5.1登录用户数据获取
5.1.1 SecurityContextHolder
Spring Security 会将登录用户数据保存在 Session 中,但是,为了使用方便,Spring Security在此基础上还做了一些改进,其中最主要的一个变化就是线程绑定:当用户登录成功后,Spring Security 会将登录成功的用户信息保存到 SecurityContextHolder 中。
SecurityContextHolder 中的数据保存默认是通过ThreadLocal 来实现的,使用 ThreadLocal 创建的变量只能被当前线程访问,不能被其他线程访问和修改,也就是用户数据和请求线程绑定在一起。当登录请求处理完毕后,Spring Security 会将 SecurityContextHolder 中的数据拿出来保存到 Session 中,同时将 SecurityContexHolder 中的数据清空。以后每当有请求到来时,Spring Security 就会先从 Session 中取出用户登录数据,保存到SecurityContextHolder 中,方便在该请求的后续处理过程中使用,同时在请求结束时将 SecurityContextHolder 中的数据拿出来保存到 Session 中,然后将SecurityContextHolder 中的数据清空。
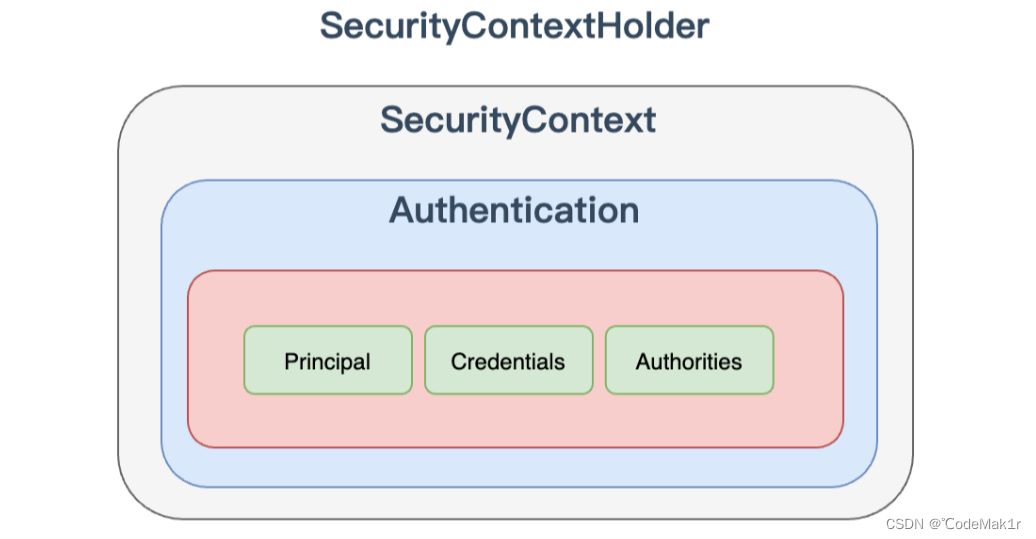
实际上 SecurityContextHolder 中存储是 SecurityContext,在 SecurityContext 中存储是 Authentication
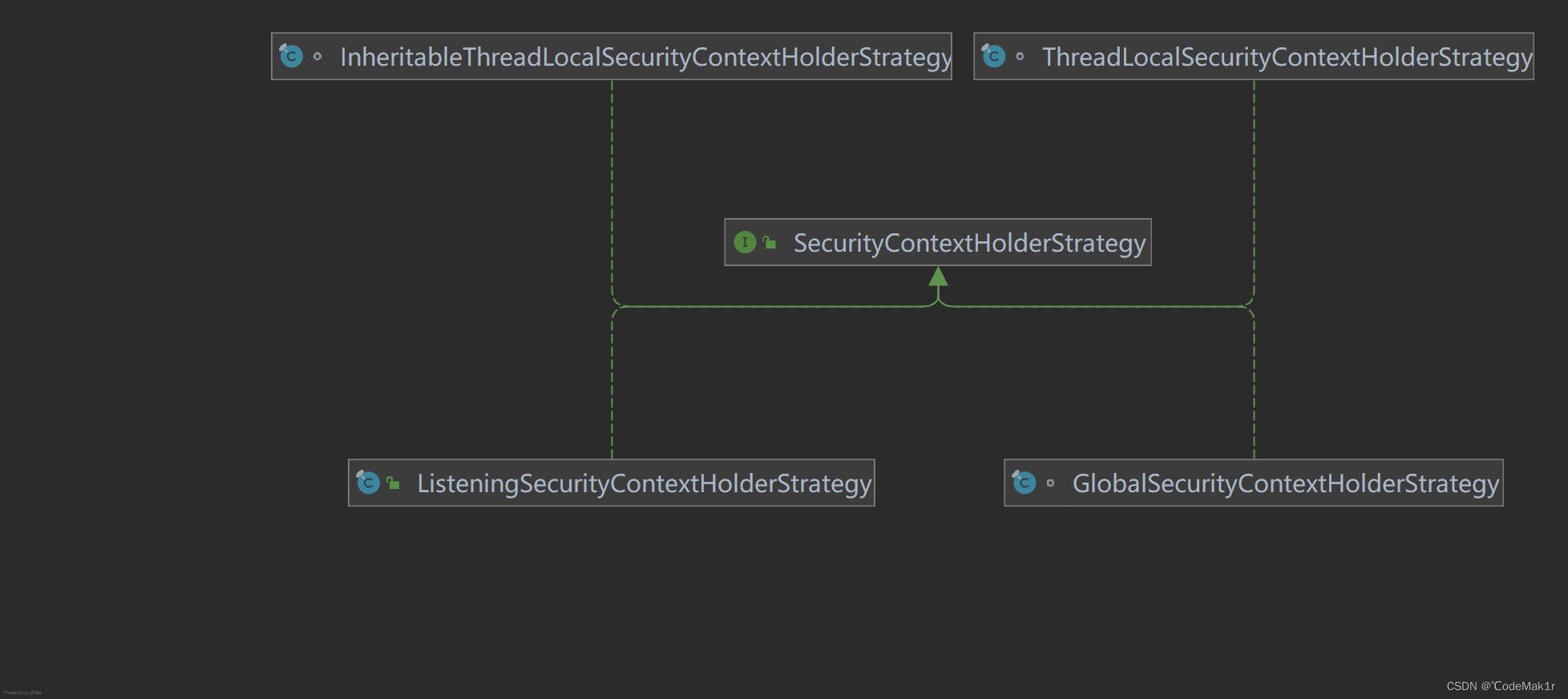
这种设计是典型的策略设计模式:
SecurityContextHolder.java
public class SecurityContextHolder {
public static final String MODE_THREADLOCAL = "MODE_THREADLOCAL";
public static final String MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL = "MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL";
public static final String MODE_GLOBAL = "MODE_GLOBAL";
private static final String MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED = "MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED";
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTY = "spring.security.strategy";
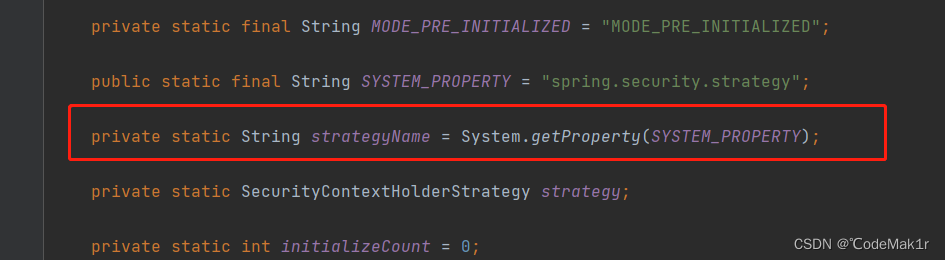
private static String strategyName = System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY);
private static SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy;
private static int initializeCount = 0;
static {
initialize();
}
private static void initialize() {
initializeStrategy();
initializeCount++;
}
private static void initializeStrategy() {
if (MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED.equals(strategyName)) {
Assert.state(strategy != null, "When using " + MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED
+ ", setContextHolderStrategy must be called with the fully constructed strategy");
return;
}
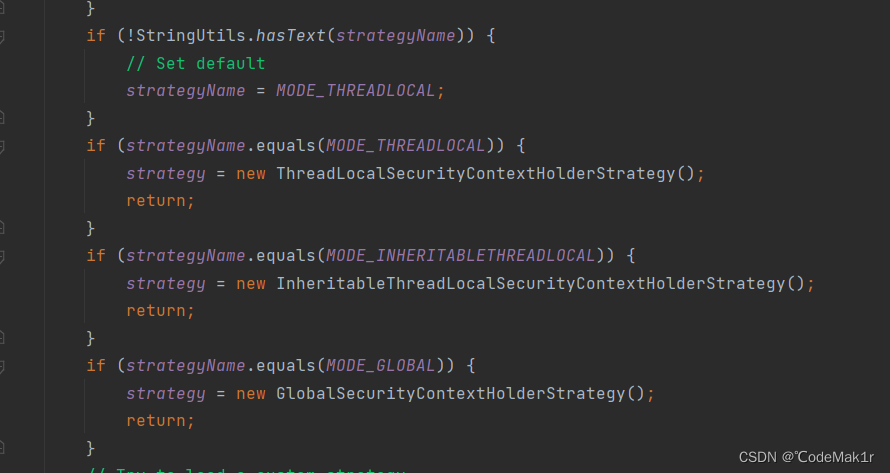
if (!StringUtils.hasText(strategyName)) {
// Set default
strategyName = MODE_THREADLOCAL;
}
if (strategyName.equals(MODE_THREADLOCAL)) {
strategy = new ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();
return;
}
if (strategyName.equals(MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL)) {
strategy = new InheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();
return;
}
if (strategyName.equals(MODE_GLOBAL)) {
strategy = new GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();
return;
}
// Try to load a custom strategy
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(strategyName);
Constructor<?> customStrategy = clazz.getConstructor();
strategy = (SecurityContextHolderStrategy) customStrategy.newInstance();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
ReflectionUtils.handleReflectionException(ex);
}
}
/**
* Explicitly clears the context value from the current thread.
*/
public static void clearContext() {
strategy.clearContext();
}
/**
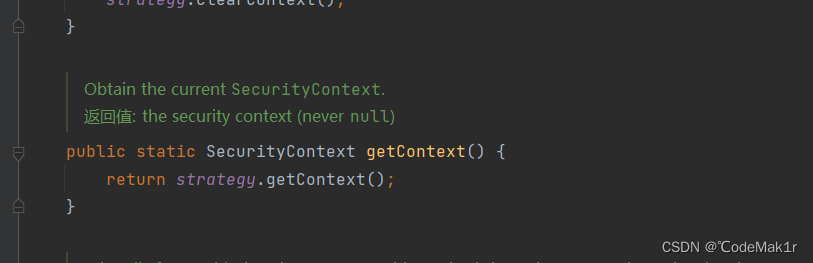
* Obtain the current <code>SecurityContext</code>.
* @return the security context (never <code>null</code>)
*/
public static SecurityContext getContext() {
return strategy.getContext();
}
/**
* Primarily for troubleshooting purposes, this method shows how many times the class
* has re-initialized its <code>SecurityContextHolderStrategy</code>.
* @return the count (should be one unless you've called
* {@link #setStrategyName(String)} or
* {@link #setContextHolderStrategy(SecurityContextHolderStrategy)} to switch to an
* alternate strategy).
*/
public static int getInitializeCount() {
return initializeCount;
}
/**
* Associates a new <code>SecurityContext</code> with the current thread of execution.
* @param context the new <code>SecurityContext</code> (may not be <code>null</code>)
*/
public static void setContext(SecurityContext context) {
strategy.setContext(context);
}
/**
* Changes the preferred strategy. Do <em>NOT</em> call this method more than once for
* a given JVM, as it will re-initialize the strategy and adversely affect any
* existing threads using the old strategy.
* @param strategyName the fully qualified class name of the strategy that should be
* used.
*/
public static void setStrategyName(String strategyName) {
SecurityContextHolder.strategyName = strategyName;
initialize();
}
/**
* Use this {@link SecurityContextHolderStrategy}.
*
* Call either {@link #setStrategyName(String)} or this method, but not both.
*
* This method is not thread safe. Changing the strategy while requests are in-flight
* may cause race conditions.
*
* {@link SecurityContextHolder} maintains a static reference to the provided
* {@link SecurityContextHolderStrategy}. This means that the strategy and its members
* will not be garbage collected until you remove your strategy.
*
* To ensure garbage collection, remember the original strategy like so:
*
* <pre>
* SecurityContextHolderStrategy original = SecurityContextHolder.getContextHolderStrategy();
* SecurityContextHolder.setContextHolderStrategy(myStrategy);
* </pre>
*
* And then when you are ready for {@code myStrategy} to be garbage collected you can
* do:
*
* <pre>
* SecurityContextHolder.setContextHolderStrategy(original);
* </pre>
* @param strategy the {@link SecurityContextHolderStrategy} to use
* @since 5.6
*/
public static void setContextHolderStrategy(SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy) {
Assert.notNull(strategy, "securityContextHolderStrategy cannot be null");
SecurityContextHolder.strategyName = MODE_PRE_INITIALIZED;
SecurityContextHolder.strategy = strategy;
initialize();
}
/**
* Allows retrieval of the context strategy. See SEC-1188.
* @return the configured strategy for storing the security context.
*/
public static SecurityContextHolderStrategy getContextHolderStrategy() {
return strategy;
}
/**
* Delegates the creation of a new, empty context to the configured strategy.
*/
public static SecurityContext createEmptyContext() {
return strategy.createEmptyContext();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SecurityContextHolder[strategy='" + strategy.getClass().getSimpleName() + "'; initializeCount="
+ initializeCount + "]";
}
}
- 三种策略详细解释:
MODE THREADLOCAL:这种存放策略是将 SecurityContext 存放在 ThreadLocal中,大家知道 Threadlocal 的特点是在哪个线程中存储就要在哪个线程中读取,这其实非常适合 web 应用,因为在默认情况下,一个请求无论经过多少
Filter 到达 Servlet,都是由一个线程来处理的,这也是 SecurityContextHolder
的默认存储策略,这种存储策略意味着如果在具体的业务处理代码中,开启了子线程,在子线程中去获取登录用户数据,就会获取不到。
MODE INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL:这种存储模式适用于多线程环境,如果希望在子线程中也能够获取到登录用户数据,那么就可以使用这种存储模式,使用时需要在VM
Options单独进行配置(实际上是将父线程的用户数据复制一份到子线程)。
MODE GLOBAL:这种存储模式实际上是将数据保存在一个全局静态变量中,在 JavaWeb开发中,这种模式很少使用到(了解即可)。
- 其中的获取SecurityContext 是根据策略获取的,也就是程序的运行参数设置的是那种策略模式
- 通过读取系统设置的参数然后进行匹配对strategy实例化不同的实现类,使用不同的策略模式
5.1.2SecurityContextHolderStrategy
- SecurityContextHolderStrategy通过策略模式去获取SecurityContext
private static SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy;
- 进入SecurityContextHolderStrategy
public interface SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
void clearContext();
SecurityContext getContext();
void setContext(SecurityContext context);
SecurityContext createEmptyContext();
}
- SecurityContextHolderStrategy
通过 SecurityContextHolder 可以得知,SecurityContextHolderStrategy 接口用来定义存储策略方法:
接口中一共定义了四个方法:
clearContext:该方法用来清除存储的 SecurityContext对象。
getContext:该方法用来获取存储的 SecurityContext 对象。
setContext:该方法用来设置存储的 SecurityContext 对象。
createEmptyContext:该方法则用来创建一个空的 SecurityContext 对象。
- 三种模式对应SecurityContextHolderStrategy 的三种实现类
MODE THREADLOCAL:ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
MODE INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL:InheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
MODE GLOBAL:GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
5.1.3SecurityContext
- 通过SecurityContextHolderStrategy的getContext返回的SecurityContext
public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable {
/**
* Obtains the currently authenticated principal, or an authentication request token.
* @return the <code>Authentication</code> or <code>null</code> if no authentication
* information is available
*/
Authentication getAuthentication();
/**
* Changes the currently authenticated principal, or removes the authentication
* information.
* @param authentication the new <code>Authentication</code> token, or
* <code>null</code> if no further authentication information should be stored
*/
void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication);
}
- SecurityContext 包含的Authentication
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
//权限结合,可使用AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin, ROLE_ADMIN")返回字符串权限集合
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
//用户名密码认证时可以理解为密码
Object getCredentials();
//认证时包含的一些信息。如remoteAddress、sessionId
Object getDetails();
//用户名密码认证时可理解时用户名
Object getPrincipal();
//是否被认证,认证为true
boolean isAuthenticated();
//设置是否被认证
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
5.1.4 代码中获取认证之后的用户数据
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("Hello Spring Security!");
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();//获得认证信息
System.out.println("authentication.getName() = " + authentication.getName());
System.out.println("authentication.getAuthorities() = " + authentication.getAuthorities());
System.out.println("authentication.getCredentials() = " + authentication.getCredentials());
System.out.println("authentication.getDetails() = " + authentication.getDetails());
System.out.println("authentication.getPrincipal() = " + authentication.getPrincipal());
User principal = (User) authentication.getPrincipal();//返回值类型为User时需要进行强制转换 org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User
System.out.println("principal.getUsername() = " + principal.getUsername());
System.out.println("principal.getPassword() = " + principal.getPassword());
System.out.println("principal.getAuthorities() = " + principal.getAuthorities());
return "hello spring security!";
}
}
启动服务,登录成功后访问:http://localhost:8080/hello,获得认证之后的用户数据。
IDEA控制台输出结果:
Hello Spring Security!
authentication.getName() = root
authentication.getAuthorities() = [ROLE_admin, ROLE_super]
authentication.getCredentials() = null
authentication.getDetails() = WebAuthenticationDetails [RemoteIpAddress=0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, SessionId=15FEA49E4810C435286FD8B6D188C87F]
authentication.getPrincipal() = org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User [Username=root, Password=[PROTECTED], Enabled=true, AccountNonExpired=true, credentialsNonExpired=true, AccountNonLocked=true, Granted Authorities=[ROLE_admin, ROLE_super]]
principal.getUsername() = root
principal.getPassword() = null
principal.getAuthorities() = [ROLE_admin, ROLE_super]
5.1.5 多线程情况下获取用户数据
package com.study.controller;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @ClassName HelloController
* @Description TODO
* @Date 2022/7/6 12:12
* @Version 1.0
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("Hello Spring Security!");
new Thread(() -> {
Authentication Authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
User childPrincipal = (User) Authentication.getPrincipal();
System.out.println("Principal.getUsername() = " + Principal.getUsername());
System.out.println("Principal.getPassword() = " + Principal.getPassword());
System.out.println("Principal.getAuthorities() = " + Principal.getAuthorities());
}).start();
return "hello spring security!";
}
}
启动服务,访问:http://localhost:8080/hello,获得认证之后的用户数据。
控制台报错
Exception in thread "Thread-2" java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.study.controller.HelloController.lambda$hello$0(HelloController.java:35)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:750)
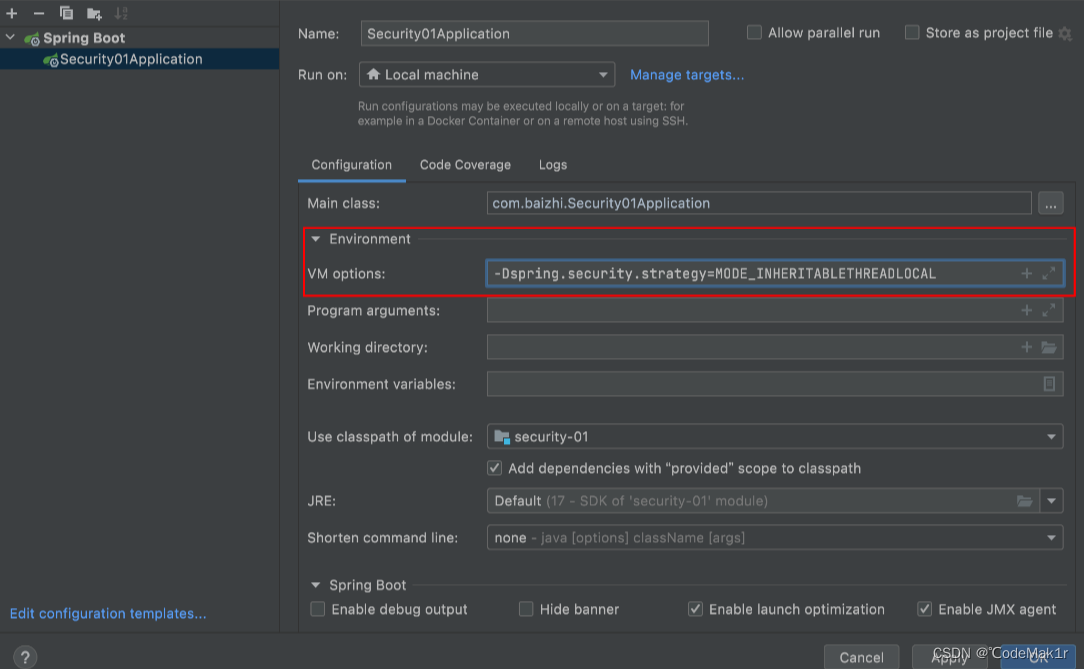
从上面可以看到默认策略,是无法在子线程中获取用户信息,如果需要在子线程中获取必须使用第二种策略,默认策略是通过 System.getProperty 加载的,因此我们可以通过增加 VM Options 参数进行修改。
-Dspring.security.strategy=MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL
IDEA控制台输出结果:
Hello Spring Security!
Principal.getUsername() = root
Principal.getPassword() = null
Principal.getAuthorities() = [ROLE_admin, ROLE_super]
5.1.6 页面上获取用户信息
- pom.xml引入依赖,可以直接在thymeleaf页面直接获取springsecurity信息
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
- logout.html页面加入命名空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security">
- logout.html页面中获取用户信息
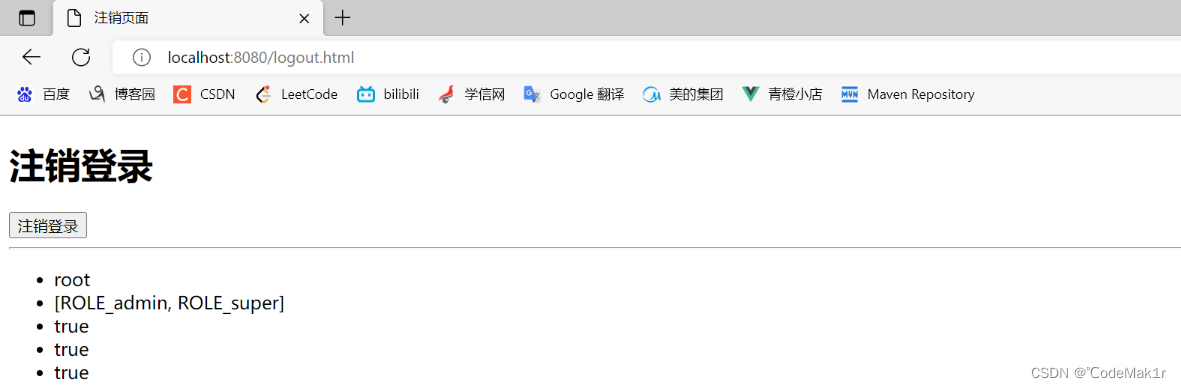
<!--获取认证用户名-->
<ul>
<li sec:authentication="principal.username"></li>
<li sec:authentication="principal.authorities"></li>
<li sec:authentication="principal.accountNonExpired"></li>
<li sec:authentication="principal.accountNonLocked"></li>
<li sec:authentication="principal.credentialsNonExpired"></li>
</ul>
启动服务,登录成功后访问logout.html:http://localhost:8080/logout.html