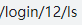vue中this. r o u t e . q u e r y 和 t h i s . route.query和this. route.query和this.route.params & query传参和params传参的使用和区别
1.query传参:
路由:
var router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/login', component: login },
{ name:'register',path: '/register', component: register }
]
})
导航:
// 注意:这是 query 两种传参方式 一种是直接跳转把字符串传过去 一种是传描述目标位置的对象
<router-link to="/login?id=10&name=zs">登录</router-link>
<router-link :to="{path:'/register',query:{id:5,name:'lili'}}">注册</router-link>
或
<router-link :to="{name:'register',query:{id:5,name:'lili'}}">注册</router-link>
等同于:
this.$router.push('/login?id=10&name=zs')
this.$router.push({path:'/register',query:{id:5,name:'lili'}})
或
this.$router.push({name:'register',query:{id:5,name:'lili'}})
注意:jquery可以通过name或path来引入路由
2.params传参
路由:
var router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/login/:id/:name', component: login },// 这里不传入对应的参数(:/id/:name) 刷新页面 参数会消失,页面中就丢失了数据
{ name:'register', path: '/register/:id/:name', component: register }
]
})
导航:
// 注意:这是 params 两种传参方式 一种是直接跳转把字符串传过去 一种是传描述目标位置的对象
<router-link to="/login/12/ls">登录</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'register',params:{id:10,name:'lili'}}">注册</router-link>
等同于:
this.$router.push('/login/12/ls')
this.$router.push({name:'register',params:{id:10,name:'lili'}})
注意:params只能通过name来引入路由,path会undefined
jquery传参和params传参的区别
1.用法上:
- 上文已经提到query可以用name或path来引入
- params必需要用name来引入,接收参数都是类似的,分别是:
this.$route.query.name和this.$route.params.name。
2.地址栏表现形式上:
query:
params:
注意:这里的12和ls 对应的是/:id/:name 这两个参数可以不写 那么就不会在地址栏上显示 不过刷新页面参数会消失 写上参数刷新页面 参数不会消失
1.query方式传参和接收参数
传参:
this.$router.push({
path:'/detail/:id',
query:{
id:id
}
})
接收参数:
this.$route.query.id
Tips:
传参是this.r o u t e r , 接 收 参 数 是 t h i s . router,接收参数是this.route**r,接收参数是thi**s.route,这里千万要看清了!!!
2.params方式传参和接收参数
传参:
this.$router.push({
name:'Detail',
params:{
id:id
}
})
接收参数:
this.$route.params.id
Tips:
params传参,push里面只能是 name:‘xxxx’,不能是path:’/xxx’,因为params只能用name来引入路由,如果这里写成了path,接收参数页面会是undefined!!!
另外,二者还有点区别:
-
- 接收参数
// query通过this.$route.query接收参数
created () {
const id = this.$route.query.id;
}
// params通过this.$route.params来接收参数
created () {
const id = this.$route.params.id;
}
-
- 切换路由
// query通过path切换路由
<router-link :to="{path: 'Detail', query: { id: 1 }}">前往Detail页面</router-link>
// params通过name切换路由
<router-link :to="{name: 'Detail', params: { id: 1 }}">前往Detail页面</router-link>复制代码
简单说query相当于get请求,页面跳转的时候,可以在地址栏看到请求参数,浏览器刷新页面不会消失,而params相当于post请求,参数不会在地址栏中显示,浏览器刷新页面后消失。
Vue监听路由
方式一:监听$router
复用组件时,想对路由参数的变化作出响应的话,你可以简单地 watch(监测变化) $route 对象:
watch: {
'$route' (to, from) {
// 对路由变化作出响应...
}
}
方式二:唯一值 key 属性
Vue 为你提供了一种方式来声明“这两个元素是完全独立的——不要复用它们”。只需添加一个具有唯一值的 key 属性即可
<router-view :key="key"></router-view>
computed: {
key() {
return this.$route.name !== undefined? this.$route.name +new Date(): this.$route +new Date()
}
}
使用computed属性和Date()可以保证每一次的key都是不同的,这样就可以如愿刷新数据了。
实践
1. 定义路由
{
path: '/hse/problem/prMain/deal/:id',
component: () => import('@/views/hse/Problem/PrDeal.vue'),
meta: {
keepAlive: true
}
},
2. 动态路由传参
handleDeal(id){
this.$router.push(
{
path: `/hse/problem/prMain/deal/${id}`,
params: {id: id}
}
)
}
3. 监听路由
watch:{
//监听路由
$route(){
if(this.$route.params!==null){
this.paramId = this.$route.params.id;
}
},
paramId(newVal,oldVal){
if(newVal !== undefined && newVal !== null){
//初始化数据
this.init();
}
}
}
4. init方法初始化数据
methods:{
//初始化数据
init(){
let vm = this;
vm.$nextTick(()=>{
vm.$axios.get(`/hse/sim/prProblem/v1/get/${vm.dataId}`).then(reply=>{
vm.form = reply.data;
}).catch(e=>{
vm.$toast.fail(e);
})
})
}
}
实例
routes: [
// 写法 (1)
{ //在路由中显示传递的参数
path: '/skipIn/:name/:age', //传递两个参数
name: 'SkipIn', //跳转页面的名字
component: SkipIn //注册组件
},
// 写法 (2)
// {
// path: '/skipIn',
// name: 'SkipIn',
// component: SkipIn
// }
]
跳转之前的页面
<template>
<div id="skip">
<div class="Input">
<el-form ref="form" :model="form" label-width="80px">
<el-row :gutter="20">
<el-col :span="6">
<el-form-item label="姓名:">
<el-input v-model="form.name" size="small"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
</el-col>
<el-col :span="6">
<el-form-item label="年龄:">
<el-input v-model="form.age" size="small"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
</el-col>
</el-row>
</el-form>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<el-button type="primary" size="small" class="skipBtn" @click="skipBtn">路由跳转</el-button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:'RouterSkip',
data(){
return{
form:{
name: "",
age: ""
}
}
},
methods:{
skipBtn: function(){
// 写法 1.如果以这种方式传递参数,那么路由的写法要以(1)为准。
// url的表现形式为(url中带参数):http://localhost:8080/#/skipIn/小明/20
this.$router.push({ path: "/skipIn/" + this.form.name + "/" + this.form.age});
// 写法 2. 如果以这种方式传递参数,那么路由的写法要以(2)就可以了。
// url的表现形式为(url中不带参数):http://localhost:8080/#/skipIn
this.$router.push({ name: 'SkipIn', params:{name: this.form.name, age:this.form.age}});
// 注:如果以2这种方式传递参数时,那么当刷新跳转后传参的页面,数据将不存在。
// 写法 3. 如果以这种方式传递参数,那么路由的写法要以(2)就可以了。
// url的表现形式为(url中带参数):http://localhost:8080/#/skipIn?name=小明&age=20
this.$router.push({ path: "/skipIn", query: {name: this.form.name, age:this.form.age}});
// 注:如果以1、3这种方式传递参数时,刷新跳转后传参的页面,数据还会显示存在。
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
#skip{
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
background: #eee;
.Input{
padding: 10px 20px;
}
.footer{
width: 100%;
background: #ccc;
padding: 5px 20px;
overflow: hidden;
.skipBtn{
float: right;
}
}
}
</style>
跳转之后的页面
<template>
<div id="skipIn">
<div class="header">
<span class="info">{{msg}}</span>
<el-button type="primary" size="small" class="backBtn" @click="back">
返回<i class="iconfont icon-fanhui back"></i>
</el-button>
</div>
<div class="information">{{params}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:'SkipIn',
data(){
return{
msg: "路由传参页面",
params: ""
}
},
methods:{
back: function(){
this.$router.go(-1); //返回
},
showInfo: function(){
// 对应写法 1. 2. 获取传过来的参数
this.params = this.$route.params.name;
// 对应写法 3. 获取传过来的参数
this.params = this.$route.query.name;
}
},
mounted(){
this.showInfo();
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
#skipIn{
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
background: red;
.header{
width: 100%;
background: #eee;
padding: 5px 20px;
overflow: hidden;
.info{
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 32px;
}
.backBtn{
float: right;
.back{
font-size: 14px;
}
}
}
.information{
font-size: 20px;
}
}
</style>