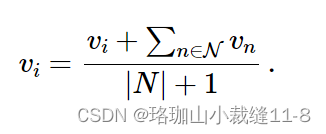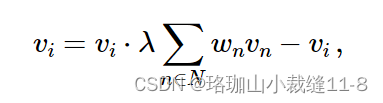官网:Mesh - Open3D 0.18.0 documentation
目录
3、表面法线估算( Surface normal estimation )
1、mesh基本数据结构
Open3D 有一种用于 3D 三角网格的数据结构,称为 TriangleMesh。下面的代码展示了如何从层叠文件中读取三角形网格并打印其顶点和三角形。
print("Testing mesh in Open3D...")
armadillo_mesh = o3d.data.ArmadilloMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(armadillo_mesh.path)
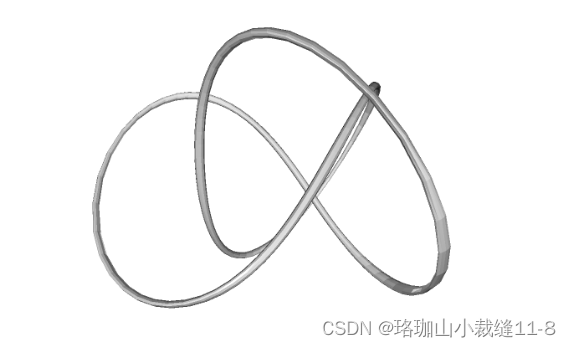
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
print(mesh)
print('Vertices:')
print(np.asarray(mesh.vertices))
print('Triangles:')
print(np.asarray(mesh.triangles))Testing mesh in Open3D... [Open3D INFO] Downloading https://github.com/isl-org/open3d_downloads/releases/download/20220201-data/KnotMesh.ply [Open3D INFO] Downloaded to /home/runner/open3d_data/download/KnotMesh/KnotMesh.ply TriangleMesh with 1440 points and 2880 triangles. Vertices: [[ 4.51268387 28.68865967 -76.55680847] [ 7.63622284 35.52046967 -69.78063965] [ 6.21986008 44.22465134 -64.82303619] ... [-22.12651634 31.28466606 -87.37570953] [-13.91188431 25.4865818 -86.25827026] [ -5.27768707 23.36245346 -81.43279266]] Triangles: [[ 0 12 13] [ 0 13 1] [ 1 13 14] ... [1438 11 1439] [1439 11 0] [1439 0 1428]]
TriangleMesh 类有几个数据字段,如顶点和三角形。Open3D 通过 numpy 提供了对这些字段的直接内存访问。
2、可视化 3D mesh
print("Try to render a mesh with normals (exist: " +
str(mesh.has_vertex_normals()) + ") and colors (exist: " +
str(mesh.has_vertex_colors()) + ")")
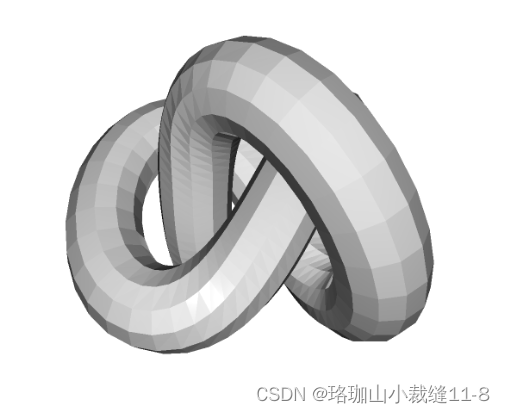
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh])
print("A mesh with no normals and no colors does not look good.")Try to render a mesh with normals (exist: False) and colors (exist: False)
没有法线和颜色的网格看起来并不好。
您可以旋转和移动网格,但网格被涂上了统一的灰色,看起来并不立体。原因是当前网格没有顶点或面的法线。因此使用的是统一颜色着色,而不是更复杂的 Phong 着色。
3、表面法线估算( Surface normal estimation )
让我们用表面法线绘制网格。
print("Computing normal and rendering it.")
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
print(np.asarray(mesh.triangle_normals))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh])Computing normal and rendering it. [[ 0.79164373 -0.53951444 0.28674793] [ 0.8319824 -0.53303008 0.15389681] [ 0.83488162 -0.09250101 0.54260136] ... [ 0.16269924 -0.76215917 -0.6266118 ] [ 0.52755226 -0.83707495 -0.14489352] [ 0.56778973 -0.76467734 -0.30476777]]
它使用了 compute_vertex_normals 和 paint_uniform_color 这两个网格成员函数。
4、网格裁剪( Crop mesh)
我们通过直接操作网格的 triangle 和 triangle_normals 数据字段来移除一半的曲面。这一操作通过 numpy.Net 技术完成。
print("We make a partial mesh of only the first half triangles.")
mesh1 = copy.deepcopy(mesh)
mesh1.triangles = o3d.utility.Vector3iVector(
np.asarray(mesh1.triangles)[:len(mesh1.triangles) // 2, :])
mesh1.triangle_normals = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(
np.asarray(mesh1.triangle_normals)[:len(mesh1.triangle_normals) // 2, :])
print(mesh1.triangles)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh1])We make a partial mesh of only the first half triangles. std::vector<Eigen::Vector3i> with 1440 elements. Use numpy.asarray() to access data.
5、上色( Paint mesh )
paint_uniform_color 为网格绘制统一的颜色。颜色采用 RGB 空间,范围为 [0,1]。
print("Painting the mesh")
mesh1.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh1])Painting the mesh
6、网格特性( Mesh properties )
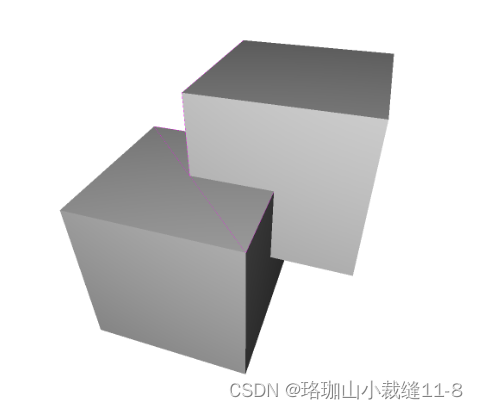
三角形网格有几个属性可以用 Open3D 进行测试。其中一个重要属性是流形属性,我们可以测试三角形网格是否为边缘流形 is_edge_manifold,是否为顶点流形 is_vertex_manifold。如果每条边都包围着一个或两个三角形,那么三角形网格就是边缘流形。函数 is_edge_manifold 有一个 bool 参数 allow_boundary_edges,用于定义是否允许边界边缘。此外,如果顶点星形是边缘流形且边缘连接(例如,两个或多个面仅由一个顶点而非一条边连接),则该三角形网格是顶点流形。
另一个属性是自交测试。如果网格中存在与另一个网格相交的三角形,函数 is_self_intersecting 返回 True。不漏水网格可以定义为边缘流形、顶点流形且不自交的网格。在 Open3D 中,函数 is_watertight 实现了这种检查。
我们还可以测试三角形网格是否可定向,即三角形的定向方式可以使所有法线都指向外部。Open3D 中的相应函数称为 is_orientable。
下面的代码根据这些属性测试了一些三角形网格,并将结果可视化。非网格边缘显示为红色,边界边缘显示为绿色,非网格顶点显示为绿色点,自交三角形显示为粉色。
def check_properties(name, mesh):
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
edge_manifold = mesh.is_edge_manifold(allow_boundary_edges=True)
edge_manifold_boundary = mesh.is_edge_manifold(allow_boundary_edges=False)
vertex_manifold = mesh.is_vertex_manifold()
self_intersecting = mesh.is_self_intersecting()
watertight = mesh.is_watertight()
orientable = mesh.is_orientable()
print(name)
print(f" edge_manifold: {edge_manifold}")
print(f" edge_manifold_boundary: {edge_manifold_boundary}")
print(f" vertex_manifold: {vertex_manifold}")
print(f" self_intersecting: {self_intersecting}")
print(f" watertight: {watertight}")
print(f" orientable: {orientable}")
geoms = [mesh]
if not edge_manifold:
edges = mesh.get_non_manifold_edges(allow_boundary_edges=True)
geoms.append(o3dtut.edges_to_lineset(mesh, edges, (1, 0, 0)))
if not edge_manifold_boundary:
edges = mesh.get_non_manifold_edges(allow_boundary_edges=False)
geoms.append(o3dtut.edges_to_lineset(mesh, edges, (0, 1, 0)))
if not vertex_manifold:
verts = np.asarray(mesh.get_non_manifold_vertices())
pcl = o3d.geometry.PointCloud(
points=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(np.asarray(mesh.vertices)[verts]))
pcl.paint_uniform_color((0, 0, 1))
geoms.append(pcl)
if self_intersecting:
intersecting_triangles = np.asarray(
mesh.get_self_intersecting_triangles())
intersecting_triangles = intersecting_triangles[0:1]
intersecting_triangles = np.unique(intersecting_triangles)
print(" # visualize self-intersecting triangles")
triangles = np.asarray(mesh.triangles)[intersecting_triangles]
edges = [
np.vstack((triangles[:, i], triangles[:, j]))
for i, j in [(0, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0)]
]
edges = np.hstack(edges).T
edges = o3d.utility.Vector2iVector(edges)
geoms.append(o3dtut.edges_to_lineset(mesh, edges, (1, 0, 1)))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries(geoms, mesh_show_back_face=True)knot_mesh_data = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
knot_mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh_data.path)
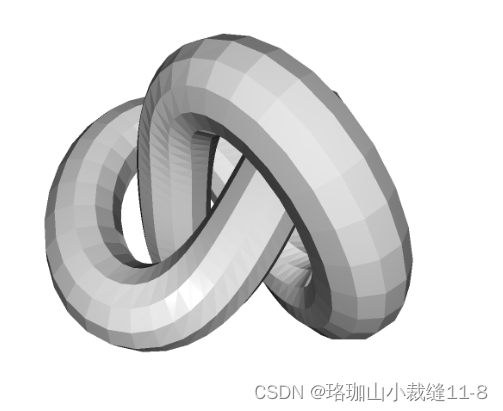
check_properties('KnotMesh', knot_mesh)
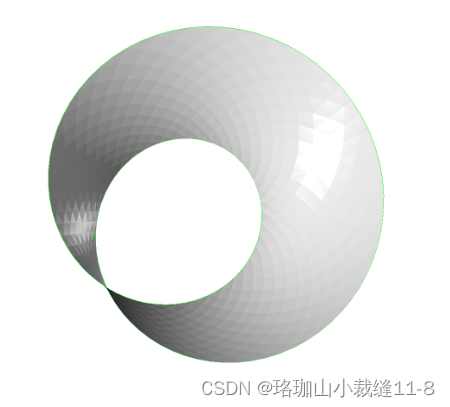
check_properties('Mobius', o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_mobius(twists=1))
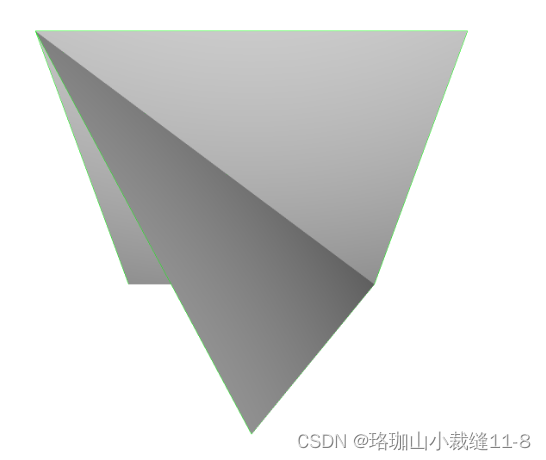
check_properties("non-manifold edge", o3dtut.get_non_manifold_edge_mesh())
check_properties("non-manifold vertex", o3dtut.get_non_manifold_vertex_mesh())
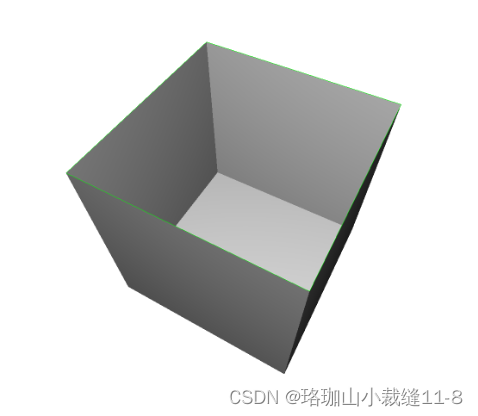
check_properties("open box", o3dtut.get_open_box_mesh())
check_properties("intersecting_boxes", o3dtut.get_intersecting_boxes_mesh())KnotMesh edge_manifold: True edge_manifold_boundary: True vertex_manifold: True self_intersecting: False watertight: True orientable: True
Mobius edge_manifold: True edge_manifold_boundary: False vertex_manifold: True self_intersecting: False watertight: False orientable: False
non-manifold edge edge_manifold: False edge_manifold_boundary: False vertex_manifold: True self_intersecting: False watertight: False orientable: True
non-manifold vertex edge_manifold: True edge_manifold_boundary: True vertex_manifold: False self_intersecting: False watertight: False orientable: True
open box edge_manifold: True edge_manifold_boundary: False vertex_manifold: True self_intersecting: False watertight: False orientable: True
intersecting_boxes edge_manifold: True edge_manifold_boundary: True vertex_manifold: True self_intersecting: True watertight: False orientable: True # visualize self-intersecting triangles
7、Mesh filtering
Open3D 包含许多过滤网格的方法。下面我们将展示用于平滑噪声三角形网格的滤波器。
Average filter
最简单的滤波器是平均滤波器。一个给定的顶点vi由相邻顶点N的平均值给出
如下代码所示,该滤波器可用于对网格进行去噪处理。函数 filter_smooth_simple 中的参数 number_of_iterations 定义了滤波器应用于网格的频率。
print('create noisy mesh')
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh_in = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
vertices = np.asarray(mesh_in.vertices)
noise = 5
vertices += np.random.uniform(0, noise, size=vertices.shape)
mesh_in.vertices = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(vertices)
mesh_in.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in])
print('filter with average with 1 iteration')
mesh_out = mesh_in.filter_smooth_simple(number_of_iterations=1)
mesh_out.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out])
print('filter with average with 5 iterations')
mesh_out = mesh_in.filter_smooth_simple(number_of_iterations=5)
mesh_out.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out])create noisy mesh
filter with average with 1 iteration
filter with average with 5 iterations
Laplacian
另一个重要的网格滤波器是拉普拉斯,其定义为
其中,ʎ是滤波器的强度,wn是与相邻顶点距离相关的归一化权重。滤波器在 filter_smooth_laplacian 中实现,参数为迭代次数(number_of_iterations)和 lambda
print('filter with Laplacian with 10 iterations')
mesh_out = mesh_in.filter_smooth_laplacian(number_of_iterations=10)
mesh_out.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out])
print('filter with Laplacian with 50 iterations')
mesh_out = mesh_in.filter_smooth_laplacian(number_of_iterations=50)
mesh_out.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out])filter with Laplacian with 10 iterations
filter with Laplacian with 50 iterations
Taubin filter
平均滤波器和拉普拉斯滤波器的问题在于它们会导致三角形网格收缩。[Taubin1995]的研究表明,使用两个不同参数lameda的拉普拉斯滤波器可以防止网格收缩。该滤波器在 filter_smooth_taubin 中实现。
print('filter with Taubin with 10 iterations')
mesh_out = mesh_in.filter_smooth_taubin(number_of_iterations=10)
mesh_out.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out])
print('filter with Taubin with 100 iterations')
mesh_out = mesh_in.filter_smooth_taubin(number_of_iterations=100)
mesh_out.compute_vertex_normals()
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out])filter with Taubin with 10 iterations
filter with Taubin with 100 iterations