HTML5+CSS3笔记
一、HTML5
1 简述
HTML用于描述页面的结构(骨头,看不见)
CSS用于控制页面中元素的样式(皮肤,外在表现)
JavaScript用于响应用户操作(动起来)
HTML:超文本标记语言,使用标签的形式来标识网页中的不同组成部分。
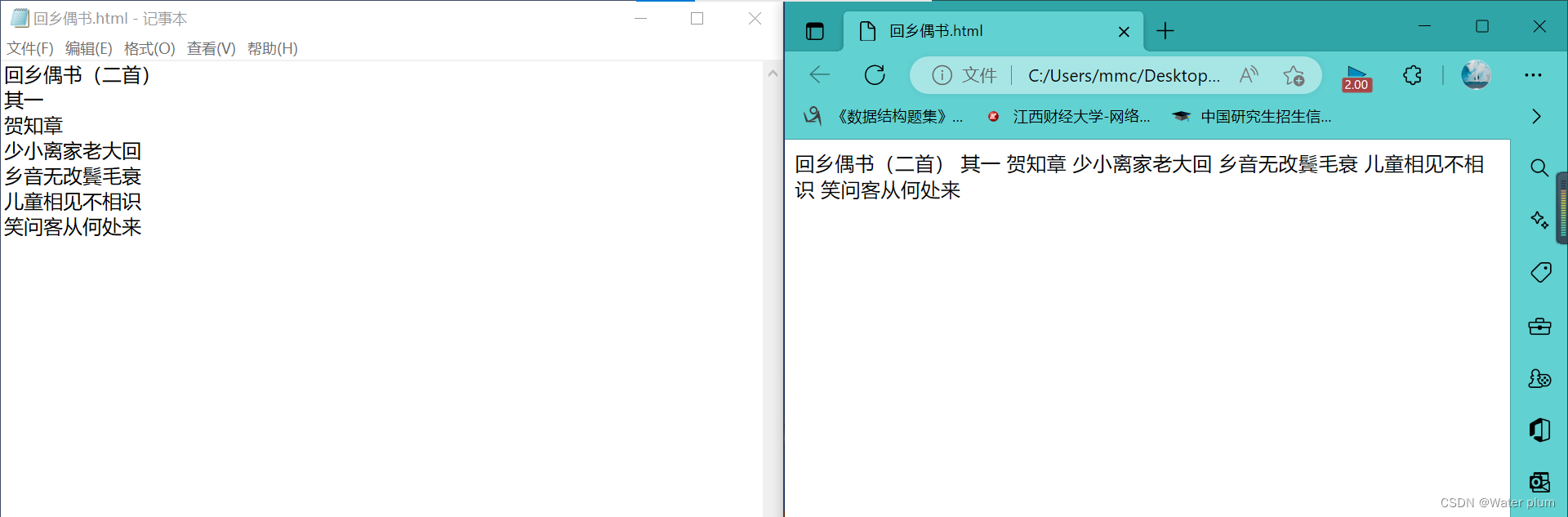
超文本:指超链接,可以让我们从一个页面跳转到另一个页面。(纯文本编辑器写的就是纯文本,比如记事本。而word里面写的是富文本)
自行操作:打开记事本(建议不要新建),开始-菜单-notepad-回车-写-ctrl+s保存为xxx.html)
左边是文本,右边是浏览器渲染出来的效果。
如果要修改网页内容,可以右键该html文件,选择用记事本打开,或者直接将html文件拖至记事本编辑页面中。
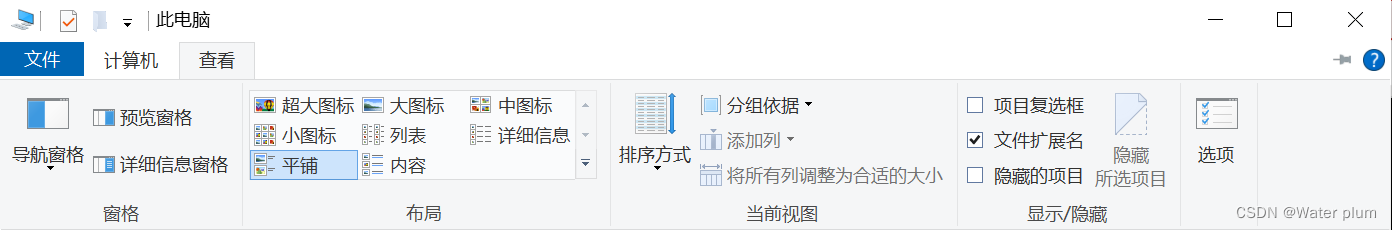
关于文件后缀名显示问题(查看->勾选文件扩展名)
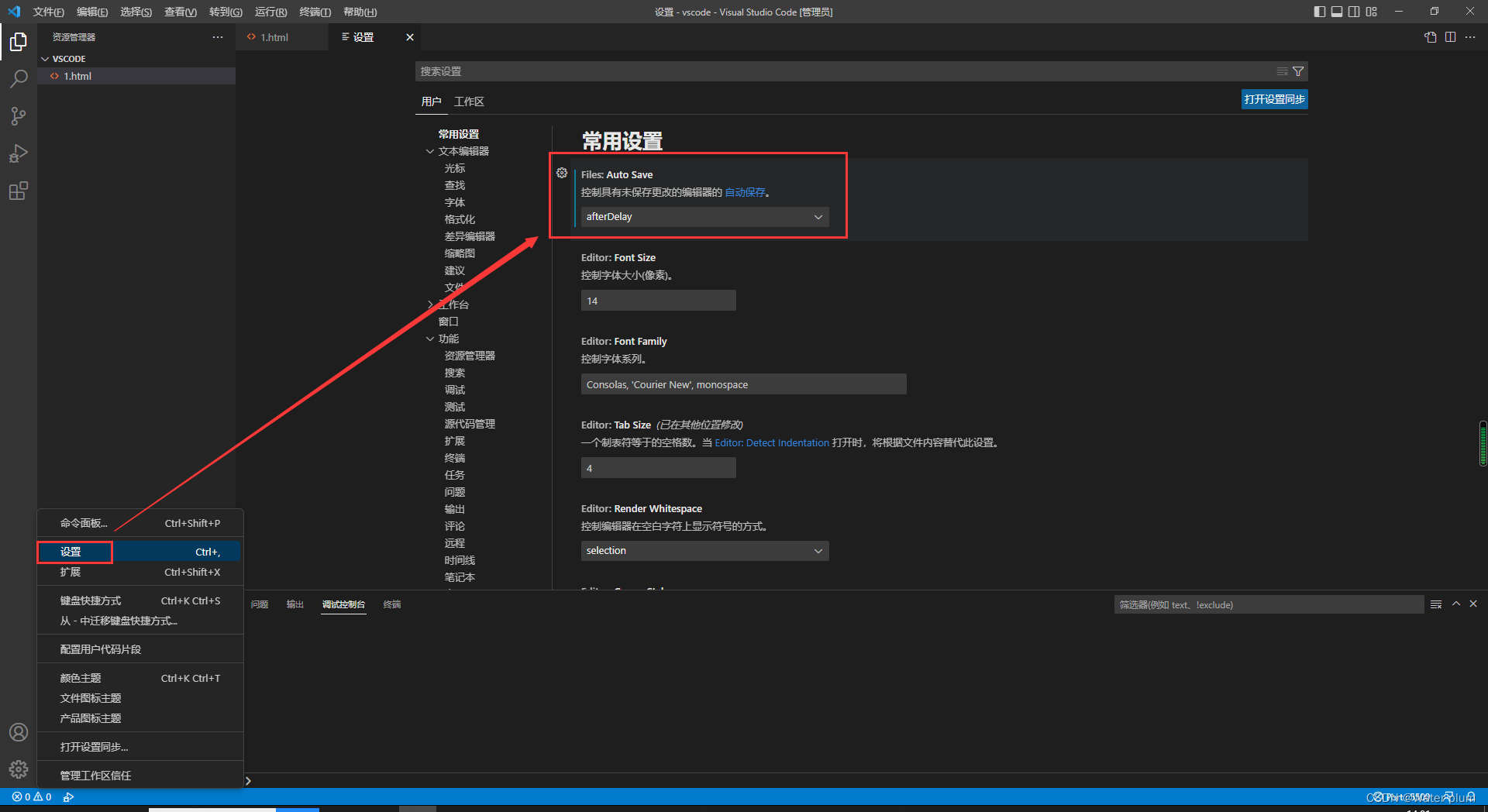
1.1 VSCode快捷键
!+回车:快速生成完整网页结构;
ctrl+/:自动生成注释;
ctrl+回车:光标下移;
Shift+Alt+⬇:向下复制;
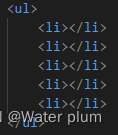
快速生成标签
·1.ul>li 再回车
2.ul+ul 再回车
3.ul>li*5再回车
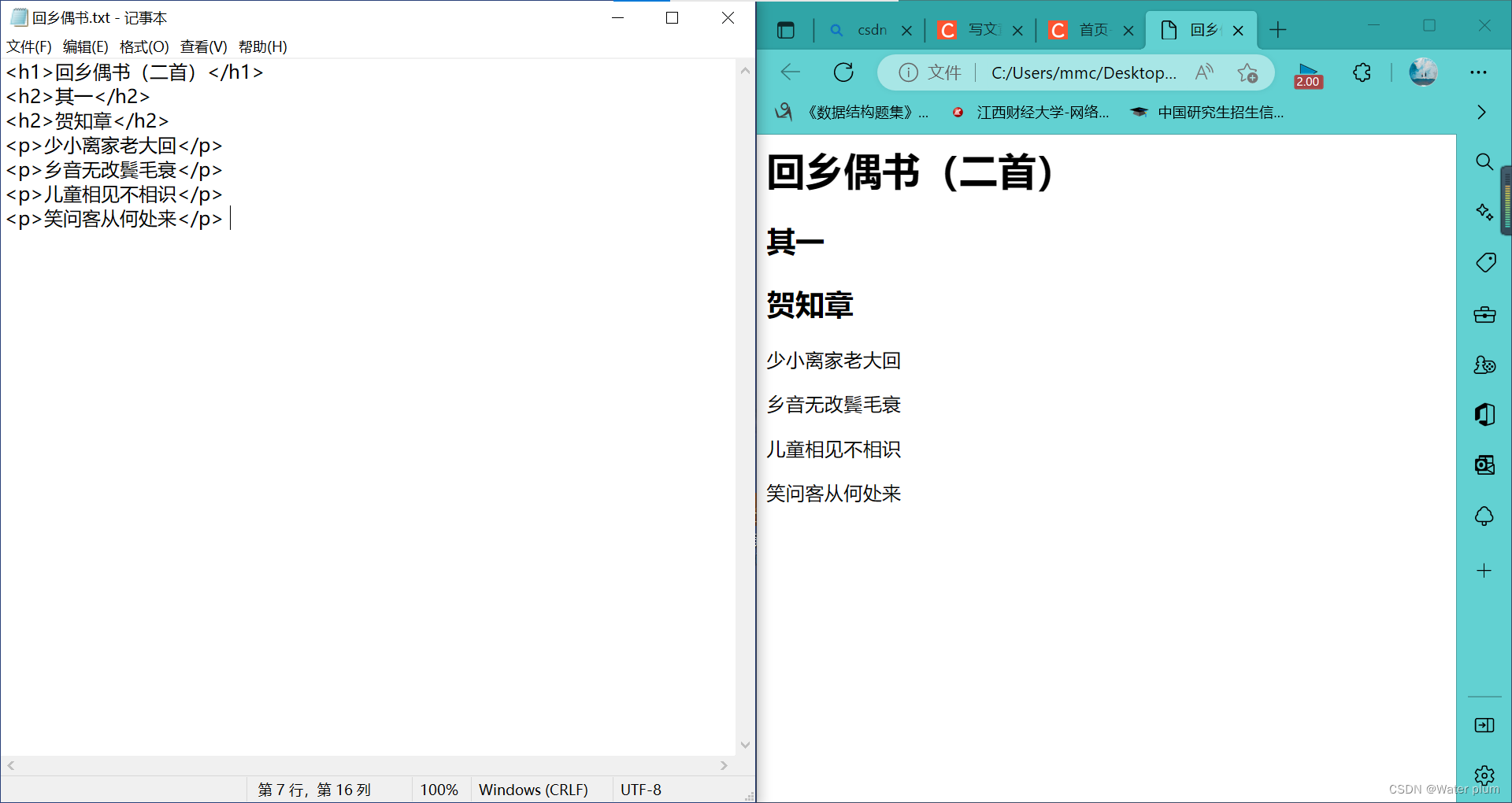
1.2 编写你的第一个网页
标记就是用来表示网页中不同内容,告诉浏览器是什么东西。
html是根标签,网页中有且只有一个,其他所有网页内容写在html标签中,html中有两个子标签,为head标签和body标签
head子标签为title
head中的内容不会出现在网页中
title中的内容出现在标题栏
1.3 自结束标签和注释
标签一般成对出现,但是也存在一些自结束标签可以这样写
<img>或 <img><img/>
<input>或<input><input/>,一般第一个
<!--
HTML的注释:注释中的内容会被浏览器所忽略,不会在网页中直接显示
但是可以在源码中查看注释,注释是用来对代码进行解释说明的,
开发中一定要养成良好的编写注释的习惯,注释要求简单明了
注释还可以将一些不希望显示的内容隐藏
注释不能嵌套
-->
1.4 标签中的属性
属性:在标签中(开始标签或自结束标签)还可以设置属性
属性是一个名值对(x=y)结构
属性用来设置标签中的内容如何显示
属性和标签名或其他属性应该使用空格隔开
属性不能瞎写,应该根据文档中的规定来编写,有些属性有属性值,有些没有
如果有属性值,属性值应该使用引号引起来
<h1>这是我的<font color="red" size='3'>第三个</font>网页!</h1>
1.5 文档声明和进制以及字符编码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- 可以通过meta标签来设置网页的字符集,避免乱码问题 -->
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>网页的基本结构</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
迭代
网页的版本
HTML4
HTML2.0
HTML5
…
文档声明(doctype)
-文档声明用来告诉浏览器当前网页的版本
-htm5的文档声明
<!doctype html>
<!Doctype HTML>
不区分大小写
进制:
十进制(日常使用)
-特点:满10进1
-计数:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
-单位数字:10个(0-9)
二进制(计算机底层的进制)
-特点:满2进1
-计数:0 1 10 11 100 101 110 111
-单位数字:2个(0-1)
-扩展:
-所有数据在计算机底层都会以二进制的形式保存
-可以将内存想象为一个有多个小格子组成的容器,每一个小格子中可以存储一个1或一个0
这一个小格子在内存中被称为1位(bit)
8bit=1byte(字节)字节是最小操作单位
1024byte=1kb(千字节)
1024kb=1mb(兆字节)
1024mb=1gb(吉字节)
1024gb=1tb(特字节)
1024tb=1pb
八进制(很少用)
-特点:满8进1
-计数:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10 11 12
-单位数字:8个(0-7)
十六进制(一般显示一个二进制数字时,都会转换为十六进制)
-特点:满16进1
-计数:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 10 11 …… 1A 1B
-单位数字:16个(0-F)
字符编码
中国->110001110111(编码)
110001110111->中国(解码)
-所有的数据在计算机中存储时都是以二进制形式存储的,文字也不例外,
所以一段文字在存储到内存时,都需要转换为二进制编码
当我们读取这段文字时,计算机会将编码转换为字符,供我们阅读
-编码
-将字符转换为二进制编码的过程称为编码
-解码
-将二进制码转换为字符的过程的称为解码
-字符集(charset)
-编码和解码所采用的规则称为字符集
-乱码问题
-如果编码和解码所采用的字符集不同就会出现乱码问题
-常见的字符集:
ASCII
ISO88591
GB2312
GBK
UTF-8(万国码,在开发时我们使用的字符集都是UTF-8)
-->
</body>
</html>
1.6 文档的使用
<!-- 文档声明,声明当前网页的版本 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!-- html的根标签(元素),网页中的所有内容都要写在根元素的里边 -->
<html lang="en">
<!-- head是网页的头部,head中内容不会在网页中直接出现,主要用来帮助浏览器或搜索引擎来解析网页 -->
<head>
<!-- meta标签用来设置网页的元数据,这里meta用来设置网页的字符集,避免乱码问题 -->
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- title中的内容会显示在浏览器的标题栏,搜索引擎会主要根据title中的内容来判断网页的主要内容 -->
<title>网页的标题</title>
</head>
<!-- body时html的子元素,表示网页的主体,网页中所有的可见内容都应该写在body里 -->
<body>
<!-- h1网页的一级标题 -->
<h1>网页的大标题</h1>
</body>
</html>
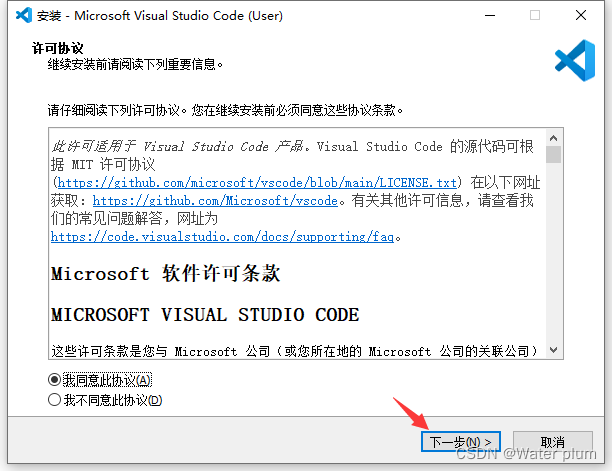
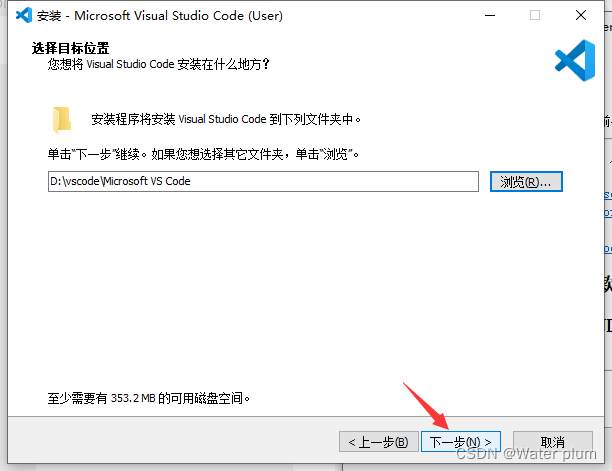
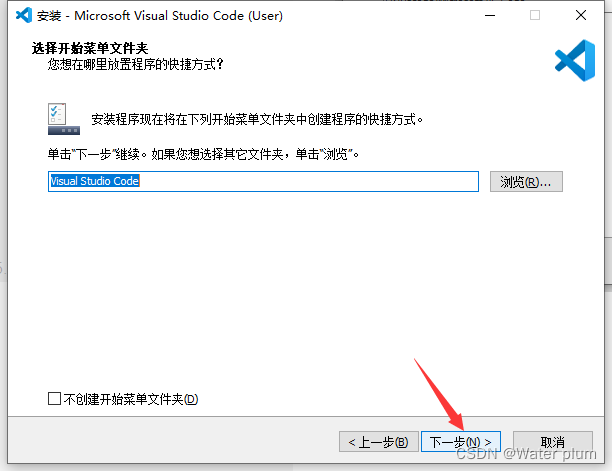
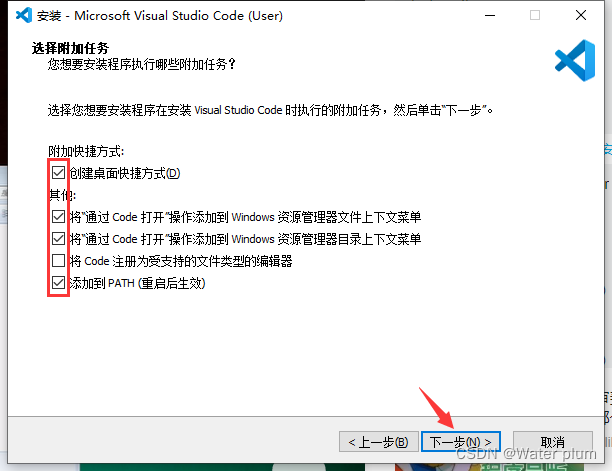
1.7 VScode安装教程并配置Live Server
安装地址:https://code.visualstudio.com/Download
电脑是哪个版本就选择哪个版本
安装完成!
相关插件安装:
中文插件:
主题插件:
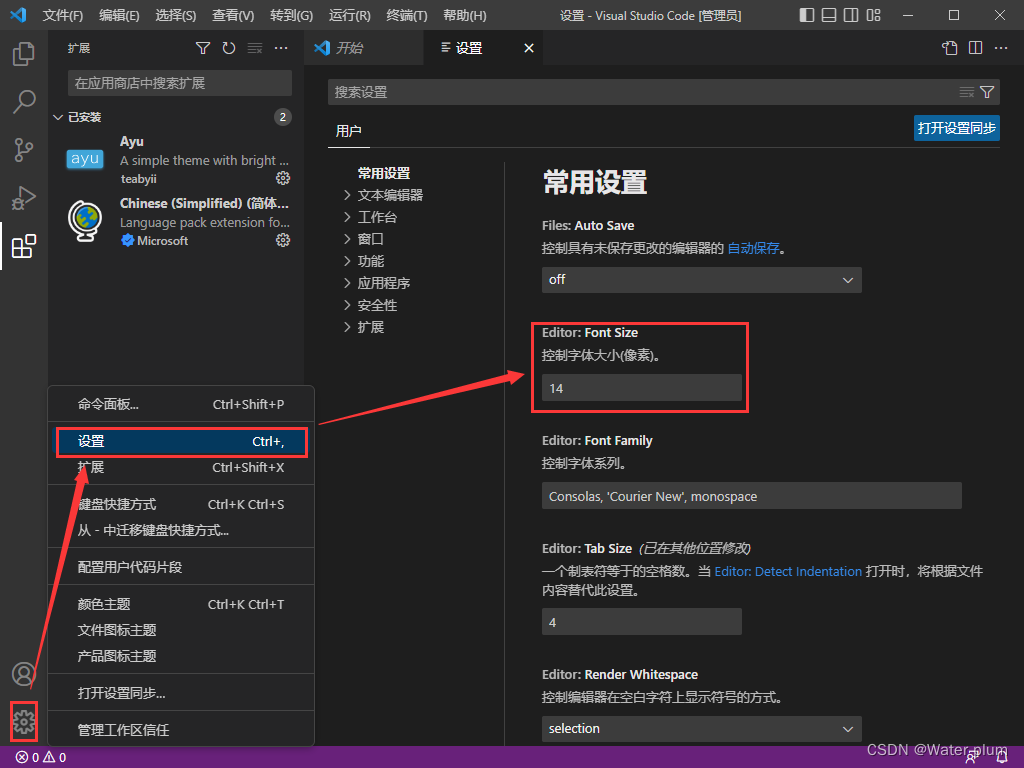
界面字体修改:
lan="en"表示网页是用英文写的,是英文网页,运行会出现下面界面。
“zh”表示中文网页
自动保存:
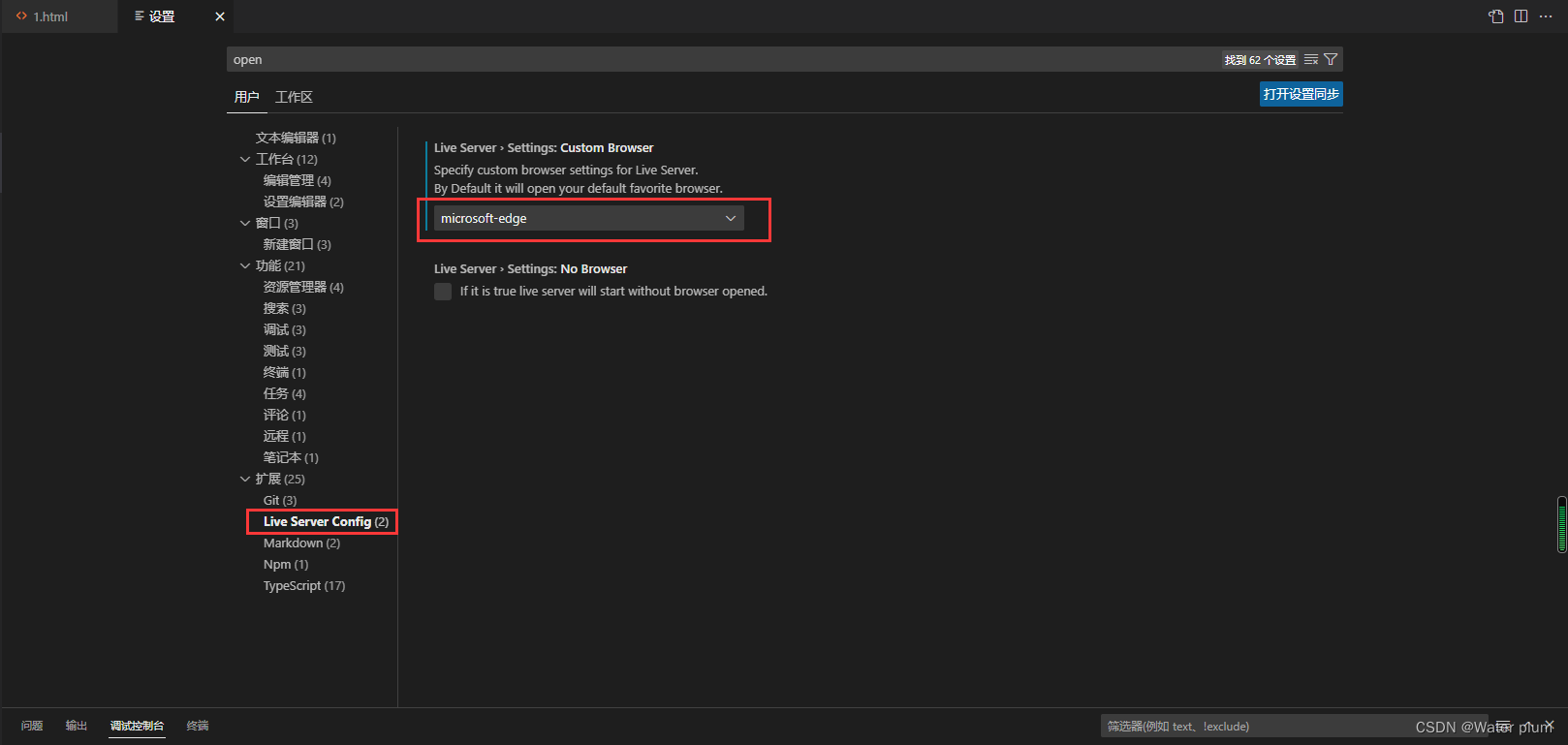
配置Live Server设置默认浏览器
安装插件
设置默认浏览器
2 实体
实体查找网站:https://www.w3school.com.cn/html/html_entities.asp
<!--
在网页中编写的多个空格默认情况会自动被浏览器解析为一个空格
在HTML中有些时候,我们不能直接书写一些特殊符号
比如,多个连续的空格,比如字母两侧的大于和小于号
如果我们需要在网页中书写这些特殊的符号,则需要使用html中的实体(转义字符)
实体的语法:
&实体的名字;
 ;空格
>;大于号
<;小于号
©;版权符号
-->
示例:
<p>
今天 天气真不错!
</p>
<p>
a<b>c
</p>
3 meta标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!--
meta主要用于设置网页中的一些元数据,元数据不是给用户看
charset 指定网页的字符集
name 指定数据的名称
content 指定数据的内容
keywords 表示网站的关键字(搜购物搜到京东),可以同时指定多个关键字,多个关键字间使用,隔开
<meta name="Keywords" content="网上购物,网上商城,家电,手机,电脑,服装,居家,母婴,美妆,个护,食品,生鲜,京东"/>
descritpion 用于指定网站的描述,网站的描述会显示在搜索引擎的搜索结果中
<meta name="description" content="京东JD.COM-专业的综合网上购物商城,为您提供正品低价的购物选择、优质便捷的服务体验。商品来自全球数十万品牌商家,囊括家电、手机、电脑、服装、居家、母婴、美妆、个护、食品、生鲜等丰富品类,满足各种购物需求。"/>
title标签的内容会作为搜索结果的超链接上的文字显示
-->
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML5,前端,CSS3">
<meta name="description" content="这是一个非常不错的网站">
<!--
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="3;url=https://www.mozilla.org">
将页面重定向到另一个网站;3s
-->
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="3;url=https://www.baidu.com">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
4 语义化标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
块元素(block element)
- 在网页中一般通过块元素来对页面进行布局
行内元素(inline element)
- 行内元素主要用来包裹文字
- 一般情况下会在块元素中放行内元素,而不会在行内元素中放块元素
- 块元素中基本上什么都能放
- p元素中不能放任何的块元素
浏览器在解析网页时,会自动对网页中不符合规范的内容进行修正
比如:
标签写在了根元素的外部
p元素中嵌套了块元素
根元素中出现了除head和body以外的子元素
……
-->
<p>
<h1>哈哈</h1>
</p>
</body>
</html>
<h1>我就要写在html标签的外部!</h1>
输出
开发者工具使用:
右键—检查
Element:查看网页源码,即网页在内存中的结构
5 结构化语义标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
布局标签(结构化语义标签)
-->
<!--
header 表示网页的头部
main 表示网页的主体部分(一个页面中只会有一个main)
footer 表示网页的底部
nav 表示网页中的导航
aside 表示和主题相关的其他内容(其他内容)
article 表示一个独立的文章
section 表示一个独立的区块,上边的标签都不能表示时使用section
div没有语义,就用来表示一个区块,目前来讲div还是我们主要的布局元素
span 行内元素,没有任何的予以,一般用于在网页中选中文字
-->
<header></header>
<main></main>
<footer></footer>
<nav></nav>
<aside></aside>
<article></article>
<section></section>
<span></span>
</body>
</html>
6 列表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
列表(list)
1、铅笔
2、尺子
3、橡皮
在html中也可以创建列表,html列表一共有三种:
1、有序列表
2、无序列表
3、定义列表
有序列表,使用ol标签来创建无序列表
使用li表示列表项
无序列表,使用ul标签来创建有序列表
使用li表示列表项
定义列表,使用dl标签来创建一个定义列表
使用dt来表示定义的内容
使用dd来对内容进行解释说明
列表之间可以互相嵌套
-->
<ol>
<li>结构</li>
<li>表现</li>
<li>行为</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>结构</li>
<li>表现</li>
<li>行为</li>
</ul>
<dl>
<dt>结构</dt>
<dd>结构表示网页的结构,结构用来规定网页中哪里是标题,哪里是段落</dd>
</dl>
<ul>
<li>
aa
<ul>
<li>aa-1</li>
<li>aa-2
<ul>
<li>aa-1</li>
<li>aa-2</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
输出
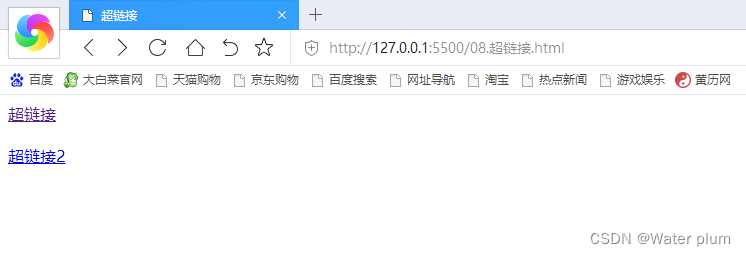
7 超链接
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>超链接</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
超链接可以让我们从一个页面跳转到其他页面
或是当前页面的其他位置
使用 a 标签来定义超链接
属性:
href 指定跳转的目标路径
- 值可以是一个外部网站的地址
- 也可以是一个内部页面的地址
超链接也是一个行内元素,在a标签中可以嵌套除它自身外的任何元素
-->
<a href="https://www.baidu.com">超链接</a>
<br><br>
<!-- <a href="https://www.baidu123.com">超链接</a> -->
<a href="07.列表.html">超链接2</a>
</body>
</html>
输出:(访问过呈紫色,未访问过呈蓝色)
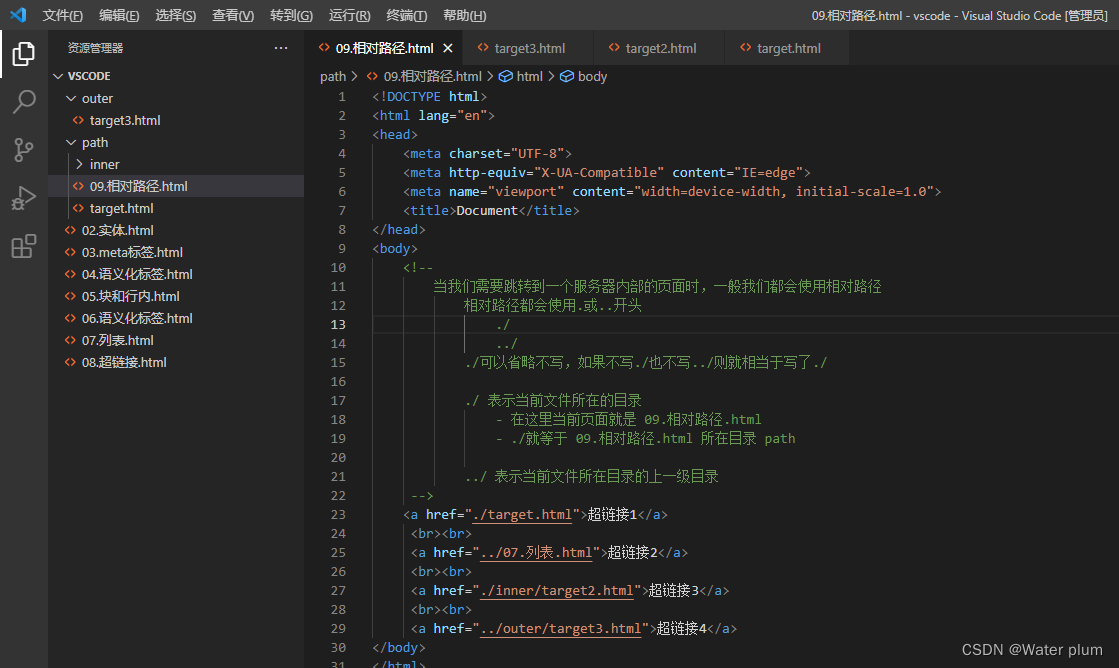
8 相对路径
9 超链接的其他用法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
target属性,用来指定超链接打开的位置
可选值:
_self 默认值 在当前页面中打开超链接
_blank 在一个新的页面中打开超链接
-->
<a href="07.列表.html" target="_blank">超链接</a>
<br><br>
<a href="#bottom">去底部</a>
<br><br>
<a href="#p3">去第三自然段</a>
<br><br>
<p>在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。</p>
<p>在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。</p>
<p id="p3">在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。</p>
<p>在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。</p>
<p>在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。</p>
<p>在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。</p>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Ipsum placeat quod iste commodi sint quam inventore architecto. Totam fugit maxime quos delectus vitae. Nobis blanditiis hic ipsam itaque saepe architecto?</p>
<!-- 在开发中可以将#作为超链接的路径的占位符使用 -->
<a href="#">这是一个新的超链接</a>
<br><br>
<!-- 可以使用 javascript:; 来作为href的属性,此时点击这个超链接什么也不会发生 -->
<a href="JavaScript:;">这是一个新的超链接</a>
<br><br>
<!--
可以直接将超链接的href属性设置为#,这样点击超链接以后
页面不会发生跳转,而是转到当前页面的顶部的位置
可以跳转到页面的指定位置,只需将href属性设置 #目标元素的id属性值
id属性(唯一不重复的)
- 每一个标签都可以添加一个id属性
- id属性就是元素的唯一标识,同一个页面中不能出现重复的id属性
-->
<a id="bottom" href="#">回到顶部</a>
</body>
</html>
10 图片标签及格式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
图片标签用于向当前页面中引入一个外部图片
使用img标签来引入外部图片,img标签是一个自结束标签
img这种元素属于替换元素(基于块和行内元素之间,具有两种元素的特点)
属性:
src 属性指定的是外部图片的路径(路径规则和超链接是一样的)
alt 图片的描述,这个描述默认情况下不会显示,有些浏览器会在图片无法加载时显示
搜索引擎会根据alt中的内容来识别图片,如果不写alt属性则图片不会被搜索引擎所收录
width 图片的宽度(单位是像素)
height 图片的高度
- 宽度和高度中如果只修改了一个,则另一个会等比例缩放
注意:
一般情况在pc端,不建议修改图片的大小,需要多大的图片就裁多大
但是在移动端,经常需要对图片进行缩放(大图缩小)
图片的格式:
jpeg(jpg)
- 支持的颜色比较丰富,不支持透明效果,不支持动图
- 一般用来显示图片
gif
- 支持的颜色比较少,支持简单透明,支持动图
- 颜色单一的图片,动图
png
- 支持的颜色丰富,支持复杂透明,不支持动图
- 颜色丰富,复杂透明图片(专为网页而生)
webp
- 这种格式是谷歌新推出的专门用来表示网页中的图片的一种格式
- 它具备其他图片格式的所有优点,而且文件还特别的小
- 缺点:兼容性不好
base64
- 将图片使用base64进行编码,这样可以将图片转换为字符,通过字符的形式来引入图片
- 一般都是一些需要和网页一起加载的图片才会使用base64,可以加快访问速度
效果一样 用小的
效果不一样,用效果好的
-->
<img src="./img/1.jpg" alt="风景">
<img width="500"src="https://www.akailibrary.com/wp-content/themes/ripro/timthumb.php?src=https://www.akailibrary.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/036-stethoscope.jpg&h=270&w=480&zc=1&a=c&q=100&s=1" alt="图标">
</body>
</html>
base64转换网站:https://base64.us/
11 内联框架
<body>
<!--
内联框架,用于向当前页面中引入一个其他页面
内联框架中的信息不会被搜索引擎搜索
src 指定要引入的网页的路径
frameborder 指定内联框架的边框
-->
<iframe src="https://www.qq.com" width="800" height="600" frameborder="0"></iframe>
</body>
12 音视频播放
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
audio 标签用来向页面中引入一个外部的音频文件的
音视频文件引入时,默认情况下不允许用户自己控制播放停止
属性:
controls 是否允许用户控制播放
autoplay 音频文件是否自动播放
- 如果设置了autoplay 则音乐在打开页面时会自动播放
但是目前来讲大部分浏览器都不会自动对音乐进行播放
loop 音乐是否循环播放
-->
<!-- <audio src="./source/audio.mp3" controls autoplay loop></audio> -->
<!-- 除了通过src来指定外部文件的路径以外,还可以通过source来指定文件的路径 -->
<audio controls>
对不起,您的浏览器不支持播放音频!请升级浏览器!
<source src="./source/audio.mp3">
<source src="./source/audio.ogg">
<embed src="./source/audio.mp3" type="audio/mp3" width="200" height="50">
</audio>
<!--
使用video标签来向网页中引入一个视频
- 使用方式和audio基本上是一样的
-->
<video controls>
<source src="./source/flower.webm">
<source src="./source/flower.mp4">
<embed src="./source/flower.mp4" type="video/mp4" allowFullScreen="true" width="500" height="300">
</video>
</body>
</html>
二、CSS
1 CSS简介
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!--
第二种方式
- 将样式编写到head中的style标签里
然后通过CSS的选择器来选中元素并为其设置各种样式
可以同时为多个标签设置样式,并且修改时只需要修改一处即可全部应用
- 内部样式表更加方便对样式进行复用
我们的内部样式表只能对一个网页起作用
它里边的样式不能跨页面进行复用
-->
<!-- <style>
p{
color: green;
font-size: 50px;
}
</style> -->
<!--
第三种方式(外部样式表) 最佳实践
- 可以将CSS样式编写到一个外部的CSS文件中
然后通过link标签来引入外部的CSS文件
- 外部样式表需要通过link标签进行引入,
意味着只要想使用这些样式的网页都可以对其进行引用
使样式可以在不同页面之间进行复用
- 将样式编写到外部的CSS文件中,可以使用浏览器的缓存机制,
从而加快网页的加载速度,提高用户的体验
-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./style.css">
</head>
<body>
<!--
网页分成三个部分:
结构(HTML)
表现(CSS)
行为(JavaScript)
CSS
- 层叠样式表
- 网页实际上是一个多层的结构,通过CSS可以分别为网页的每一个层来设置样式
最终我们能看到只是网页的最上边一层
- 总之一句话,CSS用来设置网页中元素的样式
-->
<!--
使用CSS来修改元素的样式、
第一种方式(内联样式,行内样式):
- 在标签内部通过style属性来设置元素的样式
- 问题:
使用内联样式,样式只能对一个标签生效,
如果希望影响到多个元素必须在每一个元素中都复制一遍、
并且当样式发生变化时,我们必须要一个一个修改,非常不方便
- 注意,开发时绝对不要使用内联样式
-->
<!-- <p style="color: red; font-size: 30px;">少小离家老大回,乡音无改鬓毛衰</p> -->
<p>落霞与孤鹜齐飞,秋水共长天一色</p>
<p>少小离家老大回,乡音无改鬓毛衰</p>
</body>
</html>
2 CSS的基本语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*
CSS中的注释,注释中的内容会自动被浏览器所忽略
CSS的基本语法
选择器 声明块
选择器,通过选择器可以选中页面中的指定元素
比如 p 的作用就是选中页面中所有的p元素
声明块,通过声明块来指定要为元素设置的样式
声明块由一个一个的声明组成
声明是一个名值对结构
一个样式名对应一个样式值,名和值之间以 : 连接,以 ; 结尾
*/
p{
color: red;
font-size: 40px;
}
h1{
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>我是H1</h1>
<p>今天天气真不错!</p>
<p>今天天气真不错!</p>
<p>今天天气真不错!</p>
<p>今天天气真不错!</p>
<p>今天天气真不错!</p>
</body>
</html>
3 选择器
3.1 常用选择器
元素选择器、id选择器、类选择器、通配选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*
将所有的段落设置为红色(字体)
元素选择器
作用:根据标签名来选中指定的元素
语法:标签名()
例子:p{} h1{} div{}
*/
/* p{
color: red;
}
h1{
color: green;
} */
/*
将儿童相见不相识设置为红色
id选择器
作用:根据元素的id属性值选中一个元素
语法:#id属性值{}
例子:#box{} #red{}
*/
/* #red{
color: red;
} */
/*
将 秋水…… 和 落霞…… 设置为蓝色
类选择器
作用:根据元素的class属性值选中一组元素
语法:.class属性值
*/
/* .blue{
color: blue;
}
.abc{
font-size: 20px;
} */
/*
通配选择器
作用:选中页面中的所有元素
语法:*
*/
*{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="blue abc">我是标题</h1>
<p>少小离家老大回</p>
<p>乡音无改鬓毛衰</p>
<p id="red">儿童相见不相识</p>
<p>笑问客从何处来</p>
<!--
class是一个标签的属性,它和id类似,不同的是class可以重复使用
可以通过class属性来为元素分组
可以同时为一个元素指定多个class属性
-->
<p class="blue">落霞与孤鹜齐飞</p>
<p class="blue">秋水共长天一色</p>
</body>
</html>
3.2 复合选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 将class为red的元素设置为红色(字体) */
.red{
color: red;
}
/* 将class为red的div字体大小设置为30px */
/*
交集选择器
作用:选中同时符合多个条件的元素
语法:选择器1选择器2选择器3选择器n{}
注意点:
交集选择器中如果有元素选择器,必须使用元素选择器开头
*/
div.red{
font-size: 30px;
}
.a.b.c{
color: blue;
}
/* div#box1{} 语法没有问题,但是不建议这样写,#box1就唯一指定了 */
/*
选择器分组(并集选择器)
作用:同时选择多个选择器对应的元素
语法:选择器1,选择器2,选择器3,选择器n{}
#b1,.p1,h1,span,div.red{}
*/
/* h1{
color: green;
}
span{
color: green;
} */
/* 上面两个元素选择器可以改为下面这种 */
h1,span{
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="red">我是div</div>
<p class="red">我是p元素</p>
<div class="red2 a b c">我是div2</div>
<h1>标题</h1>
<span>哈哈</span>
</body>
</html>
3.3 关系选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*
为div的子元素span设置一个字体颜色红色
(为div直接包含的span设置一个字体颜色)
子元素选择器
作用:选中指定父元素的指定子元素
语法:父元素 > 子元素
*/
/* div.box > span{
color: orange;
} */
/*
后代元素选择器
作用:选中指定元素内的指定后代元素
语法:祖先 后代
*/
/* div span{
color: skyblue;
} */
/* 选中孙子 */
/* div>p>span{
color: red;
} */
/*
选中下一个兄弟
语法:前一个 + 下一个(紧挨着)
选择下边所有的兄弟
语法:兄 ~ 弟
*/
p + span{
color: red;
}
p ~ span{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
父元素
- 直接包含子元素的元素叫做父元素
子元素
- 直接被父元素包含的元素是子元素
祖先元素
- 直接或间接包含后代元素的元素叫做祖先元素
- 一个元素的父元素也是它的祖先元素
后代元素
- 直接或间接被祖先元素包含的元素叫做后代元素、
- 子元素也是后代元素
兄弟元素
-拥有相同元素的元素是兄弟元素
-->
<div class="box">
我是一个div
<p>
我是div中的p元素
<span>我是p元素中的span</span>
</p>
<div></div>
<span>我是div中的span元素</span>
<span>我是div中的span元素</span>
<span>我是div中的span元素</span>
<span>我是div中的span元素</span>
</div>
<div>
<span>
我是div外的span
</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3.4 属性选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*
[属性名] 选择含有指定属性的元素
[属性名=属性值] 选择含有指定属性和属性值的元素
[属性名^=属性值] 选择属性值以指定值开头的元素
[属性名$=属性值] 选择属性值以指定值结尾的元素
[属性名*=属性值] 选择属性值中含有某值的元素的元素
*/
/* p[title]{} */
/* p[title=abc]{} */
/* p[title^=abc]{} */
/* p[title$=abc]{} */
p[title*=abc]{
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- title标签:当鼠标放上去就会出现提示文字 -->
<p title="abc">少小离家老大回</p>
<p title="abcdef">乡音无改鬓毛衰</p>
<p title="helloabc">儿童相见不相识</p>
<p>笑问客从何处来</p>
<p>落霞与孤鹜齐飞</p>
<p>秋水共长天一色</p>
</body>
</html>
3.5 伪类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*
将ul里的第一个li设置为红色
*/
/*
伪类(不存在的类,特殊的类)
- 伪类用来描述一个元素的特殊状态
比如:第一个子元素、被点击的元素、鼠标移入的元素
- 伪类一般情况下都是使用 : 开头
:first-child 第一个子元素
:last-child 最后一个子元素
:nth-child() 选中第n个子元素
特殊值:
n 第n个 n的范围0到正无穷
2n 或even 表示选中偶数位的元素
2n+1 或 odd 表示选中奇数位的元素
- 以上这些伪类都是根据所有的子元素进行排序
:first-of-type
:last-of-type
:nth-of-type()
- 这几个伪类的功能和上述的类似,不同点是他们在同类型元素中进行排序
- :not() 否定
- 将符合条件的元素从选择器中去除
*/
/* ul > li:first-child{
color: red;
} */
/* ul > li:last-child{
color: red;
} */
/* ul > li:nth-child(n){
color: red;
} */
/* ul > li:first-of-type{
color: red;
} */
ul>li:not(:nth-child(3)){
color: yellowgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<span>我是一个span</span>
<li>第0个</li>
<li>第一个</li>
<li>第二个</li>
<li>第三个</li>
<li>第四个</li>
<li>第五个</li>
</ul>
</html>
4 超链接的伪类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*
:link 用来表示没访问过的链接(正常的链接)
*/
a:link{
color: red;
}
/*
:visited 用来表示访问过的链接
由于隐私的原因,所以visited这个伪类只能修改链接的颜色
*/
a:visited{
/* font-size: 50px; */
color: orange;
}
/*
:hover 用来表示鼠标移入的状态
*/
a:hover{
color: aqua;
font-size: 50px;
}
/*
:active 用来表示鼠标点击
*/
a:active{
color: yellowgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
1.没有访问过的链接
2.访问过的链接
-->
<a href="https://www.baidu.com">访问过的链接</a>
<br><br>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com">没访问过的链接</a>
</body>
</html>
5 伪元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p{
font-size: 20px;
}
/*
伪元素,表示页面中一些特殊的并不真实的存在的元素(特殊的元素)
伪元素使用 :: 开头
::first-letter 表示第一个字母
::first-line 表示第一行
::selection 表示选中的内容
::before 元素的开始
::after 元素的结束
- before 和 after 必须结合content属性来使用,鼠标选不中
*/
p::first-letter{
font-size: 50px;
}
p::first-line{
background-color: yellow;
}
p::selection{
background-color: greenyellow;
}
/* div::before{
content: 'abc';
color: red;
}
div::after{
content: 'haha';
color: blue;
} */
div::before{
content: '★';
}
div::after{
content: '★';
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 双引号是通过before和after加上去的 -->
<!-- <q>hello</q> -->
<div>Hello Hello How are you</div>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Soluta voluptatibus doloremque asperiores ipsam ipsa inventore laborum veritatis corporis aliquam laudantium voluptatem sapiente similique enim sunt cupiditate ex, beatae sed praesentium.
</p>
</body>
</html>
6 继承
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* body{
font-size: 12px;
} */
/*
样式的继承,我们为一个元素设置的样式同时也会应用到它的后代元素上
继承是发生在祖先后代之间的
继承的设计是为了方便我们的开发,
利用继承我们可以将一些通用的样式统一设置到共同的祖先元素上,
这样只需设置一次即可让所有的元素都具有该样式
注意:并不是所有的样式都会被继承,
比如 背景相关的,布局相关等的这些样式都不会被继承。
*/
p{
color: red;
/* 默认的背景颜色是transparent */
background-color: orange;
}
div{
color: yellowgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
我是一个p元素
<span>我是p元素中的span</span>
</p>
<span>我是p元素外的span</span>
<div>
我是div
<span>
我是div中的span
<em>我是span中的em</em>
</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
7 选择器的权重
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* #box1{
background-color: orange;
}
div#box1{
background-color: yellow;
} */
.d1{
background-color: purple !important;
}
.red{
background-color: red;
/* font-size: 20px; */
}
/* div,p,span{
background-color: yellowgreen;
} */
/*
样式的冲突
- 当我们通过不同的选择器,选中相同的元素,并且为相同的样式设置不同的值,此时就发生了样式的冲突
发生样式冲突时,应用哪个样式由选择器的权重(优先级)决定
选择器的权重
内联样式 1000
id选择器 100
类和伪类选择器 10
元素选择器 1
通配选择器 0
继承的样式 没有优先级
比较优先级时,需要将所有的选择器的优先级进行相加计算,最后优先级越高,则越优先显示(分组选择器是单独计算的)
选择器的累加不会超过其最大的数量级,类选择器再高也不会超过id选择器
如果优先级计算后相同,此时则优先使用靠下的样式
可以在某一个样式的后边添加 !imprtant ,则此时该样式会获取到最高优先级,甚至超过内联样式
注意:在开发中这个玩意一定要慎用!
*/
*{
font-size: 50px;
}
div{
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div id="box1" class="red" style="background-color: skyblue;">我是一个div</div> -->
<div id="box1" class="red d1 d2 d3 d4" style="background-color: chocolate;">我是一个div <span>我是div中的span</span></div>
</body>
</html>
8 像素、百分比、em、rem
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
html{
font-size: 30px;
}
.box1{
/*
长度单位:
像素
- 屏幕(显示器)实际上是由一个一个的小点点构成的
- 不同屏幕的像素大小是不同的,像素越小的屏幕显示的效果越清晰
- 所以同样的200px在不同的设备下显示效果不一样
百分比
- 也可以将属性值设置为相对于其父元素属性的百分比
- 设置百分比可以使子元素跟随父元素的改变而改变
em
- em是相对于元素的字体大小来计算的
- 1em = 1 font-size
- em会根据字体大小的改变而改变
rem
- rem是相对于根元素的字体大小来计算
*/
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
}
.box2{
width: 50%;
height: 50%;
background-color: aqua;
}
.box3{
font-size: 30px;
/* width: 10em;
height: 10em; */
width: 10rem;
height: 10rem;
background-color: greenyellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
9 颜色单位(RGB值、HSL值)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
/*
颜色单位:
在CSS中可以直接使用颜色名来设置各种颜色
比如:red,orange,yellow,blue,green……
但是在css中直接使用颜色名是非常的不方便
RGB值:
- RGB通过三种颜色的不同浓度来调配出不同的颜色
- R red,G green,B blue
- 每一种颜色的范围在0 - 255(0% - 100%)之间
- 语法:RGB(红色,绿色,蓝色)
RGBA
- 就是在RGB的基础上增加了一个 a 表示不透明度
- 需要四个值,前三个和rgb一样,第四个表示不透明度
1表示完全不透明 0表示完全透明 .5半透明
十六进制的RGB值:
- 语法:#红色绿色蓝色
- 颜色过滤通过 00-ff
- 如果颜色两位两位重复可以简写
#aabbcc-->#abc
HSL值 HSLA值
H 色相(0 -360)
S 饱和度 颜色的浓度0%-100%
L 亮度,颜色的亮度0%-100%
*/
background-color: red;
background-color: rgb(255,0,0);
background-color: rgb(0,255,0);
background-color: rgb(0,0,255);
background-color: rgb(255,255,255);
background-color: rgb(106,153,85);
background-color: #ff0000;
background-color: #ffff00;
background-color: #ff0;
background-color: #bbffaa;
background-color: rgb(254,156,156);
background-color: hsl(0,100%,50%);
background-color: hsla(0,100%,50%,0.658);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
10 布局
10.1 文档流
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
文档流(normal flow)
- 网页是一个多层的结构,一层摞着一层
- 通过CSS可以分别为每一层来设置样式
- 作为用户来讲只能看到最顶上一层
- 这些层中,最底下的一层称为文档流,文档流是网页的基础
我们所创建的元素默认都是在文档流中进行排列
- 对于我们来说元素主要有两个状态
在文档流中
不在文档流中(脱离文档流)
- 元素在文档流中有什么特点:
- 块元素
- 块元素会在页面中独占一行(自上向下垂直排列)
- 默认宽度是父元素的全部(会把父元素撑满)
- 默认高度时被内容撑开(子元素)
- 行内元素
- 行内元素不会独占页面的一行,只占自身的大小
- 行内元素在页面中自左向右排列,如果一行之中不能容纳下所有的行内元素
则元素会换到第二行继续自左向右排列(书写习惯一致)
- 行内元素的默认宽度和高度都是被内容撑开
-->
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<span>我是span1</span>
<span>我是span2</span>
<span>我是span3</span>
<span>我是span4</span>
</body>
</html>
10.2 盒子模型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
/*
内容区(content),元素中的所有的子元素和文本内容都在内容区中排列
内容区的大小由width和height两个属性来设置
width 设置内容区的宽度
height 设置内容区的高度
*/
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/*
边框(border),边框属于盒子边缘,边框里边属于盒子内部,出了边框都是盒子的外部
边框的大小会影响到整个盒子的大小
要设置边框,需要至少设置三个样式:
边框的宽度 border-width
边框的颜色 border-color
边框的样式 border-style
*/
border-width: 10px;
border-color: red;
border-style: solid;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
盒模型、盒子模型、框模型(box model)
- CSS将页面中的所有元素都设置为了一个矩形的盒子
- 将元素设置为矩形的盒子后,对页面的布局就变成将不同的盒子摆放到不同的位置
内容区(content)
内边距(padding)
边框(border)
外边距(margin)
-->
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
10.3 盒子模型-边框
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/*
边框
边框的宽度 border-width
边框的颜色 border-color
边框的样式 border-style
*/
/*
border-width: 10px;
默认值,一般都是3个像素
border-width 可以用来指定四个方向的边框的宽度
值的情况
四个值:上 右 下 左
三个值:上 左右 下
两个值:上下 左右
一个值:上下左右
除了border-width还有一组 border-xxx-width
xxx 可以是top right bottom left
用来单独指定某一个边的宽度
*/
border-width: 10px;
/* border-top-width: 10px;
border-left-width: 30px; */
color: red;
/*
border-color用来指定边框的颜色,同样可以分别指定四个边的边框
规则和border-width 一样
border-color也可以省略不写,如果省略了则自动使用color的颜色值
*/
/* border-color: orange red yellow green;
border-color: orange; */
/*
border-style 指定边框的样式
solid 表示实线
dotted 点状虚线
dashed 虚线
double 双线
border-style的默认值是none 表示没有边框
*/
/* border-style: solid dotted dashed double;
border-style: solid; */
/* border-width: 10px;
border-color: orange;
border-style: solid; */
/*
border简写属性,通过该属性可以同时设置边框所有的相关样式,并且没有顺序要求
除了border以外还有四个 border-xxx
border-top
border-right
border-bottom
border-left
*/
/* border: 10px orange solid; */
border: 10px red solid;
border-right: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
10.4 盒子模型-内边距
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
border: 10px orange solid;
/*
内边距(padding)
- 内容区和边框之间的距离是内边距
- 一共有四个方向的内边距:
padding-top
padding-right
padding-bottom
padding-left
- 内边距的设置会影响到盒子的大小
- 背景颜色会延伸到内边距上
- 一个盒子可见框的大小,由内容区 内边距 和 边框共同决定
所以在计算盒子大小时,需要将这三个区域加到一起计算
*/
/* padding-top: 100px; */
/* padding-left: 100px; */
/* padding-right: 100px; */
/* padding-bottom: 100px; */
/*
padding 内边距的简写属性,可以同时指定四个方向的内边距
规则和border-width 一样
*/
padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
}
.inner{
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="innner"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
10.5 盒子模型-外边距
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
border: 10px red solid;
/*
外边距(margin)
- 外边距不会影响盒子可见框的大小
- 但是外边距会影响盒子的位置
- 一共有四个方向的外边距:
margin-top
- 上外边距,设置一个正值,元素会向下移动
margin-right
- 默认情况下设置margin-right不会产生任何效果
margin-bottom
- 下外边距,设置一个正值,其下边的元素会向下移动
margin-left
- 左外边距,设置一个正值,元素会向右移动
- margin 也可以设置负值,如果是负值则元素会向相反的方向移动
- 元素在页面中是按照自左向右的顺序排列的
所以默认情况下如果我们设置的左和上外边距则会移动元素自身
而设置下和右外边距会移动其他元素
- margin的简写属性
margin 可以同时设置四个方向的外边距,用法和padding一样
- margin会影响到盒子实际占用空间
*/
/* margin-top: 100px;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-bottom: 100px; */
/* margin-top: -100px; */
/* margin-left: -100px; */
/* margin-bottom: -100px; */
/* margin-right: 100px; */
margin-right: 100px;
}
.box2{
width: 220px;
height: 220px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>
10.6 盒子模型-水平方向的布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.outer{
width: 800px;
height: 200px;
border: 10px red solid;
}
.inner{
/* width: auto; width的值默认就是auto*/
width: auto;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
margin-right: auto;
margin-left: auto;
/*
元素的水平方向的布局:
元素在其父元素中水平方向的位置由以下几个属性共同决定
margin-left
border-left
padding-left
width
padding-right
border-right
margin-right
一个元素在其父元素中,水平布局必须要满足以下的等式
margin-left+border-left+padding-left+width+padding-right+border-right+margin-right = 其父元素内容区的大小(必须满足)
0 + 0 + 0 + 200 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 800
0 + 0 + 0 + 200 + 0 + 0 + 600 = 800
- 以上等式必须满足,如果相加结果使等式不成立,则称为过渡约束,则等式会自动调整
- 调整的情况:
- 如果这七个值中没有为 auto 的情况,则浏览器会自动调整margin-right的值以使等式满足
- 这七个值中有三个值可设置为auto
width
margin-left
margin-right
- 如果某个值为auto,则会自动调整为auto的那个值以使等式成立
0 + 0 + 0 + auto + 0 + 0 + 0 = 800 auto=800
0 + 0 + 0 + auto + 0 + 0 + 200 = 800 auto=600
200 + 0 + 0 + auto + 0 + 0 + 200 = 800 auto=400
auto + 0 + 0 + 200 + 0 + 0 + 200 = 800 auto=400
- 如果将一个宽度和一个外边距设置为auto,则宽度会调整到最大,设置为auto的外边距会自动为0
- 如果将三个值都设置为auto,则外边距都是0,宽度最大
- 如果将两个外边距设置为auto,宽度固定值,则会将外边距设置为相同的值
auto + 0 + 0 + 200 + 0 + 0 + auto = 800 auto=300
所以我们经常利用这个特点来使一个元素在其父元素中水平居中
示例:
width: xxxpx;
margin:0 auto;
*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
aaa
</div>
</body>
</html>
10.7 盒子模型-垂直方向的布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.outer{
background-color: #bfa;
height: 600px;
/*
默认情况下父元素的高度被内容撑开
*/
}
.inner{
width: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
height: 100px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/*
子元素是在父元素的内容区中排列的,
如果子元素的大小超过了父元素,则子元素会从父元素中溢出
使用 overflow 属性来设置父元素如何处理溢出的子元素
可选值:
visible 默认值 子元素会从父元素中溢出,在父元素外部的位置显示
hidden 溢出内容将会被裁剪不会显示
scroll 生成两个滚动条,通过滚动条来查看完整的内容
auto 根据需要生成滚动条
overflow-x:
overflow-y:
*/
overflow: scroll;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 400px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
<div class="inner"></div>
</div> -->
<div class="box1">
在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。
</div>
</body>
</html>
10.8 盒子模型-外边距的折叠
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1,.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
font-size: 100px;
}
/*
垂直外边距的重叠(折叠)
- 相邻的垂直方向外边距会发生重叠现象
- 兄弟元素
- 兄弟元素间的相邻垂直外边距会取两者之间的较大值(两者都是正值)
- 特殊情况:
如果相邻的外边距一正一负,则取两者的和
如果相邻的外边距都是负值,则取两者中绝对值较大的
- 兄弟元素之间的外边距的重叠,对于开发是有利的,所以我们不需要进行处理
- 父子元素
- 父子元素间相邻外边距,子元素的会传递给父元素(上外边距)
- 父子外边距的折叠会影响到页面的布局,必须要进行处理(要么不要外边距 要么不相邻)
*/
.box1{
background-color: #bfa;
/* 设置一个下外边距 */
margin-bottom: 100px;
}
.box2{
background-color: orange;
padding-top: 100px;
/* 设置一个上外边距 */
margin-top: 100px;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/* padding-top: 100px; */
/* border-top: 1px #bfa solid; */
}
.box4{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
margin-top: 99px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box3">
<div class="box4"></div>
</div>
<!-- <div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div> -->
</body>
</html>
10.9 行内元素的盒模型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.s1{
background-color: yellow;
/*
行内元素的盒模型
- 行内元素不支持设置宽度和高度
- 行内元素可以设置padding,但是垂直方向padding不会影响页面的布局
- 行内元素可以设置border,垂直方向的border不会影响页面的布局
*/
/* width: 100px;
height: 100px; */
/* padding: 100px; */
/* border: 100px solid red; */
margin: 100px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
a{
/*
display 用来设置元素显示的类型
可选值:
inline 将元素设置为行内元素
block 将元素设置为块元素
inline-block 将元素设置为行内块元素
行内块,既可以设置宽度和高度又不会独占一行
table 将元素设置为一个表格
none 元素不在页面中显示
visibility 用来设置元素的显示状态
可选值:
visible 默认值,元素在页面中正常显示
hidden 元素在页面中隐藏 不显示,但是依然占据页面的位置
*/
display: block;
visibility: visible;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="javascript:;">超链接</a>
<a href="javascript:;">超链接</a>
<span class="s1">我是span</span>
<span class="s1">我是span</span>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
10.10 浏览器的默认样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/reset.css"> -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/normalize.css">
<style>
.s1{
background-color: yellow;
/*
行内元素的盒模型
- 行内元素不支持设置宽度和高度
- 行内元素可以设置padding,但是垂直方向padding不会影响页面的布局
- 行内元素可以设置border,垂直方向的border不会影响页面的布局
*/
/* width: 100px;
height: 100px; */
/* padding: 100px; */
/* border: 100px solid red; */
margin: 100px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
a{
/*
display 用来设置元素显示的类型
可选值:
inline 将元素设置为行内元素
block 将元素设置为块元素
inline-block 将元素设置为行内块元素
行内块,既可以设置宽度和高度又不会独占一行
table 将元素设置为一个表格
none 元素不在页面中显示
visibility 用来设置元素的显示状态
可选值:
visible 默认值,元素在页面中正常显示
hidden 元素在页面中隐藏 不显示,但是依然占据页面的位置
*/
display: block;
visibility: visible;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="javascript:;">超链接</a>
<a href="javascript:;">超链接</a>
<span class="s1">我是span</span>
<span class="s1">我是span</span>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
reset.css
/* v2.0 | 20110126
http://meyerweb.com/eric/tools/css/reset/
License: none (public domain)
*/
html, body, div, span, applet, object, iframe,
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p, blockquote, pre,
a, abbr, acronym, address, big, cite, code,
del, dfn, em, img, ins, kbd, q, s, samp,
small, strike, strong, sub, sup, tt, var,
b, u, i, center,
dl, dt, dd, ol, ul, li,
fieldset, form, label, legend,
table, caption, tbody, tfoot, thead, tr, th, td,
article, aside, canvas, details, embed,
figure, figcaption, footer, header, hgroup,
menu, nav, output, ruby, section, summary,
time, mark, audio, video {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: 0;
font-size: 100%;
font: inherit;
vertical-align: baseline;
}
/* HTML5 display-role reset for older browsers */
article, aside, details, figcaption, figure,
footer, header, hgroup, menu, nav, section {
display: block;
}
body {
line-height: 1;
}
ol, ul {
list-style: none;
}
blockquote, q {
quotes: none;
}
blockquote:before, blockquote:after,
q:before, q:after {
content: '';
content: none;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
normalize.css
/*! normalize.css v8.0.1 | MIT License | github.com/necolas/normalize.css */
/* Document
========================================================================== */
/**
* 1. Correct the line height in all browsers.
* 2. Prevent adjustments of font size after orientation changes in iOS.
*/
html {
line-height: 1.15; /* 1 */
-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; /* 2 */
}
/* Sections
========================================================================== */
/**
* Remove the margin in all browsers.
*/
body {
margin: 0;
}
/**
* Render the `main` element consistently in IE.
*/
main {
display: block;
}
/**
* Correct the font size and margin on `h1` elements within `section` and
* `article` contexts in Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
*/
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
margin: 0.67em 0;
}
/* Grouping content
========================================================================== */
/**
* 1. Add the correct box sizing in Firefox.
* 2. Show the overflow in Edge and IE.
*/
hr {
box-sizing: content-box; /* 1 */
height: 0; /* 1 */
overflow: visible; /* 2 */
}
/**
* 1. Correct the inheritance and scaling of font size in all browsers.
* 2. Correct the odd `em` font sizing in all browsers.
*/
pre {
font-family: monospace, monospace; /* 1 */
font-size: 1em; /* 2 */
}
/* Text-level semantics
========================================================================== */
/**
* Remove the gray background on active links in IE 10.
*/
a {
background-color: transparent;
}
/**
* 1. Remove the bottom border in Chrome 57-
* 2. Add the correct text decoration in Chrome, Edge, IE, Opera, and Safari.
*/
abbr[title] {
border-bottom: none; /* 1 */
text-decoration: underline; /* 2 */
text-decoration: underline dotted; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Add the correct font weight in Chrome, Edge, and Safari.
*/
b,
strong {
font-weight: bolder;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the inheritance and scaling of font size in all browsers.
* 2. Correct the odd `em` font sizing in all browsers.
*/
code,
kbd,
samp {
font-family: monospace, monospace; /* 1 */
font-size: 1em; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Add the correct font size in all browsers.
*/
small {
font-size: 80%;
}
/**
* Prevent `sub` and `sup` elements from affecting the line height in
* all browsers.
*/
sub,
sup {
font-size: 75%;
line-height: 0;
position: relative;
vertical-align: baseline;
}
sub {
bottom: -0.25em;
}
sup {
top: -0.5em;
}
/* Embedded content
========================================================================== */
/**
* Remove the border on images inside links in IE 10.
*/
img {
border-style: none;
}
/* Forms
========================================================================== */
/**
* 1. Change the font styles in all browsers.
* 2. Remove the margin in Firefox and Safari.
*/
button,
input,
optgroup,
select,
textarea {
font-family: inherit; /* 1 */
font-size: 100%; /* 1 */
line-height: 1.15; /* 1 */
margin: 0; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Show the overflow in IE.
* 1. Show the overflow in Edge.
*/
button,
input { /* 1 */
overflow: visible;
}
/**
* Remove the inheritance of text transform in Edge, Firefox, and IE.
* 1. Remove the inheritance of text transform in Firefox.
*/
button,
select { /* 1 */
text-transform: none;
}
/**
* Correct the inability to style clickable types in iOS and Safari.
*/
button,
[type="button"],
[type="reset"],
[type="submit"] {
-webkit-appearance: button;
}
/**
* Remove the inner border and padding in Firefox.
*/
button::-moz-focus-inner,
[type="button"]::-moz-focus-inner,
[type="reset"]::-moz-focus-inner,
[type="submit"]::-moz-focus-inner {
border-style: none;
padding: 0;
}
/**
* Restore the focus styles unset by the previous rule.
*/
button:-moz-focusring,
[type="button"]:-moz-focusring,
[type="reset"]:-moz-focusring,
[type="submit"]:-moz-focusring {
outline: 1px dotted ButtonText;
}
/**
* Correct the padding in Firefox.
*/
fieldset {
padding: 0.35em 0.75em 0.625em;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the text wrapping in Edge and IE.
* 2. Correct the color inheritance from `fieldset` elements in IE.
* 3. Remove the padding so developers are not caught out when they zero out
* `fieldset` elements in all browsers.
*/
legend {
box-sizing: border-box; /* 1 */
color: inherit; /* 2 */
display: table; /* 1 */
max-width: 100%; /* 1 */
padding: 0; /* 3 */
white-space: normal; /* 1 */
}
/**
* Add the correct vertical alignment in Chrome, Firefox, and Opera.
*/
progress {
vertical-align: baseline;
}
/**
* Remove the default vertical scrollbar in IE 10+.
*/
textarea {
overflow: auto;
}
/**
* 1. Add the correct box sizing in IE 10.
* 2. Remove the padding in IE 10.
*/
[type="checkbox"],
[type="radio"] {
box-sizing: border-box; /* 1 */
padding: 0; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Correct the cursor style of increment and decrement buttons in Chrome.
*/
[type="number"]::-webkit-inner-spin-button,
[type="number"]::-webkit-outer-spin-button {
height: auto;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the odd appearance in Chrome and Safari.
* 2. Correct the outline style in Safari.
*/
[type="search"] {
-webkit-appearance: textfield; /* 1 */
outline-offset: -2px; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Remove the inner padding in Chrome and Safari on macOS.
*/
[type="search"]::-webkit-search-decoration {
-webkit-appearance: none;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the inability to style clickable types in iOS and Safari.
* 2. Change font properties to `inherit` in Safari.
*/
::-webkit-file-upload-button {
-webkit-appearance: button; /* 1 */
font: inherit; /* 2 */
}
/* Interactive
========================================================================== */
/*
* Add the correct display in Edge, IE 10+, and Firefox.
*/
details {
display: block;
}
/*
* Add the correct display in all browsers.
*/
summary {
display: list-item;
}
/* Misc
========================================================================== */
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 10+.
*/
template {
display: none;
}
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 10.
*/
[hidden] {
display: none;
}
10.11 盒子的大小
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px red solid;
/*
默认情况下,盒子可见框的大小由内容区、内边距和边框共同决定
box-sizing 用来设置盒子尺寸的计算方式(设置width和height的作用)
可选值:
content-box 默认值,宽度和高度用来设置内容区的大小
border-box 宽度和高度用来设置整个盒子可见框的大小
width 和 height 指的是内容区 和内边距 和 边框的总大小
*/
box-sizing: content-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
10.12 轮廓阴影和圆角
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/* box-shadow 用来设置元素的阴影效果,阴影不会影响页面布局
第一个值 左侧偏移量 设置阴影的水平位置 正值向右移动 负值向左移动
第二个值 垂直偏移量 设置阴影的水平位置 正值向下移动 负值向上移动
第三个值 阴影的模糊半径
第四个值 阴影的颜色
*/
box-shadow: 0px 0px 50px rgba(0, 0, 0, .5);
/*
outline 用来设置元素的轮廓线,用法和border一模一样
轮廓和边框不同的点,就是轮廓不会影响到可见框的大小
*/
}
/* .box1:hover{
outline: 10px red solid;
} */
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
/* border-radius: 用来设置圆角 圆角设置的圆的半径大小*/
/* border-top-left-radius: */
/* border-top-right-radius: */
/* border-bottom-left-radius: */
/* border-bottom-right-radius: */
/* border-top-left-radius: 50px 100px; */
/*
border-radius 可以分别指定四个角的圆角
四个值 左上 右上 右下 左下
三个值 左上 右上/左下 右下
*/
/* border-radius: 20px/40px; 横向都是20px,纵向都是40px*/
/* 将元素设置为一个圆形
无论多大,50%都会设置为圆形
*/
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div class="box1"></div> -->
<div class="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>
12 布置练习
12.1 图片列表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>图片列表</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/reset.css">
<style>
/* 设置body的背景颜色 */
body{
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
/* 设置外部ul的样式 */
.img-list{
/* 设置ul的宽度 */
width: 190px;
/* 设置ul的高度 */
height: 470px;
/* 裁剪溢出的内容 */
overflow: hidden;
/* 使ul在页面中居中(实际示例中不需要这么写) */
margin: 50px auto;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
}
/* 设置li的位置 */
.img-list li:not(:last-child){
margin-bottom: 9px;
}
/* 设置图片的大小(li多宽ul就多宽) */
.img-list img{
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div>
<a href=""><img src="" alt=""></a>
<a href=""><img src="" alt=""></a>
<a href=""><img src="" alt=""></a>
</div> -->
<ul class="img-list">
<li>
<a href="javascript:;">
<img src="./img/01/1.jpg" alt="">
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="javascript:;">
<img src="./img/01/2.jpg" alt="">
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="javascript:;">
<img src="./img/01/3.jpg" alt="">
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
12.2 京东左侧导航条
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>京东的左侧导航</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/reset.css">
<style>
/* 设置body */
body{
/* 设置一个网页的背景,以使我们方便查看 */
background-color: #bfa;
}
/* 设置菜单外部容器 */
.left-nav{
/* 设置宽度 */
width: 190px;
/* 设置高度 */
height: 450px;
/* 设置padding */
padding: 10px 0;
/* 设置一个背景颜色 */
background-color: #fff;
margin: 50px auto;
}
/* 设置菜单内部的item */
.left-nav .item{
height: 25px;
/* 要让一个文字在父元素中垂直居中,只需将父元素的line-height设置为一个和父元素height一样的值 */
line-height: 25px;
padding-left: 18px;
/* 设置字体大小 */
font-size: 12px;
}
/* 为item设置一个鼠标移入的状态 */
.item:hover{
background-color: #d9d9d9;
}
/* 设置超链接的样式 */
.item a{
/* 设置字体大小 */
font-size: 14px;
/* 设置字体颜色 */
color: #333;
/* 去除下划线 */
text-decoration: none;
}
/* 设置超链接的hover的样式 */
.item a:hover{
color: #c81623;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建一个外部的容器 nav(div) div(div) ul(li) -->
<nav class="left-nav">
<div class="item">
<a href="#">家用电器</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">手机</a>/
<a href="#">运营商</a>/
<a href="#">数码</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">电脑</a>/
<a href="#">办公</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">家居</a>/
<a href="#">家具</a>/
<a href="#">家装</a>
<a href="#">厨具</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">男装</a>/
<a href="#">女装</a>/
<a href="#">重装</a>
<a href="#">内衣</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">美妆</a>/
<a href="#">个护清洁</a>/
<a href="#">宠物</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">女装</a>/
<a href="#">箱包</a>/
<a href="#">钟表</a>/
<a href="#">珠宝</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">男鞋</a>/
<a href="#">运动</a>/
<a href="#">户外</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">房产</a>/
<a href="#">汽车</a>/
<a href="#">汽车用品</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">母婴</a>/
<a href="#">玩具乐器</a>/
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">食品</a>/
<a href="#">酒类</a>/
<a href="#">生鲜</a>/
<a href="#">特产</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">艺术</a>/
<a href="#">礼品鲜花</a>/
<a href="#">农资绿植</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">医药保健</a>/
<a href="#">计生情趣</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">图书</a>/
<a href="#">文娱</a>/
<a href="#">电子书</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">机票</a>/
<a href="#">酒店</a>/
<a href="#">旅游</a>/
<a href="#">生活</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">理财</a>/
<a href="#">众筹</a>/
<a href="#">白条</a>/
<a href="#">保险</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">安装</a>/
<a href="#">维修</a>/
<a href="#">清洗</a>/
<a href="#">二手</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">工业品</a>
</div>
</nav>
</body>
</html>
12.3 网易新闻列表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>网易的新闻列表</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/reset.css">
<style>
/* body{
/* background-color: #bfa; * /
} */
a{
/* 去除下划线 */
text-decoration: none;
}
/* 设置容器的样式 */
.news-wrapper{
/* 设置宽度 */
width: 300px;
/* 设置高度 */
height: 357px;
/* 设置居中 */
margin: 50px auto;
/* 设置背景颜色,显示轮廓 */
background-color: #fff;
/* 设置上边框 */
border-top: 1px solid #ddd;
}
/* 设置news-title */
.news-title{
/* 为了边框和文字宽度一致,需要将h2转换为行内块元素 */
display: inline-block;
/* 设置高度 */
height: 30px;
/* 设置上边框 */
border-top: 1px red solid;
/* 通过margin-top 将h2上移,盖住上边框 */
margin-top: -1px;
padding-top: 10px;
}
/* 设置title中超链接的样式 */
.news-title a{
/* 设置颜色 */
color: #40406B;
/* 设置文字的加粗效果 */
font-weight: bold;
}
/* 设置图片容器的高度 */
.news-img{
height: 150px;
}
/* 设置图片的文字效果 */
.news-img .img-title{
/* 向上移动文字 */
margin-top: -30px;
/* 设置字体颜色 */
color: #fff;
/* 设置加粗 */
font-weight: bold;
/* 设置padding */
padding-left: 30px;
}
/* 设置新闻列表 */
.news-list{
/* 设置上外边距 */
margin-top: 20px;
/* 设置左侧的padding */
/* padding-left: 14px; */
/* 设置项目符号 */
/* list-style: square; */
}
/* 设置li */
.news-list li{
/* 设置下外边距 */
margin-bottom: 17px;
}
/* 通过before伪元素,来为每一个li添加项目符号 */
.news-list li::before{
content: '●';
color: rgb(218, 218, 218);
font-size: 12px;
margin-right: 4px;
}
/* 设置li中文字 */
.news-list li a{
/* 设置字体大小 */
font-size: 14px;
/* 设置字体颜色 */
color: #666;
}
.news-list li a:hover{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建新闻列表的外侧的容器 -->
<div class="news-wrapper">
<!-- 创建一个标题标签 -->
<h2 class="news-title">
<a href="#">体育</a>
</h2>
<!-- 创建一个图片的容器 -->
<div class="news-img">
<a href="#">
<img src="./img/03/1.jpeg" alt="费德勒">
<!-- 创建图片标题 -->
<h3 class="img-title">
费德勒首负迪米 扶额头不满发挥
</h3>
</a>
</div>
<!-- 新闻列表 -->
<ul class="news-list">
<li>
<a href="#">乔治:我爱LA 喜欢和LBJ一起打球</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">格林:3年前降薪就在等KD 特制T恤嘲讽LBJ</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">塔克4000双鞋让保罗羡慕嫉妒 乔丹被震惊</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">CBA下季新赛制:常规赛4组循环 增至46轮</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
12.4 w3cschool导航条
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>导航条</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/reset.css">
<style>
/* 设置nav的大小 */
.nav{
/* 设置宽度和高度 */
width: 1210px;
height: 48px;
/* 设置背景颜色 */
background-color: #E8E7E3;
margin: 100px auto;
}
/* 设置nav中li */
.nav li{
/* 设置li向左浮动,以使菜单横向排列 */
float: left;
/* 设置li的高度 */
/* height: 48px; */
/* 将文字在父元素中垂直居中 */
line-height: 48px;
}
/* 设置a的样式 */
.nav a{
/* 将a转换为块元素 */
display: block;
/* 去除下划线 */
text-decoration: none;
/* 设置字体颜色 */
color: #777777;
/* 修改字体大小 */
font-size: 18px;
padding: 0 39px;
}
.nav li:last-child a{
padding: 0 42px 0 41px;
}
/* 设置鼠标移入的效果 */
.nav a:hover{
background-color: #3f3f3f;
color:#E8E7E3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建导航条的结构 -->
<ul class="nav">
<li>
<a href="#">HTML/CSS</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Browser Side</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Server Side</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Programming</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">XML</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Web Building</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Reference</a>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
12.5 京东轮播图
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/reset.css">
<style>
/* 设置图片的容器 */
.img-list{
width: 590px;
height: 470px;
margin: 100px auto;
/* 为ul开启相对定位,目的是使ul中的pointer可以相对于ul定位而不是相对于初始包含块 */
position: relative;
}
/* 设置li */
.img-list li{
position: absolute;
}
/* 通过修改元素的层级来显示指定的图片 */
.img-list li:nth-child(4){
z-index: 1;
}
/* 设置导航点的样式 */
.pointer{
position: absolute;
z-index: 9999;
bottom: 20px;
left: 40px;
}
.pointer a{
/* 设置元素向左移动 */
float: left;
width: 10px;
margin: 0px 2px;
height: 10px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, .3);
/* 将背景颜色值设置到内容区,边框和内边距不再有背景颜色 */
background-clip: content-box;
border: 2px solid transparent;
}
.pointer a.active,
.pointer a:hover{
background-color: #fff;
border: 2px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, .3);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="img-list">
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/1.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/2.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/3.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/4.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/5.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/6.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/7.jpg"></a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;"><img src="./img/05/8.jpg"></a></li>
<div class="pointer">
<a class="active" href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
<a href="javascript:;"></a>
</div>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
13 浮动
13.1 浮动的简介
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/*
通过浮动可以使一个元素向其父元素的左侧或右侧移动
使用 float 属性来设置元素的浮动
可选值:
none 默认值 元素不浮动
left 元素向左移动
right 元素向右浮动
注意:元素设置浮动以后,水平布局的等式便不需要强制成立
元素设置浮动以后,会完全从文档流中脱离,不再占用文档流的位置,
所以元素下边的还在文档流中的元素会自动向上移动
浮动的特点:
1、浮动元素会完全脱离文档流,不再占据文档流中的位置
2、设置浮动以后元素会向父元素的左侧或右侧移动
3、浮动元素默认不会从父元素中移除
4、浮动元素向左或向右移动时,不会超过它前边的其他浮动元素
5、如果浮动元素的上边是一个没有浮动的块元素,则浮动元素无法上移
6、浮动元素不会超过它上边的浮动的兄弟元素,最多最多就是和它一样高
简单总结:
浮动目前来讲它的主要作用就是让页面中的元素可以水平排列,
通过浮动可以制作一些水平方向的布局
*/
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
float: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
13.2 浮动的特点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
/*
浮动元素不会盖住文字,文字会自动环绕在浮动元素的周围,
所以我们可以利用浮动来设置文字环绕图片的效果
*/
float: left;
}
.box2{
background-color: yellowgreen;
/*
元素设置浮动以后,将会从文档流中脱离,从文档流中脱离后,元素的一些特点也会发生变化
脱离文档流的特点:
块元素:
1、块元素不再独占页面的一行
2、脱离文档流以后,块元素的宽度和高度默认都被内容撑开
行内元素:
行内元素脱离文档流以后会变成块元素,特点和块元素一样
脱离文档流以后,不需要再区分块和行内了
*/
float: left;
}
.box3{
background-color: orange;
}
.s1{
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div class="box1"></div>
<p>
在我的后园,可以看见墙外有两株树,一株是枣树,还有一株也是枣树。这上面的夜的天空,奇怪而高,我生平没有见过这样的奇怪而高的天空。他仿佛要离开人间而去,使人们仰面不再看见。然而现在却非常之蓝,闪闪地着几十个星星的眼,冷眼。他的口角上现出微笑,似乎自以为大有深意,而将繁霜洒在我的园里的野花草上。我不知道那些花草真叫什么名字,人们叫他们什么名字。我记得有一种开过极细小的粉红花,现在还开着,但是更极细小了,她在冷的夜气中,瑟缩地做梦,梦见春的到来,梦见秋的到来,梦见瘦的诗人将眼泪擦在她最末的花瓣上,告诉她秋虽然来,冬虽然来,而此后接着还是春,胡碟乱飞,蜜蜂都唱起春词来了。她于是一笑,虽然颜色冻得红惨惨地,仍然瑟缩着。枣树,他们简直落尽了叶子。先前,还有一两个孩子来打他们别人打剩的枣子,现在是一个也不剩了,连叶子也落尽了。他知道小粉红花的梦,秋后要有春;他也知道落叶的梦,春后还是秋。他简直落尽叶子,单剩干子,然而脱了当初满树是果实和叶子时候的弧形,欠伸得很舒服。但是,有几枝还低亚着,护定他从打枣的竿梢所得的皮伤,而最直最长的几枝,却已默默地铁似的直刺着奇怪而高的天空,使天空闪闪地鬼��眼;直刺着天空中圆满的月亮,使月亮窘得发白。
</p> -->
<span class="s1">我是一个span</span>
<!-- <div class="box2">helloaa</div>
<div class="box3">hello</div> -->
</body>
</html>
13.3 网页的布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
header,main,footer{
width: 1000px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* 设置头部 */
header{
height: 150px;
background-color: silver;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* 设置主体 */
main{
height: 500px;
background-color: #bfa;
margin: 10px auto;
}
nav,article,aside{
float: left;
height: 100%;
}
/* 设置左侧的导航 */
nav{
width: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
/* 设置中间的内容 */
article{
width: 580px;
background-color: orange;
margin: 0 10px;
}
/* 设置右侧的内容 */
aside{
width: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
/* 设置底部 */
footer{
width: 1000px;
height: 150px;
background-color: tomato;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建头部 -->
<header></header>
<!-- 创建网页的主体 -->
<main>
<!-- 左侧导航 -->
<nav></nav>
<!-- 中间的内容 -->
<article></article>
<!-- 右边的边栏 -->
<aside></aside>
</main>
<!-- 网页的底部 -->
<footer></footer>
</body>
</html>
13.3 高度塌陷和BFC
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.outer{
/* 没有内容,合在一起 */
border: 10px red solid;
/*
BFC(Block Formatting Context) 块级格式化环境
- BFC 是一个CSS中的一个隐含的属性,可以为一个元素开启BFC
开始BFC该元素会变成一个独立的布局区域
- 元素开启后的特点:
1.开启BFC的元素不会被浮动元素所覆盖
2.开启BFC的元素子元素和父元素外边距不会重叠
3.开启BFC的元素可以包含浮动的子元素
- 可以通过一些特殊方式来开启元素的BFC
1、设置元素的浮动(不推荐)
2、将元素设置为行内块元素(不推荐)
3、将元素的overflow设置为一个非visible的值
- 常用的方式 为元素设置 overflow hidden 开启其BFC 以使其可以包含浮动元素
*/
/* float: left; */
/* display: inline-block; */
overflow: hidden;
}
.inner{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
/*
高度塌陷的问题:
在浮动布局中,父元素的高度默认是被子元素撑开的,
当子元素浮动后,其会完全脱离文档流,子元素从文档流中脱离
将会无法撑起父元素的高度,导致父元素的高度丢失
父元素高度丢失以后,其下的元素会自动上移,导致页面的布局混乱
所以高度塌陷是浮动布局中比较常见的一个问题,这个问题我们必须要进行处理!
*/
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
<div style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;"></div>
</body>
</html>
13.4 BFC的演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
/* float: left; */
/* margin-top只会对box3起作用,而不会对box1起作用 */
overflow: hidden;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
overflow: hidden;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
<!-- <div class="box2"></div> -->
</body>
</html>
13.5 clear
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
font-size: 50px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 400px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #ff0;
float: right;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
/*
由于box1的浮动,导致box3位置上移
也就是box3受到了box1浮动的影响,位置发生了改变
如果我们不希望某个元素元素因为其他元素浮动的影响而改变位置,
可以通过clear属性来清除浮动元素对当前元素所产生的影响
clear
- 作用:清除浮动元素对当前元素所产生的影响
- 可选值:
left 清楚左侧浮动元素对当前元素的影响
right 清除右侧浮动元素对当前元素的影响
both 清除两侧中最大影响的那侧
原理:
设置清除浮动以后,浏览器会自动为元素添加一个上外边距,
以使其位置不受其他元素的影响
*/
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
<div class="box3">3</div>
</body>
</html>
13.6 使用aftert伪类解决高度塌陷
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
border: 10px red solid;
/* overflow: hidden; */
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
float: left;
}
.box3{
clear: both;
}
/* 伪类元素默认是行内元素 */
.box1::after{
content: 'hello';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
13.7 clearfix
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
/* .box1::before{
content: '';
display: table;
} */
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
margin-top: 100px;
}
/* clearfix 这个样式可以同时解决高度塌陷和外边距重叠问题,当你在遇到这些问题时,直接使用clearfix这个类即可 */
.clearfix::before,
.clearfix::after{
content: '';
display: table;
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1 clearfix">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
14 定位
14.1 相对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body{
font-size: 60px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
/*
定位(position)
- 定位是一种更加高级的布局手段
- 通过定位可以将元素摆放到页面的任意位置
- 使用position属性来设置定位
可选值:
static 默认值,元素是静止的没有开启定位
relative 开启元素的相对定位
absolute 开启元素的绝对定位
fixed 开启元素的固定定位
sticky 开启元素的粘滞定位
- 相对定位:
- 当元素的position属性值设置为relative时则开启了元素的相对定位
- 相对定位的特点:
1.元素开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何的变化
2.相对定位是参照于元素在文档流中的位置进行定位的
3.相对定位会提升元素的层级
4.相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流
5.相对定位不会改变元素的性质,块还是块,行内还是行内(看原来的位置)
- 偏移量(offset)
- 当元素开启了定位以后,可以通过偏移量来设置元素的位置
top
- 定位元素和定位位置上边的距离
bottom
- 定位元素和定位位置下边的距离
- 定位元素垂直方向的位置由top和bottom两个属性来控制
通常情况下我们只会使用其中一个
- top值越大,定位元素越向下移动
left
- 定位元素和定位位置的左侧距离
right
- 定位元素和定位位置的右侧距离
- 定位元素水平方向的位置由left和right两个属性控制
通常情况下只会使用一个
- left越大元素越靠右
- right越大元素越靠左
left往右边,top往左边
*/
position: relative;
left: 200px;
bottom: 200px;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
<div class="box3">3</div>
</body>
</html>
14.2 绝对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body{
font-size: 60px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
/*
绝对定位
- 当元素的position属性值设置为absolute时,则开启了元素的绝对定位
- 绝对定位的特点:
1.开始绝对定位后,如果不设置偏移量元素的位置不会发生变化
2.开启绝对定位后,元素会从文档流中脱离
3.绝对定位会改变元素的性质
4.绝对定位会使元素提升一个层级
5.绝对定位元素是相对于其包含块进行定位的
包含块(containing block)
- 正常情况下:
包含块就是离当前元素最近的祖先块元素
<div> <div></div> </div>
<div><span><em>hello</em></span></div>
- 绝对定位的包含块:
包含块就是离它最近的开启了定位的祖先元素
如果所有的祖先元素都没有开启定位则根元素就是它的包含块
- html(根元素、初始包含块)
*/
position: absolute;
/* left: 0;
top: 0; */
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.box4{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: tomato;
position: relative;
}
.box5{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: aliceblue;
/* position: relative; */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box4">4
<div class="box5">5
<div class="box2">2</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="box3">3</div>
</body>
</html>
14.3 固定定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body{
font-size: 60px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
/*
固定定位:
- 将元素的position属性设置为fixed则开启了元素的固定定位
- 固定定位也是一种绝对定位,所以固定定位的大部分都和绝对定位一样
唯一不同的是固定定位永远参照与浏览器的视口进行定位
固定定位的元素不会随网页的滚动条滚动
*/
position: fixed;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.box4{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: tomato;
}
.box5{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: aliceblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box4">4
<div class="box5">5
<div class="box2">2</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="box3">3</div>
</body>
</html>
14.4 粘滞定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>导航条</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../exercise/css/reset.css">
<style>
body{
height: 3000px;
}
/* 设置nav的大小 */
.nav{
/* 设置宽度和高度 */
width: 1210px;
height: 48px;
/* 设置背景颜色 */
background-color: #E8E7E3;
margin: 100px auto;
/*
粘滞定位
- 当元素的position属性设置为sticky时则开启了元素的粘滞定位
- 粘滞定位和相对定位的特点基本一致,
不同的是粘滞定位可以在元素到达某个位置时将其固定
*/
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
}
/* 设置nav中li */
.nav li{
/* 设置li向左浮动,以使菜单横向排列 */
float: left;
/* 设置li的高度 */
/* height: 48px; */
/* 将文字在父元素中垂直居中 */
line-height: 48px;
}
/* 设置a的样式 */
.nav a{
/* 将a转换为块元素 */
display: block;
/* 去除下划线 */
text-decoration: none;
/* 设置字体颜色 */
color: #777777;
/* 修改字体大小 */
font-size: 18px;
padding: 0 39px;
}
.nav li:last-child a{
padding: 0 42px 0 41px;
}
/* 设置鼠标移入的效果 */
.nav a:hover{
background-color: #3f3f3f;
color:#E8E7E3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建导航条的结构 -->
<ul class="nav">
<li>
<a href="#">HTML/CSS</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Browser Side</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Server Side</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Programming</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">XML</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Web Building</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">Reference</a>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
14.5 绝对定位元素的位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #bfa;
/* position: relative; */
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
margin: 0;
/*
水平布局
left + margin-left + border-left + padding-left + width +padding-right + border-right + margin-right right = 包含块的内容区的宽度
- 当我们开启了绝对定位后:
水平方向的布局等式就需要添加left和right两个值
此时规则和之前一样只是多添加了两个值:
当发生过度约束:
如果9个值中没有 auto 则自动调整right值以使等式满足
如果有auto,则自动调整auto的值以使等式满足
- 可设置auto的值
margin width left right
- 因为left和right的值默认是auto,所以如果不知道left和right
则等式不满足时,会自动调整这两个值
垂直方向布局的等式也必须要满足
top + margin-top/bottom + padding-top/bottom + border-top/bottom + height = 包含块的高度
*/
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
14.6 元素的层级
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body{
font-size: 60px;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
position: absolute;
/*
对于开启了定位元素,可以通过z-index属性来指定元素的层级
z-index 需要一个整数作为参数,值越大元素的层级越高
元素的层级越高越优先显示
如果元素的层级一样,则优先显示靠下的元素
祖先元素的层级再高也不会盖住后代元素
*/
/* z-index: 3; */
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgba(255, 0, 0, .3);
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
/* z-index: 3; */
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
z-index: 3;
}
.box4{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
<div class="box3">3
<div class="box4">4</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
15 字体和背景
15.1 字体
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* font-face 可以将服务器中的字体直接提供给用户去使用
问题:
1.加载速度
2.版权
3.字体格式
*/
@font-face{
/* 指定字体的名字 */
font-family: 'myfont';
/* 服务器中字体的路径 */
src: url('') format("truetype");
}
p{
/* 字体相关的样式
color 用来设置字体颜色
font-size 字体的大小
和font-size相关的单位
em 相当于当前元素的一个font-size
rem 相对于根元素的一个font-size
font-family 字体族(字体的格式)
可选值:
serif 衬线字体
sans-serif 非衬线字体
monospace 等宽字体
- 指定字体的类别,浏览器会自动使用该类别下的字体
- font-family 可以同时指定多个字体,多个字体间使用,隔开
字体生效时优先使用第一个,第一个无法使用则使用第二个 以此类推
*/
color: red;
font-size: 40px;
/* font-family: 'Courier New', Courier, monospace; */
font-family: myfont;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
今天天气真不错,Hello Hello How are you!
</p>
</body>
</html>
15.2 图标字体的其他使用方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./fa/css/all.css">
<!--
all.css 没有压缩过
all.min.css 压缩过
-->
</head>
<body>
<!--
图标字体(iconfont)
- 在网页中经常需要使用一些图标,可以通过图片来引入图标
但是图片大小本身比较大,并且非常不灵活
- 所以在使用图标时,我们还可以将图标直接设置为字体,
然后通过font-face的形式来对字体进行引入
-这样我们就可以通过使用字体的形式来使用图标
fontawesome 使用步骤
1.下载 https://fontawesome.com/
2.解压
3.将css和wenfonts移动到项目中(二者须在同一级目录下)
4.将all.css引入到网页中
5.使用图标字体
- 直接通过类名来使用图标字体
class="fas fa-bell"
class="fab fa-accessible-icon"
-->
<i class="fas fa-bell" style="font-size: 80px; color: red;"></i>>
<i class="fas fa-bell-slash"></i>>
<i class="fab fa-accessible-icon"></i>>
<i class="fas fa-otter" style="font-size: 160px; color: green;"></i>>
</body>
</html>