树
C++数组实现
tree.h
#program once
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
Tree(int size, int *pRoot);
~Tree();
int *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);
bool AddNode(int nodeIndex, int direction, int *pNode);
bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex, int *pNode);
void TreeTraverse();
private:
int *m_pTree;
int m_iSize;
};
tree.cpp
#include "tree.h"
Tree::Tree(int size, int *pRoot)
{
m_iSize = size;
m_pTree = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
m_pTree[i] = 0;
}
m_pTree[0] = *pRoot;
}
Tree::~Tree()
{
delete[]m_pTree;
m_pTree = NULL;
}
int *Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
if (nodeIndex < 0 || nodeIndex >= m_iSize)
{
return NULL;
}
if (m_pTree[nodeIndex] == 0)
{
return NULL;
}
return &m_pTree[nodeIndex];
}
bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex, int direction, int *pNode)
{
if (nodeIndex < 0 || nodeIndex >= m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
if (m_pTree[nodeIndex] == 0)
{
return false;
}
if (direction == 0)
{
if (nodeIndex * 2 + 1 >= m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
if (m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 1] != 0)
{
return false;
}
m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 1] = *pNode;
}
if (direction == 1)
{
if (nodeIndex * 2 + 2 >= m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
if (m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 2] != 0)
{
return false;
}
m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 2] = *pNode;
}
}
bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex, int *pNode)
{
if (nodeIndex < 0 || nodeIndex >= m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
if (m_pTree[nodeIndex] == 0)
{
return false;
}
*pNode = m_pTree[nodeIndex];
m_pTree[nodeIndex] = 0;
return true;
}
void Tree::TreeTraverse()
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_iSize; ++i)
{
cout << m_pTree[i] << " ";
}
}
demo.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tree.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int root = 1;
Tree *pTree = new Tree(10, &root);
int node1 = 2;
int node2 = 3;
int node3 = 4;
int node4 = 5;
int node5 = 6;
int node6 = 7;
pTree->AddNode(0, 0, &node1);
pTree->AddNode(0, 1, &node2);
pTree->AddNode(1, 0, &node3);
pTree->AddNode(1, 1, &node4);
pTree->AddNode(2, 0, &node5);
pTree->AddNode(2, 1, &node6);
pTree->TreeTraverse();
int *p = pTree->SearchNode(2);
cout << endl << "node = " << *p << endl;
delete pTree;
return 0;
}
C++链表实现
node.h
#program once
class Node
{
public:
Node();
Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);
void DeleteNode();
void PreoderTraversal();
void InorderTraversal();
void PostorderTraversal();
int index;
int data;
Node *pLChild;
Node *pRChild;
Node *pParent;
};
node.cpp
#include "Node.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Node::Node()
{
index = 0;
data = 0;
pLChild = NULL;
pRChild = NULL;
pParent = NULL;
}
Node *Node::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
if (this->index == nodeIndex)
{
return this;
}
Node *temp = NULL;
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
{
if (this->pLChild->index == nodeIndex)
{
return this->pLChild;
}
else
{
temp = this->pLChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if (temp != NULL)
{
return temp;
}
}
}
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
{
if (this->pRChild->index == nodeIndex)
{
return this->pRChild;
}
else
{
temp = this->pRChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
return temp;
}
}
return NULL;
}
void Node::DeleteNode()
{
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
{
this->pLChild->DeleteNode();
}
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
{
this->pRChild->DeleteNode();
}
if (this->pParent != NULL)
{
if (this->pParent->pLChild == this)
{
this->pParent->pLChild = NULL;
}
}
if (this->pParent != NULL)
{
if (this->pParent->pRChild == this)
{
this->pParent->pRChild = NULL;
}
}
delete this;
}
void Node::PreoderTraversal()
{
cout << this->index << " " << this->data << endl;
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
{
this->pLChild->PreoderTraversal();
}
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
{
this->pRChild->PreoderTraversal();
}
}
void Node::InorderTraversal()
{
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
{
this->pLChild->InorderTraversal();
}
cout << this->index << " " << this->data << endl;
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
{
this->pRChild->InorderTraversal();
}
}
void Node::PostorderTraversal()
{
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
{
this->pLChild->PostorderTraversal();
}
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
{
this->pRChild->PostorderTraversal();
}
cout << this->index << " " << this->data << endl;
}
tree.h
#include "Node.h"
class Tree
{
public:
Tree();
~Tree();
Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);
bool AddNode(int nodeIndex, int direction, Node *pNode);
bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex, Node *pNode);
void PreoderTraversal();
void InorderTraversal();
void PostorderTraversal();
private:
Node *m_pRoot;
};
tree.cpp
#include "tree.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
Tree::Tree()
{
m_pRoot = new Node();
}
Tree::~Tree()
{
DeleteNode(0, NULL);
// m_pRoot->DeleteNode();
}
Node *Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
return m_pRoot->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
}
bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex, int direction, Node *pNode)
{
Node *temp = SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if (temp == NULL)
{
return false;
}
Node *node = new Node();
if (node == NULL)
{
return false;
}
node->index = pNode->index;
node->data = pNode->data;
node->pParent = temp;
if (direction == 0)
{
temp->pLChild = node;
}
if (direction == 1)
{
temp->pRChild = node;
}
return true;
}
bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex, Node *pNode)
{
Node *temp = SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if (temp == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if (pNode != NULL)
{
pNode->data = temp->data;
}
temp->DeleteNode();
return true;
}
void Tree::PreoderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->PreoderTraversal();
}
void Tree::InorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->InorderTraversal();
}
void Tree::PostorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->PostorderTraversal();
}
demo.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tree.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Node *node1 = new Node();
node1->index = 1;
node1->data = 5;
Node *node2 = new Node();
node2->index = 2;
node2->data = 4;
Node *node3 = new Node();
node3->index = 3;
node3->data = 3;
Node *node4 = new Node();
node4->index = 4;
node4->data = 2;
Node *node5 = new Node();
node5->index = 5;
node5->data = 1;
Node *node6 = new Node();
node6->index = 6;
node6->data = 7;
Tree *tree = new Tree();
tree->AddNode(0, 0, node1);
tree->AddNode(0, 1, node2);
tree->AddNode(1, 0, node3);
tree->AddNode(1, 1, node4);
tree->AddNode(2, 0, node5);
tree->AddNode(2, 1, node6);
tree->DeleteNode(6, NULL);
tree->PostorderTraversal();
delete tree;
return 0;
}
二叉树的链式存储结构
typedef struct BiTNode{
ElemType data;//数据域
struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;//左、右孩子指针
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
二叉树的遍历
例: 1
2 3
4 5
6
先序遍历(PreOrder)
根->左->右
void PreOrder(BiTree T){
if (T != NULL){
visit(T);//访问根节点
PreOrder(T->lchild);//递归遍历左子树
PreOrder(T->rchild);//递归遍历右子树
}
}
中序遍历(InOrder)
左->根->右
void InOrder(BiTree T){
if (T != NULL){
InOrder(T->lchild);//递归遍历左子树
visit(T);//访问根节点
InOrder(T->rchild);//递归遍历右子树
}
}
后序遍历(PostOrder)
左->右->根
void PostOrder(BiTree T){
if (T != NULL)
{
PostOrder(T->lchild);//递归遍历左子树
PostOrder(T->rchild);//递归遍历右子树
visit(T);//访问根节点
}
}
时间复杂度都是O(n),空间复杂度为O(n)。
中序遍历的非递归算法
void InOrder2(BiTree T){
//二叉树中序遍历的非递归算法,算法需要借助一个栈
InitStack(S);
BiTree p = T; //初始化栈;p是遍历指针
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)){ //栈不空或p不空时循环
if (p){ //根指针进展,遍历左子树
Push(S, p); //每遇到非空二叉树先向左走
p = p->lchild;
}
else{ //根指针退栈,访问根节点,遍历右子树
Pop(S, p); visit(p); //退栈,访问根节点
p = p->rchild; //再向右子树走
}
}
}
二叉树的层次遍历
void LevelOrder(BiTree T){
InitQueue(Q);//初始化辅助队列
BiTree p;
EnQueue(Q, T);//将根结点入队
while (!IsEmpty(Q)){//队列不空循环
DeQueue(Q, p);//队头元素出队
visit(p);//访问当前p所指向结点
if (p->lchild != NULL)
{
EnQueue(Q, p->lchild);//左子树不空,则左子树入队列
}
if (p->rchild != NULL)
{
EnQueue(Q, p->rchild);//右子树不空,则右子树入队列
}
}
}
树的存储结构
双亲表示法
#define MAX_TREE_SIZE 100 //树中最多结点数
typedef struct{ //树的结点定义
ElemType data; //数据元素
int parent; //双亲位置域
}PTNode;
typedef struct{ //树的类型定义
PTNode nodes[MAX_TREE_SIZE]; //双亲表示
int n; //结点数
}PTree;
求结点的孩子时需遍历整个结构。
孩子表示法
typedef struct CTNode //孩子结点
{
int child;
struct CTNode *next;
}*ChildPtr;
typedef struct
{
TElemType data;
ChildPtr firstchild;//孩子链表头指针
}CTBox;
typedef struct
{
CTBox nodes[MAX_TREE_SIZE];
int n, r; //结点数和根的位置
}CTree;
求结点的双亲时需遍历N个结点中孩子链表指针域所指向的N个孩子链表。
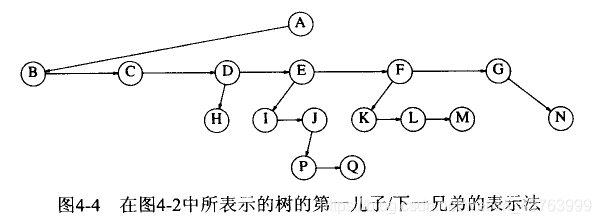
孩子兄弟表示法(二叉树表示法)
typedef struct CSNode
{
ElemType data; //数据域
struct CSNode *firstchild, *nextsibling; //第一个孩子和右兄弟指针
}CSNode, *CSTree;
易查找结点的孩子,若为每个结点增设一个parent域指向其父节点,则查找结点的父结点也很方便。
树转换为二叉树的规则:每个结点左指针指向它的第一个孩子结点,右指针指向它在树中的相邻兄弟结点,可表示为“左孩子右兄弟”。由于根节点没有兄弟,所以由树转换而得的二叉树没有右子树。
例: