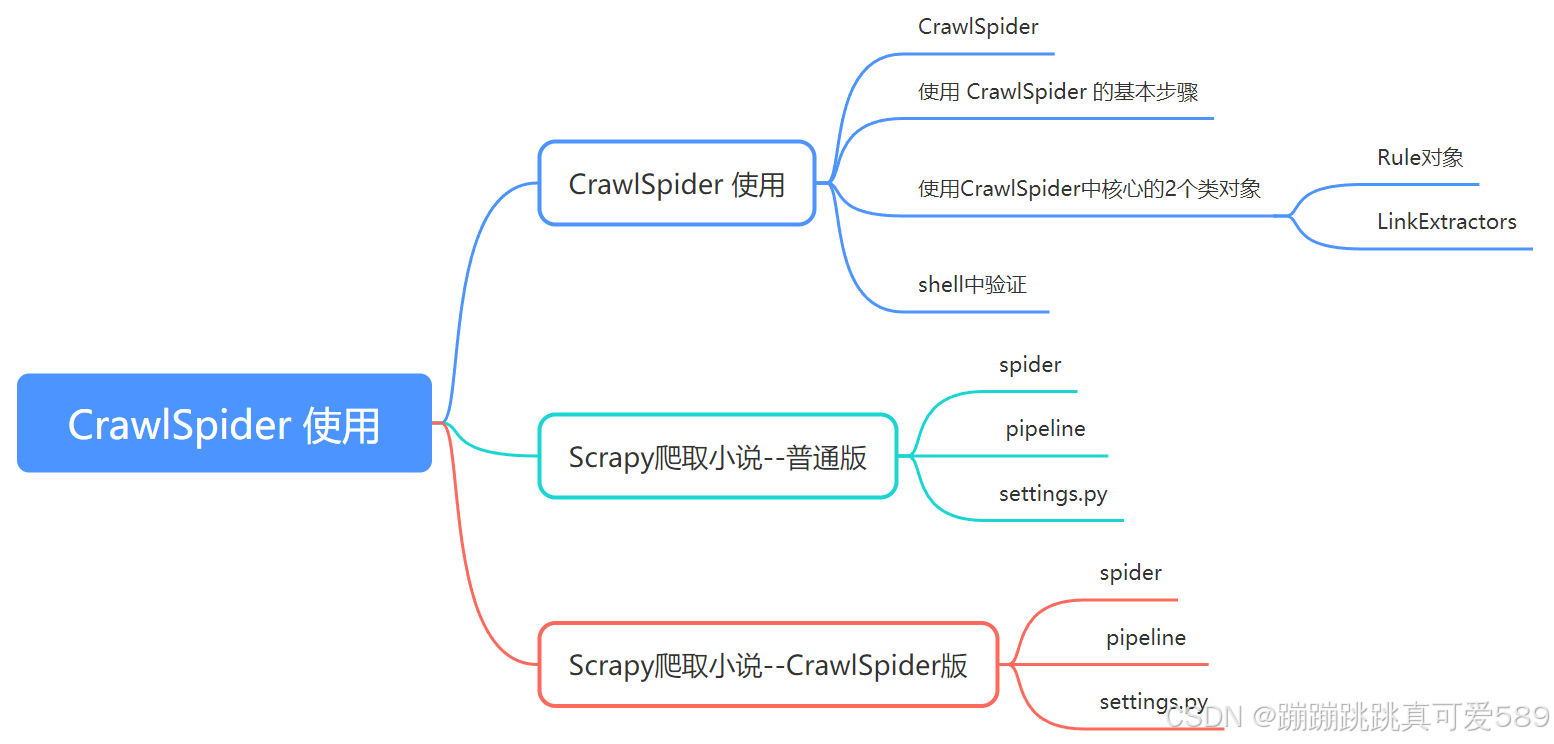
一、CrawlSpider 使用
1.1、CrawlSpider
CrawSpiders 是 Scrapy 框架中的一个特殊爬虫类,它用于处理需要跟随链接并抓取多个页面的情况。相比于基本的 Spider 类,CrawSpiders 提供了一个更灵活、更强大的方式来定义爬取规则。
在Scrapy中Spider是所有爬虫的基类,而CrawSpiders就是Spider的派生类。
适用于先爬取start_url列表中的网页,再从爬取的网页中获取link并继续爬取的工作
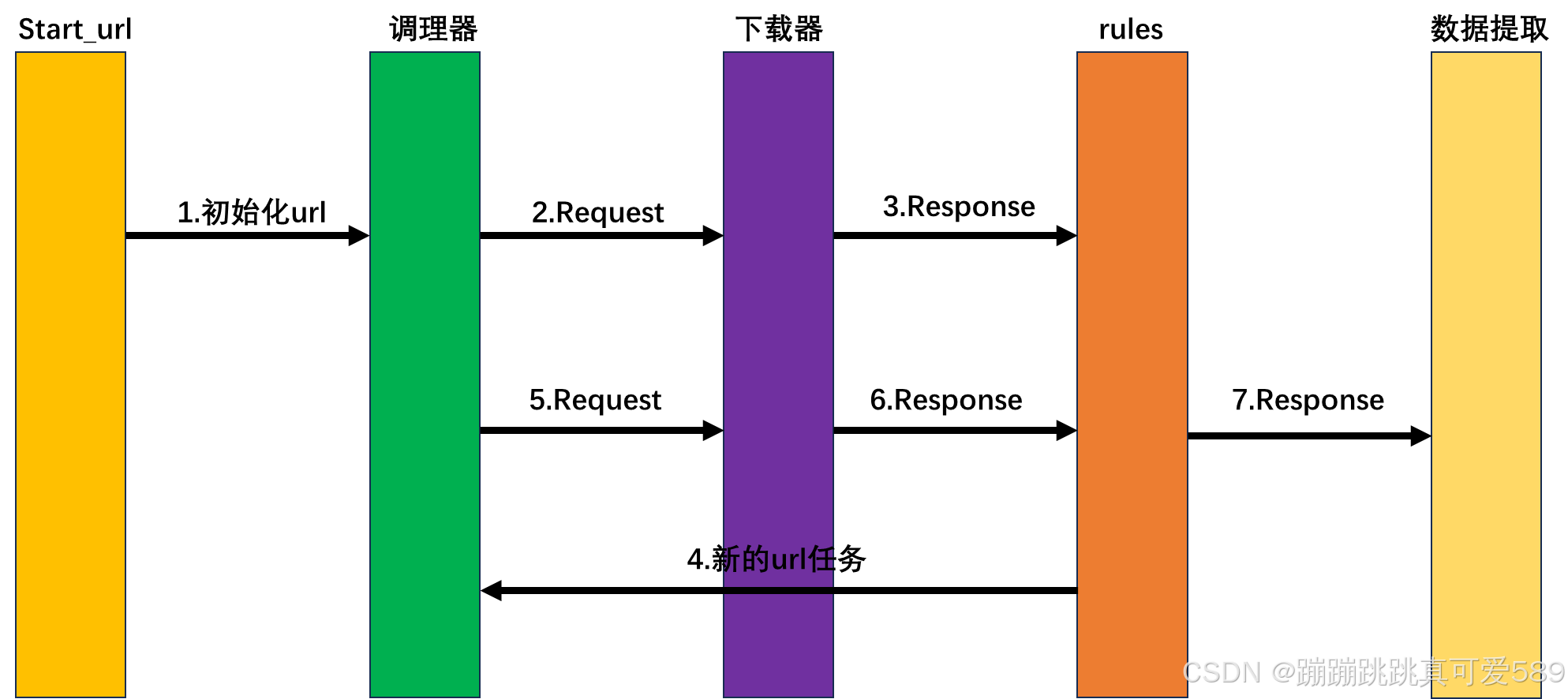
1.2、使用 CrawlSpider 的基本步骤
定义爬虫类:从 CrawlSpider 继承并定义爬虫类。
设置起始 URL:通过 start_urls 属性定义要开始爬取的 URL。
定义解析规则:通过 rules 属性设置爬取规则,这通常包括为页面提取数据和跟随链接的规则。
创建CrawlSpider
scrapy genspider -t crawl 爬虫名 (allowed_url)
1.3、使用CrawlSpider中核心的2个类对象
1.3.1、Rule对象
Rule类与CrawlSpider类都位于
scrapy.contrib.spiders模块中
class scrapy.contrib.spiders.Rule(
link_extractor,
callback=None,
cb_kwargs=None,
follow=None,
process_links=None,
process_request=None)
参数含义:
link_extractor为LinkExtractor,用于定义需要提取的链接
callback参数:当link_extractor获取到链接时参数所指定的值作为回调函数
注意 回调函数尽量不要用parse方法,crawlspider已使用了parse方法
follow:指定了根据该规则从response提取的链接是否需要跟进。当callback为None,默认值为True
process_links:主要用来过滤由link_extractor获取到的链接
process_request:主要用来过滤在rule中提取到的request
1.3.2、LinkExtractors
顾名思义,链接提取器
response对象中获取链接,并且该链接会被接下来爬取 每个LinkExtractor有唯一的公共方法是 extract_links(),它接收一个 Response 对象,并返回一个 scrapy.link.Link 对象
class scrapy.linkextractors.LinkExtractor(
allow = (),
deny = (),
allow_domains = (),
deny_domains = (),
deny_extensions = None,
restrict_xpaths = (),
tags = ('a','area'),
attrs = ('href'),
canonicalize = True,
unique = True,
process_value = None
)
allow:满足括号中“正则表达式”的值会被提取,如果为空,则全部匹配。
deny:与这个正则表达式(或正则表达式列表)不匹配的URL一定不提取。
allow_domains:会被提取的链接的domains。
deny_domains:一定不会被提取链接的domains。
restrict_xpaths:使用xpath表达式,和allow共同作用过滤链接(只选到节点,不选到属性)
restrict_css:使用css表达式,和allow共同作用过滤链接(只选到节点,不选到属性)
1.4、shell中验证
首先运行
scrapy shell 'https://www.52wx.com/335_335954/131105239.html'
继续import相关模块:
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
提取当前网页中获得的链接
link = LinkExtractor(restrict_xpaths=(r'//div[@class="section-opt m-bottom-opt"]/a[3]'))
调用LinkExtractor实例的extract_links()方法查询匹配结果
link.extract_links(response)
- callback后面函数名用引号引起
- 函数名不要用parse
- 参数的括号嵌套,不要出问题
二、Scrapy爬取小说--普通版
spider
import scrapy
class XiaoshuoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "xiaoshuo"
allowed_domains = ["52wx.com"]
start_urls = ["https://www.52wx.com/335_335954/131105239.html"]
def parse(self, response):
name=response.xpath('//div[@class="reader-main"]/h1/text()').get()
new_url=response.xpath('//div[@class="section-opt m-bottom-opt"]/a[3]/@href').get()
content=response.xpath('//div[@class="content"]/text()').extract()
yield{
'name':name,
'content':content
}
next_url='https://www.52wx.com/335_335954/'+new_url
yield scrapy.Request(next_url,callback=self.parse)pipeline
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
class Scrapy03Pipeline:
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.file=open('xiaoshuo.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.file.write(item['name']+'\n')
self.file.write(''.join(item['content']).replace('\r\n',''))
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.file.close()settings.py
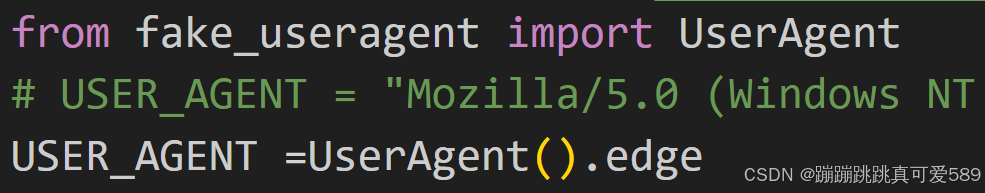
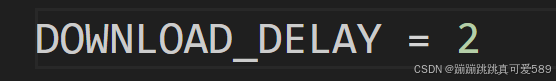
三、Scrapy爬取小说--CrawlSpider版
spider
import scrapy
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
class XsSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = "xs"
allowed_domains = ["52wx.com"]
start_urls = ["https://www.52wx.com/335_335954/"]
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(restrict_xpaths=('//div[@class="section-box"][2]/ul/li/a[1]')), callback="parse_item", follow=True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(restrict_xpaths=('//div[@class="section-opt m-bottom-opt"]/a[3]')), callback="parse_item", follow=True),
)
def parse_item(self, response):
name=response.xpath('//div[@class="reader-main"]/h1/text()').get()
content=response.xpath('//div[@class="content"]/text()').extract()
print(content)
yield{
'name':name,
'content':content
}pipeline
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
class Scrapy03Pipeline:
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.file=open('xiaoshuo.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.file.write(item['name']+'\n')
self.file.write(''.join(item['content']).replace('\r\n',''))
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.file.close()settings.py