m ) 、 c o u n t ( sum)、count( sum)、count(sum)、join($lookup)
SELECT cust_id, SUM(price) as total
FROM orders
WHERE status = 'A'
GROUP BY cust_id
HAVING total > 250
db.orders.aggregate([
{$match: {status: 'A'}},
{$group: {_id: "$cust_id",total: { $sum: "$price"}}},
{$match: {total: { $gt: 250}}}
])
更加字段长度排序
db.collection.aggregate(
[
{$project: {
"field": 1,
"field_length": { $strLenCP: "$field" }
}},
{$sort: {"field_length": -1}},
{$project: {"field_length": 0}},
]
)
聚合统计之$count表达式
普通查询:db.foo.find({name:{$ne:null}}).count()
$count 表达式等价于以下形式的 $sum 表达式:
{ $sum: 1 }
$count 示例
接下来我们将会使用以下集合进行演示:
db.sales.insertMany([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "Americanos", "price" : 5, "size": "Short", "quantity" : 22, "date" : ISODate("2022-01-15T08:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "Cappuccino", "price" : 6, "size": "Short","quantity" : 12, "date" : ISODate("2022-01-16T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "Lattes", "price" : 15, "size": "Grande","quantity" : 25, "date" : ISODate("2022-01-16T09:05:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "Mochas", "price" : 25,"size": "Tall", "quantity" : 11, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-17T08:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "Americanos", "price" : 10, "size": "Grande","quantity" : 12, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-18T21:06:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 6, "item" : "Cappuccino", "price" : 7, "size": "Tall","quantity" : 20, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-20T10:07:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 7, "item" : "Lattes", "price" : 25,"size": "Tall", "quantity" : 30, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-21T10:08:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 8, "item" : "Americanos", "price" : 10, "size": "Grande","quantity" : 21, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-22T14:09:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 9, "item" : "Cappuccino", "price" : 10, "size": "Grande","quantity" : 17, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-23T14:09:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 10, "item" : "Americanos", "price" : 8, "size": "Tall","quantity" : 15, "date" : ISODate("2022-02-25T14:09:00Z")}
]);
示例一:分组统计文档的数量
以下示例使用 $count 表达式计算不同种类咖啡的数量:
db.sales.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: '$item',
itemCount: { $count: {} },
},
},
])
返回结果如下:
[
{ _id: 'Mochas', itemCount: 1 },
{ _id: 'Americanos', itemCount: 4 },
{ _id: 'Lattes', itemCount: 2 },
{ _id: 'Cappuccino', itemCount: 3 }
]
其中,
- _id: “$item” 用于将文档按照 item 字段进行分组,返回 4 个组;
- $count: {} 用于统计每个分组内的文档数据,并将结果赋予 itemCount 字段。
示例二:统计与过滤
以下示例使用 $count 表达式计算不同种类咖啡的数量,并且返回数量大于 2 的结果:
db.sales.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: '$item',
itemCount: { $count: {} },
},
},
{
$match: { itemCount: { $gt: 2 } },
},
]);
返回结果如下:
[
{ _id: 'Americanos', itemCount: 4 },
{ _id: 'Cappuccino', itemCount: 3 }
]
MongoDB 聚合操作- < / f o n t > a n d </font>and </font>andor
Booking.aggregate([
{ $match:
{ $and: [
{ $or: [
{ isDoubleRoom },
{ chosenRoom }
]},
{ month },
{ year },
] }},
{ $group: { _id: "$fullDate", count: { $sum: 1 } } }
]
MongoDB 聚合操作- $lookup
数据准备
db.orders.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "almonds", "price" : 12, "quantity" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "pecans", "price" : 20, "quantity" : 1 },
{ "_id" : 3 }
])
db.inventory.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "sku" : "almonds", "description": "product 1", "instock" : 120 },
{ "_id" : 2, "sku" : "bread", "description": "product 2", "instock" : 80 },
{ "_id" : 3, "sku" : "cashews", "description": "product 3", "instock" : 60 },
{ "_id" : 4, "sku" : "pecans", "description": "product 4", "instock" : 70 },
{ "_id" : 5, "sku": null, "description": "Incomplete" },
{ "_id" : 6 }
])
查询
'''
SELECT *, inventory_docs
FROM orders
WHERE inventory_docs IN (SELECT *
FROM inventory
WHERE sku= orders.item);
'''
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$lookup:
{
from: "inventory",
localField: "item",
foreignField: "sku",
as: "inventory_docs"
}
}
])
db.getCollection('A').aggregate([
{
$lookup:{
from:'B',
localField:'userid',
foreignField:'userid',
as:'userinfo'
}
},
{
$unwind:'$userrole'//把一个数组展成多个,就比如说按多表连查的userrole数组中有10数据,那么用$unwind将把一条带数组的数据分成10条,这10条数据除了userrole不同之外,其它数据都是相同的,就类似于一个展开操作
},
{
$match:{'username':'zhangsan'}
},
{
$group:{
_id:{
userid:'$userid',//这个属性必须是要A表中有的
userrole:'$userrole.roleid',//A表中有一个集合,里面存放的对象有一个名为roleid的属性
},
operateTime:{
$last:'$operateTime'//取A表操作时间最后一条件数
}
info:{
$first:'$userinfo'//因为数组的扩展,造成了大量的重复数据(只有userrole不同),$first是只取最新的一条
}
}
},
{
$sort:{'operateTime':-1}//操作时间倒序,-1:倒序,1:升序
},
{
$skip:0//跳过几条数据,也就是从第几条数据开始取
},
{
$limit:5//每页显示几条数据
}
]);
参考案例
1. 主表
主表id为ObjectId类型
db.getCollection('note').find();
查询结果:
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316"),
"noteCode" : "20201102144804000001",
"userId" : 93,
"title" : "标题",
"content" : "内容"
},
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9fabb06b299d1336f9d31c"),
"noteCode" : "20201102144816000001",
"userId" : 93,
"title" : "标题",
"content" : "内容"
}
2. 子表
外键noteId为String类型
/* 1 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9faba46b299d1336f9d317"),
"noteId" : "5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316",
"imgId" : 316,
"imgUrl" : "https://xxx/selection1577778815396.png",
"createTime" : ISODate("2020-11-02T14:48:04.356+08:00")
}
/* 2 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9faba46b299d1336f9d318"),
"noteId" : "5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316",
"imgId" : 3165,
"imgUrl" : "https://xxx/selection157777881521.png",
"createTime" : ISODate("2020-11-02T14:48:04.356+08:00")
}
3. 关联查询,将关联ID类型转换为一致(objectId to string)
db.getCollection("note").aggregate(
[{
"$project":
{
"id":
{
"$convert": {
"input": "$_id",
"to": "string"
}
},
"noteCode": 1
}
}, {
"$lookup":
{
"from": "noteImage",
"localField": "id",
"foreignField": "noteId",
"as": "image_docs"
}
}]
);
输出结果:
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316"),
"noteCode" : "20201102144804000001",
"id" : "5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316",
"image_docs" : [
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9faba46b299d1336f9d317"),
"noteId" : "5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316",
"imgId" : 316,
"imgUrl" : "https://xxx/selection1577778815396.png",
"createTime" : ISODate("2020-11-02T14:48:04.356+08:00")
},
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5f9faba46b299d1336f9d318"),
"noteId" : "5f9faba46b299d1336f9d316",
"imgId" : 3165,
"imgUrl" : "https://xxx/selection1577778815396.png",
"createTime" : ISODate("2020-11-02T14:48:04.356+08:00")
}
]
}
4. 关联查询,将关联ID类型转换为一致(string to objectId)
db.getCollection("noteImage").aggregate(
[{
"$project":
{
"nid":
{
"$convert": {
"input": "$noteId",
"to": "objectId"
}
},
"imgId": 1
}
}, {
"$lookup":
{
"from": "note",
"localField": "nid",
"foreignField": "_id",
"as": "noteDocs"
}
}]
);
输出结果:
// 1
{
"_id": ObjectId("5fa9eab6e7e2af281425d0c9"),
"imgId": 2686,
"nid": ObjectId("5fa9eab6e7e2af281425d0c8"),
"noteDocs": [
{
"_id": ObjectId("5fa9eab6e7e2af281425d0c8"),
"noteCode": "9223372036854775807",
"userId": NumberInt("99"),
"title": "联调专用",
"content": "联调数据"
}
]
}
// 2
{
"_id": ObjectId("5fa9ee7ae7e2af281425d10a"),
"imgId": 2872,
"nid": ObjectId("5fa9ee7ae7e2af281425d109"),
"noteDocs": [
{
"_id": ObjectId("5fa9ee7ae7e2af281425d109"),
"noteCode": "9223372036854775807",
"userId": NumberInt("90"),
"title": "吃饭",
"content": "吃饭"
}
]
}
两表关联,每个表都有条件
db.Rel_QQDetails.aggregate([
{ $match: {
ReconciliationId:CSUUID("bb54bee7-187f-4d38-85d7-88926000ac7a")
}
},
{ $lookup:
{
from: "Fct_QQStatements",
localField: "OrderId",
foreignField: "OrderStatementsId",
as: "inventory_docs"
}
},
{ $match : {
"inventory_docs.StatementsPriceException" :false
}
}
])
MongoDB 聚合操作- $group
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/operator/aggregation/group/
语法示例:
{
$group:
{
_id: <expression>, // Group By Expression
<field1>: { <accumulator1> : <expression1> },
...
}
}
db.sales.insertMany([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "abc", "price" : NumberDecimal("10"), "quantity" : NumberInt("2"), "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T08:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "jkl", "price" : NumberDecimal("20"), "quantity" : NumberInt("1"), "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "xyz", "price" : NumberDecimal("5"), "quantity" : NumberInt( "10"), "date" : ISODate("2014-03-15T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "xyz", "price" : NumberDecimal("5"), "quantity" : NumberInt("20") , "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T11:21:39.736Z") },
{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "abc", "price" : NumberDecimal("10"), "quantity" : NumberInt("10") , "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T21:23:13.331Z") },
{ "_id" : 6, "item" : "def", "price" : NumberDecimal("7.5"), "quantity": NumberInt("5" ) , "date" : ISODate("2015-06-04T05:08:13Z") },
{ "_id" : 7, "item" : "def", "price" : NumberDecimal("7.5"), "quantity": NumberInt("10") , "date" : ISODate("2015-09-10T08:43:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 8, "item" : "abc", "price" : NumberDecimal("10"), "quantity" : NumberInt("5" ) , "date" : ISODate("2016-02-06T20:20:13Z") },
])
Count the Number of Documents in a Collection
'''
SELECT COUNT(*) AS count FROM sales
'''
db.sales.aggregate( [
{
$group: {
_id: null,
count: { $sum: 1 }
}
}
] )
>>> { "_id" : null, "count" : 8 }
Retrieve Distinct Values
db.sales.aggregate( [ { $group : { _id : "$item" } } ] )
>>>{ "_id" : "abc" }
{ "_id" : "jkl" }
{ "_id" : "def" }
{ "_id" : "xyz" }
Group by Item Having
'''
SELECT item,
Sum(( price * quantity )) AS totalSaleAmount
FROM sales
GROUP BY item
HAVING totalSaleAmount >= 100
'''
db.sales.aggregate(
[
// First Stage
{
$group :
{
_id : "$item",
totalSaleAmount: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } }
}
},
// Second Stage
{
$match: { "totalSaleAmount": { $gte: 100 } }
}
]
)
>>>{ "_id" : "abc", "totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("170") }
{ "_id" : "xyz", "totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("150") }
{ "_id" : "def", "totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("112.5") }
Group by Day of the Year
'''
SELECT date,
Sum(( price * quantity )) AS totalSaleAmount,
Avg(quantity) AS averageQuantity,
Count(*) AS Count
FROM sales
GROUP BY Date(date)
ORDER BY totalSaleAmount DESC
'''
db.sales.aggregate([
// First Stage
{
$match : { "date": { $gte: new ISODate("2014-01-01"), $lt: new ISODate("2015-01-01") } }
},
// Second Stage
{
$group : {
_id : { $dateToString: { format: "%Y-%m-%d", date: "$date" } },
totalSaleAmount: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } },
averageQuantity: { $avg: "$quantity" },
count: { $sum: 1 }
}
},
// Third Stage
{
$sort : { totalSaleAmount: -1 }
}
])
>>>{ "_id" : "2014-04-04", "totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("200"), "averageQuantity" : 15, "count" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "2014-03-15", "totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("50"), "averageQuantity" : 10, "count" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "2014-03-01", "totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("40"), "averageQuantity" : 1.5, "count" : 2 }
Group by null
The following aggregation operation specifies a group _id of null, calculating the total sale amount, average quantity, and count of all documents in the collection.
'''
SELECT Sum(price * quantity) AS totalSaleAmount,
Avg(quantity) AS averageQuantity,
Count(*) AS Count
FROM sales
'''
db.sales.aggregate([
{
$group : {
_id : null,
totalSaleAmount: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } },
averageQuantity: { $avg: "$quantity" },
count: { $sum: 1 }
}
}
])
>>>{
"_id" : null,
"totalSaleAmount" : NumberDecimal("452.5"),
"averageQuantity" : 7.875,
"count" : 8
}
Pivot Data
From the [mongo](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/program/mongo/#mongodb-binary-bin.mongo) shell, create a sample collection named books with the following documents:
db.books.insertMany([
{ "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 },
{ "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 },
{ "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }
])
Group title by author
db.books.aggregate([
{ $group : { _id : "$author", books: { $push: "$title" } } }
])
>>>{ "_id" : "Homer", "books" : [ "The Odyssey", "Iliad" ] }
{ "_id" : "Dante", "books" : [ "The Banquet", "Divine Comedy", "Eclogues" ] }
Group Documents by author
The following aggregation operation groups documents by author:
db.books.aggregate([
// First Stage
{
$group : { _id : "$author", books: { $push: "$$ROOT" } }
},
// Second Stage
{
$addFields:
{
totalCopies : { $sum: "$books.copies" }
}
}
])
>>> {
"_id" : "Homer",
"books" :
[
{ "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 },
{ "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }
],
"totalCopies" : 20
}
{
"_id" : "Dante",
"books" :
[
{ "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 },
{ "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 }
],
"totalCopies" : 5
}
MongoDB 之 aggregate $group 巧妙运用
有这样一组数据:
{
"campaign_id": "A",
"campaign_name": "A",
"subscriber_id": "123"
},
{
"campaign_id": "A",
"campaign_name": "A",
"subscriber_id": "123"
},
{
"campaign_id": "A",
"campaign_name": "A",
"subscriber_id": "456"
}
按照 campaign_id 与 campaign_name 分组,并查询出每个分组下的记录条数 及 subscriber_id 不同记录的个数
关系型数据库SQL示例:
select campaign_id,campaign_name,count(subscriber_id),count(distinct subscriber_id)
group by campaign_id,campaign_name from campaigns;
在MongoDB下就存在两种组合:
1) campaign_id, campaign_name, subscriber_id 三个相同的分为一组,
2) campaign_id, campaign_name 两个相同,subscriber_id 不同分为一组,
最后通过这两种分组查询出按照 campaign_id 与 campaign_name 分组,subscriber_id 不同记录的个数
MongoDB示例:
db.campaigns.aggregate([
{ "$match": { "subscriber_id": { "$ne": null }}},
// Count all occurrences
{ "$group": {
"_id": {
"campaign_id": "$campaign_id",
"campaign_name": "$campaign_name",
"subscriber_id": "$subscriber_id"
},
"count": { "$sum": 1 }
}},
// Sum all occurrences and count distinct
{ "$group": {
"_id": {
"campaign_id": "$_id.campaign_id",
"campaign_name": "$_id.campaign_name"
},
"totalCount": { "$sum": "$count" },
"distinctCount": { "$sum": 1 }
}}
])
文档结果:第一个 group:
{
"_id" : {
"campaign_id" : "A",
"campaign_name" : "A",
"subscriber_id" : "456"
},
"count" : 1
}
{
"_id" : {
"campaign_id" : "A",
"campaign_name" : "A",
"subscriber_id" : "123"
},
"count" : 2
}
文档结果:第二个 group:
{
"_id" : {
"campaign_id" : "A",
"campaign_name" : "A"
},
"totalCount" : 3,
"distinctCount" : 2
}
至此,我们已经查询出一共有 3 条记录,subscriber_id 有两种不同的值
reference:Mongodb中Aggregation特性
【mongoDB高级篇①】聚集运算之group,aggregate - 菜问 - 博客园
MongoDB聚合group的操作指南
MongoDB 聚合
MongoDB中聚合(aggregate)主要用于处理数据(诸如统计平均值,求和等),并返回计算后的数据结果。有点类似sql语句中的 count(*)。
基本语法为:db.collection.aggregate( [ , , … ] )
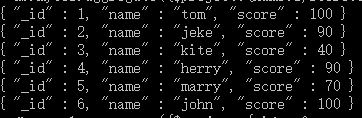
现在在mycol集合中有以下数据:
{ “_id” : 1, “name” : “tom”, “sex” : “男”, “score” : 100, “age” : 34 }
{ “_id” : 2, “name” : “jeke”, “sex” : “男”, “score” : 90, “age” : 24 }
{ “_id” : 3, “name” : “kite”, “sex” : “女”, “score” : 40, “age” : 36 }
{ “_id” : 4, “name” : “herry”, “sex” : “男”, “score” : 90, “age” : 56 }
{ “_id” : 5, “name” : “marry”, “sex” : “女”, “score” : 70, “age” : 18 }
{ “_id” : 6, “name” : “john”, “sex” : “男”, “score” : 100, “age” : 31 }
1、$sum计算总和。
Sql: select sex,count(*) frommycol group by sex
MongoDb: db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, personCount: {$sum: 1}}}])
Sql: select sex,sum(score) totalScore frommycol group by sex
MongoDb: db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, totalScore: { s u m : ′ sum: ' sum:′score’}}}])
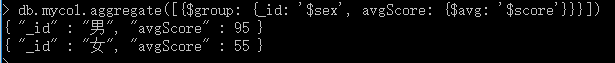
2、$avg 计算平均值
Sql: select sex,avg(score) avgScore frommycol group by sex
Mongodb: db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, avgScore: { a v g : ′ avg: ' avg:′score’}}}])
3、$max获取集合中所有文档对应值得最大值。
Sql: select sex,max(score) maxScore frommycol group by sex
Mongodb: db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, maxScore: { m a x : ′ max: ' max:′score’}}}])
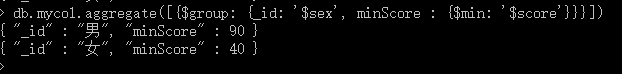
4、$min 获取集合中所有文档对应值得最小值。
Sql: select sex,min(score) minScore frommycol group by sex
Mongodb: db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, minScore: { m i n : ′ min: ' min:′score’}}}])
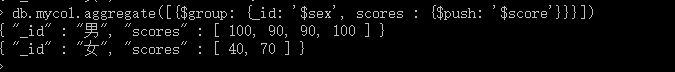
5、$push 把文档中某一列对应的所有数据插入值到一个数组中。
Mongodb: db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, scores : { p u s h : ′ push: ' push:′score’}}}])
6、$addToSet把文档中某一列对应的所有数据插入值到一个数组中,去掉重复的
db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, scores : { a d d T o S e t : ′ addToSet: ' addToSet:′score’}}}])
7、 $first根据资源文档的排序获取第一个文档数据。
db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, firstPerson : { f i r s t : ′ first: ' first:′name’}}}])
8、 $last根据资源文档的排序获取最后一个文档数据。
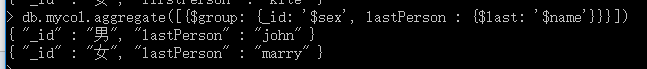
db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group: {_id: 'sex’, lastPerson : { l a s t : ′ last: ' last:′name’}}}])
9、全部统计null
db.mycol.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …ll,totalScore:{push:‘$score’}}}])
例子
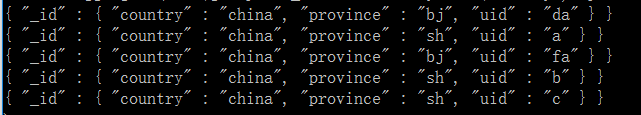
现在在t2集合中有以下数据:
{ “country” : “china”, “province” : “sh”, “userid” : “a” }
{ “country” : “china”, “province” : “sh”, “userid” : “b” }
{ “country” : “china”, “province” : “sh”, “userid” : “a” }
{ “country” : “china”, “province” : “sh”, “userid” : “c” }
{ “country” : “china”, “province” : “bj”, “userid” : “da” }
{ “country” : “china”, “province” : “bj”, “userid” : “fa” }
需求是统计出每个country/province下的userid的数量(同一个userid只统计一次)
过程如下。
首先试着这样来统计:
db.t2.aggregate([{KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …d":{"country":"country",“prov”:"KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 10: province"}̲,"number":{sum:1}}}])
结果是错误的:
原因是,这样来统计不能区分userid相同的情况 (上面的数据中sh有两个 userid = a)
为了解决这个问题,首先执行一个group,其id 是 country, province, userid三个field:
db.t2.aggregate([ { KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …{ "country" : "country", “province”: “ p r o v i n c e " , " u i d " : " province" , "uid" : " province","uid":"userid” } } } ])
可以看出,这步的目的是把相同的userid只剩下一个。
然后第二步,再第一步的结果之上再执行统计:
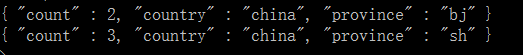
db.t2.aggregate([
{ $group: {"_id": { "country" : "$country", "province": "$province" , "uid" : "$userid" } } } ,
{ $group: {"_id": { "country" : "$_id.country", "province": "$_id.province" }, count : { $sum : 1 } } }
])
这回就对了
加入一个$project操作符,把_id去掉
db.t2.aggregate([ { $group: {"_id": { "country" : "$country", "province": "$province" , "uid" : "$userid" } } } ,
{ $group: {"_id": { "country" : "$_id.country", "province": "$_id.province" }, count: { $sum : 1 } } },
{ $project : {"_id": 0, "country" : "$_id.country", "province" : "$_id.province", "count" : 1}}
])
最终结果如下:
管道的概念
MongoDB 加减乘除 a d d 、 add、 add、subtract、 m u l 、 mul、 mul、divide
| 类别 | 操作符 | 语法 | 功能用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 逻辑运算符 | a d d 、 add、 add、subtract、 m u l 、 mul、 mul、divide | ||
| 布尔表达式 | $and | {$and: [ , , … ]} | 如果所有表达式的值为true,那就返回true,否则返回false。 |
| $or | {$or: [ , , … ]} | 只要有任意表达式的值为true,那就返回true,否则返回false。 | |
| $not | { $not: [ ] } | 对expression取反。 | |
| 控制表达式 | $cond | { $cond: { if: , then: , else: } } 或者 { $cond: [ , , ] } | 如果boolean-expression为的值是true,那就返回true-case,否则返回false-case。 |
| $ifNull | { $ifNull: [ , ] } | 如果expression是null,那就返回replacement-expression-if-null,否则返回expression。 | |
| 比较表达式 | $cmp | { $cmp: [ , ] } | 比较expression1和expression2,如果相等,返回0;如果前者大于后者,返回一个正数1;如果前者小于后者。返回一个负数-1。 |
| $strcasecmp | { $strcasecmp: [, ] } | $cmp的细化。用来比较expression1和expression2;区分大小写,主要针对ASCII characters。如果相等,返回0;如果前者大于后者,返回一个正数1;如果前者小于后者。返回一个负数-1。 | |
| e q / eq/ eq/ne/ g t / gt/ gt/gte/ l t / lt/ lt/lte | e q / eq/ eq/ne/ g t / gt/ gt/gte/ l t / lt/ lt/lte :[ , ] | 对expression1和expression2执行相应的比较操作,返回比较的结构(true或false)。 |
1、$add
加法运算,基础语法:{ $add : [ < expression1 > , < expression2 > , ... ] }
2、$subtract
减法运算,基础语法:{ $subtract: [ <expression1>, <expression2> ] } expression1减去expression2
3、$multiply
乘法运算,基础语法:{ $multiply : [ < expression1 > , < expression2 > , ... ] }
4、$divide
除法运算,基础语法:{ $divide: [ <expression1>, <expression2> ] }expression1为被除数,expression2为除数
有文档3个
**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">{ </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"_id"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 1, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"item"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"abc"</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"price"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 10, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"fee"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 2, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">date</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: ISODate(</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"2014-03-01T08:00:00Z"</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">) }</font>**
**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">{ </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"_id"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 2, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"item"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"jkl"</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"price"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 20, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"fee"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 1, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">date</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: ISODate(</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"2014-03-01T09:00:00Z"</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">) }</font>**
**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">{ </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"_id"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 3, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"item"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"xyz"</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"price"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 5, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"fee"</font>****<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: 10, </font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">date</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">: ISODate(</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">"2014-03-15T09:00:00Z"</font>**``**<font style="color:#36CFC9;background-color:#FFECE0;">) }</font>**
求和
db.sales.aggregate(
[{ $project: { item: 1, total: { $add: [ "$price", "$fee" ] }}}
])
结果:
{ “_id” : 1, “item” : “abc”, “total” : 12 }
{ “_id” : 2, “item” : “jkl”, “total” : 21 }
{ “_id” : 3, “item” : “xyz”, “total” : 15 }
date字段数据 + 3天
db.sales.aggregate(
[
{ $project: { item: 1, expire_date: { $add: [ "$date", 3*24*60*60*1000 ] } } }
])
结果显示为 :
{ “_id” : 1, “item” : “abc”, “expire_date” : ISODate(“2014-03-04T08:00:00Z”) }
{ “_id” : 2, “item” : “jkl”, “expire_date” : ISODate(“2014-03-04T09:00:00Z”) }
{ “_id” : 3, “item” : “xyz”, “expire_date” : ISODate(“2014-03-18T09:00:00Z”) }
求差
属于add的逆运算,用法等同
求积
db.sales.aggregate(
[
{ $project: { item: 1, total_price: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$fee" ] } } }
])
结果:
{ “_id” : 1, “item” : “abc”, “total_price” : 20 }
{ “_id” : 2, “item” : “jkl”, “total_price” : 20 }
{ “_id” : 3, “item” : “xyz”, “total_price” : 50 }
重新插入documents
{ “_id” : 1, “name” : “A”, “hours” : 80, “resources” : 7 },
{ “_id” : 2, “name” : “B”, “hours” : 40, “resources” : 4 }
求商
db.planning.aggregate(
[
{ $project: { name: 1, workdays: { $divide: [ "$hours", 8 ] } } }
])
结果取整:
{ “_id” : 1, “name” : “A”, “workdays” : 10 }
{ “_id” : 2, “name” : “B”, “workdays” : 5 }
db.planning.aggregate(
[
{ $project: { remainder: { $mod: [ "$hours", "$tasks" ] } } }
])
结果取余:
{ “_id” : 1, “remainder” : 3 }
{ “_id” : 2, “remainder” : 0 }
mongoDB inc操作符更新字段值加减
使用$inc操作符将一个字段的值增加或者减少的格式是:
{ $inc: { <field1>: <amount1>, <field2>: <amount2>, ... } }
$inc操作符接收正的和负的值
如果指定的字段不存在则$inc操作符创建这个字段并且设置这个字段的值为指定的在值;
使用$inc操作符的字段的值如果值为null则将会报异常;
$inc操作符是原子性的在单个文档中;
{
_id: 1,
sku: "abc123",
quantity: 10,
metrics: {
orders: 2,
ratings: 3.5
}
}
$inc操作符将quantity减2,metrics.orders内嵌文档字段加1
db.products.update(
{ "_id": 1},
{ $inc: { quantity: -2, "metrics.orders": 1 } }
)
{
"_id" : 1,
"sku" : "abc123",
"quantity" : 8,
"metrics" : {
"orders" : 3,
"ratings" : 3.5
}
}
mongo条件操作
$exists判断字段是否存在
查询所有存在age 字段的记录
db.users.find({age: {$exists: true}});
大小比较操作符
<, <=, >, >= 这个操作符就不用多解释了,最常用也是最简单的。
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $gt: value } } ); // 大于: field > value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $lt: value } } ); // 小于: field < value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $gte: value } } ); // 大于等于: field >= value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $lte: value } } ); // 小于等于: field <= value
如果要同时满足多个条件,可以这样做
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $gt: value1, $lt: value2 } } ); // value1 < field < value2
Null空值处理
在users文档找出"sex"值为"null"并且字段存在的记录。
> db.users.find({sex:{"$in":[null], "$exists":true}});
$mod取模运算
查询age 取模6 等于1 的数据
> db.c1.find({age: {$mod : [ 6 , 1 ] } })
{ "_id" : ObjectId("4fb4af85afa87dc1bed94330"), "age" : 7, "length_1" : 30 }
$ne不等于
在users文档中查询"age"不等于20的记录:
db.users.find({age:{$ne:20}});
$size数组元素个数
$size对于查询数组来说是非常有用的,顾名思义,可以用它查询特定长度的数组。例如:
> db.users.find({favorite_number: {$size: 3}})
$size并不能与其他查询条件(比如$gt) 组合使用,但是这种查询可以通过在文档中添加一个"size"键的方式来实现。这样每一次向 指定数组添加元素时,同时增加"size"的值。比如
> db.users.update(criteria,{"$push":{"favorite_number":"1"},"$inc":{"$size":1}})
自增操作的速度非常快,所以对性能的影响微乎其微。这样存储文档后,就可以像下面这样查询了:
> db.users.find({"$size":{"$gt":3}})
db.articleLikes.aggregate(
[
{
$match:{
articleId: "559581876487065600"
}
},
{
$project:{
count: {
$size: "$likedUsers"
}
}
}
])
$regex正则表达式匹配
查询name字段以B开头的记录
db.users.find({name: {$regex: /^B.*/}});
字段值长度限制
假设我们有一个集合(collection)存储了用户的个人信息,其中一个字段是姓名(name),类型为字符串。我们希望查询名字长度大于10个字符的用户。我们可以使用如下的查询操作:
db.users.find({ "name": { "$regex": ".{10,}" } })
这个查询操作通过正则表达式匹配来查找名字长度大于10的用户。在这个例子中,我们没有对字段值长度设置具体的限制,而是在查询时通过正则表达式来进行过滤。
问题:mongoDB中的字符串字段值长度
该字段的数据类型是字符串。我想获取字段名称字符长度大于 40 的数据。
我尝试了这些查询但返回错误。 1.
db.usercollection.find(
{$where: "(this.name.length > 40)"}
).limit(2);
output :error: {
"$err" : "TypeError: Cannot read property 'length' of undefined near '40)' ",
"code" : 16722
}
这适用于 2.4.9 但我的版本是 2.6.5
解答
对于 MongoDB 3.6 和更新版本:
e x p r < / f o n t > 运算符允许在查询语言中使用聚合表达式 , 因此您可以利用 < f o n t s t y l e = " c o l o r : r g b ( 198 , 120 , 221 ) ; b a c k g r o u n d − c o l o r : r g b ( 40 , 44 , 52 ) ; " > expr</font>运算符允许在查询语言中使用聚合表达式,因此您可以利用<font style="color:rgb(198, 120, 221);background-color:rgb(40, 44, 52);"> expr</font>运算符允许在查询语言中使用聚合表达式,因此您可以利用<fontstyle="color:rgb(198,120,221);background−color:rgb(40,44,52);">strLenCP运算符的使用来检查字符串的长度,如下所示:
db.usercollection.find({
name: { $exists: true },
$expr: { $gt: [{ $strLenCP: '$name' }, 40] }
})
考虑运行以下展示上述概念的聚合操作:
db.usercollection.aggregate([
{ $match: { name: { $exists: true } } },
{ $redact: {
$cond: [
{ $gt: [ { $strLenCP: "$name" }, 40] },
"$$KEEP",
"$$PRUNE"
]
} },
{ $limit: 2 }
])
如果使用$where,请尝试不带括号的查询:
db.usercollection.find({ $where: "this.name.length > 40" }).limit(2);
更好的查询是检查字段是否存在,然后检查长度:
db.usercollection.find({ name: { $type: 2 }, $where: "this.name.length > 40" }).limit(2);
或者:
db.usercollection.find({ name: { $exists: true }, $where: "this.name.length >
40" }).limit(2);
MongoDB 在 w h e r e < / f o n t > 表达式和非 < f o n t s t y l e = " c o l o r : r g b ( 198 , 120 , 221 ) ; b a c k g r o u n d − c o l o r : r g b ( 40 , 44 , 52 ) ; " > where</font>表达式和非<font style="color:rgb(198, 120, 221);background-color:rgb(40, 44, 52);"> where</font>表达式和非<fontstyle="color:rgb(198,120,221);background−color:rgb(40,44,52);">where查询语句之前评估非 w h e r e < / f o n t > 查询操作可以使用索引。更好的性能是将字符串的长度存储为另一个字段 , 然后您可以对其进行索引或搜索 ; 与此相比 , 应用 < f o n t s t y l e = " c o l o r : r g b ( 198 , 120 , 221 ) ; b a c k g r o u n d − c o l o r : r g b ( 40 , 44 , 52 ) ; " > where</font>查询操作可以使用索引。更好的性能是将字符串的长度存储为另一个字段,然后您可以对其进行索引或搜索;与此相比,应用<font style="color:rgb(198, 120, 221);background-color:rgb(40, 44, 52);"> where</font>查询操作可以使用索引。更好的性能是将字符串的长度存储为另一个字段,然后您可以对其进行索引或搜索;与此相比,应用<fontstyle="color:rgb(198,120,221);background−color:rgb(40,44,52);">where会慢得多。当您无法以任何其他方式构造数据或处理一小部分数据时,建议使用 JavaScript 表达式和$where运算符作为最后的手段。
避免使用 w h e r e < / f o n t > 运算符的另一种更快的方法是 < f o n t s t y l e = " c o l o r : r g b ( 198 , 120 , 221 ) ; b a c k g r o u n d − c o l o r : r g b ( 40 , 44 , 52 ) ; " > where</font>运算符的另一种更快的方法是<font style="color:rgb(198, 120, 221);background-color:rgb(40, 44, 52);"> where</font>运算符的另一种更快的方法是<fontstyle="color:rgb(198,120,221);background−color:rgb(40,44,52);">regex运算符。考虑以下搜索模式
db.usercollection.find({"name": {"$type": 2, "$regex": /^.{41,}$/}}).limit(2);
forEach遍历游标
MongoDB 还有另一种方式来处理游标,即forEach()方法:
> db.t3.find().forEach( function(u) { printjson(u); } );
MongoDB只查询数据第1个元素
db.your_collection.find({},{"array_field" : {"$slice":1}})
//$slice可指定第n个,也可指定n-m个,点这里查看官方文档
目前,在聚合管道的 p r o j e c t 操作中, project操作中, project操作中,slice运算符不可用.
首先是 u n w i n d , m y f i e l d 数组,然后将它们组合在一起,取组中的 unwind,my_field数组,然后将它们组合在一起,取组中的 unwind,myfield数组,然后将它们组合在一起,取组中的first元素.
复制代码
db.my_collection.aggregate([
{$unwind:"$my_field"},
{$group:{"_id":"$_id","resp":{$first:"$my_field"}}},
{$project:{"_id":0,"resp":1}}
])
任意数组位置
初始化成员数据
db.persons.insertMany([
{ "_id" : "1001", "name" : "张三", "fruits" : [ "apple", "orange" ] },
{ "_id" : "1002", "name" : "李四", "fruits" : [ "banana", "apple" ] },
{ "_id" : "1003", "name" : "王五", "fruits" : [ "banana", "apple", "orange" ] },
{ "_id" : "1004", "name" : "赵六", "fruits" : [ ] },
{ "_id" : "1005", "name" : "田七" },
])
语法:{ $arrayElemAt: [ , ] }
例子1:找到每个人最喜欢吃的第一个水果
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$project: {
"name": 1,
"firstFruit": { $arrayElemAt: [ "$fruits", 0 ] }
}
}
])
//结果如下
{ "_id" : "1001", "name" : "张三", "firstFruit" : "apple" }
{ "_id" : "1002", "name" : "李四", "firstFruit" : "banana" }
{ "_id" : "1003", "name" : "王五", "firstFruit" : "banana" }
{ "_id" : "1004", "name" : "赵六" }
{ "_id" : "1005", "name" : "田七", "firstFruit" : null }
官方文档
https://www.mongodb.com/zh-cn/docs/manual/reference/operator/aggregation/count/
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42752574/article/details/111938743
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/operator/aggregation/