本文参考 二叉搜索树 - LeetBook - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
二叉搜索树(BST)
二叉搜索树是二叉树的一种特殊形式,满足:
- 每个节点中的值必须大于或等于储存在其左侧子树的任何值。
- 每个节点中的值必须小于或等于储存在其右侧子树的任何值。
题目1:验证二叉搜索树
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
- 节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树
方法1:递归
- 如果当前节点为空(即
node == null),则返回true,因为空树是有效的 BST。 - 如果当前节点的值小于等于
lower或大于等于upper,则返回false,因为违反了二叉搜索树的条件。 - 对于左子树和右子树的检查:
- 对左子树的递归调用时,设置上界为当前节点的值(因为左子树的所有节点值都必须小于当前节点的值)。
- 对右子树的递归调用时,设置下界为当前节点的值(因为右子树的所有节点值都必须大于当前节点的值)。
- 最终结果是:当前节点以及其左右子树都满足二叉搜索树的条件时返回
true,否则返回false。
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root){
return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode node, long lower, long upper){
if(node == null){
return true;
}
if(node.val <= lower || node.val >= upper){
return false;
}
return isValidBST(node.left, lower, node.val) && isValidBST(node.right, node.val, upper);
}
}
- 时间复杂度为
O(n),其中n是树中节点的数量,因为每个节点都被访问一次。 - 空间复杂度为
O(h),其中h是树的高度,代表递归栈的深度。故最坏情况下空间复杂度为 O(n)
方法2:中序遍历
中序遍历的时候实时检查当前节点的值是否大于前一个中序遍历到的节点的值即可。
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root){
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
double inorder = - Double.MAX_VALUE;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
while (root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if(root.val <= inorder){
return false;
}
inorder = root.val; // 中序遍历
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。二叉树的每个节点最多被访问一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。栈最多存储 n 个节点,因此需要额外的 O(n) 的空间。
二叉搜索树的基本操作
搜索
方法1:中序遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val){
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode node = null;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
while (root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if(root.val == val){
node = root;
break;
}
root = root.right;
}
return node;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。二叉树的每个节点最多被访问一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。栈最多存储 n 个节点,因此需要额外的 O(n) 的空间。
方法2:递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (val == root.val) {
return root;
}
return searchBST(val < root.val ? root.left : root.right, val);
}
}
方法3:迭代
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
while (root != null) {
if (val == root.val) {
return root;
}
root = val < root.val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return null;
}
}
插入
与搜索相似
方法1:迭代
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return new TreeNode(val);
}
TreeNode pos = root; // 记录根节点
while(pos != null){
if(val < pos.val){
if(pos.left == null){
pos.left = new TreeNode(val); // 如果为空,则新建
break;
}else {
pos = pos.left; // 如果不为空,继续迭代,直到空为止
}
}else {
if(pos.right == null){
pos.right = new TreeNode(val);
break;
}else {
pos = pos.right;
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
删除
方法1:递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.val > val){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, val); // 交到下一层进行递归
return root; // 该层的递归完成,不执行删除操作
}
if(root.val < val){
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, val);
return root;
}
if(root.val == val){ // 找到目标节点,在该层递归执行删除操作
// 目标节点没有子节点
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return null; // 上层执行类似 root.left = null 的删除操作
}
// 目标节点只有一个子节点
if(root.right == null){
return root.left; // 上层执行类似 root.left = root.left.left 的删除操作
}
if(root.left == null){
return root.right;
}
// 否则目标节点有两个子节点
TreeNode successor = root.right;
while (successor.left != null){
successor = successor.left; // 找到右子树中最小值节点
}
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, successor.val); // 删除(断开)右子树中最小值节点
successor.right = root.right; // 右子树的最小值节点替代目标节点
successor.left = root.left;
return successor; //实现替代功能,目标节点被遗忘
}
return root;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为 root 的节点个数。最差情况下,寻找和删除 successor 各需要遍历一次树。
-
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为 root 的节点个数。递归的深度最深为 O(n)。
方法2:迭代
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode cur = root, curParent = null; // 初始化当前节点 cur 和其父节点 curParent
// 在二叉搜索树中查找要删除的节点
while (cur != null && cur.val != key) {
curParent = cur; // 更新父节点
if (cur.val > key) {
cur = cur.left; // 如果当前节点的值大于 key,搜索左子树
} else {
cur = cur.right; // 如果当前节点的值小于 key,搜索右子树
}
}
// 如果没有找到要删除的节点,直接返回根节点
if (cur == null) {
return root;
}
// 情况 1:删除的节点没有左子树和右子树(即叶子节点)
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {
cur = null; // 删除当前节点
}
// 情况 2:删除的节点只有右子树
else if (cur.right == null) {
cur = cur.left; // 让父节点指向当前节点的左子树
}
// 情况 3:删除的节点只有左子树
else if (cur.left == null) {
cur = cur.right; // 让父节点指向当前节点的右子树
}
// 情况 4:删除的节点既有左子树也有右子树
else {
// 找到当前节点的右子树中的最小节点(即中序后继节点)
TreeNode successor = cur.right, successorParent = cur;
// 一直向左寻找右子树中的最小节点
while (successor.left != null) {
successorParent = successor;
successor = successor.left;
}
// 如果后继节点的父节点是当前节点,则直接将后继节点的右子树接到父节点的右子树
if (successorParent.val == cur.val) {
successorParent.right = successor.right;
} else {
// 否则,将后继节点的右子树接到后继父节点的左子树
successorParent.left = successor.right;
}
// 将后继节点的左子树和右子树接到当前节点
successor.right = cur.right;
successor.left = cur.left;
cur = successor; // 使当前节点成为后继节点
}
// 如果当前节点是根节点,则返回新的根节点
if (curParent == null) {
return cur;
} else {
// 否则更新父节点的子节点指向删除后的节点(cur)
if (curParent.left != null && curParent.left.val == key) {
curParent.left = cur;
} else {
curParent.right = cur;
}
return root; // 返回原树的根节点
}
}
}
- 时间复杂度为
O(h),其中h是树的高度,因为最坏情况下需要遍历整棵树。 - 空间复杂度为
O(1),因为没有使用额外的空间,所有操作都在原地进行。
小结
二叉搜索树适合有序地储存数据或者需要同时执行搜索、插入、删除等操作。
什么是优先队列
优先队列(PriorityQueue) 是一种数据结构,具有以下特点:
- 元素优先级:在优先队列中,每个元素都有一个优先级。元素被出队的顺序是由其优先级决定的,而不是它们进入队列的顺序。
- 出队顺序:优先队列按照优先级顺序处理元素,通常优先级高的元素会先被出队。具体的优先级规则可能依赖于队列的实现,通常会使用最小堆(Min-Heap)或最大堆(Max-Heap)来实现。
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class PriorityQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个默认的最小堆优先队列
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 向队列中插入元素
pq.offer(10);
pq.offer(20);
pq.offer(15);
pq.offer(30);
// 获取并移除队列中的元素(按照优先级顺序)
System.out.println("Polling elements from the priority queue:");
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(pq.poll()); // 按照升序输出:10, 15, 20, 30
}
// 创建一个自定义的最大堆优先队列
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a); // 降序排序
maxHeap.offer(10);
maxHeap.offer(20);
maxHeap.offer(15);
maxHeap.offer(30);
System.out.println("\nPolling elements from the max heap priority queue:");
while (!maxHeap.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(maxHeap.poll()); // 按照降序输出:30, 20, 15, 10
}
}
}
- 插入元素的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。
- 移除或查看优先级最高元素的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。
题目1:数据流中第k大元素
设计一个找到数据流中第 k 大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第 k 大元素,不是第 k 个不同的元素。
请实现 KthLargest 类:
KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) 使用整数 k 和整数流 nums 初始化对象。
int add(int val) 将 val 插入数据流 nums 后,返回当前数据流中第 k 大的元素。
方法1:优先队列
使用一个大小为k的优先队列存储前k大的元素。
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class KthLargest {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq;
int k;
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums){
this.k = k;
pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for(int x : nums){
add(x);
}
}
public int add(int val){
pq.offer(val);
if(pq.size() > k){
pq.poll();
}
return pq.peek();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
KthLargest kthLargest = new KthLargest(3, new int[]{4, 5, 8, 2});
System.out.println(kthLargest.add(3)); // 输出 4
System.out.println(kthLargest.add(5)); // 输出 5
System.out.println(kthLargest.add(10));// 输出 5
System.out.println(kthLargest.add(9)); // 输出 8
System.out.println(kthLargest.add(4)); // 输出 8
}
}
1、时间复杂度:
-
初始化时间复杂度为:O(nlogk) ,其中 n 为初始化时 nums 的长度;
-
单次插入时间复杂度为:O(logk)。
2、空间复杂度:O(k)。需要使用优先队列存储前 k 大的元素
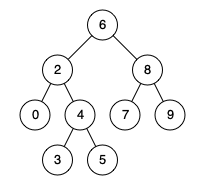
题目2:二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
方法1:一次遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
TreeNode ancestor = root;
while (true) {
if (p.val < ancestor.val && q.val < ancestor.val) {
ancestor = ancestor.left;
} else if (p.val > ancestor.val && q.val > ancestor.val) {
ancestor = ancestor.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
return ancestor;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是给定的二叉搜索树中的节点个数。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。