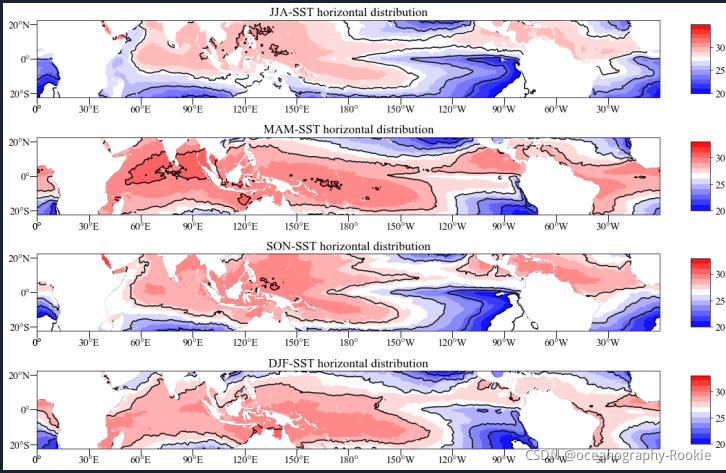
一般来说,我们研究分析一些海温或者降水等要素的的变化规律时,通常会进行季节特征变化分析,这就需要我们绘制不同季节的空间分布图来进行分析,这就需要我们掌握子图的绘制方法。
绘图进阶学习
一般这种我们可以通过设置不同的ax进行绘制,简单介绍在这篇博客中:进阶绘图–axes
- 通过对于每个子图的不同命令,可以绘制填色图、折线图等等,这种方法的不好的地方在于需要多次重复一些语句设置,比如地形、坐标、标签等等,当然,如果不怕麻烦也可以忽略。
- 对于不同的子图,只需要对于不同的ax进行不同的绘图即可,同时对于不同的子图属性设置也要对应不同的ax序号,如果你第一个字图的ax是ax1,那么所有关于这个子图的命令语句,都要以ax1开头。
- 下面给出一个通过ax命令海温的季节空间分布图绘制的例子:
ax绘制不同子图
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Aug 12 22:20:52 2021
@author: 纪
"""
## 导入库
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
from cartopy.util import add_cyclic_point
from cartopy.mpl.ticker import LongitudeFormatter, LatitudeFormatter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import xarray as xr
## 路径
path='D:\\sst.nc'
### =================================================================
# 准备数据、选择区域、求季节平均
###==================================================================
sst=xr.open_dataset(path)
lon=sst.lon
lat=sst.lat
lat_range = lat[(lat>-22.5) & (lat<22.5)]
sst_region =sst.sel(lat=lat_range,lon=lon)
season =sst_region.groupby(
'time.season').mean('time', skipna=True)
#=====================draw==============================================
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(20,12))#设置一个画板,将其返还给fig
###=================设置全局字体、字体大小==============================
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'Times New Roman'
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 15
###=========================绘制第一个子图=================================
ax = fig.add_subplot(4, 1, 1, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude =180))
### 添加地形,并且设置陆地为白色遮盖
ax.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '50m', \
edgecolor='white',facecolor='white',zorder=2))
### 添加循环,为了避免经线180°出现白色竖线
cycle_sst, cycle_lon = add_cyclic_point(season.sst[1], coord=lon)
cycle_LON, cycle_LAT = np.meshgrid(cycle_lon, lat_range)
### 绘制填色图
cb=ax.contourf(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst,levels=np.arange(20,36),cmap='bwr',\
zorder=0,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree())
### 设置横纵坐标的范围
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, 361, 30),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-20, 40, 20),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label =False))#经度0不加标识
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(LatitudeFormatter())
### 绘制等值线
contour = ax.contour(lon,lat_range, season.sst[1],colors='k',zorder=1,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree())
#zorder 显示图层叠加顺序
### 设置坐标轴的轴长、宽、离轴的距离、
ax.tick_params(which='major', direction='out', length=10, width=0.99, pad=0.2, bottom=True, left=True, right=False, top=False)
### 设置子图的标题
ax.set_title('JJA-SST horizontal distribution')
### 设置子图的colorbar
cbar = fig.colorbar(cb,shrink=0.7,ticks=[20,25,30],pad=0.04,aspect=3.5)
###=========================绘制第2个子图=================================
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(4, 1, 2, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))#中心线为180°
ax1.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '110m', \
edgecolor='black', facecolor='white'))
cycle_sst1, cycle_lon = add_cyclic_point(season.sst[2], coord=lon)
cb=ax1.contourf(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst1,levels=np.arange(20,34),cmap='bwr',\
zorder=0,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree() )
contour = plt.contour(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst1,colors='k',zorder=1,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax1.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '50m', \
edgecolor='white', facecolor='white',zorder=2))
ax1.tick_params(which='major', direction='out', length=10, width=0.99, pad=0.2, bottom=True, left=True, right=False, top=False)
ax1.set_xticks(np.arange(0, 361, 30),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax1.set_yticks(np.arange(-20, 40, 20),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax1.xaxis.set_major_formatter(LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label =False))#经度0不加标识
ax1.yaxis.set_major_formatter(LatitudeFormatter())
ax1.set_title('MAM-SST horizontal distribution')
cbar = fig.colorbar(cb,shrink=0.7,ticks=[20,25,30],pad=0.04,aspect=3.5)
###=========================绘制第3个子图=================================
ax2= fig.add_subplot(4, 1, 3, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))#中心线
ax2.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '110m', \
edgecolor='black', facecolor='white'))
cycle_sst2, cycle_lon = add_cyclic_point(season.sst[3], coord=lon)
cb=ax2.contourf(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst2,levels=np.arange(20,34),cmap='bwr',\
zorder=0,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree() )
contour = plt.contour(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst2,colors='k',zorder=1,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax2.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '50m', \
edgecolor='white', facecolor='white',zorder=2))
ax2.tick_params(which='major', direction='out', length=10, width=0.99, pad=0.2, bottom=True, left=True, right=False, top=False)
ax2.set_xticks(np.arange(0, 361, 30),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax2.set_yticks(np.arange(-20, 40, 20),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax2.xaxis.set_major_formatter(LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label =False))#经度0不加标识
ax2.yaxis.set_major_formatter(LatitudeFormatter())
ax2.set_title('SON-SST horizontal distribution')
cbar = fig.colorbar(cb,shrink=0.7,ticks=[20,25,30],pad=0.04,aspect=3.5)
###=========================绘制第4个子图=================================
ax3= fig.add_subplot(4, 1, 4, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))#中心线
ax3.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '110m', \
edgecolor='black', facecolor='white'))
cycle_sst3, cycle_lon = add_cyclic_point(season.sst[0], coord=lon)
cb=ax3.contourf(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst3,levels=np.arange(20,34),cmap='bwr',\
zorder=0,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree() )
contour = plt.contour(cycle_LON,cycle_LAT, cycle_sst3,colors='k',zorder=1,transform= ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax3.add_feature(cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', '50m', \
edgecolor='white', facecolor='white',zorder=2))
ax3.tick_params(which='major', direction='out', length=10, width=0.99, pad=0.2, bottom=True, left=True, right=False, top=False)
ax3.set_xticks(np.arange(0, 361, 30),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax3.set_yticks(np.arange(-20, 40, 20),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax3.xaxis.set_major_formatter(LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label =False))#经度0不加标识
ax3.yaxis.set_major_formatter(LatitudeFormatter())
ax3.set_title('DJF-SST horizontal distribution')
cbar = fig.colorbar(cb,shrink=0.7,ticks=[20,25,30],pad=0.04,aspect=3.5)
### 保存图片到指定路径
#fig.savefig('D:\\desktopppp\\picture\\'+'SST_horizontal_distribution.tiff',format='tiff',dpi=150)
绘图结果如下,海温的四个季节的空间水平分布:
通过绘图函数封装绘制不同子图
其实,通过上面的代码,我们可以发现,有部分代码完全是重复设置的,非常的麻烦,所以我们完全可以设置一个绘图函数,减少我们的代码量。
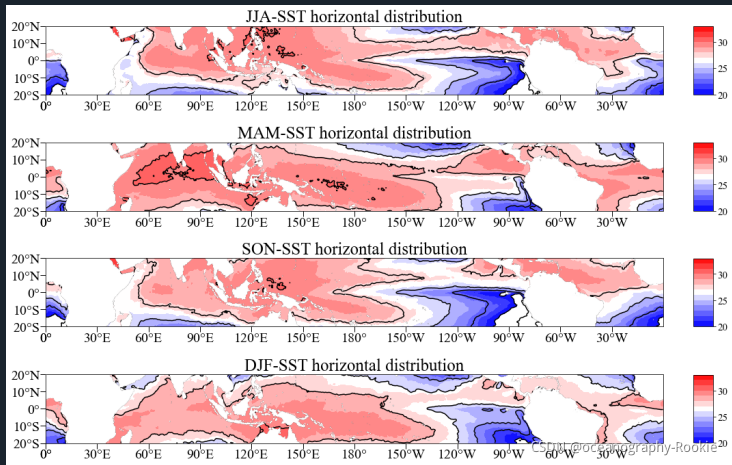
下面给出一个使用代码封装后的绘图例子,可以前后对比一下:
"""
Created on Thu Nov 4 19:47:58 2021
@author: (ji)
E-mail : [email protected]
Introduction: keep learning
"""
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
from cartopy.mpl.ticker import LongitudeFormatter, LatitudeFormatter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import xarray as xr
path2='D:\\sst.nc'
ds=xr.open_dataset(path2).sortby("lat", ascending= True)
sst=ds.sel(lat=slice(-20,20),time=slice('2010','2010'))
season =sst.groupby('time.season').mean('time', skipna=True)
def make_map(ax, title):
# set_extent set crs
ax.set_extent(box, crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
land = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical',
'land',
scale,
edgecolor='white',
facecolor='white',
zorder=2)
ax.add_feature(land) # set land color
ax.coastlines(scale) # set coastline resolution
# set coordinate axis
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, 360+30, 30),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-20, 30, 10),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label =False))#经度0不加标识
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(LatitudeFormatter())
# plt.tick_params(labelsize=25)
lon_formatter = LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label=False)
# zero_direction_label set 0 without E or W
lat_formatter = LatitudeFormatter()
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(lon_formatter)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(lat_formatter)
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=25, loc='center')
ax.tick_params(which='major',
direction='out',
length=8,
width=0.99,
pad=0.2,
labelsize=20,
bottom=True, left=True, right=False, top=False)
return ax
# # prepare
box = [0, 361, -20, 20]
scale = '50m'
xstep, ystep = 30, 5
cmap=plt.get_cmap('bwr')#'RdYlBu_r'
levels=np.arange(20,34)
zorder=0
# name=['DJF-SST horizontal distribution','JJA-SST horizontal distribution',\
# 'MAM-SST horizontal distribution','SON-SST horizontal distribution']
sea=['JJA','MAM','SON','DJF']
#=================draw picture =================================
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(20,12))#设置一个画板,将其返还给fig
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'Times New Roman'
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 15
proj=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180)
count=0
for i in range(len(sea)):
count+=1
ax=fig.add_subplot(4,1,count,projection=proj)
make_map(ax,sea[i]+'-SST horizontal distribution')
plot=ax.contourf(sst.lon,sst.lat,season.sel(season=sea[i]).sst,cmap=cmap,levels=levels,\
zorder=0,transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
contour=ax.contour(sst.lon,sst.lat,season.sel(season=sea[i]).sst,colors='k',zorder=1,transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# pcolor=ax.pcolormesh(sst.lon,sst.lat,season.sst[i],transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),\
# cmap='bwr', zorder=0)
# fig.colorbar(pcolor,ax=ax,shrink=0.7,ticks=[20,25,30],pad=0.04,aspect=3.5)
fig.colorbar(plot,ax=ax,shrink=0.7,ticks=[20,25,30],pad=0.04,aspect=3.5)
plt.show()
# fig.savefig('G:\\daily\\'+'SST_horizontal_distribution.tiff',format='tiff',dpi=150)
结果是一样的:
可以明显的发现,代码更简洁了,也可以将这个封装函数进行保存,以后直接导入这个函数,大大节省我们绘图时间!!!
有兴趣的小伙伴们可以尝试一下~
测试数据有点大,不方面传在这里,有需要的找我要
一个努力学习python的海洋
水平有限,欢迎指正!!!
欢迎评论、收藏、点赞、转发、关注。
关注我不后悔,记录学习进步的过程~~