实验目的:
(1)掌握一维数组和二维数组的定义、初始化方法。
(2)了解和初步应用java.lang.Math类的random()方法处理实际问题。
(3)了解增强for循环,并使用增强for循环顺序访问数组元素。
(4)掌握String类中split方法、charAt方法以及length方法的使用。
(5)掌握Double、Integer等数据包装类的parseDouble、parseInt等方法。
(6)掌握数组的length属性的应用
实验内容:
(1)foreach循环
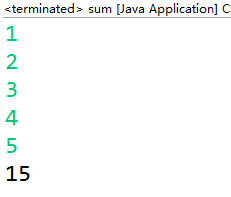
编写一个程序,使用命令行参数的方式从控制台读入一组整数,利用foreach循环对其进行求和并输出结果。
程序源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class sum {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Integer[] num = new Integer[5];
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
num[i]=input.nextInt();
int sum = 0;
//foreach循环
for(int i:num)
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
程序运行结果贴图
(2)分别用一维数组(例子数组如下 { 7, 4, 3, 9, 0, 6 })实现冒泡排序、选择排序和插入排序中的两种排序算法,程序中要求加注释。
程序代码:
运行结果贴图:
(3)编写程序实现两个矩阵的相加、相乘。
要求程序运行结果形如如下显示:
Array c
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Array d
2 2 2
1 1 1
3 3 3
Array c+d
3 4 5
5 6 7
10 11 12
Array c*d
13 13 13
31 31 31
49 49 49
程序代码:
运行结果贴图:
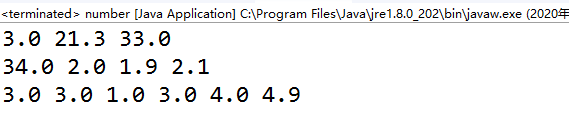
(4)将用“;”和“,”分割的包含数字字符的字符串“23, 21.3, 33;34, 2, 1.9, 2.1;3, 3, 1, 3, 4, 4.9”中的数据解析出来放在一个double类型的二维数组中,以分号分割二维数组的每一行,以逗号分割每行中的各个元素。(利用String 的split方法)
程序代码:
public class number {
public static void main (String args[]){
String[]str = ("3, 21.3, 33; 34, 2, 1.9, 2.1; "
+ "3, 3, 1, 3, 4, 4.9").split(";");//将每一行分开
double [][]num = new double[str.length][]; //建立最终的储存数组
for(int i = 0;i < str.length;i++)
{
String []temp = str[i].split(","); //在某行中数字按","分开
num[i] = new double[temp.length];
for(int j = 0;j < temp.length;j++)
num[i][j] = Double.parseDouble(temp[j]); //转换为double数组
}
for(int i = 0;i < num.length;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < num[i].length;j++)
{
System.out.print(num[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果贴图:
(5)查看帮助、编写例子
利用System类中的arraycopy()方法复制数组。
分别用Arrays类中的sort方法和binarySearch方法实现数组的排序和折半查找。
程序代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class text5 {
public static void main (String args[]){
int []a = {1,6,8,4,2,13,5,7,9,10};
//输出原数组
for(int i = 0;i < a.length;i++)
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
//复制数组并输出
int[] a1 = new int[a.length];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, a1, 0, a.length);
System.out.println("\n复制之后的数组:");
for(int i = 0;i < a1.length;i++)
System.out.print(a1[i]+" ");
//对数组排序
Arrays.sort(a1);
System.out.println("\n排序之后的数组:");
for(int i = 0;i < a1.length;i++)
System.out.print(a1[i]+" ");
}
}
运行结果贴图:
(6)随机生成100个小写字母,统计每个字母出现的次数,并显示出来。
(利用Math.random()方法随机产生)
程序代码:
public class test3_6 {
public static void main(String []args){
char []s = new char[100];
char a = 'a';
//随机产生小写字母
for(int i = 0;i < 100;i++){
s[i] = (char)( 'a' + Math.floor(Math.random()*('z'-'a'+1)) );
}
int []num = new int[26];
//统计字母个数
for(int i =0;i < 99;i++)
num[s[i]-a] = num[s[i]-a] + 1;
for(int i =0;i < 99;i++){
System.out.print((char)(a+i) + " : " + num[i] + " ");
if(i%5==0)
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果贴图:
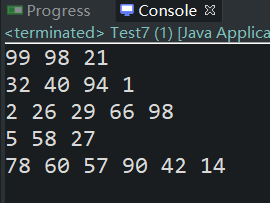
(7)建立一个不规则的二维数组如下,并在控制台显示,数组如下
1 3 5
2 4 6 8
1 9 16 25 36
10 20 30
1 2 3 4 5 6
程序代码:
public class Test7{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = new int[5][];
a[0] = new int[3];
a[1] = new int[4];
a[2] = new int[5];
a[3] = new int[3];
a[4] = new int[6];
//赋值
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
a[i][j] = (int)(Math.random()*100+1);
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果贴图:
(8)编写两个重载的方法分别交换两个整型变量,和整型数组的第一个和第二个元素,运行并分析结果
程序代码:
class Num {
int number;
public Num(int number){
this.number=number;
}
}
public class test3_8 {
public static void main(String []args){
Num a = new Num(1);
Num b = new Num(2);
int []c = {3,4};
System.out.println("交换前:");
System.out.println("a=" + a.number + " " + "b=" + b.number);
System.out.println("c[0]=" + c[0] + " " + "c[1]=" + c[1]);
swap(a,b);
swap(c);
System.out.println("交换后:");
System.out.println("a=" + a.number + " " + "b=" + b.number);
System.out.println("c[0]=" + c[0] + " " + "c[1]=" + c[1]);
}
public static void swap(Num a,Num b){
int temp = a.number;
a.number = b.number;
b.number = temp;
}
public static void swap(int []c){
int t;
t = c[0];
c[0] = c[1];
c[1] = t;
}
}
运行结果贴图: