文章目录
知识点
Vscoede配置C/C++
vscode for c/c++(ACM配置)_vscosd配置acm-CSDN博客
【VS Code】c++环境配置 && .vscode文件 && Code Runner的exe文件指定生成位置 && c++未定义标识符问题 - 稻花香里亦江湖 - 博客园
【C/C++】在VSCode中配置C/C++环境(使用gdb和code-runner两种方式配置)vscode_不言-GitCode 开源社区
Code Runner使用说明(快速运行调试代码,无需配置繁杂的环境)-CSDN博客
【整理总结】VSCode常用插件和好用配置(小白必看)_vscode 插件-CSDN博客
Visual Studio Code August 2021
最新最全 VSCODE 插件推荐(2024版)_vscode插件-CSDN博客
c_cpp_properties.json
//c_cpp_properties.json
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE"
],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.22621.0",
"compilerPath": "D:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/gcc.exe",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "gcc-x64"
},
{
"name": "C++",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE"
],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.22621.0",
"compilerPath": "D:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/g++.exe",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "gcc-x64"
},
{
"name": "MinGW64",
"intelliSenseMode": "gcc-x64",
"compilerPath": "D:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/g++.exe",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}"
],
"cppStandard": "c++17"
}
],
"version": 4
}
launch.json
//launch.json
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "C++ Launch (GDB)", // 配置名称,将会在启动配置的下拉菜单中显示
"type": "cppdbg", // 配置类型,这里只能为cppdbg
"request": "launch", // 请求配置类型,可以为launch(启动)或attach(附加)
"targetArchitecture": "x64", // 生成目标架构,一般为x86或x64
"program": "${fileDirname}/exe/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe", // 将要进行调试的程序的路径
"args": [], // 程序调试时传递给程序的命令行参数,一般设为空即可
"stopAtEntry": false, // 设为true时程序将暂停在程序入口处,一般设置为false
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}", // 调试程序时的工作目录,一般为${workspaceRoot}
"externalConsole": false, // 调试时是否显示控制台窗口,一般设置为true显示控制台
"internalConsoleOptions": "neverOpen", // 如果不设为neverOpen,调试时会跳到“调试控制台”选项卡",
"MIMode": "gdb", // 指定连接的调试器
"miDebuggerPath": "D:\\Program Files\\mingw64\\bin\\gdb.exe", // 调试器路径
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for GDB",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": false
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "Compile"
},
{
"name": "(gdb) 启动",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${fileDirname}\\exe\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe", //输入程序名称(也就是需要调试的文件),例如 ${workspaceFolder}/a.exe
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "D:\\Program Files\\mingw64\\bin\\gdb.exe", //调试的工具(mingw,bin中有gdb) /path/to/gdb
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "为 gdb 启用整齐打印",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
},
{
"description": "将反汇编风格设置为 Intel",
"text": "-gdb-set disassembly-flavor intel",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
settings.json
//settings.json
{
"files.associations": {
"*.cjson": "jsonc",
"*.wxss": "css",
"*.wxs": "javascript",
"memory": "cpp",
"deque": "cpp",
"string": "cpp",
"vector": "cpp",
"iostream": "cpp",
"array": "cpp",
"bitset": "cpp",
"string_view": "cpp",
"initializer_list": "cpp",
"regex": "cpp",
"utility": "cpp",
"valarray": "cpp",
"*.tcc": "cpp",
"optional": "cpp",
"istream": "cpp",
"ostream": "cpp",
"ratio": "cpp",
"system_error": "cpp",
"functional": "cpp",
"tuple": "cpp",
"type_traits": "cpp",
"list": "cpp",
"unordered_map": "cpp",
"unordered_set": "cpp",
"forward_list": "cpp",
"map": "cpp",
"typeindex": "cpp",
"typeinfo": "cpp",
"atomic": "cpp",
"cctype": "cpp",
"cfenv": "cpp",
"charconv": "cpp",
"chrono": "cpp",
"cinttypes": "cpp",
"clocale": "cpp",
"cmath": "cpp",
"codecvt": "cpp",
"complex": "cpp",
"condition_variable": "cpp",
"csetjmp": "cpp",
"csignal": "cpp",
"cstdarg": "cpp",
"cstddef": "cpp",
"cstdint": "cpp",
"cstdio": "cpp",
"cstdlib": "cpp",
"cstring": "cpp",
"ctime": "cpp",
"cuchar": "cpp",
"cwchar": "cpp",
"cwctype": "cpp",
"exception": "cpp",
"algorithm": "cpp",
"iterator": "cpp",
"memory_resource": "cpp",
"numeric": "cpp",
"random": "cpp",
"set": "cpp",
"fstream": "cpp",
"future": "cpp",
"iomanip": "cpp",
"iosfwd": "cpp",
"limits": "cpp",
"mutex": "cpp",
"new": "cpp",
"scoped_allocator": "cpp",
"shared_mutex": "cpp",
"sstream": "cpp",
"stdexcept": "cpp",
"streambuf": "cpp",
"thread": "cpp"
},
"C_Cpp.errorSquiggles": "Tag Parser"
}
tasks.json
//tasks.json
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Compile",
"command": "g++",
"args": [
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}/exe/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"-O0",
"-ggdb3",
"-Wall",
"-static-libgcc",
"-std=c++17",
"-finput-charset=UTF-8",
"-fexec-charset=GB18030",
"-D _USE_MATH_DEFINES"
],
"problemMatcher": {
"owner": "cpp",
"fileLocation": [
"absolute"
],
"pattern": {
"regexp": "^(.*):(\\d+):(\\d+):\\s+(warning|error):\\s+(.*)$",
"file": 1,
"line": 2,
"column": 3,
"severity": 4,
"message": 5
}
},
"type": "shell",
"group": "build",
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "always",
"focus": false,
"panel": "shared"
}
},
{
"type": "cppbuild",
"label": "C/C++: g++.exe 生成活动文件",
"command": "D:\\Program Files\\mingw64\\bin\\g++.exe",
"args": [
"-fdiagnostics-color=always",
"-g",
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}\\exe\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${fileDirname}"
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"detail": "调试器生成的任务。"
}
]
}
代码模板
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
return 0;
}
scanf,printf & cin, cout(2)
输入大量数据的速度问题
cin, cout输入数据达到1e6或1e7后会变慢,则
改为scanf,printf
or 关闭同步流
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
注意:关闭同步流后不可与scanf,printf同时使用!!!
cout的输出格式
cout默认保留小数点后4位cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<endl;保留小数点后2位
切割字符串
方法1:使用std::istringstream
std::istringstream是C++标准库中的一个输入字符串流,它允许你像从文件或其他输入流中读取数据一样从字符串中读取数据。当你从std::istringstream中读取数据时,它会自动按空格(或其他空白字符)分割字符串。
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string sentence = "This is a sample sentence.";
std::istringstream iss(sentence); //思考与 stringstream 的区别
std::string word;
std::vector<std::string> words;
// 读取单词直到没有更多数据
while (iss >> word) {
words.push_back(word);
}
// 打印结果
for (const auto& w : words) {
std::cout << w << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法2:使用正则表达式
虽然对于简单的空格分隔任务,std::istringstream更为直接和高效,但正则表达式提供了更强大的文本处理能力。如果你需要处理更复杂的分隔符(比如逗号、分号或标点符号),或者你想要在分割单词时保留标点符号(例如,将"hello,"作为一个单独的单词),那么正则表达式将是一个不错的选择。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <regex>
int main() {
std::string sentence = "This, is a sample; sentence.";
std::regex word_regex("[^\\s,;\\.]+"); // 匹配一个或多个非空白、非逗号、非分号、非句点的字符
std::sregex_token_iterator iter(sentence.begin(), sentence.end(), word_regex, 0);
std::sregex_token_iterator end;
std::vector<std::string> words(iter, end);
// 打印结果
for (const auto& w : words) {
std::cout << w << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
请注意,上面的正则表达式示例"[^\\s,;\\.]+"可能并不完全符合你的需求,因为它将逗号、分号和句点视为单词的一部分。如果你想要完全按空格分割单词,并且忽略其他所有标点符号,你可能需要调整正则表达式。但是,如果你的目的是按多种分隔符分割单词,并且保留这些分隔符作为单词的一部分,那么你可以根据需要修改正则表达式。
对于简单的空格分隔任务,推荐使用std::istringstream,因为它更简单、更直接,并且性能通常更好。对于更复杂的文本处理任务,正则表达式提供了更灵活和强大的解决方案。
stringstream和isitringstream的区别
stringstream 和 istringstream 都是 C++ 标准模板库(STL)中的类,它们提供了将字符串与输入/输出流操作相结合的功能。这两个类在功能和用途上存在一些关键的区别,具体如下:
stringstream
- 功能:
stringstream类同时支持从字符串中读取数据和向字符串中写入数据,即它支持C风格字符串的输入输出操作。这使得stringstream成为一个非常灵活的类,可以在需要同时处理字符串的读写操作时使用。 - 用途:
stringstream常用于需要将数值类型数据格式化为字符串,或者将字符串拆分为数值类型数据的场景。此外,它还可以用于字符串的拼接和格式化输出等。 - 示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stringstream ss;
ss << "Hello";
ss << " ";
ss << "World!";
cout << ss.str() << endl; // 输出: Hello World!
return 0;
}
istringstream
- 功能:
istringstream类主要用于从字符串中读取数据,它提供了类似于std::cin的接口,可以方便地从字符串中提取数据,并将其转换为不同的数据类型。但是,与stringstream不同,istringstream不支持向字符串中写入数据。 - 用途:
istringstream常用于需要从字符串中解析出多种类型数据的场景,如解析包含数字、单词等的复杂字符串。 - 示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str = "123 4.56 hello";
istringstream iss(str);
int num;
float fnum;
string word;
iss >> num >> fnum >> word;
cout << num << " " << fnum << " " << word << endl; // 输出: 123 4.56 hello
return 0;
}
总结
| stringstream | istringstream | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 同时支持从字符串中读取数据和向字符串中写入数据 | 仅支持从字符串中读取数据 |
| 用途 | 字符串的读写操作、数值类型与字符串的相互转换、字符串拼接等 | 从字符串中解析出多种类型的数据 |
| 示例 | 字符串的拼接和输出 | 从字符串中提取并转换数据 |
通过对比可以看出,stringstream 和 istringstream 在功能上各有侧重,选择哪个类取决于你的具体需求。如果你需要同时处理字符串的读写操作,那么 stringstream 是更好的选择;如果你只需要从字符串中读取数据,那么 istringstream 将更加高效和方便。
queue队列
queue的定义
队列Queue是一种常见的数据结构,其主要特点是先进先出(FIFO:First In First Out)。
在队列中,数据的插入和删除操作分别在表的不同端进行。具体来说,向队列中添加新元素的一端称为“队尾”rear,而从队列中移除元素的一端称为“队头”front.
队列和栈的区别:
栈只能知道最后插进去的元素,队列可以知道最先和最后插进去的元素;栈是后进先出,队列是先进后出
queue的语法
| 例子 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| q.front(); | 返回队首元素 |
| q.back(); | 返回队尾元素 |
| q.push(); | 在队尾插入元素 |
| q.pop(); | 弹出队首元素 |
| q.empty; | 队列是否为空 |
| q.size(); | 返回队列中的元素的数量 |
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;int tmp;
cin>>n>>m;
queue <int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
q.push(i);
}
while (!q.empty())
{
tmp++;
if(tmp%m!=0){
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
}
else{
cout<<q.front()<<" ";
q.pop();
}
}
return 0;
}
堆/优先队列(priority_queue)
堆的定义
堆是一种特殊的数据结构,通常可以被看作是一棵完全二叉树的数组对象。
其主要特性包括:
完全二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的节点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干节点。
值的性质:对于大顶堆,每个父节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值;对于小顶堆,每个父节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值。
高效性:堆是实现优先队列的一种非常高效的方法,能够快速找到包含最大值或最小值的节点。
优先队列的定义
优先队列priority_queue是一种特殊的队列,其中元素被赋予优先级,当访问队列元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除。
优先队列与普通队列最大的不同点在于它根据元素的优先级进行排序和处理。
具体来说:
优先级:每个元素都有一个优先级,优先级高的元素会先于优先级低的元素被访问或删除。
操作:支持查找最高优先级元素、删除最高优先级元素和插入指定优先级的新元素等操作。
实现基础:优先队列通常基于堆来实现,因此其性能也依赖于堆的性质和实现方式。
优先队列的语法
| 例子 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pq.push(int x); | 向优先队列中插入一个整数 |
| pq.pop(); | 删除并返回优先队列中的最大元素 |
| pq.top(); | 返回但不移除优先队列中的最大元素 |
| pq.empty(); | 检查优先队列是否为空。 |
C++中的优先队列是标准模板库(STL)的一部分,通常使用priority_queue模板类来实现。
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
priority_queue<int> pq;
// 插入元素
pq.push (5);
pq.push (3);
pq.push (7);
// 删除最高优先级的元素
pq.pop ();
// 获取最高优先级的元素
cout << pq.top () << endl;
return 0;
}
在C++中,priority_queue默认为最大堆从大到小,即最大的元素会首先被移除。
可以通过第三个模板参数来指定排序方式,例如:
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
这样可以将优先队列变为最小堆。
1.元素类型:int表示优先队列中存储的元素类型。
2.底层容器:vector<int>表示用于存储元素的容器类型。在优先队列中,默认使用vector作为底层容器。
3.比较函数对象:greater<int>,这是一个仿函数,用于指定元素的排序方式。由于使用了greater<int>,因此该优先队列会按照从小到大的顺序排列元素,即小顶堆。
默认情况下,priority_queue使用std::less作为其比较函数,这意味着它会创建一个大顶堆。
访问priority_queue的顶部元素top()的时间复杂度是O(1),但插入push()和删除顶部元素pop()的时间复杂度是O(log n),其中n是队列中元素的数量。priority_queue不保证元素的顺序(除了顶部元素),也不提供随机访问。
结构体类型
struct Node {
int a, b;
// 重载小于操作符,以实现自定义排序规则
bool operator<(const Node& other) const { //[记住格式]
// 假设我们希望先按a升序排序,如果a相同,则按b降序排序
if (a != other.a) return a < other.a;
return b > other.b; // 注意这里使用'>'来实现b的降序
}
};
int main() {
priority_queue<Node> pq;
Node n1{ 1, 9 };
Node n2{ 1, 5 };
Node n3{ 9, 1 };
pq.push(n1);
pq.push(n2);
pq.push(n3);
while (!pq.empty()) {
Node top = pq.top();
pq.pop();
cout << top.a << " " << top.b << endl;
}
return 0;
}
双端队列
Deque的定义
双端队列(Double-Ended Queue,简称Deque)是一种具有队列和栈性质的数据结构。
其主要特点是允许在两端进行插入和删除操作,即可以在队首(前端)和队尾(后端)同时进行入队和出队操作。
双端队列是限定插入和删除操作在表的两端进行的线性表。这两端分别称为端点1和端点2。
双端队列的元素可以从两端弹出,因此它兼具了队列和栈的特性.
Deque的语法
在C++中,标准模板库(STL)提供了std::deque来实现双端队列的功能。std::deque可以被视为一个固定大小的数组,但它可以动态增长和缩减,且不需要在每次插入或删除时重新分配整个数组的内存。这种特性使得std::deque在插入和删除操作上非常高效。
在C++中,使用双端队列需要包含相应的头文件:
#include <deque>
定义一个双端队列对象的基本语法如下:
deque<element_type> deq;
其中element_type可以是任意类型的数据,例如整数、字符串等。
| 例子 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| deq.push_back(x); | 在队列尾部插入元素x |
| deq.push_front(x); | 在队列头部插入元素x |
| deq.pop_back(); | 删除队列尾部的元素 |
| deq.pop_front(); | 删除队列头部的元素 |
| deq.at(size_type pos); | 返回位置pos处的元素,如果位置超出范围则引发异常 |
| deq.find(const value_type& val); | 查找指定值val的位置,并返回迭代器指向该位置,如果未找到则返回end() |
以下是定义和使用 std::deque 的基本语法:
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
int main()
{
// 定义一个 int 类型的双端队列
std::deque<int> myDeque;
// 向队列头部插入元素
myDeque.push _back(10);
myDeque.push _back(20);
myDeque.push _back(30);
// 向队列尾部插入元素
myDeque.push _back(40);
myDeque.push _back(50);
// 删除队列头部元素
myDeque.pop _back();
// 删除队列尾部元素
myDeque.pop _back();
// 查找并打印所有元素
for (int num : myDeque)
{
std::cout << num << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Set集合
Set的定义
在C++中,set是标准模板库(STL)的一部分,用于存储已排序且唯一的一组元素。其主要特点包括:
数据结构:set通常使用红黑树red-black tree实现,这使得它具有对数时间复杂度O(logn)的查找、插入和删除操作。
元素特性:集合中的每个元素都是唯一的,并且按照升序排列,但也可以通过自定义比较函数来实现其他的排序方式,如降序加上greater<int>。
不可变性:一旦元素被插入到set中,其值不能被修改,但可以进行插入或删除操作。
迭代器:set提供了迭代器,用于遍历集合中的元素。
有什么用:去重、排序
Set的语法
| 例子 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| St.insert(); | 当set里没有等价函数时,将x插入到set中 |
| St.erase(); | 从set中删除指定元素(若无则也无影响,即无操作) |
| St.clear(); | 清空set容器 |
| st.count(x); | 返回set内的x元素的数量,因为最多存在一个,返回值 1 or 0 |
| St.empty(); | 判断set是否为空 |
| St.size(); | 返回set内的元素个数 |
| St.find(); | 函数用于查找指定值的位置 |
以下是一个完整的示例程序,演示如何定义和操作一个set:
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建并初始化set
set<int> my_set = {1, 2, 3};//默认升序
set<int,greater<int> > my_set2 = {1, 2, 3};//降序
// 插入新元素
my_set.insert(4);
// 查找元素
auto it = my_set.find(2);
if (it != my_set.end())
{
cout << *it << endl; // 输出2
}
// 删除元素
my_set.erase(my_set.find(1));
// 遍历集合并输出所有元素
for (const auto &val : my_set)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Multiset可重集合
Multiset的定义
在C++中,multiset是一个非常有用的STL(标准模板库)容器类型,用于存储和操作具有相同键值对的元素集合。
与set不同的是,multiset允许重复的元素存在,并且能够保持这些元素的有序性。St.begin();返回set第一个元素的地址的迭代器St.end();返回set最后一个元素的地址的下一个地址的迭代器St.erase(T x/iterator it)Lower_bound二分查找 upper_bound()
元素特性:集合中的每个元素都是唯一的,并且按照升序排列,
但也可以通过自定义比较函数来实现其他的排序方式,如降序加上greater<int>
Map
Map的定义
在C++中,Map是一种关联容器,它存储的元素是键值对key-value pairs。
每个元素都是一个键值对,其中键(key)是唯一的,而值(value)则可以是任何数据类型。
Map内部通常实现为一个红黑树(或类似的平衡二叉搜索树),这意味着 map 中的元素总是按照键的升序排列。因此,map 提供了快速的查找、插入和删除操作,这些操作的时间复杂度通常为对数时间O(log n),其中n是map中元素的数量。
也可以理解成一个结构体数组,只是数组的下标和值都是任意的。
[注意事项]map中的键必须是唯一的。map中的元素按照键的升序排列。
访问不存在的键时,使用下标操作符会创建一个新元素。如果你只是想检查键是否存在,应该使用 find 成员函数。map的插入、删除和查找操作的时间复杂度通常为O(log n)。
Map的语法
基本的std::map声明语法如下:
map<KeyType, ValueType> mapName;KeyType 是键的类型,它必须支持 < 操作符,以便map可以对其元素进行排序ValueType 是与键相关联的值的类型。mapName 是你定义的map的名称。
常用函数
| 例子 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Mp.insert(const value_type& val); | 插入一个键值对。如果键已存在,则更新其值 |
| Mp.erase(key_type const& k); | 删除与指定键相关联的元素,释放空间 |
| Mp.find(key_type const& k); | 查找具有指定键的元素。如果找到,返回一个指向该元素的迭代器;否则,返回一个指向map末尾的迭代器 |
| Mp.size(); | 返回map中元素的数量 |
| Mp.empty(); | 如果map为空,则返回true |
| Mp.operator[]; | 使用键作为索引访问元素。如果键不存在,则插入一个具有该键的新元素,并将其值初始化为ValueType()的默认构造值 |
| Mp.count(); | 统计这个下标出现的次数 |
使用方法
创建 map
创建一个空的 map,键类型为 int,值类型为 std::string
map<int, string> myMap;
// key value
or 使用初始化列表
map<int, string> myMap2 = {
{1, "one"},
{2, "two"},
{3, "three"}
};
插入元素
1.使用下标操作符[](如果键不存在,则插入新元素,并初始化其值为ValueType的默认值):
myMap[1] = "one";
2.使用insert成员函数:
auto result = myMap.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));
if (!result.second) {
// 插入失败,通常是因为键已存在
}
访问元素
string value = myMap[1]; // 访问键为 1 的元素的值
注意:如果键不存在,则使用下标操作符会创建一个新元素,其值会被初始化为值类型的默认值
or
更安全的访问方式(验证键更安全)
auto it = myMap.find(1);// 验证键更安全
if (it != myMap.end()) {
string value = it->second; // 访问找到的元素的值
} // `myMap.first`为键,`myMap.second`为值
删除元素
myMap.erase(1); // 删除键为 1 的元素
or 使用迭代器
auto it = myMap.find(2);
if (it != myMap.end()) {
myMap.erase(it);
} // 验证键更安全
遍历 map
for (const auto& pair : myMap) {
cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << endl;
}
or 使用迭代器
for (auto it = myMap.begin(); it != myMap.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
} // 验证键更安全
Map的坑
1.会爆栈
如果键不存在,则使用下标操作符会创建一个新元素,其值会被初始化为值类型的默认值0。
2.无限循环
可以需要用count()去判断键是否存在,再去访问键,否则会一直新建键值对无限循环。 or 用find()
if (mp.count()>0){code}
unordered_map
unordered_map是基于哈希表的map,在使用方面和map没有任何区别。map:
优点:有序性,效率十分稳定Olog(n)unordered_map:
优点:查找速度非常的快近似O(1)
缺点:无序,插入操作的效率不如map
如果说你需要遍历整个map,且想要的是有序的(for(autolx,c]:mp)那么就用map,其他就用unordered_mapunordered_map在codeforces一定会TLE
能让你用map,那么大概率能用unordered_map,有概率会卡unordered_map
相反亦然,有的题你用unordered_map能过,有可能map会被卡
数组
数组最好声明在main函数的外面!!!:
只有在放外面时,数组才可以开得很大;
放在main函数内时,数组稍大就会异常退出。
memset的使用
memset(数组名称,需要初始化的值,数组的每个元素的大小)
注意:memset初始化的值只能是0和-1
signed main() {
// 【memset(数组名称,需要初始化的值,数组的每个元素的大小)】
int a[10]; //请注意:memset() 仅能的初始化值仅能为 0 或者 -1
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
for (auto x : a) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
memset(a, -1, sizeof(a));
for (auto x : a) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
注意事项memset函数按字节进行操作,因此不能直接用于将整型数组(如int数组)初始化为非0和非-1之外的其他值。
如果需要对指针变量所指向的内存单元进行清零初始化,必须先确保这个指针变量已经指向了一个有效的地址。memset函数只能用于字符数据类型或者无符号整型数据类型,即只能设置1字节大小的值。
例题
有n盏灯,编号为1~n,第1个人把所有灯打开,第2个人按下所有编号为2的倍数的开关(这些灯将被关掉),第3个人按下所有编号为3的倍数的开关(其中关掉的灯被打开,开着灯将被关闭),依此类推。一共有k个人,问最后有哪些灯开着?
输入:n和k
输出:开着的灯编号。k<=n<=1000
样例输入:7 3
样例输出:1 5 6 7
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
memset(a, -1, sizeof(a));//-1表示开灯
for (int i = 2; i <= k; i++){
for (int j = i; j <= n;j+=i){
a[j] *= -1;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){
if(a[i]==-1){cout << i << endl;}
}
return 0;
}
多组样例输入
1.函数scanf()的返回值 就是:“所输入的数据与格式中匹配次数.”
简单来说就是,它返回已成功赋值的数据项数;出错时则返回EOF.
(注:EOF(End Of File)是一个预定义的常量,等于-1.)
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)==2){}
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF) {}
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=-1) {}
while(~scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)) {}
2.cin实现的多组输入
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c;
while(cin>>a>>b>>c){
...
}
}
3.例题
HDU-1021
解题代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int n;
int main(){
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){
if(n % 8 == 2 || n % 8 == 6)
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
string 类 字符串
C语言字符串常用函数
strcpy:拷贝字符串
strcat:拼接两个字符串
strcmp:字符串比较
string 类 语法
常用函数
| 例子 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| length(); size(); | 求长度 |
| empty(); | 判断是否为空串 |
| substr(); | 截取字符串 |
| erase(); | 删除若干个字符 |
| insert(); | 插入字符 |
| replace(); | 替换字符 |
| find(); | 寻找字符 |
| count(); | 计算字符个数 |
| stoi(); | string转int |
| to_string(); | int转string |
string重载了一些运算符,可以直接使用
str1=str2; //str1成为str2的拷贝
str1+=str2; //str2的字符数据连接到str1的尾部
str1+str2; //将str2连接到str1的尾部,str1不改变
str1==str2; str1!=str2; str1<str2;
str1>str2; str1<=str2; str1>=str2;
//基于字典序的比较,返回布尔值,true或false
字符串读取getchar()输入一个字符cin能读到空格,读不到换行符getline()可以读到换行符
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<getchar();//输入一个字符
string s;
cin>>s;//`cin`能读到空格,读不到换行符
cout<<s;
string s;
getline(cin,s);//`getline()`可以读到换行符
cout<<s;
}
substr()截取字符串
string.substr(起始位,数几个)
int main (){
string s="hello, world!";
string ss1 = s.substr(2);//llo, world!
//从2开始往后取完
string ss2 = s.substr(2,3);//llo
//从2开始往后取3位
cout<<ss1<<endl<<ss2<<endl;
}
erase()删除若干个字符string.erase(起始位,数几个)有规律地指定删除
s1.erase(1, 2)//从1开始删2个
cout << s1 << endl;
insert()插入字符
string.insert(要插入的位置,要插入的元素);
s1.insert(0, "1");
cout << s1 << endl;
replace()替换字符
string.replace(索引,要替换几个字符,替换上去的元素)
s1.replace(0, 1, "HaHa");
cout << s1 << endl;
find()寻找字符
在 C++ 中,string::npos是一个特殊的常量值,用于表示在字符串中未找到子字符串或字符时的位置。
这个常量实际上是std::string类型所能表示的最大值,即 std::string::size_type的最大值。
由于字符串的索引是从0开始的,因此任何有效的索引值都小于 std::string::npos。
if (s1.find("666") == string::npos) {
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
count()计算字符个数count(string.begin(),string.end(),'要找的字符')
string s = "Hello world";
cout << count(s.begin(), s.end(), 'l') << endl;
string和int相互互换
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//string 和 int 相互转换
string s="123";
string s2="6";
cout<<stoi(s)+stoi(s2);
int a=123,b=345;
string s=to_string(a)+to_string(b);
cout<<s;
}
解题集
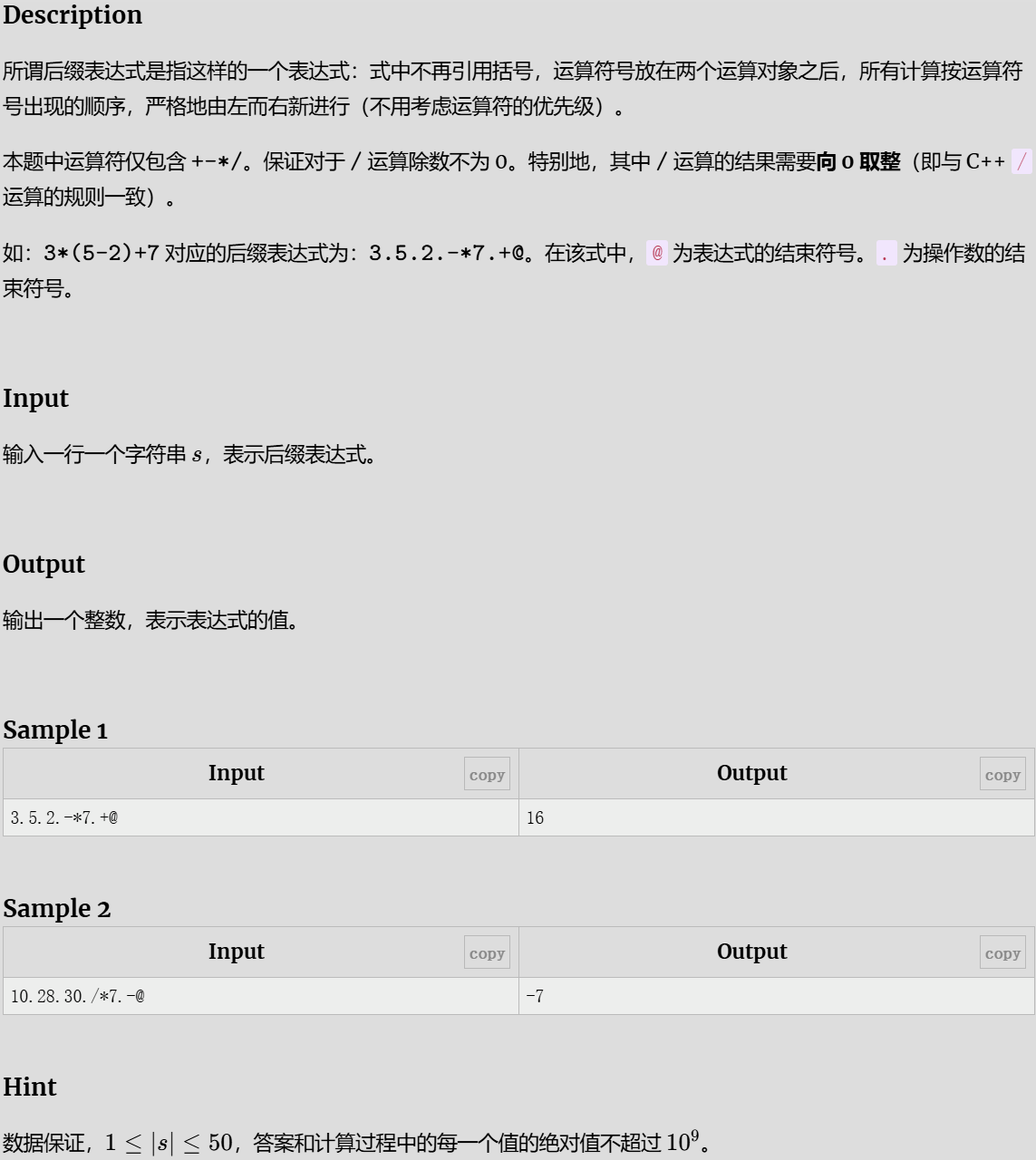
后缀表达式
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
vector <char> fh;
stack <int> num;
int sum(int n1, int n2, char x);
queue<char> s;
signed main() {
string a; int cnt = 0;
cin >> a;
for (char n : a) {
if (n == '@') break;
//先对字符串处理入栈
if (n >= '0' && n <= '9') {//如果是数据
s.push(n);
}
else {//如果是符号
if (n == '.') {//整合
int sum = 0;
while (!s.empty()) {
sum = sum * 10 + (int)s.front() - '0';
s.pop();
}
num.push(sum);
}
else{//计算
int n2 = num.top();
num.pop();
int n1 = num.top();
num.pop();
int x2 = sum(n1, n2, n);
num.push(x2);
}
}
}
cout << num.top();
return 0;
}
int sum(int n1, int n2, char x) {
if (x == '+')return n1 + n2;
if (x == '-')return n1 - n2;
if (x == '*')return n1 * n2;
if (x == '/')
if (n1 >= n2)return n1 / n2;
else return 0;
}
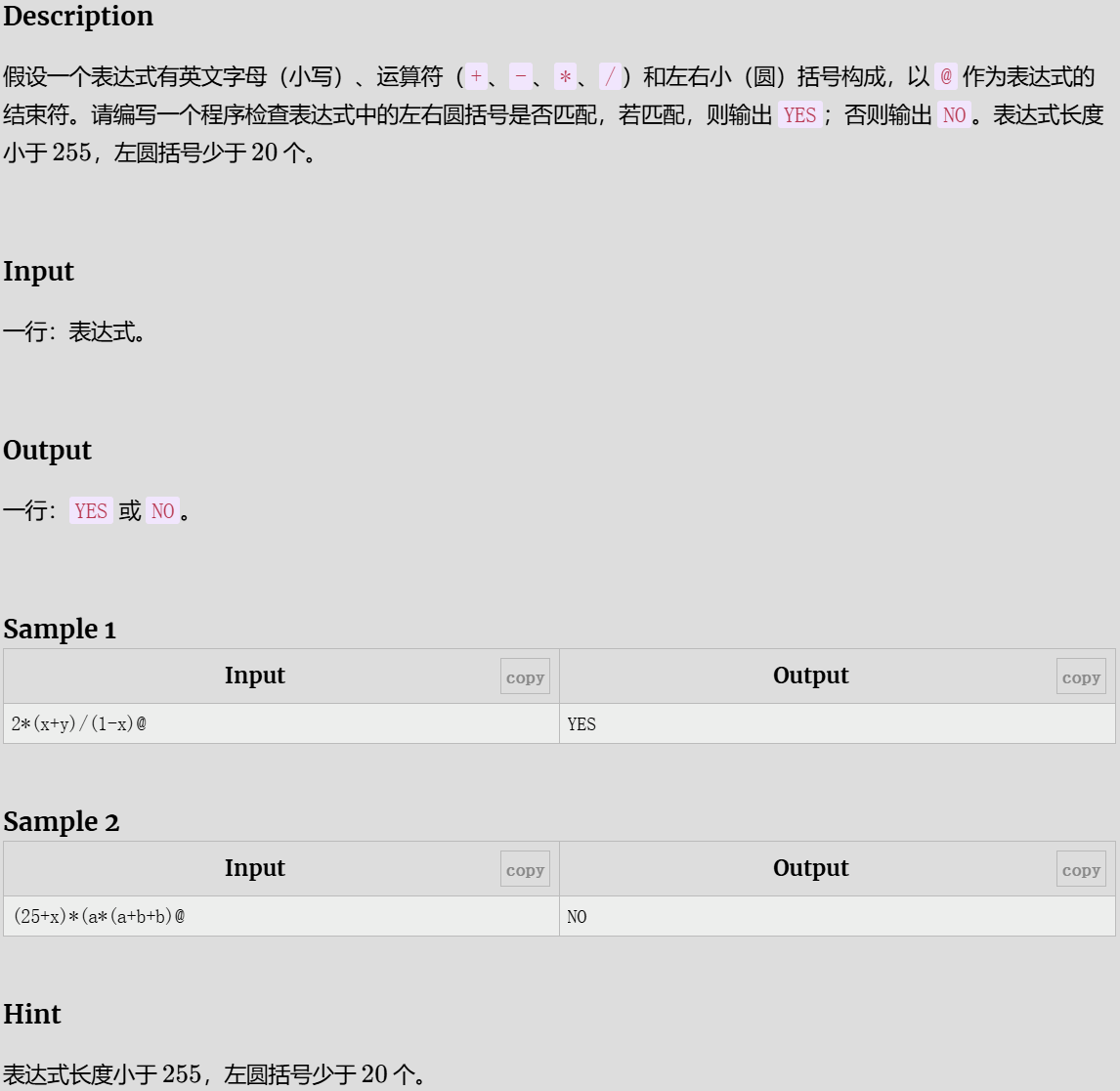
表达式括号匹配
参考代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<limits.h>
#define pb emplace_back()
#define endl '\n'
#define i64 long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define Endl endl
#define END endl
#define mod3 998244353
#define mod7 1000000007
#define de(x) cerr << #x <<" "<<x <<" ";
#define deb(x) cerr << #x <<" "<<x <<endl;
using namespace std;
void solve(){
stack<int>of;
string s;
cin >> s;
int len = s.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
if(s[i] =='@'){break;}
else if(s[i] == '('){
of.push(1);
}else if(s[i] == ')'){
if(of.empty()){cout <<"NO"<<endl;return ;}
of.pop();
}
}
cout << ((of.empty()) ? "YES" : "NO" ) <<endl;
}
int main(){
solve();
return 0;
}
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
//priority_queue<char, vector<char>, greater<char>> fh;
stack <int> num;
//int sum(int n1, int n2, char x);
signed main() {
string a; int cnt = 0; int flag = 1;
cin >> a;
for (char x: a) {
if (x != '@') {
if (x == '(')num.push(x);
if (x == ')') {
if (!num.empty())num.pop();
else { flag = 0; break; }
}
}
else break;
}
if (num.empty()&&flag==1)cout << "YES";
else cout << "NO";
}
表达式求值(计算器)
参考代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<limits.h>
#define pb emplace_back()
#define endl '\n'
#define i64 long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define Endl endl
#define END endl
#define mod 10000
#define mod3 998244353
#define mod7 1000000007
#define de(x) cerr << #x <<" "<<x <<" ";
#define deb(x) cerr << #x <<" "<<x <<endl;
using namespace std;
int main(){
stack<i64>q;
string s;
cin >> s;
int len = s.size();
i64 cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
if(isdigit(s[i])){
cnt = (cnt * 10 + (1LL * (s[i] - '0'))) % mod;
}
if( i == len-1 || !isdigit(s[i+1]) ){
cnt %= 10000;
q.push(cnt);
cnt = 0;
}
if(s[i] == '*'){
while(isdigit(s[i+1])){
cnt = (cnt * 10 + (1LL * (s[i+1] - '0'))) % mod;
i ++;
}
i64 top = q.top(),ans = cnt;
ans = ans * top%mod;
q.pop();
q.push(ans);
cnt = 0;
}
}
i64 ans = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
ans = (ans + q.top()) % mod;
q.pop();
}
cout << ans <<endl;
return 0;
}
解题代码
//简单计算机
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define llu long long
int level(char e) {
if (e == '*') return 2;
else if (e == '+') return 1;
else return 0;//
}
int main() {
stack<int> number; stack<char> symbol;
llu x1; scanf("%lld", &x1);
x1 = x1 % 10000;
number.push(x1);
char tmp;
int flag = 0;
while (~scanf("%c", &tmp) && tmp != '\n') {
llu TMP; scanf("%lld", &TMP); TMP = TMP % 10000;
flag = level(tmp);
if (flag == 2) {
llu X = number.top(); number.pop();
X *= TMP;
X = X % 10000;
number.push(X);
flag = 0;
}
else {
symbol.push(tmp);
number.push(TMP);
}
}
while (!symbol.empty()) {
char c = symbol.top(); symbol.pop();
llu a = number.top(); number.pop();
llu b = number.top(); number.pop();
llu X = (a + b) % 10000;
number.push(X);
}
llu out = number.top()%10000;
printf("%lld", out);
return 0;
}
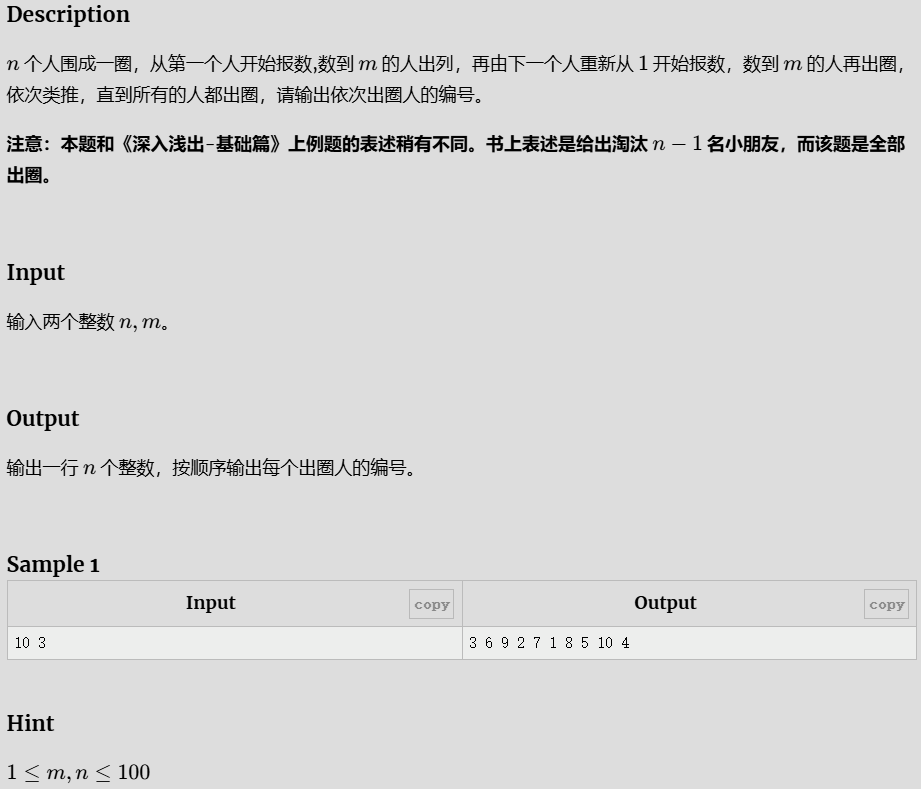
约瑟夫问题
解题代码
P1996 约瑟夫问题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;int tmp;
cin>>n>>m;
queue <int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
q.push(i);
}
while (!q.empty())
{
tmp++;
if(tmp%m!=0){
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
}
else{
cout<<q.front()<<" ";
q.pop();
}
}
return 0;
}
堆
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> s;
while (n--)
{
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
if (m == 1)
{
int k;
scanf("%lld", &k);
s.push(k);
}
if (m == 2)
{
cout << s.top() << endl;
}
if (m == 3){
s.pop();
}
}
return 0;
}
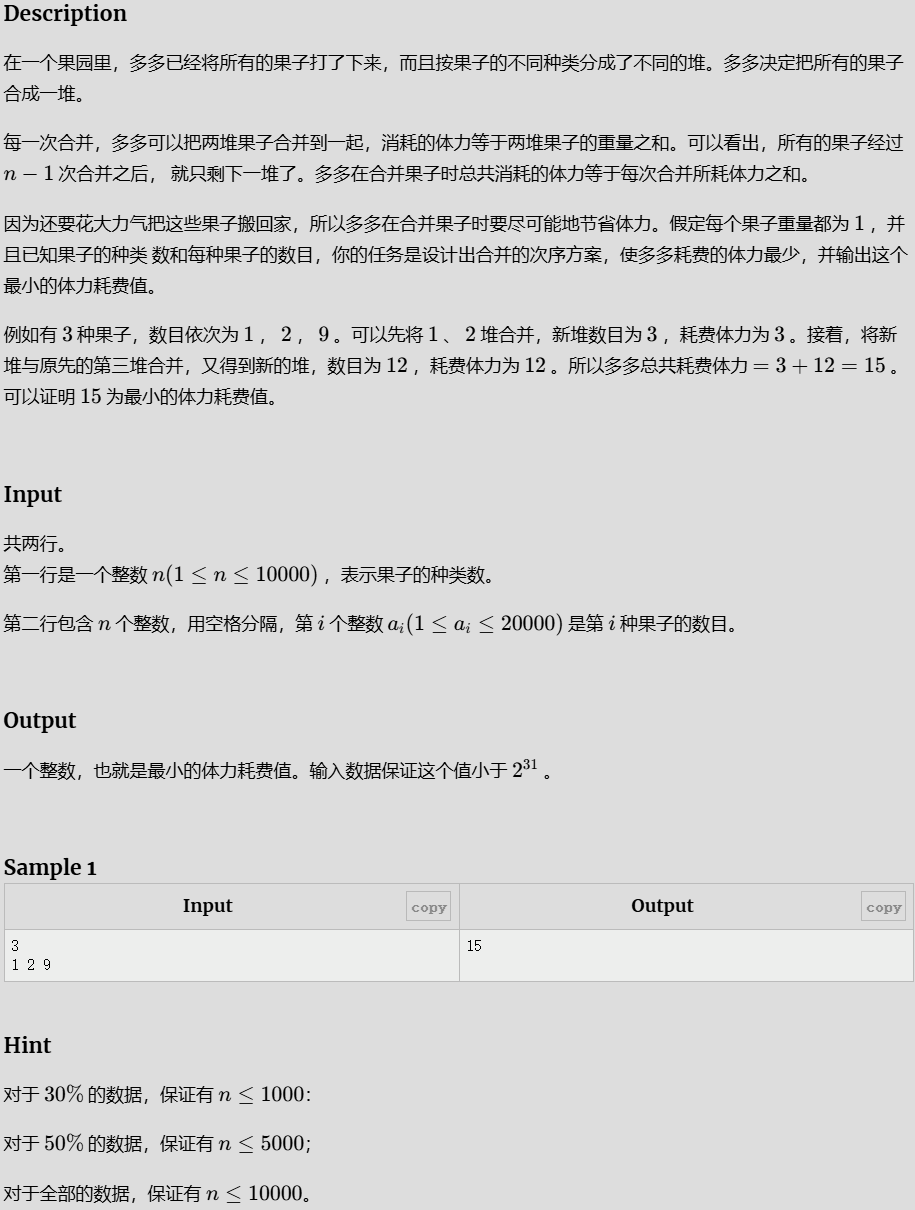
合并果子
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
#define ll long long int
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int t;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > a;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> t;
a.push(t);
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int sum1 = 0;
sum1 += a.top();
a.pop();
sum1 += a.top();
a.pop();
sum += sum1;
a.push(sum1);
}
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
中位数
参考代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<limits.h>
#define pb emplace_back()
#define endl '\n'
#define i64 long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define Endl endl
#define END endl
#define mod3 998244353
#define mod7 1000000007
#define de(x) cerr << #x <<" "<<x <<" ";
#define deb(x) cerr << #x <<" "<<x <<endl;
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n+1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
cin >> a[i];
}
cout << a[1] << endl;
priority_queue<int>q1;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>q2;
if(a[1] > a[2]){q1.push(a[2]),q2.push(a[1]);}
else{q1.push(a[1]),q2.push(a[2]);}
for(int i = 3;i <= n;i ++){
int x = a[i];
if(x < q1.top()){ q1.push(x);}
else{ q2.push(x);}
if(i % 2){
while( llabs(q1.size() - q2.size()) > 1){
if(q1.size() > q2.size()){
int tmp = q1.top();
q2.push(tmp);
q1.pop();
}else{
int tmp = q2.top();
q1.push(tmp);
q2.pop();
}
}
cout <<((q1.size() > q2.size()) ?q1.top():q2.top()) <<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
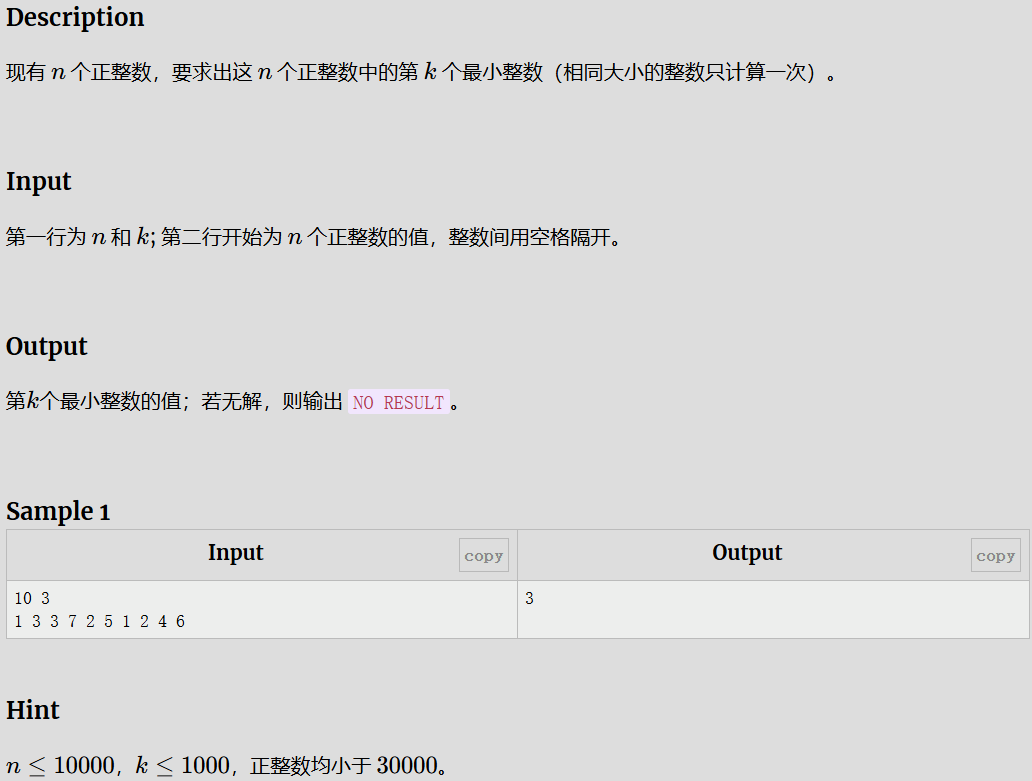
第 k 小整数
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define N 1e5 + 10
signed main(){
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
set <int> s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int m;
cin >> m;
s.insert(m);
}
if (s.size() < k)
cout << "NO RESULT" << endl;
else
{
int y = 0;
for (auto x : s)
{
if (s.count(x))
{
y++;
}
if (y == k)
cout << x << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Andy’s First Dictionary
8岁的安迪有一个梦想——他想制作自己的词典。这对他来说不是一件容易的事,因为他知道的单词数量还不够。他没有自己想好所有的话,而是有一个巧妙的想法。他会从书架上挑选一本他最喜欢的故事书,从中抄出所有独特的单词。通过按字母顺序排列单词,他就完成了!当然,这是一项非常耗时的工作,而这正是计算机程序提供帮助的地方。系统要求您编写一个程序,列出输入文本中的所有不同单词。在这个问题中,一个单词被定义为连续的字母序列,采用大写和/或小写。只有一个字母的单词也要考虑在内。此外,您的程序必须是 CaSe InSeNsItIvE。例如,“Apple”、“apple”或“APPLE”等词语必须被视为相同。
Input
输入文件是不超过 5000 行的文本。输入行最多包含 200 个字符。输入由 EOF 终止。
Output
您的输出应给出输入文本中出现的不同单词的列表,一个在一行中。单词都应为小写,按字母顺序排序。您可以确定文本中不同单词的数量不超过 5000 个。
Sample Input
Adventures in Disneyland
Two blondes were going to Disneyland when they came to a fork in the road. The sign read: "Disneyland Left."
So they went home.
Sample Output
a
adventures
blondes
came
disneyland
fork
going
home
in
left
read
road
sign
so
the
they
to
two
went
were
when
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define N 1e5 + 10
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
string s;
set<string> set;
while (cin >> s){
int len=(int)s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (isalpha(s[i])) // 检查字符串s中的第i个字符是否是字母
{
s[i] = (tolower(s[i])); // 如果是的话,将其转换为小写
}
else s[i]=' ';
}
stringstream iss(s);
string word;
// 循环读取单词,直到iss中没有更多数据
while (iss >> word)
{
set.insert(word);
}
}
for (auto x : set)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
return 0;
}
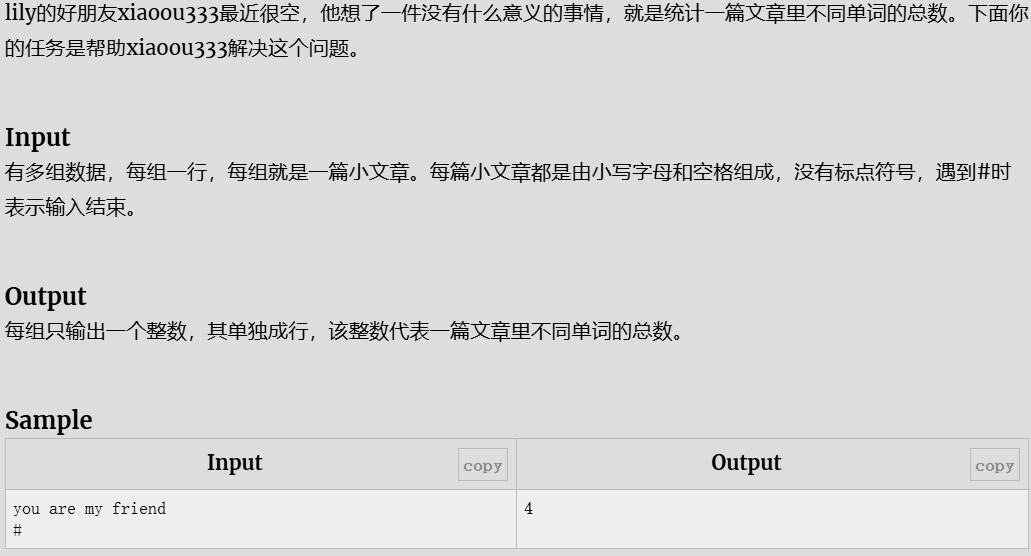
单词数
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define N 1e5 + 10
signed main(){
string s;
set <string> st;
while (getline(cin, s))
{
if(s=="#")break;
st.clear();
istringstream iss(s);
string word;
// 循环读取单词,直到iss中没有更多数据
while (iss >> word) {
st.insert(word);
}
cout << st.size() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
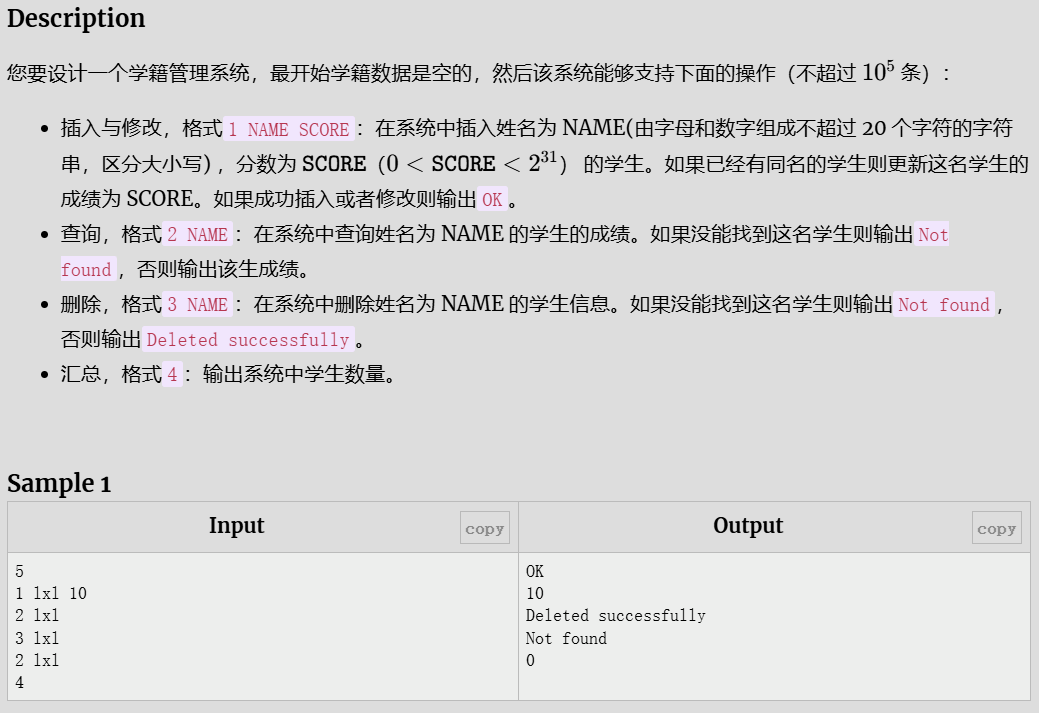
学籍管理
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define N 1e5 + 10
signed main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
map <string, int> myMap;
while (n--){
int cz, cj;
string name;
cin>>cz;
if (cz == 1){
cin>>name>>cj;
myMap[name] = cj;
cout << "OK" << endl;
}
if (cz == 2){
cin>>name;
auto it = myMap.find(name); // 验证键更安全
if (it != myMap.end())
{
int value = it->second; // 访问找到的元素的值
cout << value << endl;
} // `myMap.first`为键,`myMap.second`为值
else
{
cout << "Not found" << endl;
}
}
if (cz == 3){
cin>>name;
auto it = myMap.find(name);
if (it != myMap.end())
{
myMap.erase(it);
cout << "Deleted successfully" << endl;
} // 验证键更安全
else
{
cout << "Not found" << endl;
}
}
if (cz == 4){
int tmp=myMap.size();
cout << tmp <<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Cities and States S
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define N 1e6 + 10
const long long inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
int v[1010][1010]={0};
signed main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int ta = ((a[0] - 'A') * 26) + a[1] - 'A'; // city2
int tb = ((b[0] - 'A') * 26) + b[1] - 'A'; // state
ans += v[tb][ta]; //[state,city2]存在的数
if (ta == tb) // 自检
{
ans -= v[ta][tb];
}
v[ta][tb]++; //[city2,state]存在则加一
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
小明爱集合
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define N 1e5 + 10
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
set<int> st;
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int nm=n+m,k;
while (nm--)
{
cin >> k;
st.insert(k);
}
int xsd = (m+n-st.size()) * 100/st.size();
printf("%lld\n", xsd);
}
return 0;
}
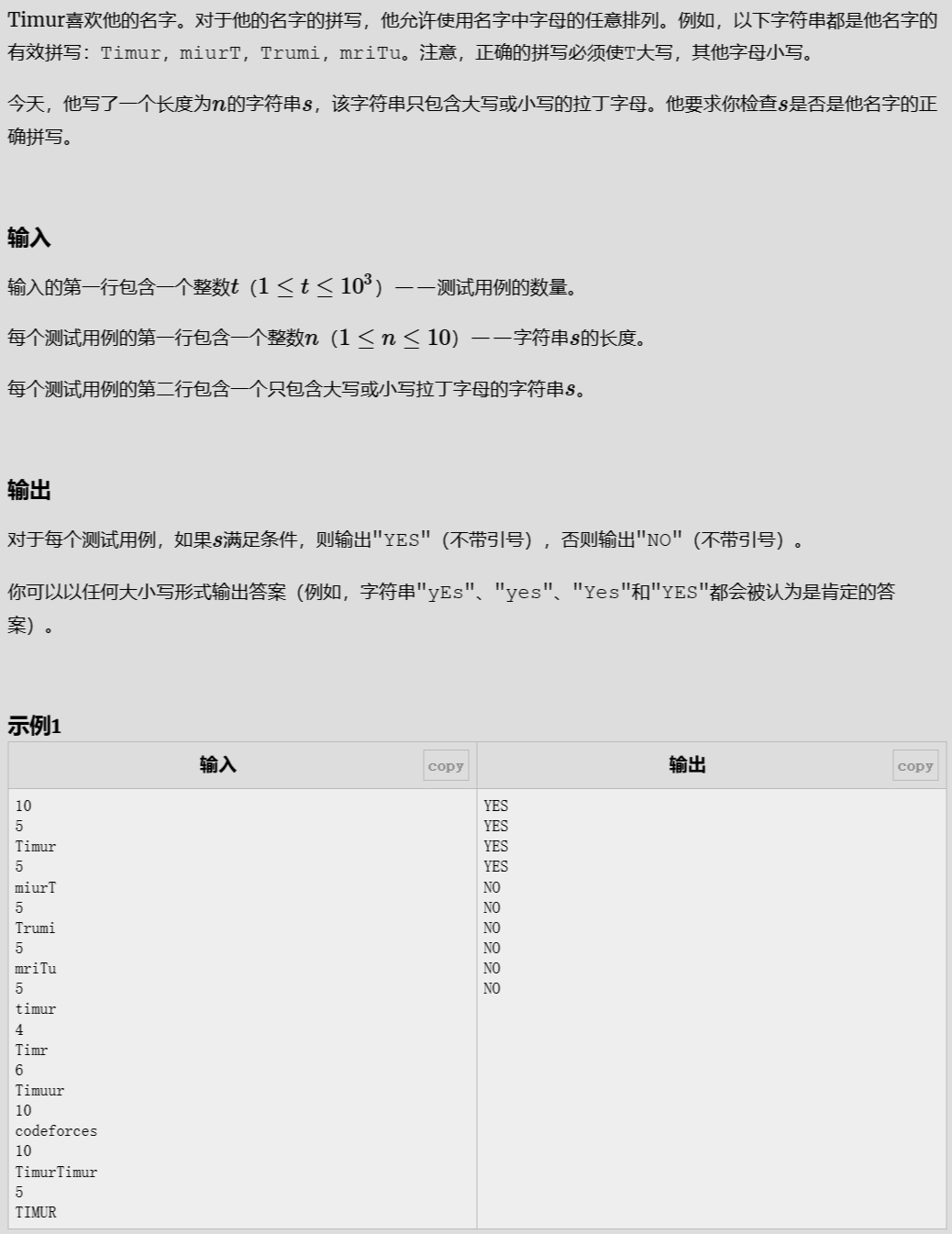
名字拼写正确判别
Problem - 1722A - Codeforces
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
void solve();
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
int n;
cin>>n;
string s;
while(n--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
void solve(){
int m;
cin>>m;
string s;
cin>>s;
if(m!=5){
cout <<"NO"<<endl;
return ;
}
map<char,int> map;
for(char x:s){
map[x]++;
}
if(!map['T']||!map['i']||!map['m']||!map['u']||!map['r']){
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
return;
}
序列1/0操作
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
void solve();
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
int n;
cin>>n;
string s;
while(n--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
void solve(){
int m;
cin>>m;
string s;
cin>>s;
if(m!=5){
cout <<"NO"<<endl;
return ;
}
map<char,int> map;
for(char x:s){
map[x]++;
}
if(!map['T']||!map['i']||!map['m']||!map['u']||!map['r']){
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
return;
}
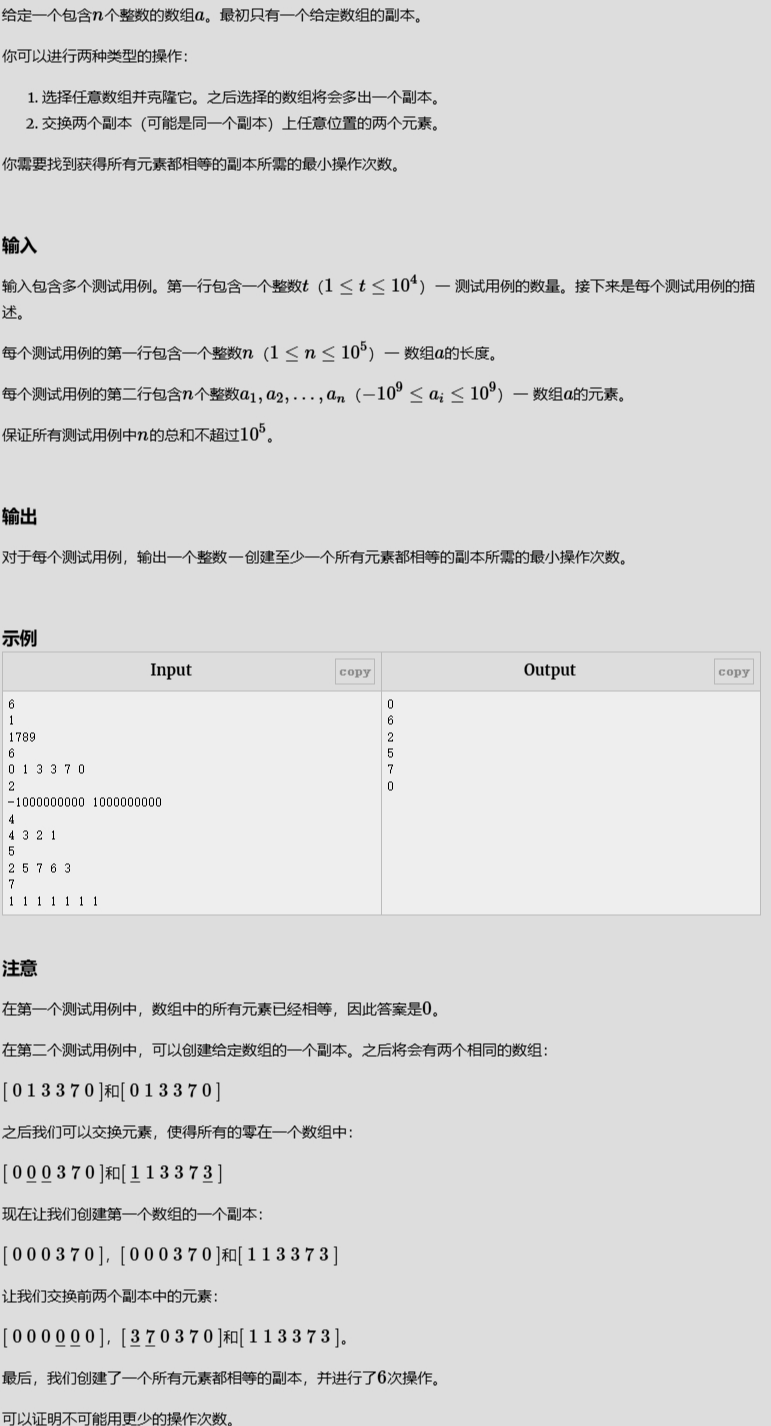
副本操作
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr); // 关闭同步流
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int m;
cin >> m;
map<string, int> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
string k;
cin >> k;
mp[k]++;
}
string name;
int max_num = 0;
int sum_num = 0;
for (auto x : mp)
{
sum_num += x.second; // 累计总数
if (x.second > max_num)
{ // 找最大数和其键
max_num = x.second;
name = x.first;
}
}
int cnt = 0; // 操作次数
while (max_num < sum_num)
{ // 查杀
cnt++; // fz
cnt += max_num;
max_num *= 2;
}
cnt -= (max_num - sum_num); // 操作数-超出数
cout << cnt << endl;
}
return 0;
}
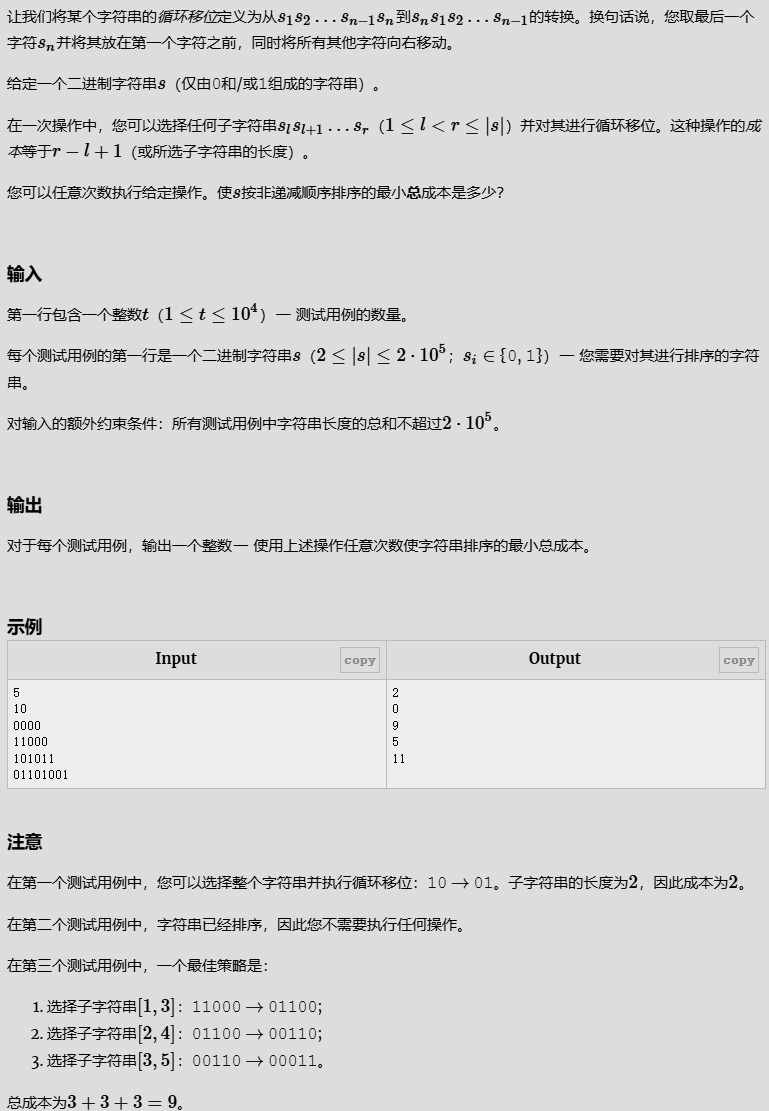
循环位移
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
void solve();
signed main(){
int t; cin >> t; getchar();
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
stack<char> s;
char tmp;
int num_0 = 0;
int chenben = 0;
while (~scanf("%c", &tmp) && tmp != '\n') {
if (tmp == '1') {
s.push(tmp);
}
else if (tmp == '0' && s.size() == 0) {
num_0++;
}
else {
chenben += s.size()+1;
num_0++;
}
}
cout << chenben << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
四舍五入
解题代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
int x1 = 0;
while (t--) {
string s1,s2;
cin >> s1;
int count = 0;
for (int i = s1.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int x = (int)(s1[i]) - 48;
if (x1 == 1) {
x += 1;
x1 = 0;
}
if (x >= 5) {
if (i == 0) {
s2 = '1';
count = s1.size();
}
else{
s2 = '0';
count = s1.size() - i - 1;
x1 = 1;
}
}
else {
s2 = to_string(x) + s2;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
s2 = s2 + '0';
}
cout << s2 << "\n";
x1 = 0;
}
return 0;
}
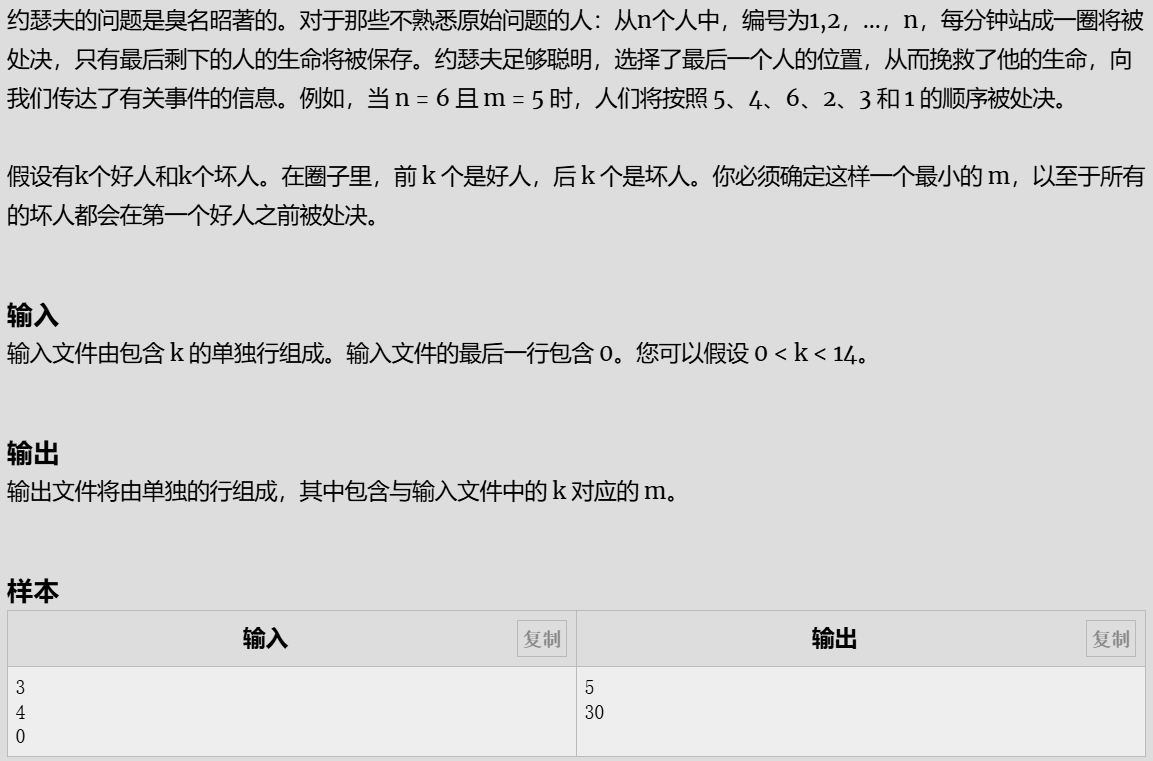
约瑟夫
解题代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[14];
int bushu(int x){//步数
int remain,p;
if(a[x]) return a[x];//
for(int i=x+1;;i++){//找步数
for( p=0,remain=2*x;remain>x;remain--){
p = (p + i - 1) % remain;//循环//杀人
if(p<x) remain=0; //不杀好人
}//找到就退出(最小步数)
if(remain==x){//只剩下好人
a[x]=i;
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int k;
while(scanf("%d",&k)==1) {
if(k==0) break;
else printf("%d\n",bushu(k));
}
return 0;
}
斐波那契数列2
解题思路
菜鸟题解 HDU-1021 Fibonacci Again
解题代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int n;
int main(){
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){
if(n % 8 == 2 || n % 8 == 6)
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
最右边的数字
解题思路
个位数4次一循环,若按n次循环会爆
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--){
int m;
cin >> m;
int x = m % 10;
if (x == 5 || x == 6){
cout << x << endl;
continue;
}
int sum=x;
for (int i = 0; i < (m-1)%4;i++){
sum *= x;
}
cout << sum%10 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
整除的尾数
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// #define int long long;
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int s;
int n;
while (cin >> s >> n && !(s == 0 && n == 0)){
s *= 100;
bool flag = false;
for (int x = 0; x < 100;x++)
if ((s + x) % n == 0){
if (flag) cout << " "; // 如果不是第一个满足条件的 x,则输出空格
cout << (x < 10 ? "0" : "") << x; // 如果 x 是个位数,则前面补 0
flag = true;
}
if (!flag) {
cout << "00"; // 如果没有找到满足条件的 x,则输出 00
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
键盘打字加密
WERTYU
题目
一个常见的打字错误是将手放在键盘上,放在正确位置右侧一排。因此,“Q”被输入为“W”,“J”被输入为“K”,依此类推。您将对以这种方式键入的消息进行解码。
输入
输入由几行文本组成。每行可以包含数字、空格、大写字母(Q、A、Z 除外)或上面所示的标点符号 [反引号 (') 除外]。输入中不表示标有单词 [Tab、BackSp、Control 等] 的键。
输出
您将用上面显示的“QWERTY”键盘上紧挨着左侧的字母或标点符号替换每个字母或标点符号。输入中的空格应在输出中回显。
Sample Input
O S, GOMR YPFSU/
Sample Output
I AM FINE TODAY.
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
string n;
while (getline(cin, n))
{
string a = "`1234567890-=";
string b = "QWERTYUIOP[]\\";
string c = "ASDFGHJKL;'";
string d = "ZXCVBNM,./";
for (char k : n)
{
if (k == ' ')
{
cout << ' ';
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)a.size(); i++)
{
if (a[i] == k)
{
cout << (i > 0 ? a[i - 1] : a[i]);
continue;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)b.size(); i++)
{
if (b[i] == k)
{
cout << (i > 0 ? b[i - 1] : b[i]);
continue;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)c.size(); i++)
{
if (c[i] == k)
{
cout << (i > 0 ? c[i - 1] : c[i]);
continue;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)d.size(); i++)
{
if (d[i] == k)
{
cout << (i > 0 ? d[i - 1] : d[i]);
continue;
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
XO统计
Score
题目
有一个客观的测试结果,例如“OOXXOXXOOO”。“O”表示问题的正确答案,“X”表示错误的答案。该测试的每个问题的分数都是由自身计算的,并且只有当答案正确时,它才计算出它之前连续的“O”。例如,第 10 个问题的分数是 3,它是由它自己和它的前两个连续的“O”获得的。因此,“OOXXOXXOOO”的分数是10,由“1+2+0+0+1+0+0+1+2+3”计算得出。你要编写一个程序来计算测试结果的分数。
输入
您的程序将从标准输入中读取。输入由 T 个测试用例组成。测试用例 T 的数量在输入的第一行中给出。每个测试用例都从一行开始,其中包含由 ‘O’ 和 ‘X’ 组成的字符串,字符串的长度大于 0 且小于 80。“O”和“X”之间没有空格。
输出
您的程序将写入标准输出。为每个测试用例打印一行。该行用于包含测试用例的分数。
样例输入
5
OOXXOXXOOO
OOXXOOXXOO
OXOXOXOXOXOXOX
OOOOOOOOOO
OOOOXOOOOXOOOOX
样例输出
10
9
7
55
30
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
cin.ignore();
while(n--){
string s;
getline(cin, s);
int cnt = 0;
int sum = 0;
for(char x:s){
if(x=='O')
{cnt++;
sum += cnt;}
if(x=='X'){
cnt = 0;
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
}
计算0 - 9出现次数
Digit Counting
题目
Trung 对他的数学作业感到厌烦。他拿起一支粉笔,开始写一系列从 1 到 N(1 < N < 10000)的连续整数。之后,他计算每个数字(0 到 9)在序列中出现的次数。例如,当 N = 13 时,序列为:
12345678910111213
在此序列中,0 出现一次,1 出现 6 次,2 出现 2 次,3 出现 3 次,4 到 9 之间的每个数字出现一次。玩了一会儿后,Trung 又感到无聊了。他现在想写一个程序来为他做这件事。你的任务是帮助他编写这个程序。
输入
输入文件由多个数据集组成。输入文件的第一行包含数据集的数量,该数据集是一个正整数,不大于 20。以下几行描述了数据集。对于每个测试用例,都有一行包含数字 N。
输出
对于每个测试用例,在一行中按顺序写下数字 0、1、. .9 用空格分隔。
样例输入
2
3
13
样例输出
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 6 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--){
int m;
map<char, int> mp;
cin >> m;
string sum;
for (int i=1; i <= m;i++){
string x = to_string(i);
sum =sum+x;
}
for(char p:sum){
int x = p - '0';
mp[x]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9;i++){
// char u = i;
cout<<mp[i]<<" ";
}
cout << mp[9] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
子序列加密
All in All
题目
您设计了一种新的加密技术,该技术通过以巧妙的方式在其字符之间插入随机生成的字符串来编码消息。由于专利问题悬而未决,我们不会详细讨论如何生成字符串并将其插入到原始消息中。但是,为了验证您的方法,有必要编写一个程序来检查消息是否真的在最终字符串中编码。
给定两个字符串 s 和 t,您必须确定 s 是否是 t 的子序列,即是否可以从 t 中删除字符,使得剩余字符的串联为 s。
输入
输入包含多个测试用例。每个字符串都由两个字符串 s 指定,t 由空格分隔的字母数字 ASCII 字符。输入由 EOF 终止。
输出
对于每个测试用例输出,如果 s 是 t 的子序列。
样例输入
sequence subsequence
person compression
VERDI vivaVittorioEmanueleReDiItalia
caseDoesMatter CaseDoesMatter
样例输出
Yes
No
Yes
No
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(nullptr);
// cout.tie(nullptr);
string n,m;
while(cin>>n>>m){
int x = n.size(),p=m.size();
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <p;i++){
if(m[i]==n[flag]){
flag++;
}
if(flag==x){
cout << "Yes" << endl;
break;
}
}
if(flag!=x)
cout << "No" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
学长喜欢拆分
学长喜欢拆分
思路
因式分解(x+1)(y+1)=n+1
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= n + 1; ++i) {
if ((n + 1) % i == 0) {
int j = (n + 1) / i;
if (i > 1 && j > 1) {
flag = true;
}
}
}
if (flag)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
return 0;
}
AK比赛!
AK比赛!
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e9+10
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
int a, b, sum = 0,time=0,s=0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a >> b;
time =time + a + b * k;//时间点
s= b * 20;//罚时
sum += (time + s);
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
春游
春游
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e9+10
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
map<int, int,greater<int>> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m;i++)
{
int s;
cin >> s;
mp[s]++;
}
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (mp[i]==0)
{
cout << i << " ";
flag = false;
}
}
if (flag)//判断是否齐
cout << n ;
return 0;
}
A-B 数对
A-B 数对
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, c;
cin >> n >> c;
map<int,int,greater<int>> mp;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int s;
cin >> s;
mp[s]++;
}
int samsun = 0;
for (const auto &pair1 : mp){
auto sum = pair1.first - c;
auto it = mp.find(sum);
if (it!=mp.end())
{
int x = it->second;
samsun += pair1.second * x;
}
}
cout << samsun << endl;
return 0;
}
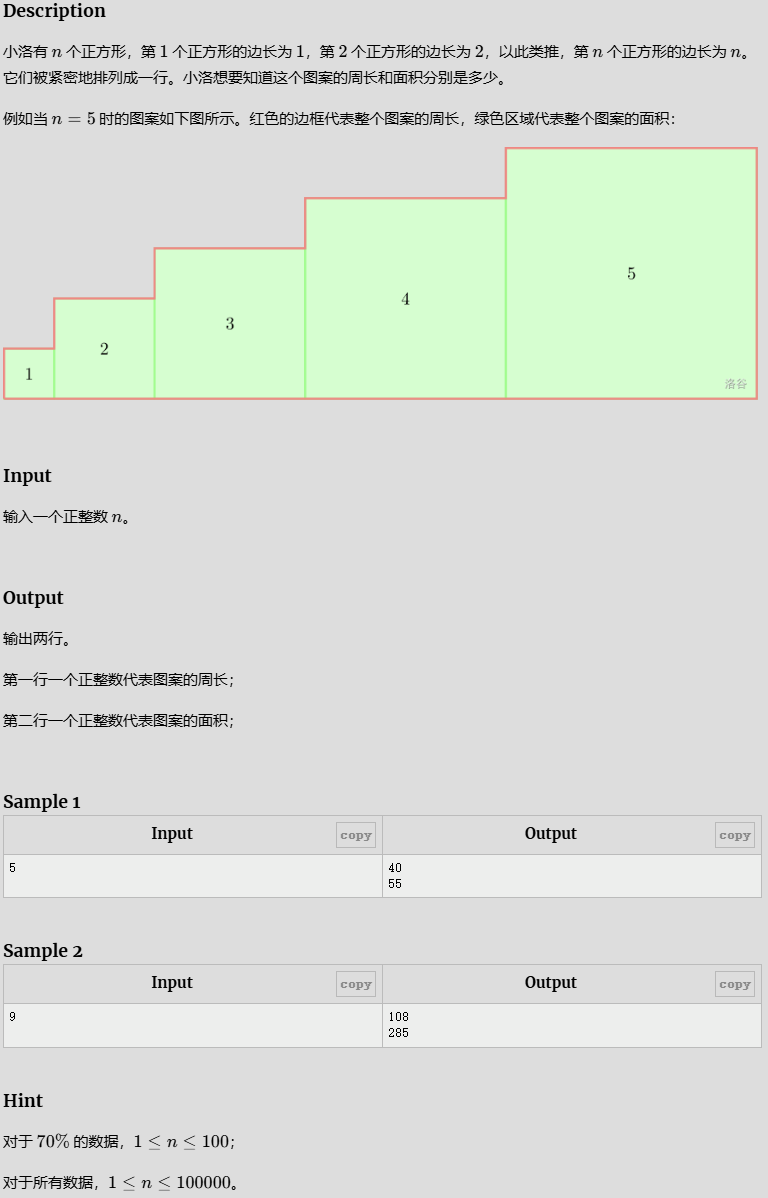
周长与面积计算
周长与面积计算
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
#define N 1e6+10
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
int l=0, s=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
l += i;
s += i * i;
}
l = l * 2 + 2 * n;
cout << l << endl;
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}