由于对于一些非查询操作,有时候需要保证该操作是幂等的,该帖子设计幂等注解的原理是使用AOP和反射机制获取方法的类、方法和参数,然后拼接形成一个幂等键,当下一次有重复操作过来的时候,判断该幂等键是否存放,如果存在则为”重复操作“,不继续执行;如果不存在,则为”第一次操作“,可以执行。
javaer可以在自己的项目中,加入这个点,增加项目的亮点。
1、配置依赖、配置redis
1.1、在pom文件中加入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.2、配置redis地址
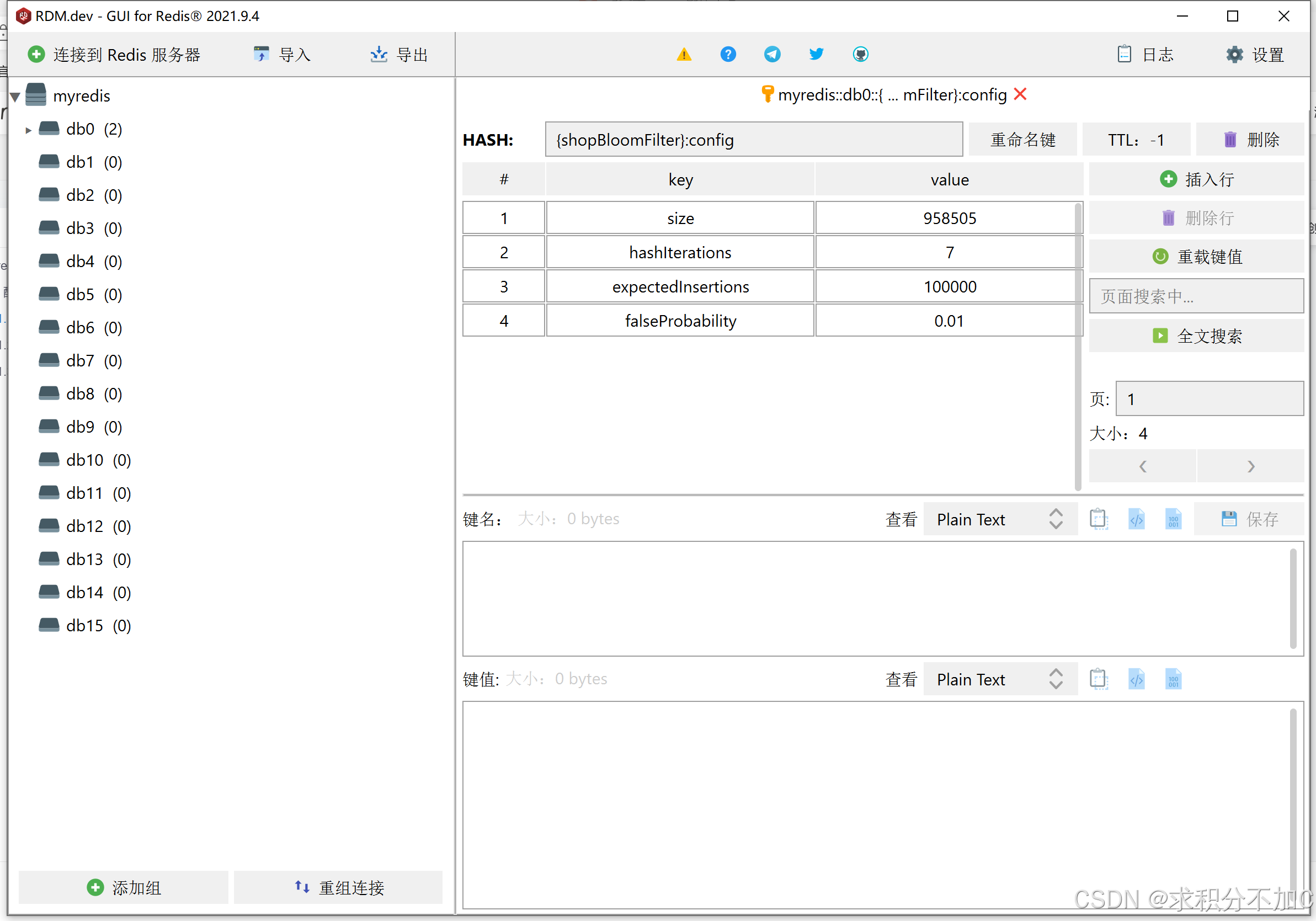
如何安装redis、获取redis的ip地址,以及redis可视化工具RDM的使用,参考以下博客的1、2点Spring Boot项目中加入布隆过滤器————实战-CSDN博客如果不想使用docker容器安装redis,可以自己下载安装redis。
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.57.111 #替换为自己redis所在服务器的ip
port: 6378 #替换为自己redis的端口
password: # 如果无密码则留空
1.3、使用RDM连接redis
如何连接,参考以下博客的1、2点Spring Boot项目中加入布隆过滤器————实战-CSDN博客
2、主要逻辑代码
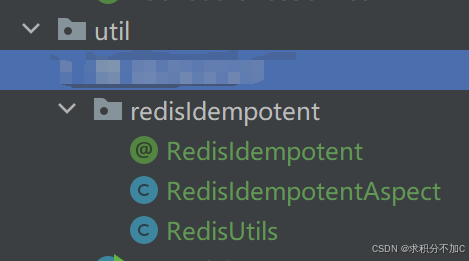
2.1、创建目录和文件
创建类似的目录结构,util与service同一级即可,并如下创建3个java文件
2.2、RedisIdempotent.java
/**
* Redis幂等性注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RedisIdempotent {
}
2.3、handleRedisIdempotent.java
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Aspect
@Component
public class RedisIdempotentAspect {
private final RedisUtils redisUtils;
public RedisIdempotentAspect(RedisUtils redisUtils) {
this.redisUtils = redisUtils;
}
/**
* 定义Pointcut,用于拦截service包中的所有方法
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(redisIdempotent)")
public void redisIdempotentMethods(RedisIdempotent redisIdempotent) {
}
/**
* 定义环绕通知,处理幂等性逻辑
*/
@Around("redisIdempotentMethods(redisIdempotent)")
public Object handleRedisIdempotent(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RedisIdempotent redisIdempotent) throws Throwable {
// 生成幂等键
String key = generateKey(joinPoint);
if (key == null || key.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("无法生成幂等键");
}
boolean success = redisUtils.setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
if (!success) {
throw new IllegalStateException("重复操作");
// //这里可使用自己定义的结果返回类包裹信息,就可以不抛出错误
}
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
// 可选:操作完成后清理key,视业务需求决定是否需要
}
}
/**
* 动态生成幂等键
*/
private String generateKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 获取类名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
// 获取方法名
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
// 获取参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String argsString = Arrays.toString(args);
// 原始键内容
String rawKey = String.format("%s:%s:%s", className, methodName, argsString);
// 对键进行MD5编码
return "IDEMPOTENT:" + md5(rawKey);
}
private String md5(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] hashBytes = md.digest(input.getBytes());
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : hashBytes) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("MD5算法不可用", e);
}
}
}在该代码里,使用的是这个,虽然可以用但不严谨,因为更严谨一点,我们只运行幂等注解被我们的几题的service类里的方法使用,因为如果用在其他类的方法上的话,会造成同一个操作出现两个不同的幂等键,造成混乱。
@Pointcut("@annotation(idempotent)")
所以建议这一行注释掉,然后使用下面面这一行代码,但包的路径需要换
@Pointcut("execution(* com.xxx.service..*(..)) && @annotation(redisIdempotent)")2.4、RedisUtils
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Component
public class RedisUtils {
private final StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public RedisUtils(StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
public boolean setIfAbsent(String key, String value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value, timeout, unit);
return result != null && result;
}
public void delete(String key) {
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
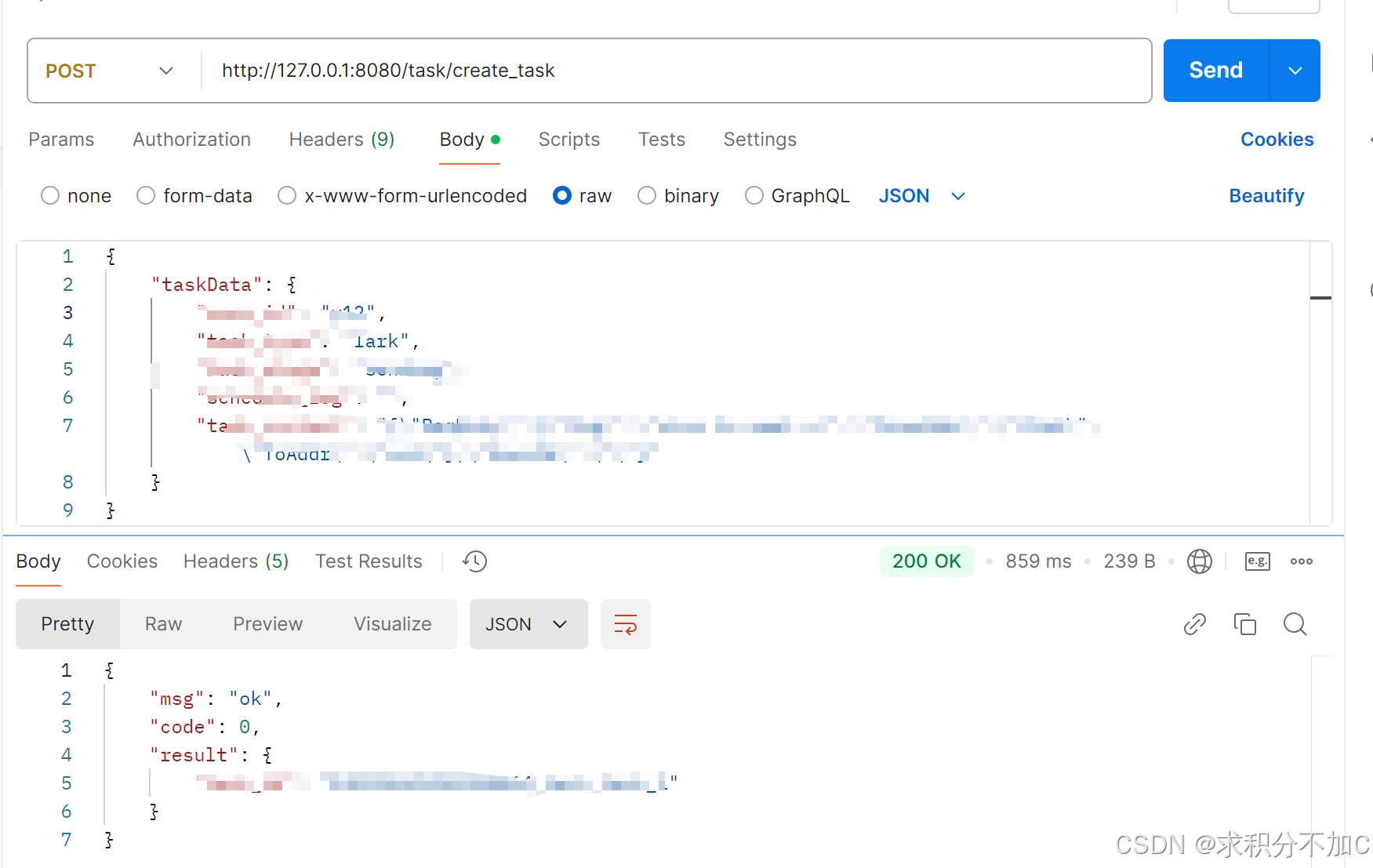
3、在业务代码上测试
@RedisIdempotent只要把注解扣在方法头上就能用了,如下
@Override
@RedisIdempotent
public <T> ReturnStatus<T> createTask(TaskRequest TaskRequest) {
//业务代码
}以下是演示,使用postman调用createTask方法
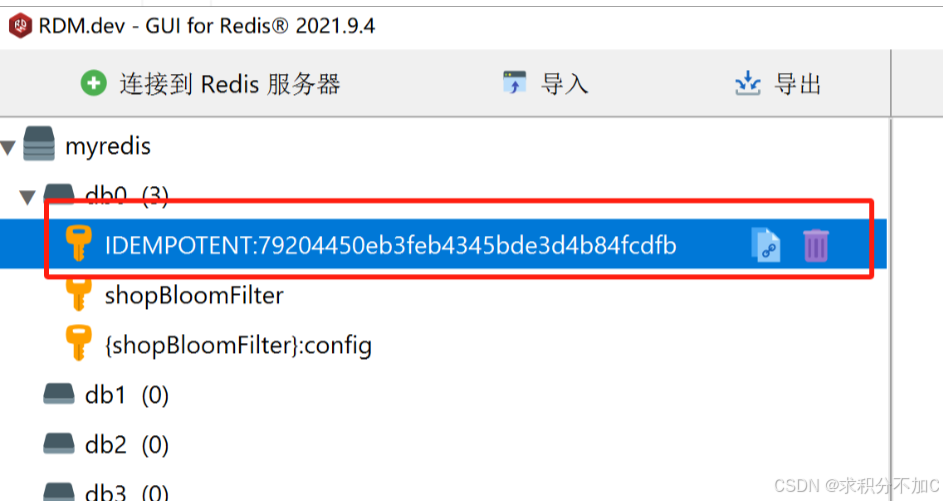
查看RDM中redis的数据
redis幂等键存在,同一个接口同样的参数再调用一次postman
因为已经存在幂等键了,调用失败,再查看idea控制台打印的日志,有”重复操作“的信息,符合实际,测试成功