在之前的文章AppCompatActivity#setContentView源码分析和Android开发Activity的setContentView源码分析中已经介绍了Activity和AppCompatActicity的setContentView加载视图的流程,本文通过一个小例子来看看它们两个的视图层级到底是怎样的。
新建一个工程,布局里面代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/main_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ball"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ball" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="获取图片宽高"
android:onClick="buttonClick" />
</LinearLayout>
布局很简单,里面只有一个篮球图片和一个按钮,效果是这样的:
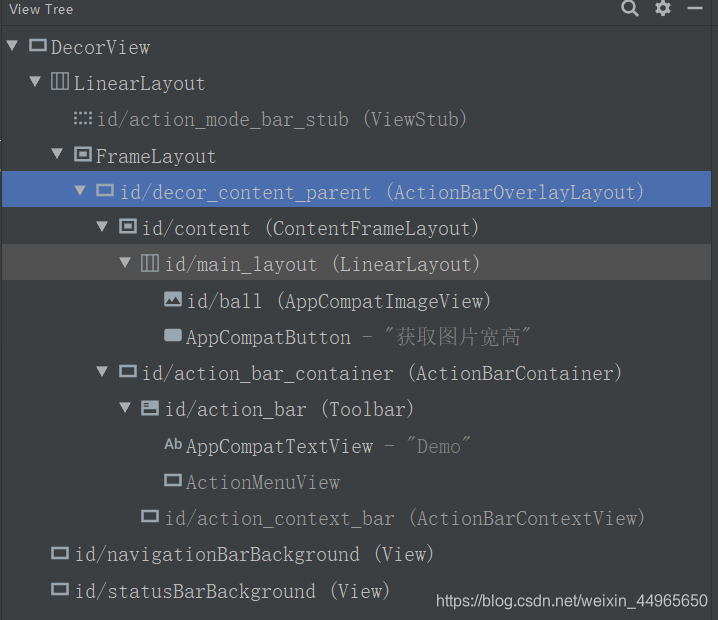
新建的工程AS会让MainActivity默认继承AppCompatActivity,这时候我们点击Tools -> Layout Inspector看一看它的视图层级结构:
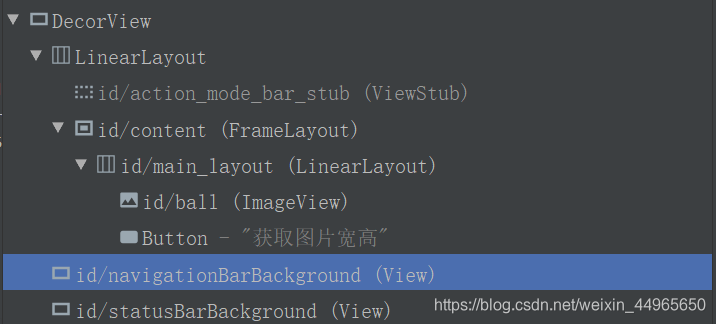
再让MainActivity继承Activity,打开Layout Inspector查看层级:
我们先从比较简单的Activity开始说起,在之前的文章中提过,在generateLayout方法中通过mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource)方法将一个系统布局加载到mDecor中,如果自己没修改主题样式的话加载的应该是R.layout.screen_simple这个布局,那我们就打开它看一看:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundInsidePadding="false"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</LinearLayout>
最外层是一个LinearLayout,里面有一个ViewStub和一个id为content的FrameLayout,这正好和Layout Inspector里面看到的层级是一样的,我们自己编写的布局被添加到了id为content的FrameLayout中。
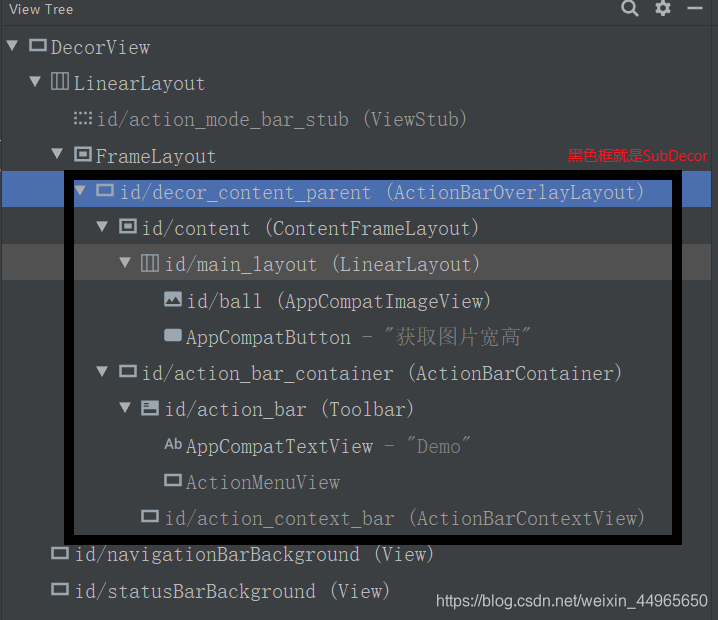
接下来再说AppCompatActivity,之前已经说过了,AppCompatActivity就是在mContentParent中又多了一层SubDecor,我们自己编写的布局就加载到了SubDecor中id为R.id.action_bar_activity_content的ContentFrameLayout中(后来id被改成content了),下图看的更明白一些:
可以看到,SubDecor上面的FrameLayout的id已经被清空了,现在id为content的是SubDecor中的ContentFrameLayout。
如果我们没有做什么修改的话,系统为SubDecor加载的布局应该是R.layout.abc_screen_toolbar.xml,打开这个布局看一下:
<android.support.v7.widget.ActionBarOverlayLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/decor_content_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<include layout="@layout/abc_screen_content_include"/>
<android.support.v7.widget.ActionBarContainer
android:id="@+id/action_bar_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
style="?attr/actionBarStyle"
android:touchscreenBlocksFocus="true"
android:gravity="top">
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/action_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:navigationContentDescription="@string/abc_action_bar_up_description"
style="?attr/toolbarStyle"/>
<android.support.v7.widget.ActionBarContextView
android:id="@+id/action_context_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="gone"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme"
style="?attr/actionModeStyle"/>
</android.support.v7.widget.ActionBarContainer>
</android.support.v7.widget.ActionBarOverlayLayout>
可以看到,里面的ActionBarOverlayLayout、ActionBarContainer、Toolbar、ActionBarContextView都跟Layout Inspector中对应上了,唯独ContentFrameLayout没有找到。这时候我们可以猜到,它是被包含到里面的,点开它:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<android.support.v7.widget.ContentFrameLayout
android:id="@id/action_bar_activity_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</merge>
在这个文件里找到了ContentFrameLayout,它就是加载我们编写布局的地方。