题目
结合高性能并行计算领域算例,使用MPI + OpenMP并行化编写代码,并撰写报告,测试并行效率。
方法
- 定义快速排序quickSort函数,定义排序总数NUM;
- 生成大小为size * calculateSize的二维逆序数组,其中使用MPI_Comm_size获取size,size * calculateSize = NUM;
- MPI_Comm_rank获取进程ID,通过通信函数MPI_Scatter将每个子矩阵发送到每个子进程,然后每个子进程通过quickSort函数进行快速排序,使用OpenMP的sections集合函数进行线程划分;
- 将每个子进程通过通信函数MPI_Gather收回到0号进程中,再对收回了所有数的0号进程中的数组进行最后一次排序,即size路归并排序,就能得到排完序的数组;
- 利用MPI_Wtime()函数进行计时。
代码
#include "mpi.h"
#include "omp.h"
#include <iostream>
#define NUM 12800
using namespace std;
void swap(int &a, int &b) //交换函数
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void printArray(int *array, int len) //输出数组
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void quickSort(int *array, int l, int r) //快速排序
{
int i, m;
if (l >= r) return;
m = l;
for (i = l + 1; i <= r; i++)
if (array[i] < array[l])
swap(array[++m], array[i]);
swap(array[l], array[m]);
#pragma omp parallel sections //sections使用2个线程即两个并行块
{
#pragma omp section
quickSort(array, l, m - 1);
#pragma omp section
quickSort(array, m + 1, r);
};
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
double time; //时间标记
time = MPI_Wtime(); //返回调用处理器上经过的挂钟时间
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv); //MPI初始化
int size; //通信域comm中所包含的进程数
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size); //返回指定通信器中MPI进程的总数
int calculateSize = (int)(NUM / size); //每个进程分配的计算个数
int processId; //进程在comm中的标识号id
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &processId); //获取MPI进程编号
int arr[size][calculateSize]; //初始数组
int arrMerge[size][calculateSize]; //合并数组
int arrEach[calculateSize]; //size分之一个初始数组的数
int figure = size * calculateSize; //用于给数组赋值
int arrFinal[size * calculateSize]; //排完序的完整数组
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) //生成数组
{
for (int j = 0; j < calculateSize; j++) {
arr[i][j] = figure--;
}
}
//并行排序,将数组平均分成size块后分给每个子进程排序
MPI_Scatter(arr, calculateSize, MPI_INT, arrEach, calculateSize, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
//每个进程里的排序
quickSort(arrEach, 0, calculateSize - 1);
//将子进程排完序的数组合并成一个
MPI_Gather(arrEach, calculateSize, MPI_INT, arrMerge, calculateSize, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
cout << "The current array of " << processId << ":" << endl; //输出当前进程排序结果
printArray(arrEach, calculateSize);
//数组用于记录存放选择次数
int numTimes[size] = {0};
//用于存放合并数组时最大的四个数的数组
int arrNumMax[size];
for (int i = calculateSize * size - 1; i >= 0; i--) //按升序顺序合并为一个数组
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) //找出szie个数组里面分别最大的数
{
if (numTimes[j] >= calculateSize)
arrNumMax[j] = 0;
else
arrNumMax[j] = arrMerge[j][calculateSize - numTimes[j] - 1];
}
int maxNum = arrNumMax[0]; //找出size个数里面最大的数即size路归并
for (int k = 1; k < size; k++)
{
if (arrNumMax[k] > maxNum)
maxNum = arrNumMax[k];
}
for (int n = 0; n < size; n++) //标记数最大的数组
{
if (maxNum == arrNumMax[n])
{
numTimes[n] = numTimes[n] + 1;
break;
}
}
arrFinal[i] = maxNum; //存入数组
}
if (!processId)
{
time = MPI_Wtime() - time; //结束计时
cout << "The final array :" << endl; //输出数组
printArray(arrFinal, size * calculateSize);
cout << "NUM = "<< NUM << "\t" << "size = " << size << "\t" << "time = " << time * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
}
MPI_Finalize(); //终止MPI
return 0;
}
结果分析
1、简单输出测试:共100个数据进行排序,使用10个进程,其中线程数export OMP_NUM_THREADS=2。
$ mpicc -o quicksort -fopenmp quicksort.cpp -lstdc++
$ time mpirun -np 10 ./quicksort
The current array of 2:
71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
The current array of 5:
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
The current array of 6:
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
The current array of 7:
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
The current array of 9:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
The current array of 1:
81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
The current array of 4:
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
The current array of 0:
91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
The final array :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
Parallel running time = 54.8629 ms
The current array of 3:
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
The current array of 8:
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
结果分析:程序会根据输入进程数自动平均分配排序任务,因此采用二维数组方便进行数据的分布与收集,初始数组为逆序,每个进程排序完毕后进行归并收集,最后变为升序数组。
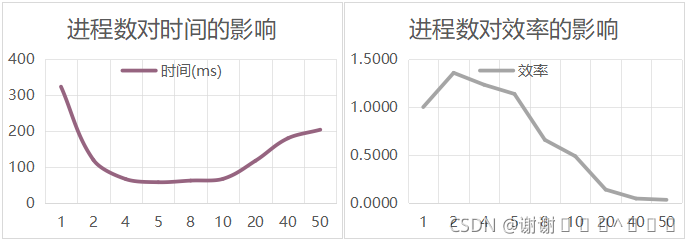
2、效率测试:在排序总数NUM=10000时,测试不同进程数对时间的影响。
结果分析:在本实验中,线程数设置为2;由于通信函数MPI_Scatter限制,故进程数选择需要能被10000整除。通过实验数据可得,当排序数目为10000时,进程数5的时间最快,也具有不错的效率;随着进程数不断增加,如50时,每个进程需要排序2000个数据,使得通信花费大于排序花费,因此时间反弹。
总结
在大规模节点间的并行时,由于节点间通讯的量是成平方项增长的,所以带宽很快就会显得不够。所以用MPI+OpenMP混合编写并行部分,即每个MPI进程执行多个OpenMP线程。OpenMP部分由于不需要进程间通信,直接通过内存共享方式交换信息,所以可以显著减少程序所需通讯的信息。