文章目录
- 贪心算法
- 双指针
- 前缀和与差分
- 整数二分&&实数二分
- 解题集
- 陶陶摘苹果(升级版)
- 骑士的工作
- 混合牛奶 Mixing Milk
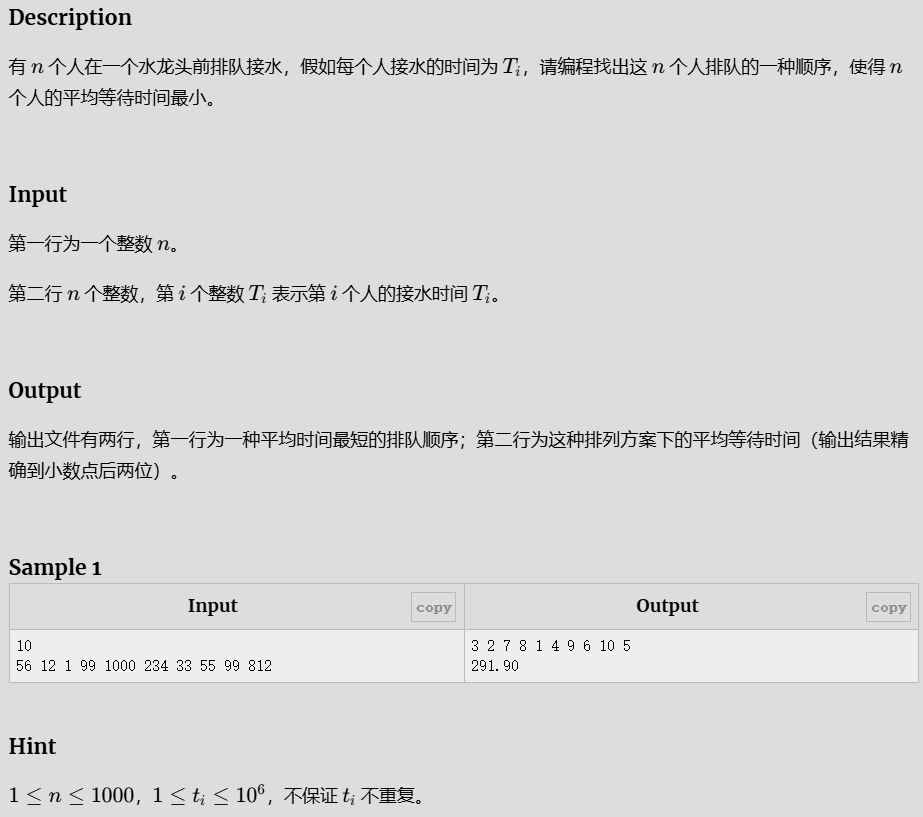
- 排队接水
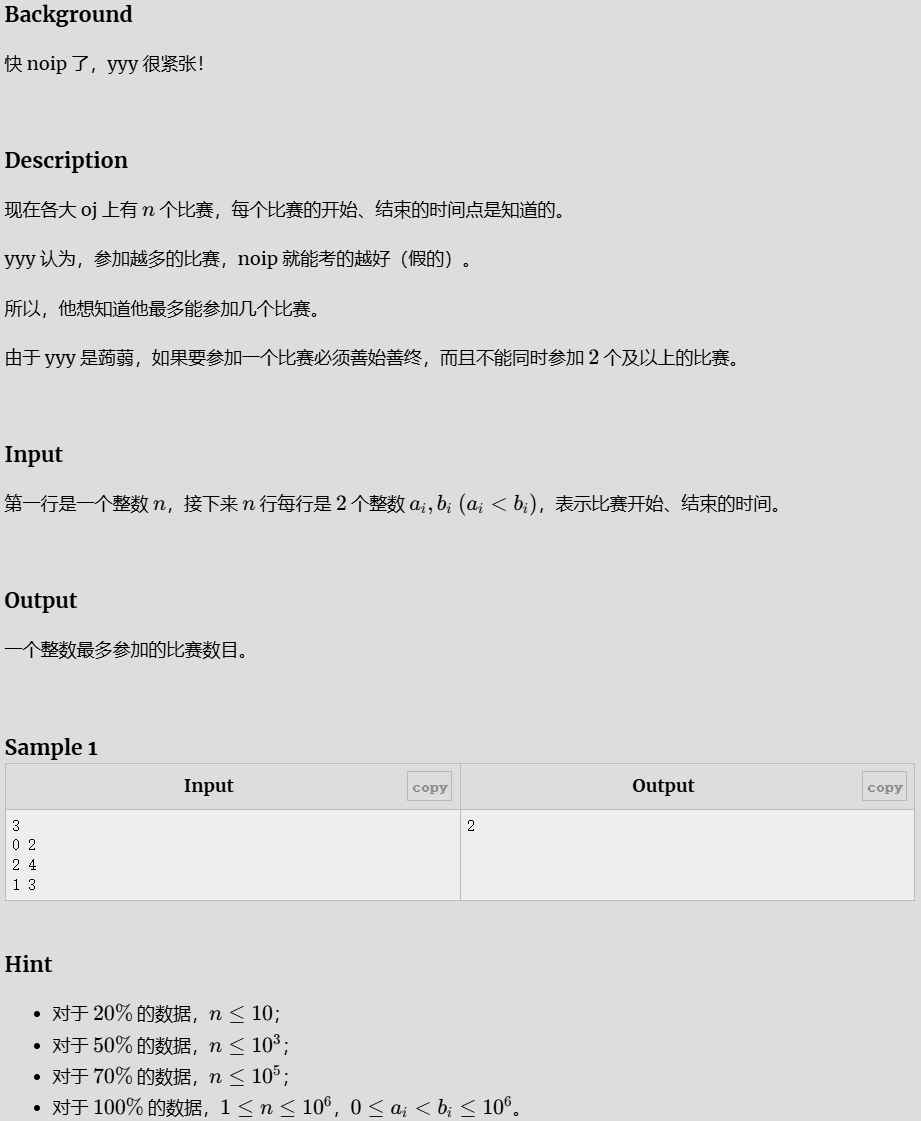
- 凌乱的yyy / 线段覆盖
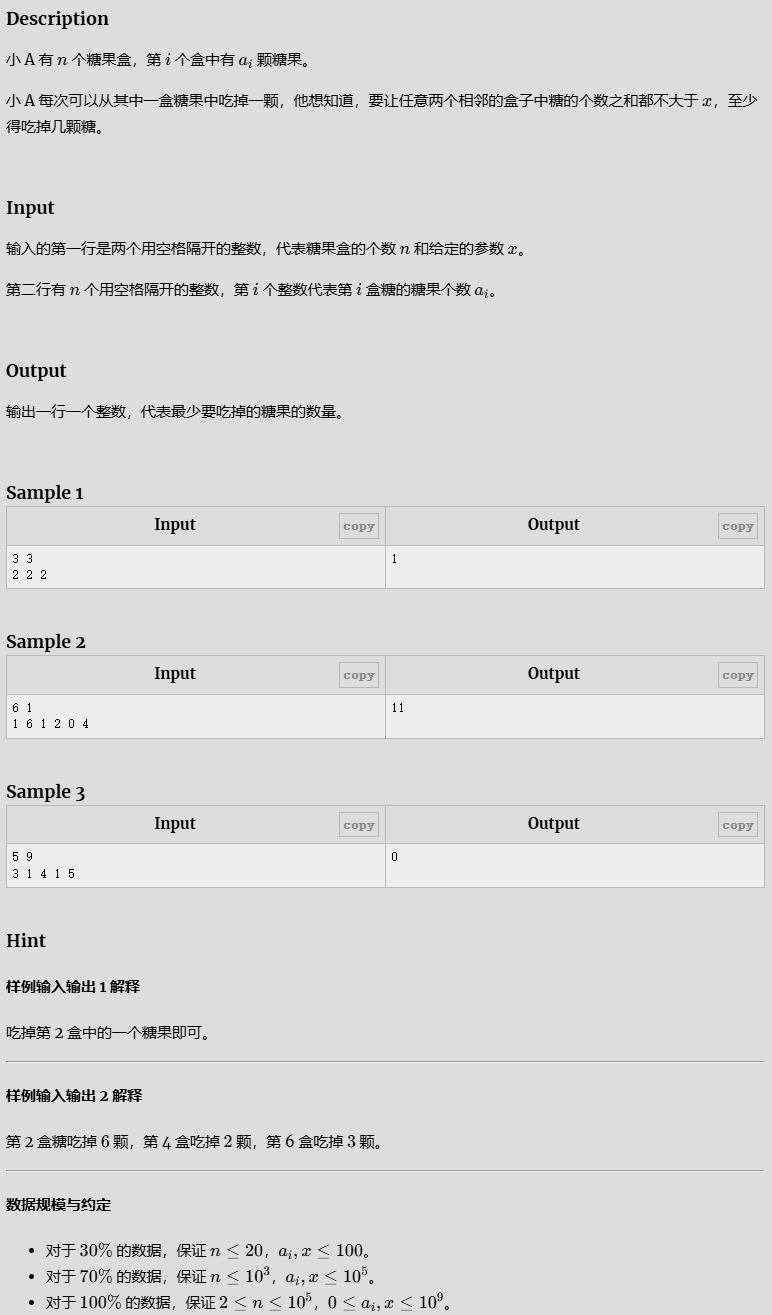
- 小A的糖果
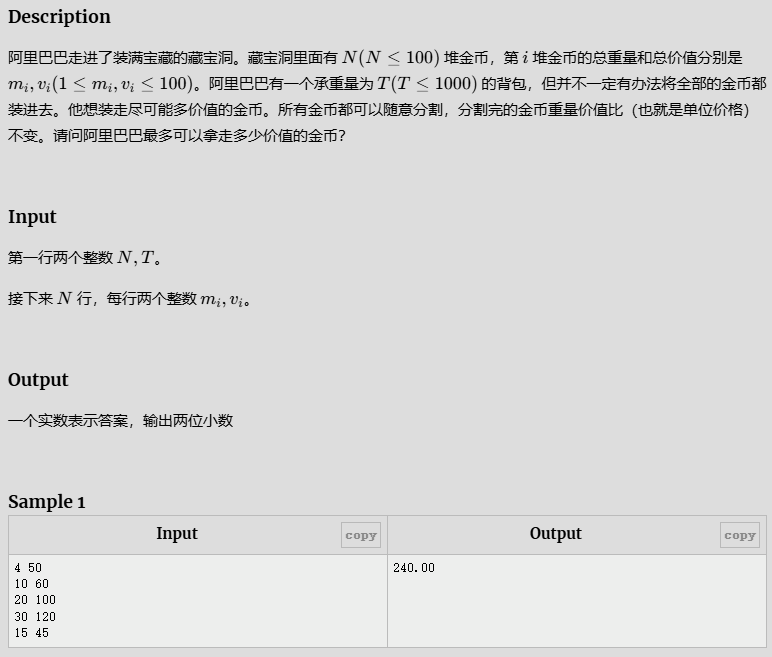
- 部分背包问题
- 铺设道路
- 今年暑假不AC
- 回文串
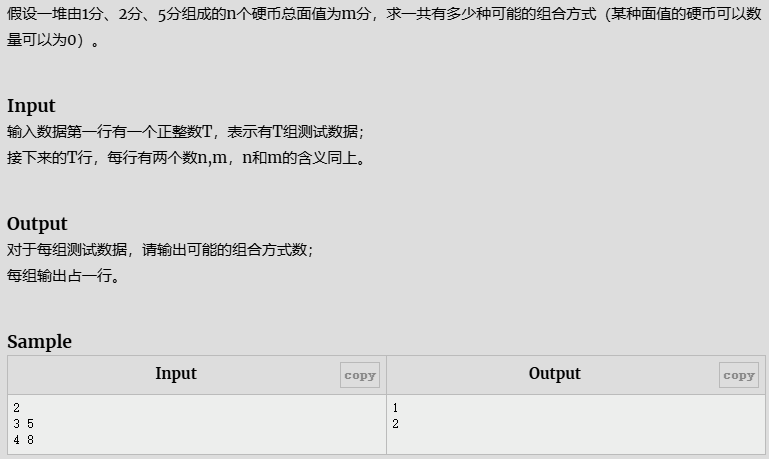
- 统计硬币
- A-B 数对
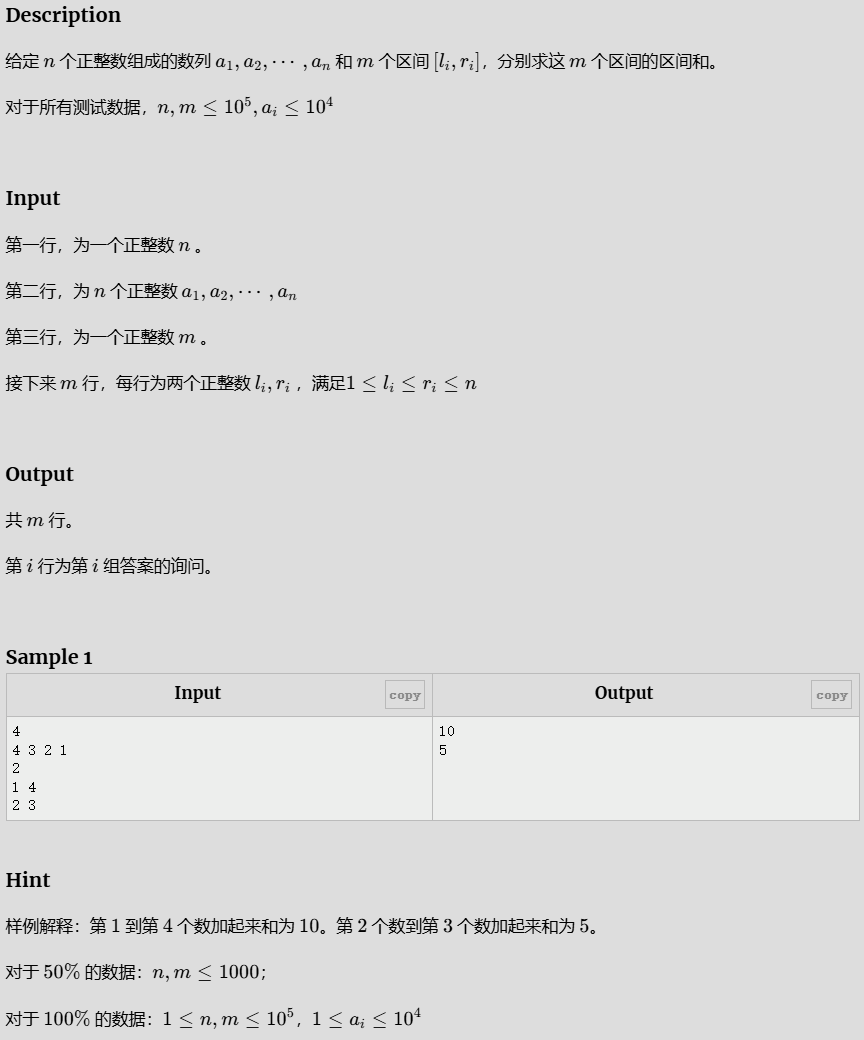
- 求区间和
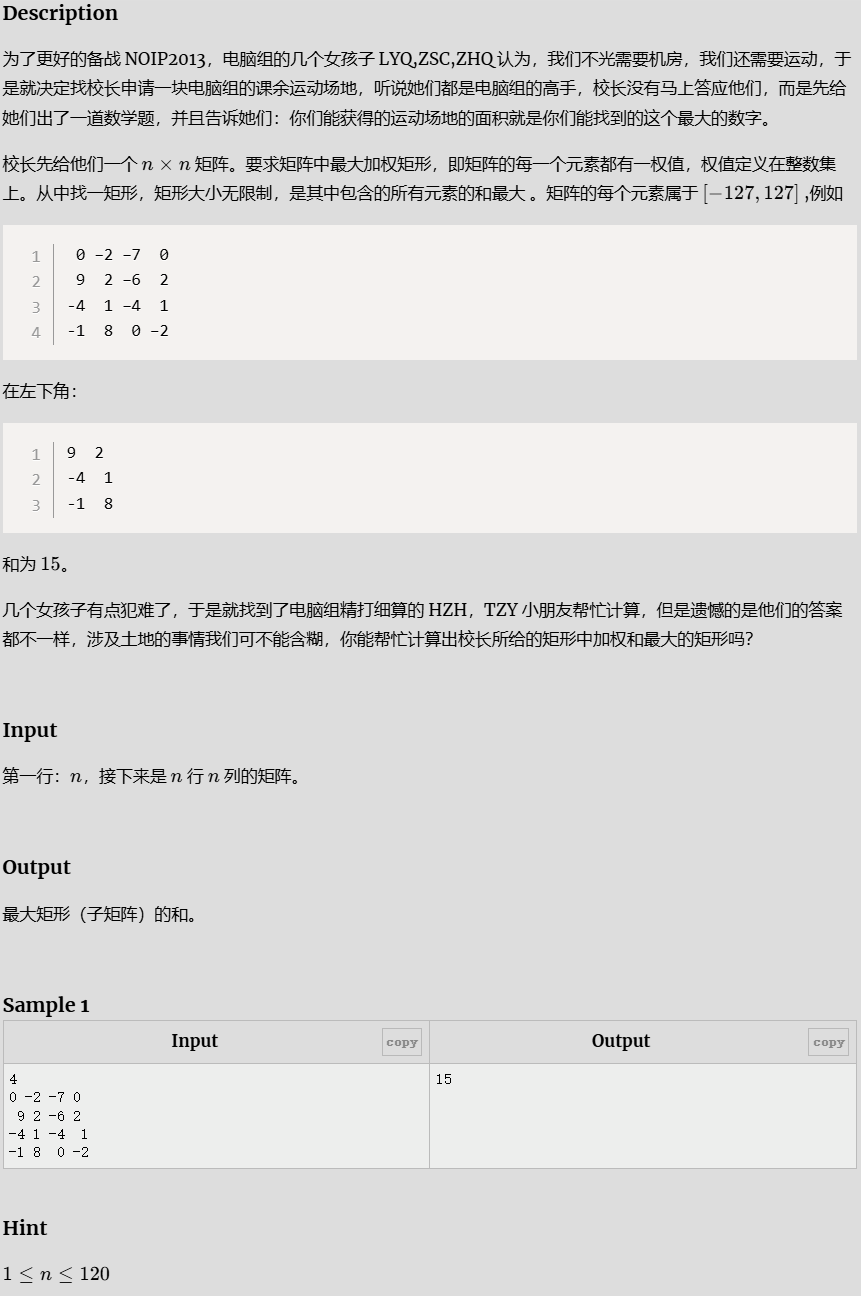
- 最大加权矩形
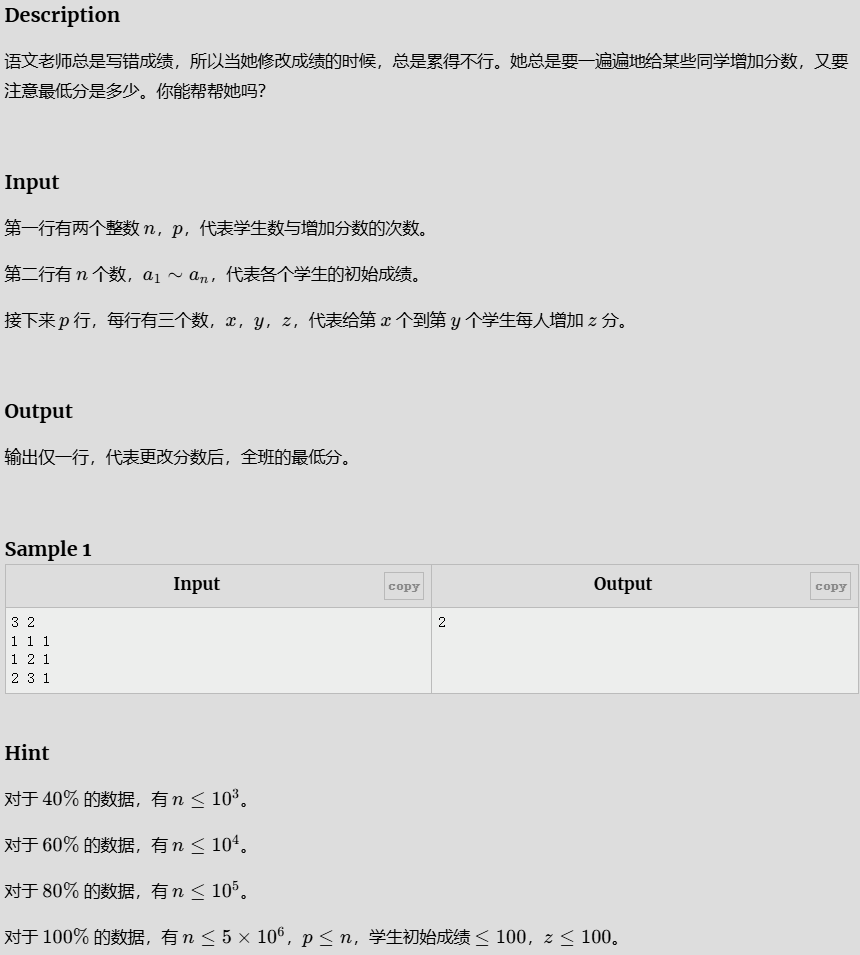
- 语文成绩
- 地毯
- 气球涂颜色
- 最高的奶牛
- 纪念品分组
- 小 E 与美食
- 机器猫斗恶龙
- 做题
- 学生分组
- 连续自然数和
- 宝箱
- 排列排序
- 合并果子 / [USACO06NOV] Fence Repair G
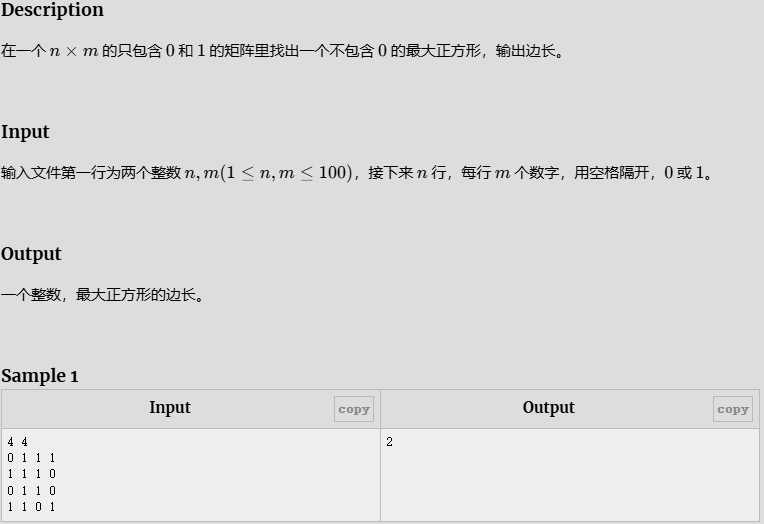
- 最大正方形
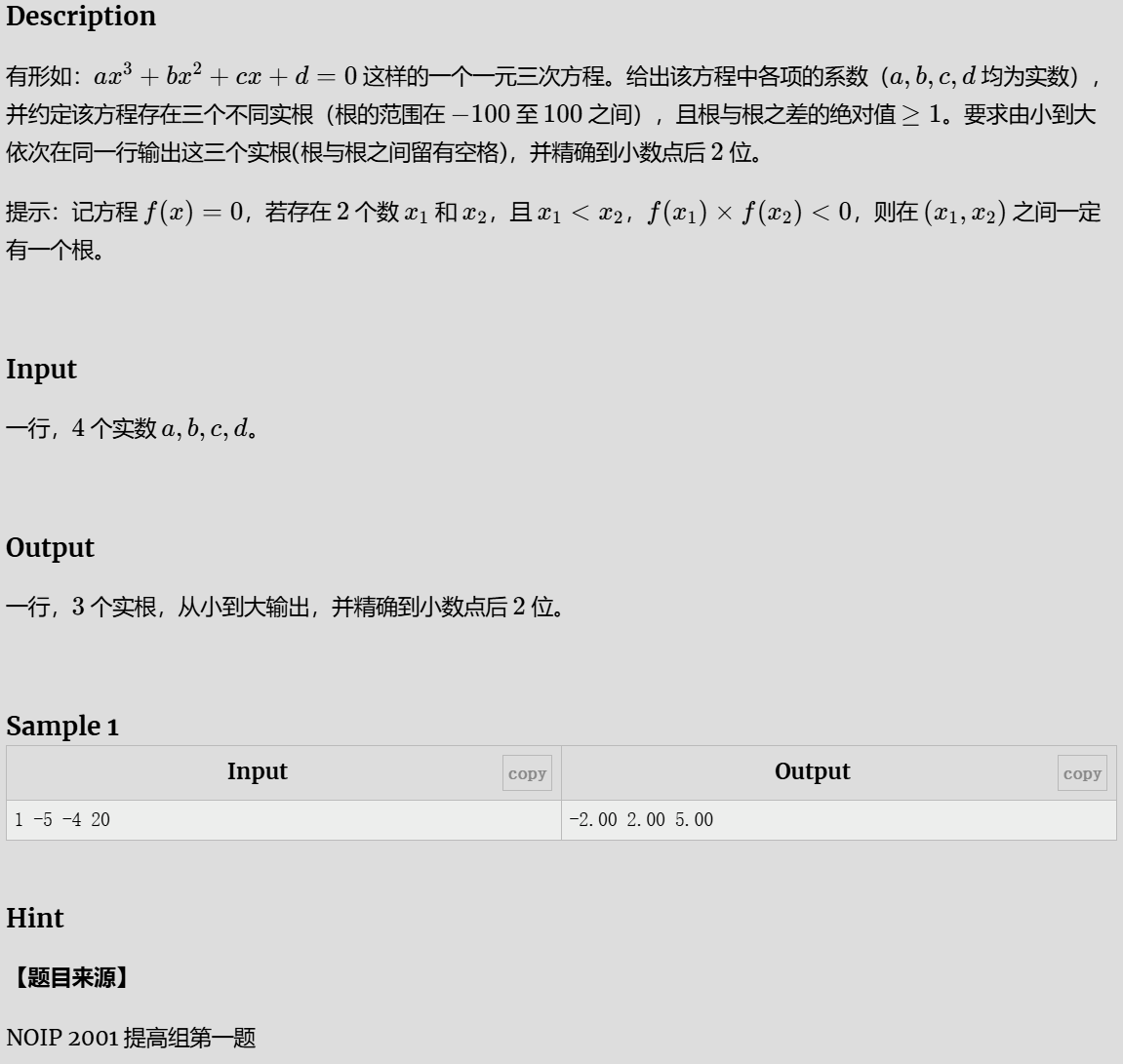
- 一元三次方程求解
- 立方根
- 机器人繁殖
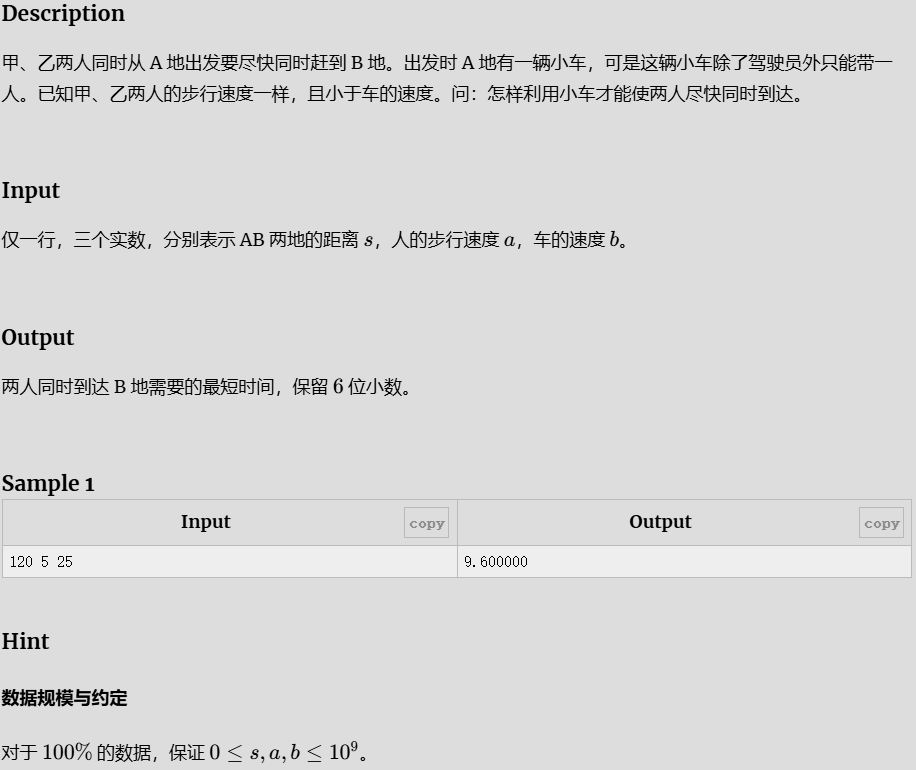
- 小车问题
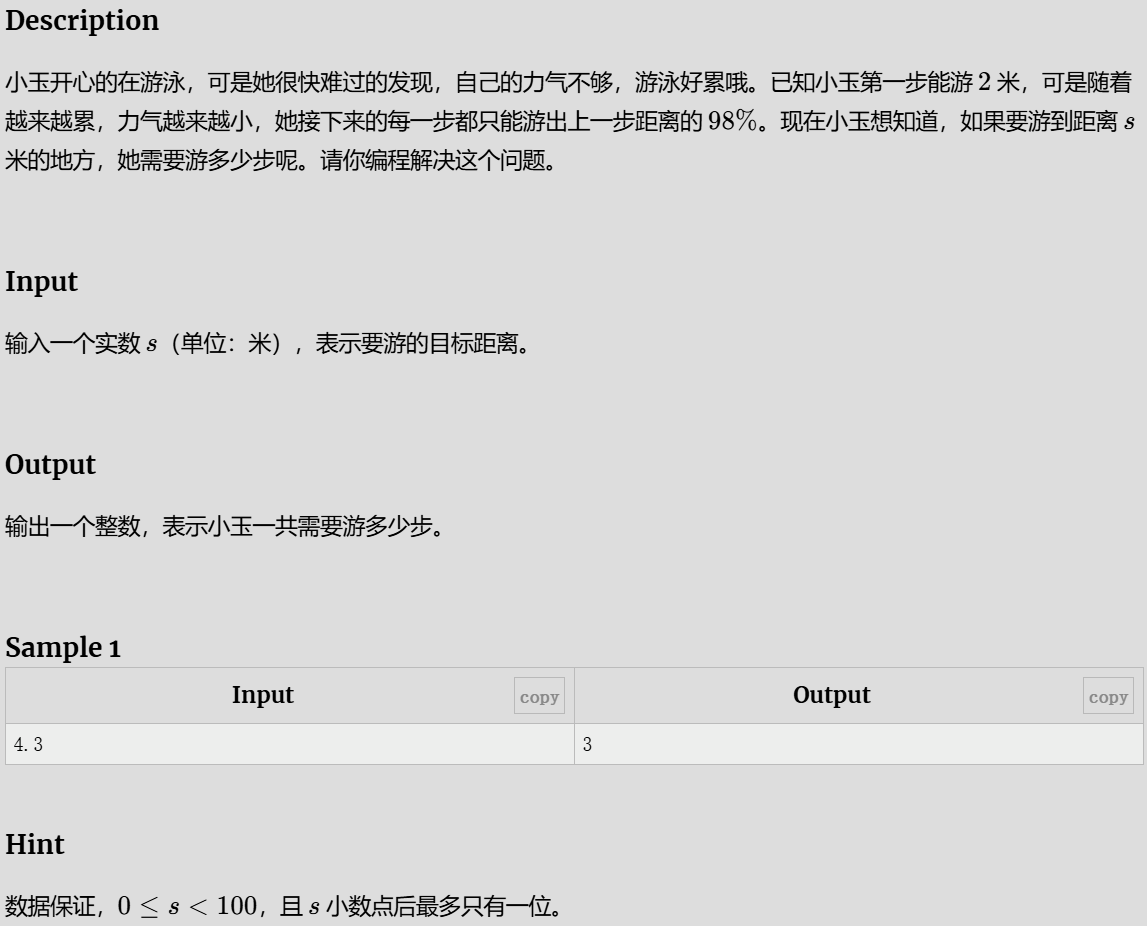
- 小玉在游泳
- Sanitize Hands
- Subsegment Reverse
- Adjacent Product
- Uppercase and Lowercase
- Nutrients
- Piano
- Sierpinski carpet
- Rudolf and the Ugly String
贪心算法
贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm),也称贪婪算法,是一种在每一步决策中都选择当前状态下最优的选项,以期达到全局最佳结果的优化算法。其核心思想是通过一系列局部最优选择来实现整体最优解。
定义
贪心算法的基本定义如下:
在每一步决策时,总是采取在当前状态下的最好选择,从而希望导致结果是最好或最优的。
贪心算法不考虑未来可能产生的影响,只关注当前的局部最优解。
贪心算法通常运行迅速,因为它们不涉及复杂的回溯或多次迭代。
特性
局部最优选择:在每步只选择当前看似最优的决策,不考虑长远后果。
不回溯:一旦做出选择,不会回溯或重新评估这些决策。
简单直接:由于算法逻辑简单,易于编码和快速实现。
高效性:运行迅速,因为不需要复杂的回溯或多次迭代。
原理与使用方法
贪心算法的基本原理是从问题的某个初始解出发,逐步地进行选择,直到达到最终求解的过程。每一步选择都是基于当前的局部最优,并且不能回退。因此累积到的这些局部最优的选择结果,就是全局最优解。
使用贪心算法需要满足以下两个条件:
问题具有贪心选择性质,即使用当前最优解能够得到全局最优解;
问题的子问题具有最优子结构性质,即原问题的最优解可以通过对子问题的最优解组合而得到。
设计步骤
设计贪心算法一般包括以下几个步骤:
确定问题的最优子结构;
基于问题的最优子结构设计一个递归算法;
证明我们做出的贪心选择,只剩下一个子问题;
证明贪心选择总是安全的;
设计一个递归算法实现贪心策略;
将贪心算法转化为迭代算法。
贪心算法的应用示例:
最小生成树:在加权无向图中,Prim算法和Kruskal算法都是基于贪心策略的算法,用于求解最小生成树。
活动选择问题:给定一系列活动,每个活动都有一个开始时间和一个结束时间,求可以安排的最大活动数,使得没有两个活动的时间重叠。这个问题可以通过贪心算法求解。
背包问题(部分情况):虽然背包问题通常使用动态规划求解,但在某些特定条件下(如0-1背包问题的贪心版本,即“分数背包问题”),贪心算法也可以得到最优解。
哈夫曼编码:在数据压缩中,哈夫曼编码是一种使用贪心算法构建的用于无损数据压缩的广泛使用的可变长编码方式。
例如:在找零钱问题中,假设我们有面值为1元、5元、10元、50元、100元、500元的货币,现在要找零786元,贪心算法会从最大面额开始逐步减少,直到找到最优解。
贪心算法的优缺点:
优点:
算法简单,易于实现。
在某些问题中,能够产生最优解或近似最优解。
时间复杂度低,效率高。
缺点:
不适用于所有问题,特别是那些需要全局最优解的问题。
贪心策略的选择对结果有很大影响,如果贪心策略选择不当,可能导致无法得到最优解。
例题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct apple{
int high;
int power;
}ap[N];
int cmp(apple a,apple b){
return a.power<b.power;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n,s;//苹果数,力气
cin>>n>>s;
int a,b;//椅子高度,手臂长
cin>>a>>b;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>ap[i].high>>ap[i].power;
}
sort(ap+1,ap+n+1,cmp);//对苹果按照力气从小到大排序
//摘苹果
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
//判断高度是否足够
if(ap[i].high>a+b){//超出高度
continue;
}
else if(s>=ap[i].power){
s-=ap[i].power;
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct gold{
int x;
int y;
double pj;
}jb[N];
int cmp(gold a,gold b){
return a.pj>b.pj;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n,t;
cin>>n>>t;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>jb[i].x>>jb[i].y;
jb[i].pj=(double)jb[i].y/(double)jb[i].x;
}
sort(jb,jb+n,cmp);
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(t>=jb[i].x){
sum+=jb[i].y;
t-=jb[i].x;
}
else if(t>0){
sum+=(t)*jb[i].pj;
break;
}
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<sum;
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct time1{
int x;
int y;
} bs[N];
bool cmp(time1 a, time1 b){
return a.y < b.y;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){
cin >> bs[i].x >> bs[i].y;
}
sort(bs, bs + n,cmp);
int cnt=0;int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){
if(last<=bs[i].x){
cnt++;
last = max(last, bs[i].y);
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
双指针
概念
双指针(Two Pointers)是一种在遍历对象过程中,使用两个指针进行访问以达到特定目的的算法思想。根据两个指针的移动方向和相对位置,可以分为以下几种类型:
快慢指针:两个指针从同一侧开始遍历数组或链表,一个指针移动速度快(快指针),另一个移动速度慢(慢指针)。这种模式常用于解决需要判断某个条件是否满足的问题,如寻找有序数组中的某个值、判断是否存在某对元素等。
对撞指针:两个指针分别从数组的两端开始向中间移动,通常一个指针向前移动,另一个向后移动。这种模式适用于需要找到一对特定条件下的元素对,例如两数之和问题。
滑动窗口:当两个指针指向同一数组且遍历方向相同且不相交时,称为滑动窗口。这种模式常用于区间搜索问题,如寻找最长的子串满足某种条件
例题
回文数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;cin>>s;
int i=0,j=s.size()-1;
while(i<j){
if(s[i]!=s[j]){
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return 0;
}
i++;j--;
}
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
return 0;
}
找指定和的整数对
输入n个整数,放入数组a。找出其中的两个数,他们的和等于m。
输入样例:
9 28
21 4 5 6 13 65 32 9 23
输出
5 23
解题代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
int a[10000];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a,a+n);
int i=0,j=n-1;
while(i<j){
if(a[i]+a[j]>m){
j--;
}
if(a[i]+a[j]<m){
i++;
}
if(a[i]+a[j]==m){
cout<<a[i]<<" "<<a[j]<<endl;
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
移动0
给定一个数组nums,编写一个函数将所有0移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序
输入:nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
输出:[1,3,12,0,0]
解题代码
int a[5] = { 0,1,0,3,12 };
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (j <= 4) {
if (a[i] != 0) {
i++, j++;
}
else if (a[j] != 0) {
swap(a[i], a[j]);
i++;
}
j++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
寻找区间和
给定一个长度为n的数组a和一个数s;在这个数组中寻找一个区间,使得这个区间的元素之和等于s,输出区间的起点和终点
输入样例:
15 6
6 1 2 3 4 6 4 2 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
输出样例
0 0
1 3
5 5
6 7
解题代码
略
A-B 数对
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int maxn = 2e6+10;
int a[maxn];
signed main(){
int n, c;
cin >> n >> c;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
// i 是用来枚举b
// j and k are used to determine the interval range of a
// i is used to determine the left endpoint of the interval
// k is used to determine the right endpoint of the interval
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 1, j = 1, k = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while(j <= n && a[j] - a[i] < c) j++;
while(k <= n && a[k] - a[i] <= c) k++;
ans += k - j;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
前缀和与差分
概括
一维前缀和:
定义:s[i]前i项的和
构造:s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i]
使用:快速求出区间和
求出3-5之间的区间和:s[5] - s[2] = (1+2+3+4+5) - (1+2)
一维差分(标记思想)
定义:b[i]前ix项的和等于原数组a[i]
构造:b[i] = a[i] - a[i-1]
使用:快速区间修改
在3-5之间都+1,b[3]++,b[6]–
求和的时候同时进行前缀和运算即可
二维前缀和
定义:s[i][j]第i行,第j列的子矩阵的和
构造:s[i][j] = s[i-1][j] + s[i][j-1] + a[i][j] - s[i-1][j-1]
使用:快速求出矩阵中任意子矩阵(2,2)(5,5)
sum = s[5][5] - s[1][5] - s[5][1] + s[2][2]
二维差分
详见解题集:地毯
前缀和的概念和用法
概念:
前缀和是指一个数组的某下标之前的所有数组元素的和(即数列的前n项求和)。在算法中,前缀和是一种重要的预处理手段,能够降低算法的时间复杂度,快速地求出某一段的和,对于处理区间之间的问题往往十分高效。
用法:
- 预处理前缀和数组:首先,对原始数组进行一次遍历,累加计算出前缀和数组的每一个元素。具体实现时,可以创建一个与原始数组相同长度的前缀和数组,其中第
i个元素代表原始数组从下标0到下标i-1的元素之和(或者从下标1到下标i的元素之和,具体取决于实现方式)。 - 查询区间和:在预处理得到前缀和数组后,可以通过计算两个位置的前缀和之差来快速得到任意区间的和。例如,对于区间
[a, b],其和等于前缀和数组中第b+1个元素(如果下标从0开始)减去第a个元素(如果a不为0)。
作用:
1.高效计算区间和:前缀和可以用来快速计算数组中某个区间的和。例如,要计算区间l,r之间的和,只需用s[r]减去s[l-1]即可。
2.二维前缀和:在处理二维数组时,如矩阵的最大子矩阵和问题,前缀和同样适用。通过预处理二维前缀和,可以大大降低查询的时间复杂度。
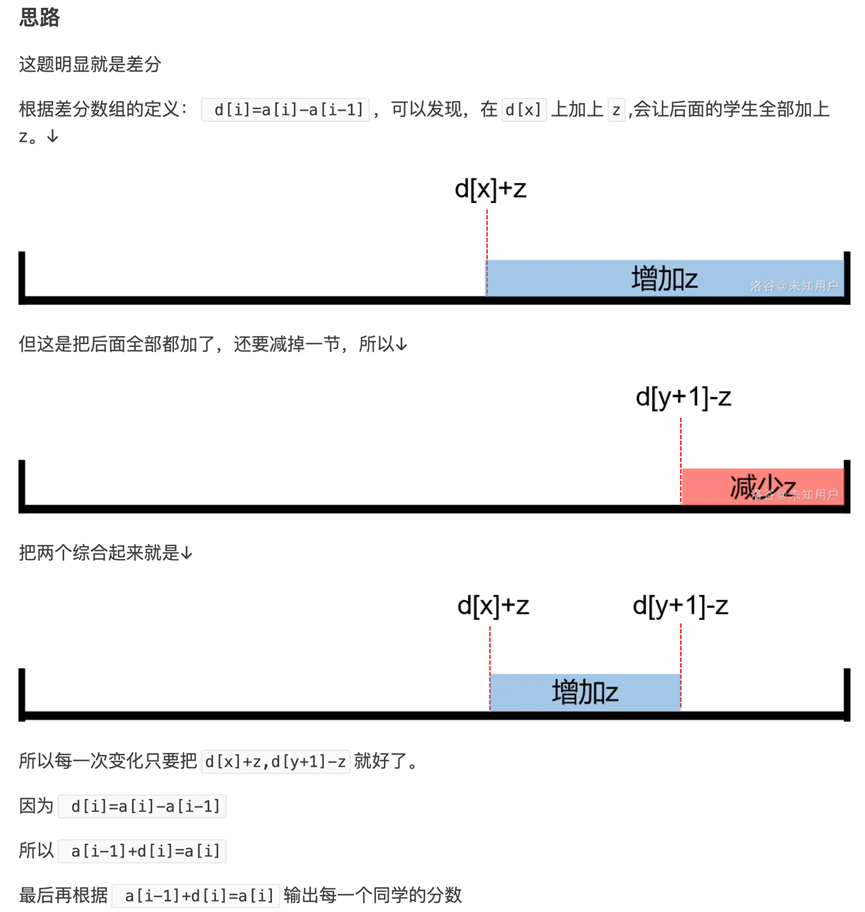
差分的概念和用法
概念:
差分,又名差分函数或差分运算,是数学中的一种概念,差分的结果反映了离散量之间的一种变化,是研究离散数学的一种工具。差分运算可以看作是前缀和的逆运算,它将原函数映射到其差分表示上。差分运算在数学、物理和信息学等领域有广泛应用。
用法:
- 构建差分数组:对于一维数组,差分数组d的每个元素
d[i]表示原数组a中第i个元素与第i-1个元素的差(即d[i] = a[i] - a[i-1],注意d[0]通常没有定义或设为0)。通过差分数组,可以方便地实现对原数组某个区间的批量加减操作。 - 区间修改:当需要对原数组的某个区间[l, r]内的所有元素都加上一个值c时,可以通过修改差分数组来实现。具体操作为:
d[l] += c(表示从l位置开始增加c),d[r+1] -= c(表示在r+1位置结束增加,防止对后续区间产生影响)。之后,通过对差分数组进行前缀和运算,即可得到修改后的原数组。 - 降低时间复杂度:通过差分,可以将区间修改操作的时间复杂度从
O(n)降低到O(1)(对于差分数组的修改操作)和O(n)(对于通过前缀和还原原数组的操作),从而在处理大量区间修改和查询问题时提高效率。
作用:
1.快速修改区间值:差分法主要用于对数组的某一个区间每个数加上一个常数。例如,如果要将区间l,r的所有元素赠加一个常数d,则只需将差分数组c中的c[i]加上d,并且c[r+1]减去d。
2.逆向操作:当需要对原数组进行某些特定的修改时(如在某个区间内增加或减少某个值),可以通过差分数组来实现。首先对差分数组进行相应的修改,然后通过前缀和恢复原数组。
综上所述,前缀和与差分是算法中常用的两种技巧,它们分别通过预处理和逆运算的方式,降低了算法的时间复杂度,提高了处理区间问题的效率。
详见解题集(求区间和~最高的牛奶)
整数二分&&实数二分
原理理解
搜索法和二分法
搜索法
把区间[a, b]分成n等份,每个子区间长度是x,计算点xk = a + k*x(k=0,1,2,3,4,…,n)的函数值f(xk),
若f(xk) = 0,则是一个实根,若相邻两点满足f(xk) * f(xk+1) < 0,则在(xk, xk+1)内至少有一个实根,可以取(xk+ xk+1)/2为近似根。
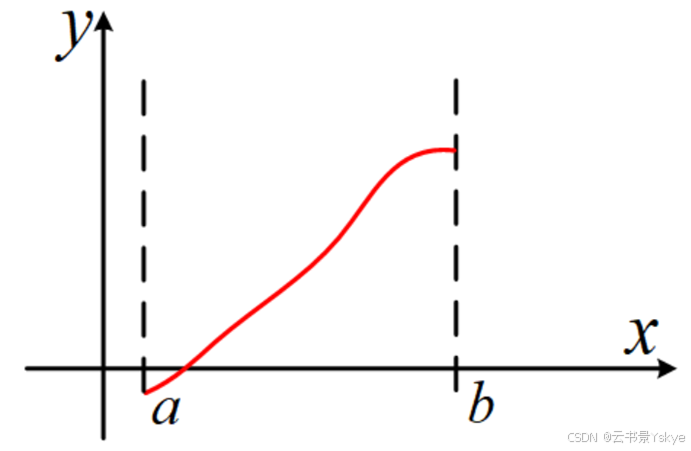
二分法
如果确定f(x)在区间[a, b]内连续,且f(a) * f(b) < 0,则至少有一个实根。
二分法的操作,就是把[a, b]逐次分半,检查每次分半后区间两端点函数值符号的变化,确定有根的区间。
用二分的两个条件:
上下界[a, b]确定
函数在[a, b]内单调。
二分法复杂度
n次二分后,区间缩小到(b - a)/2n。
给定a、b和精度要求ε,可以算出二分次数n,即满足(b - a)/2n < ε。
二分法的复杂度是O(logn)的。
例如,如果函数在区间[0, 100000]内单调变化,要求根的精度是10-8,那么二分次数是44次。
整数二分
二分模板一共有两个,分别适用于不同情况。
算法思路:
假设目标值在闭区间[l, r]中, 每次将区间长度缩小一半,当l = r时,我们就找到了目标值。
int bin_search(int *a, int n, int x){ //a[0]~a[n-1]是单调递增的
int left = 0, right = n; //注意:不是 n-1
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
//int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (a[mid] >= x) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
} //终止于left = right
return left; //特殊情况:a[n-1] < x时,返回n
}
(1)代码执行完后,left = right,即答案所处的位置。
(2)中间值midmid = left + (right-left)/2 mid = (left + right) >> 1
如果left + right很大,用前一种更好。
版本1:
当我们将区间[l, r]划分成[l, mid]和[mid + 1, r]时,其更新操作是l = mid + 1或者r = mid;(计算mid时不需要加1)
C++ 代码模板:
int bsearch_1(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1; //等同于mid=(l+r)/2
if (check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1; //+1为避免死循环
}
return l;
}
版本2:
当我们将区间[l, r]划分成[l, mid - 1]和[mid, r]时,其更新操作是l = mid或者r = mid - 1;(此时为了防止死循环,计算mid时需要加1)
C++ 代码模板:
int bsearch_2(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
实数二分
const double eps =1e-7; //精度。如果下面用for,可以不要eps
while(right - left > eps){ //for(int i = 0; i<100; i++){
double mid = left+(right-left)/2;
if (check(mid)) right = mid; //判定,然后继续二分
else left = mid;
}
循环用2种方法都可以:while(right - left > eps) { ... }for(inti = 0; i<100; i++) { ... }
如果用for循环,由于循环内用了二分,执行100次,相当于 1/2100的精度,比eps更精确。
8.2二分法.pptx
解题集
陶陶摘苹果(升级版)
P1478 陶陶摘苹果(升级版)
贪心:先将苹果根据力气从小到大排序,尽量省力;
然后开始高度判断,符合高度的就摘下来;
因为要求的是最多的苹果数量所以要尽量省力
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct apple{
int high;
int power;
}ap[N];
int cmp(apple a,apple b){
return a.power<b.power;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n,s;//苹果数,力气
cin>>n>>s;
int a,b;//椅子高度,手臂长
cin>>a>>b;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>ap[i].high>>ap[i].power;
}
sort(ap+1,ap+n+1,cmp);//对苹果按照力气从小到大排序
//摘苹果
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
//判断高度是否足够
if(ap[i].high>a+b){//超出高度
continue;
}
else if(s>=ap[i].power){
s-=ap[i].power;
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
骑士的工作
例题中5个头和4个头要分开算,每次挑选一次骑士,之前理解错误合并计算报错;
这里用了动态数组,因为骑士只能用一次,用完则删
最后判断有没有剩余头
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int sum=0;
vector <int> t;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int tou;
cin >> tou;//头
t.push_back(tou);
}
vector <int> a;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int qs;
cin >> qs;//骑士
a.push_back(qs);
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());//骑士从小到大排序
int money=0;
int tou = 0, qis = 0;
int cnt = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){//遍历头
tou = t[i];
int size1 = a.size();
for (int j = 0; j < size1; j++){//遍历骑士
qis = a[j];
if (tou <= qis){
money += a[j];
a.erase(a.begin() + j);
cnt--;
break;
}
}
}
if(cnt>0)//头没杀完
cout << "you died!" << endl;
else
cout << money << endl;
return 0;
}
混合牛奶 Mixing Milk
贪心:为了求性价比,单价从小到大排序;
需求量 > 供给 ?全收 : 剩余部分
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct nongmin{
int x;
int y;
double pj;
}jb[N];
int cmp(nongmin a,nongmin b){
return a.x<b.x;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n,t;
cin>>n>>t;//总量,个数
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
cin>>jb[i].x>>jb[i].y;//x为单价y为数量
}
sort(jb,jb+t,cmp);//根据单价从小到大采购
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(n>=jb[i].y){
sum += jb[i].x * jb[i].y;
n-=jb[i].y;
}
else if(n>0){
sum += (n)*jb[i].x;
break;
}
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(0)<<sum;
return 0;
}
排队接水
等待时间从小到大排序,每个人的等待时间是前面人的总和,求和平均
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct paidui{
int id;
double time;
} pd[N];
int cmp(paidui a,paidui b){
return a.time < b.time;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> pd[i].time;
pd[i].id = i+1;
}
sort(pd, pd + n,cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){
cout << pd[i].id << " ";
}
double sum = 0.00,x=0.00;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++){
x += pd[j].time;
}
sum += x;
x = 0;
}
sum = sum / (double)n;
cout <<endl << fixed << setprecision(2) << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
凌乱的yyy / 线段覆盖
P1803 凌乱的yyy / 线段覆盖
为了参加更多的比赛,所以结束时间越靠前越容易参加的多
则排序结束时间,再与开始时间比较
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct time1{
int x;
int y;
} bs[N];
bool cmp(time1 a, time1 b){
return a.y < b.y;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);//关闭同步流
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){
cin >> bs[i].x >> bs[i].y;
}
sort(bs, bs + n,cmp);
int cnt=0;int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){
if(last<=bs[i].x){
cnt++;
last = max(last, bs[i].y);
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
小A的糖果
如果超出,先看后者够不够?后者减少 :后者清零前者再减少还需减的量
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5+10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, x;
cin >> n >> x;
int a[N];int sum = 0;//总共要吃的糖
cin >> a[0];//先吃第一个,否则最后一个算不到!!!
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];//糖果列表
if (a[i] + a[i - 1] > x){//如果超出
int cnt = a[i] + a[i - 1] - x;//要吃的量
if(cnt>a[i]){//如果后者不够
a[i-1] = cnt - a[i];//前者吃掉剩余的糖
a[i] = 0;//后者清空
}
else{
a[i] -= cnt;
}
sum += cnt;
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
部分背包问题
P2240 【深基12.例1】部分背包问题
贪心:排序性价比,从大到小拿;
总重量 < 承重量 ?全拿 :拿部分
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct gold{
int x;
int y;
double pj;
}jb[N];
int cmp(gold a,gold b){
return a.pj>b.pj;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n,t;
cin>>n>>t;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>jb[i].x>>jb[i].y;
jb[i].pj=(double)jb[i].y/(double)jb[i].x;
}
sort(jb,jb+n,cmp);
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(t>=jb[i].x){
sum+=jb[i].y;
t-=jb[i].x;
}
else if(t>0){
sum+=(t)*jb[i].pj;
break;
}
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<sum;
return 0;
}
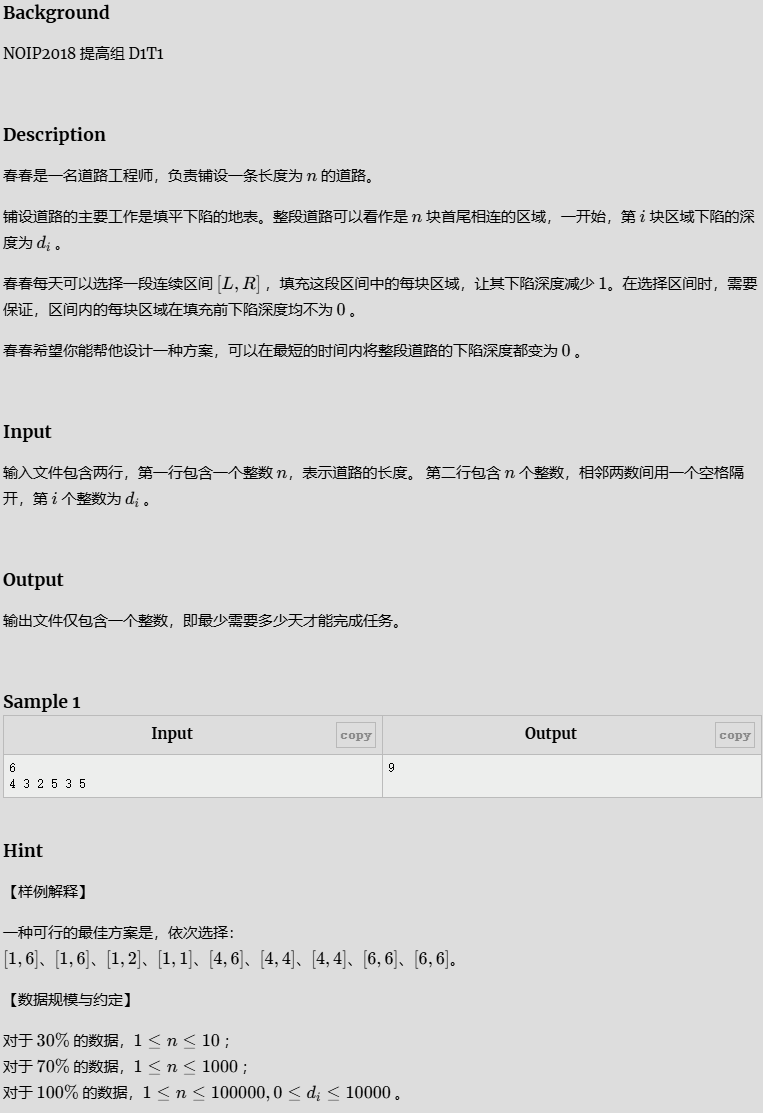
铺设道路
先找最低点,然后计算比最低点多出多少,同时更新低点
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
int a[N];
cin >> a[0];
int min = a[0];
int sum = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
if(min<a[i]){
sum += a[i] - min;
}
min = a[i];
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
今年暑假不AC
贪心:排序结束时间,比较开始时间,累计个数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct time1{
int x;
int y;
} bs[N];
bool cmp(time1 a, time1 b){
return a.y < b.y;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
while (cin >> n && n != 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> bs[i].x >> bs[i].y;
}
sort(bs, bs + n, cmp);
int cnt = 0;
int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (last <= bs[i].x)
{
cnt++;
last = max(last, bs[i].y);
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
return 0;
}
回文串
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;cin>>s;
int i=0,j=s.size()-1;
while(i<j){
if(s[i]!=s[j]){
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return 0;
}
i++;j--;
}
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
return 0;
}
统计硬币
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n - i; j++)
{
int k = n - i - j;
{
if ( i + 2 * j + 5 * k == m)
{
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
return 0;
}
A-B 数对
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int maxn = 2e6+10;
int a[maxn];
signed main(){
int n, c;
cin >> n >> c;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
// i 是用来枚举b
// j and k are used to determine the interval range of a
// i is used to determine the left endpoint of the interval
// k is used to determine the right endpoint of the interval
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 1, j = 1, k = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while(j <= n && a[j] - a[i] < c) j++;
while(k <= n && a[k] - a[i] <= c) k++;
ans += k - j;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
求区间和
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
const int maxn = 1e5 + 100;
int s[maxn];
int s2[maxn];
signed main() {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> s[i];
s2[i] = s[i] + s2[i - 1];//累计前i个的和的数组
}
int m; cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;//区间
cout << s2[r] - s2[l - 1] << endl;//前r个的和 - 前l-1个的和 == l~r之间的和
}
return 0;
}
最大加权矩形
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
const int maxn = 1e3 + 100;
int a[maxn][maxn];
int sum[maxn][maxn];
signed main() {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];//导入矩阵
sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1][j] + sum[i][j - 1] + a[i][j] - sum[i - 1][j - 1];
//求和矩阵:左d和+上d和+自身-左上d和(重复)
}
}
int maxx = -10000;
for (int x1 = 1; x1 <= n; x1++) {
for (int y1 = 1; y1 <= n; y1++) {
for (int x2 = x1; x2 <= n; x2++) {
for (int y2 = y1; y2 <= n; y2++) {
int s = sum[x2][y2] - sum[x1-1][y2] - sum[x2][y1-1] + sum[x1-1][y1-1];
//坐标x2y2到x1y1的矩阵之和,要减去x1y2和x2y1的重复部分
maxx = max(maxx, s);
}
}
}
}
cout << maxx << endl;
return 0;
}
语文成绩
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
const int maxn = 1e7 + 100;
//前缀和 :某一序列前 n 项的和 (我昨天的C题就是用前缀和过的,否则会 TL)
/*
差分数组
原数组(差分数组的前缀和数组)
前缀和数组(原数组的前缀和数组)
*/
//修改差分 -> 原数组
//s2[x]+1 s2[x+1]-1 -> [x-y]
int a[maxn] = { 0 };
int b[maxn] = { 0 };
signed main() {
int n, p; cin >> n >> p;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];//原数组
}
while (p--) {
int x, y, z; cin >> x >> y >> z;//调整
b[x] += z;
b[y + 1] -= z;//y之后不要加分,提前减去用来后续不加上
}
int minn = a[1] + b[1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
b[i] = b[i] + b[i - 1];//将差分数组变成原数组,根据前面的差分进行相加
a[i] = a[i] + b[i]; //将两个数组相加//原数字加上差分
minn = min(minn, a[i]);
}
cout << minn << endl;
}
地毯
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[2000][2000];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
while(m--){
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
for (int i = x1; i <= x2;i++){
a[i][y1]++;//首列记录
a[i][y2 + 1]--;//尾列减少截至
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
a[i][j] += a[i][j - 1];//根据上一排的压缩数据展开
cout << a[i][j]<<(j < n ? " " : "\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
气球涂颜色
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int x[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
while(cin >> n&&n!=0){
fill(x, x + N, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
x[a]++;
x[b + 1]--;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= n;k++){
x[k] += x[k - 1];
cout << x[k] << (k < n ? " " : "\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
最高的奶牛
思路
每次 [ a , b ] 颜色次数+1,典型的区间修改,最后求每个气球颜色修改次数,区间操作即对差分数组操作,对差分数组求前缀和就是原数组,因此此题差分
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
const int maxn = 1e5 + 100;
map<pair<int, int>, bool>cow;//去重
int s[maxn] = { 0 };
signed main() {
int n, I, h, r; cin >> n >> I >> h >> r;
// 几头 编号 高度 行
while (r--) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (a > b) {
swap(a, b);
}
if (cow[make_pair(a, b)]) {
continue;
}
s[a+1]--; s[b]++;
cow[make_pair(a, b)] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
s[i] = s[i] + s[i - 1];
cout << s[i] + h << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
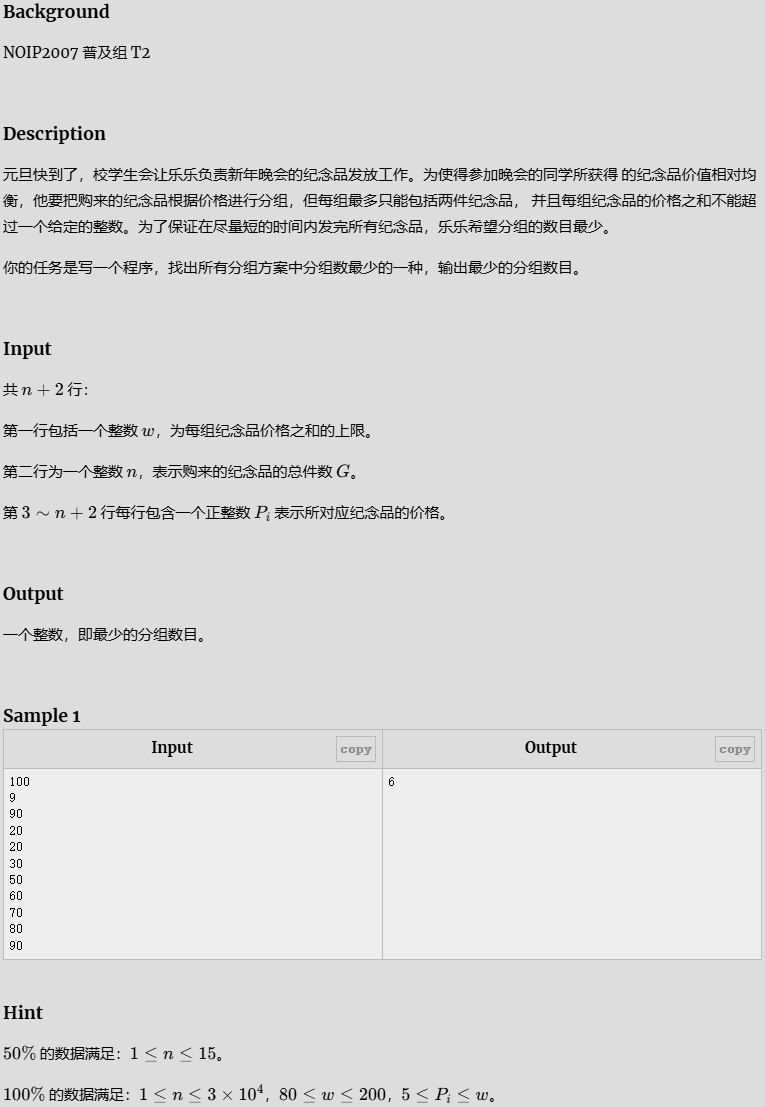
纪念品分组
贪心:一组两个,则先从小到大排序,再头尾选择组合,累计组数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int w;
cin >> w;
int n;
cin >> n;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n);
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while(i<=j){
if(i==j){
cnt++;
break;
}
if(a[i]+a[j]<=w){
cnt++;
i++;
j--;
}
else{
j--;
cnt++;
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
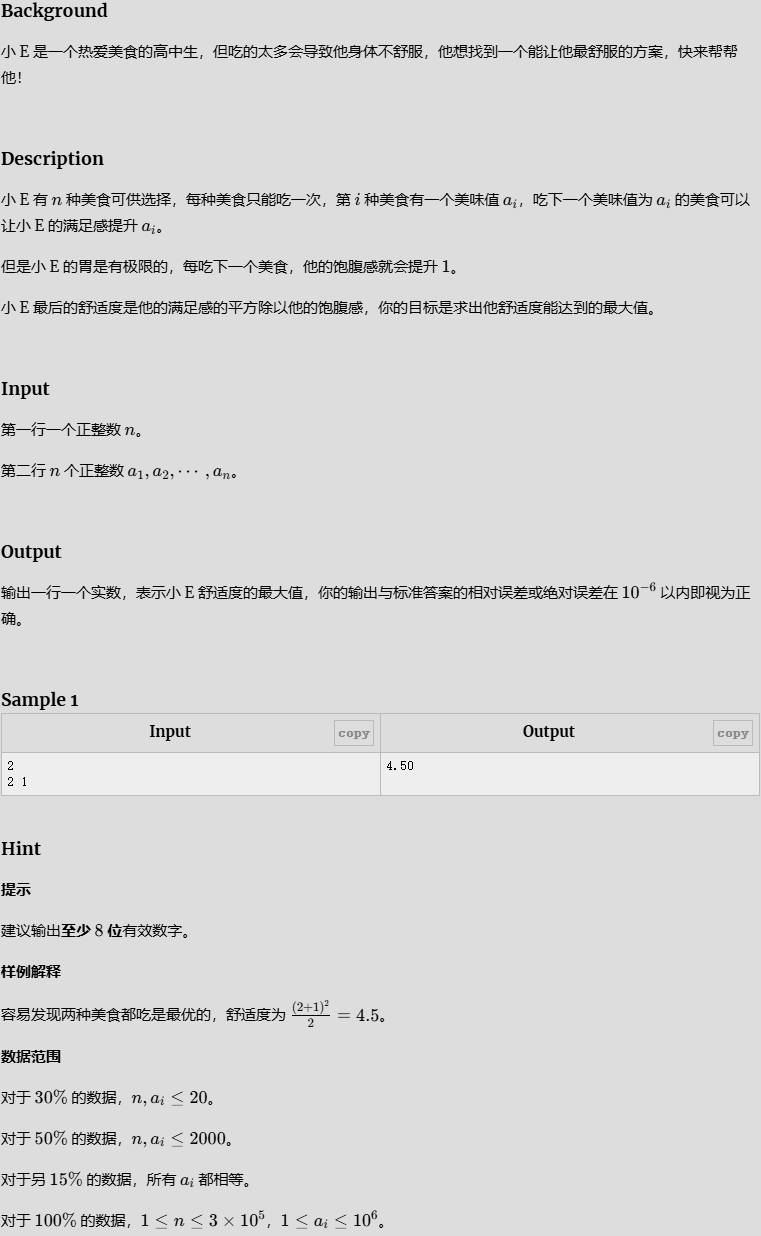
小 E 与美食
贪心:满意度从大到小排序,先吃前面,计算max
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
bool cmp(int a, int b){
return a > b;
}
int a[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n, cmp);
double sum=0.00,pj=0.00,max=0.00;
for (int j = 0; j < n;j++){
sum += a[j];
pj = (double)(sum * sum) / (double)(j+1);
if(pj>max){
max = pj;
}
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(8) << max << endl;
return 0;
}
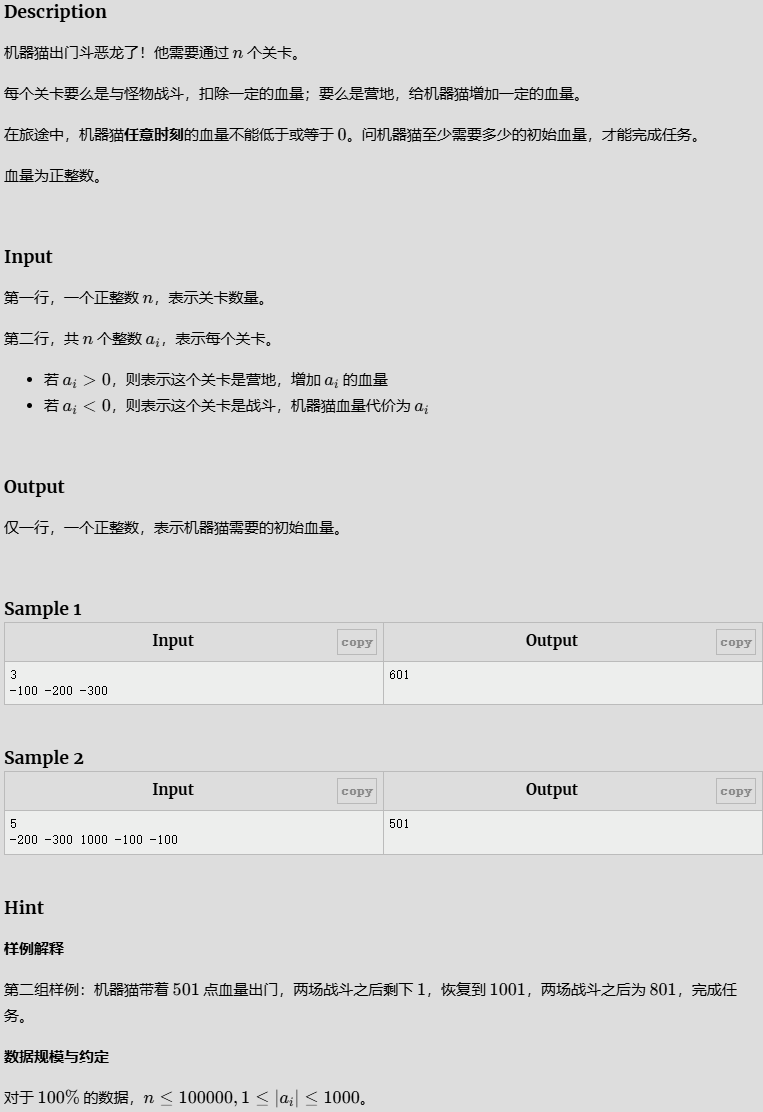
机器猫斗恶龙
控制血条,如果负了就累加到初始值
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
int sum=0, max=0;
int xt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
xt += x;
if(xt<0 && -1*xt>max){
max = xt * -1;
}
}
cout << max + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
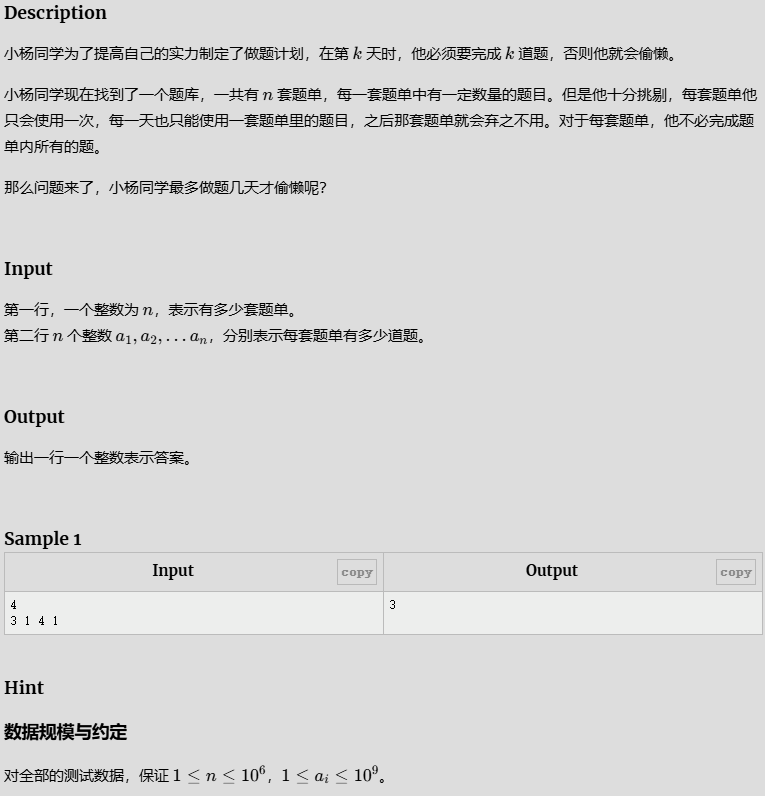
做题
天数越多题目越多,先题库从小到大排序,然后符合就看下一天
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a+1, a + n+1);
int k = 1;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++)
{
if(a[i]>=k){
k++;
}
}
cout << k-1 << endl;
return 0;
}
学生分组
先要考虑边缘问题,总共低于下限或高于上限都不行;
然后考虑调整,则考虑超出和缺少的数量,优先考虑下限缺少部分
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[60];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum += a[i];
}
if (sum < n * l || sum > n * r)
{
cout << "-1";
return 0;
}
int more = 0, less = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(a[i]>r){
more += (a[i] - r);
}
if(a[i]<l){
less += (l - a[i]);
}
}
cout << (less > more ? less : more) << endl;
return 0;
}
连续自然数和
遍历,双指针,多了减左边,少了加右边
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
int p1 = 0, p2 = 1;
int sum = p1+p2;
while(p1<p2&&p2<=n){
if(sum==n){
cout << p1 << " " << p2 << endl;
sum -= p1;
p1++;
}
if (sum > n){
sum -= p1;
p1++;
}
if(sum<n){
p2++;
sum += p2;
}
}
return 0;
}
宝箱
从大到小排序,双指针,求最高和最低的差值,求符合条件的区间的和的max;
如果只是取第一个和后面符合差值比较会报错,理解题目错误,因为可能第一个很大超出差值,导致数量少总和不一定多
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[1010];
bool cmp(int a, int b){
return a > b;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n,cmp);
int p1 = 0, p2 = 1;
int sum = a[p1];
int cz = 0;
int max = 0;
while(p1<p2&&p2<=n){
cz = a[p1] - a[p2];
if (cz > k){
if(sum>max){
max = sum;
}
sum -= a[p1];
p1++;
}
if(cz <= k){
sum += a[p2];
p2++;
}
}
cout << max << endl;
return 0;
}
排列排序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e6;
int a[maxn];
signed main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
int i=1;
int ans=0;
while(i<=n){//所有数1对1对应且连续
if(a[i]==i) i++;//数字在原来该在的位置
else{//没有在原来位置,则开始记录区间
//找到乱序中最大的数,因为要排到他原来位置,所有长度即为就要排序的长度
int maxx=a[i];
int j=i+1;
maxx=max(maxx,a[j]);
while(maxx>j){//找最大值原来的位置,至少到这个位置都要重新排序
j++;
maxx=max(maxx,a[j]);
}
ans+=j-i+1;
i=j+1;//更新区间
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
合并果子 / [USACO06NOV] Fence Repair G
双向队列先进先出,但是这里排序了,从小到大(省力),
取出两个小的合并成大的,因为要再次合并,则重新放入数组,
每次合并前端小的两个数字最省力
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
#define ll long long int
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int t;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > a;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> t;
a.push(t);
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int sum1 = 0;
sum1 += a.top();
a.pop();
sum1 += a.top();
a.pop();
sum += sum1;
a.push(sum1);
}
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
最大正方形
二维前缀和&&二维差分,创建两个二位数组,一个放原数据,一个放前缀和数据,
后续两个坐标之间的数据和则用差分处理;
因为数据1or0,则坐标之间的数据和则为边长积(面积)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[1000][1000], sum[1000][1000];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> a[i][j];
sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1][j] + sum[i][j - 1] + a[i][j] - sum[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
int max = 0;
for (int x1 = 1; x1 <= n;x1++){
for (int y1 = 1; y1 <= m;y1++){
for (int x = 0; x <= (n-x1); x++)
{
int x2 = x1 + x;
int y2 = y1 + x;
int s = sum[x2][y2] - sum[x2][y1 - 1] - sum[x1 - 1][y2] + sum[x1 - 1][y1 - 1];
if(s==(x+1)*(x+1)&&(x+1)>max)
max = x+1;
}/*
for (int x2 = x1; x2 <= n; x2++)
{
int len = x2 - x1 + 1;
int y2 = y1 + len - 1;
int s = sum[x2][y2] - sum[x2][y1 - 1] - sum[x1 - 1][y2] + sum[x1 - 1][y1 - 1];
if (s == len * len && len > max)
{
max = len;
}
} */
}
}
cout << max;
return 0;
}
一元三次方程求解
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double a, b, c, d;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c, &d);
double l, r, m, x1, x2;
int s = 0;
for (int i = -100; i < 100; i++){
l = i;
r = i + 1;
x1 = a * l * l * l + b * l * l + c * l + d;
x2 = a * r * r * r + b * r * r + c * r + d;
if (!x1){
printf("%.2lf ", l);
s++;
}
if (x1 * x2 < 0){
while (r - l >= 0.001){
m = (l + r) / 2;
if ((a * m * m * m + b * m * m + c * m + d) * (a * r * r * r + b * r * r + c * r + d) <= 0)
l = m;
else
r = m;
}
printf("%.2lf ", r);
s++;
}
}
}
立方根
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
int i=0, j=sqrt(n);
while (i<j) {
int mid = i + (j-i+1)/2;
if(fabs(mid*mid*mid)<=n)
i = mid;
else
j = mid-1;
}
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
机器人繁殖
python
def f(z, n):
if z == 1:
return n + n * 2 - 1
return f(z - 1, 2 * n - 1) + n
def main():
import sys
input = sys.stdin.read
data = input().split()
n = int(data[0])
s = int(data[1])
l = 0
r = 100
while l < r:
m = (l + r) // 2
if f(n, m) >= s:
r = m
else:
l = m + 1
print(l)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
小车问题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
double s, a, b;
cin >> s >> a >> b;
double l,r, t1, t2, tj, ty, m;
l = 0;
r = s;
do{
m = (l+r) / 2.0;
t1 = m / b;
t2 = (m - t1 * a) / (a + b);
tj = t1 + (s - m) / a;
ty = t1 + t2 + (s - (t1 + t2) * a) / b;
if (tj < ty)
r = m;
else
l = m;
}while (fabs(tj - ty) > 1e-8);
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << tj << endl;
return 0;
}
小玉在游泳
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
double s;
cin >> s;
double sum = 0.00;
int cnt = 0;
double x = 2.0;
while(sum<s){
sum += x;
cnt++;
x *= 0.98;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
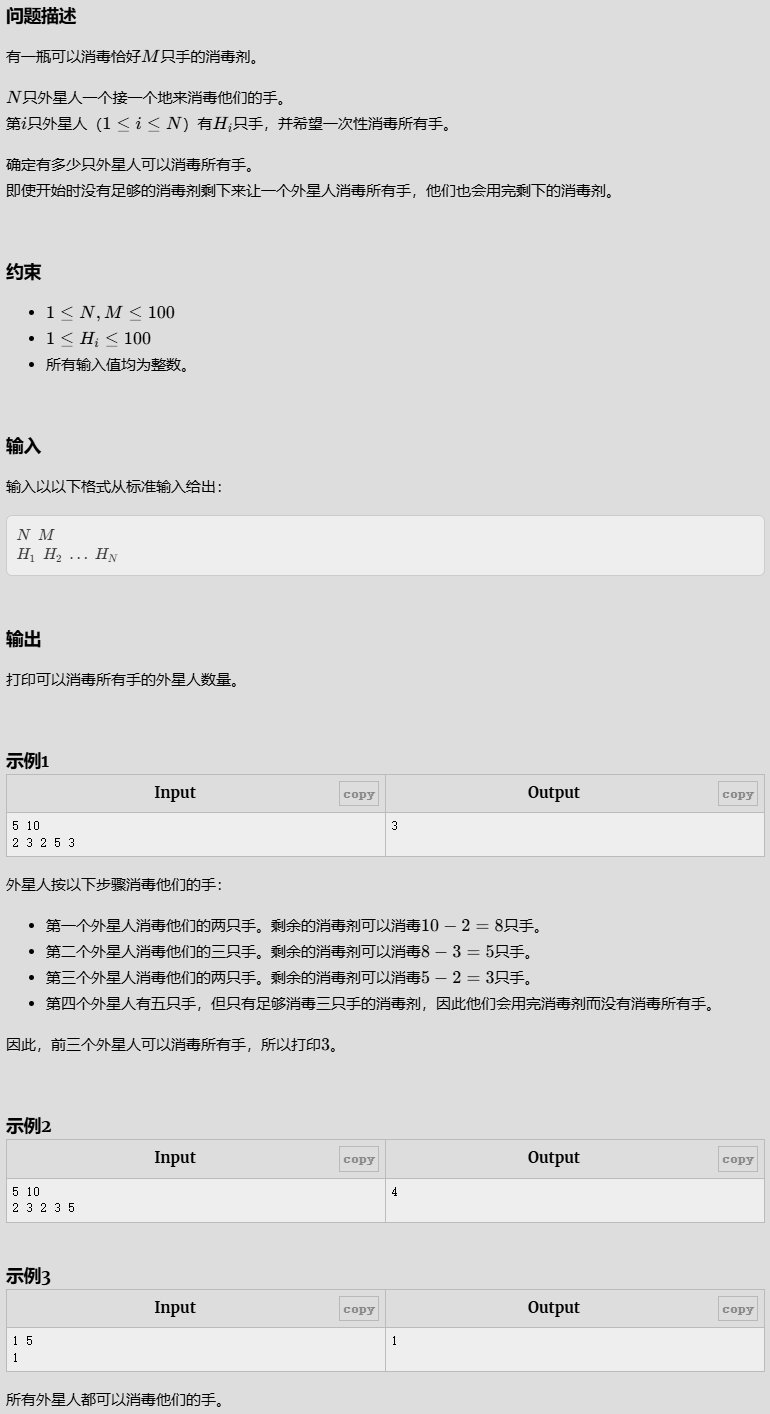
Sanitize Hands
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
int a[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n>>m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){
if(m>=a[i]){
m -= a[i];
cnt++;
}
else
break;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
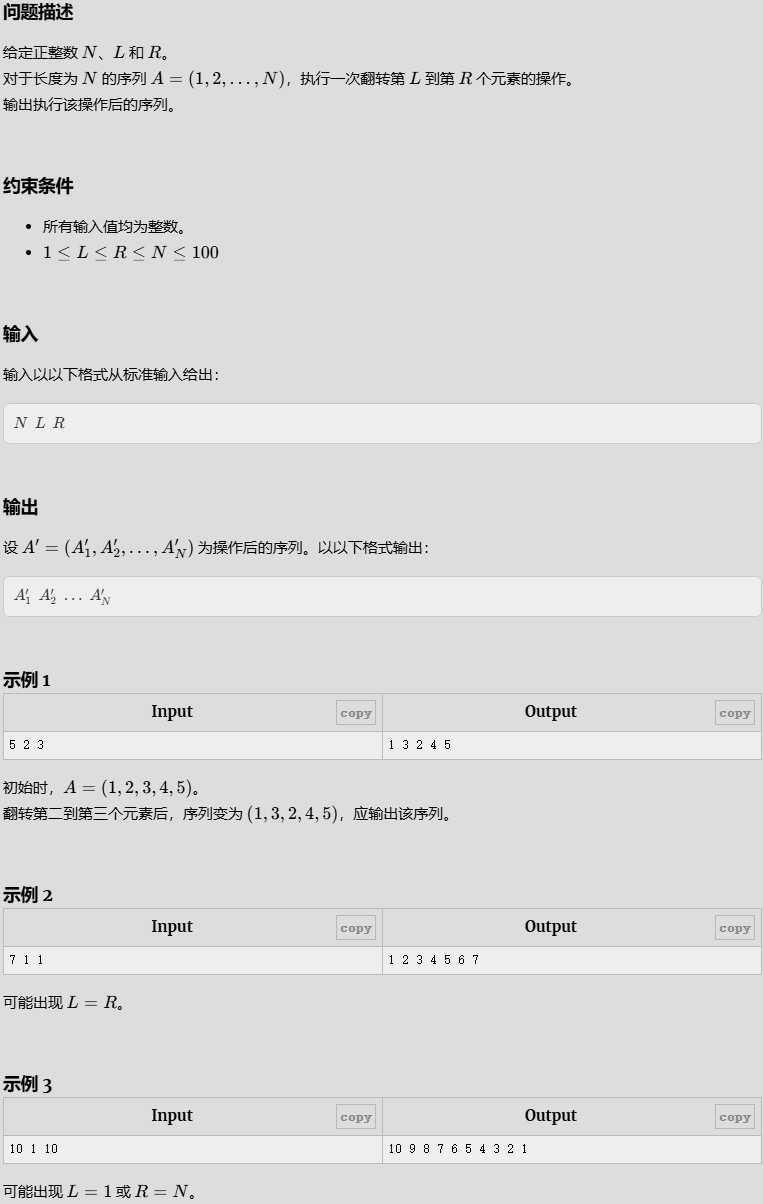
Subsegment Reverse
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, l, r;
cin >> n >> l >> r;
vector<int> a;
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++){
a.push_back(i);
}
if(l!=r)
reverse(a.begin()+l-1, a.begin()+r);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout << a[i] << (i < n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
return 0;
}
Adjacent Product
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
int a[N], b[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++){
b[i]=a[i]*a[i+1];
cout<<b[i]<<(i < n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
return 0;
}
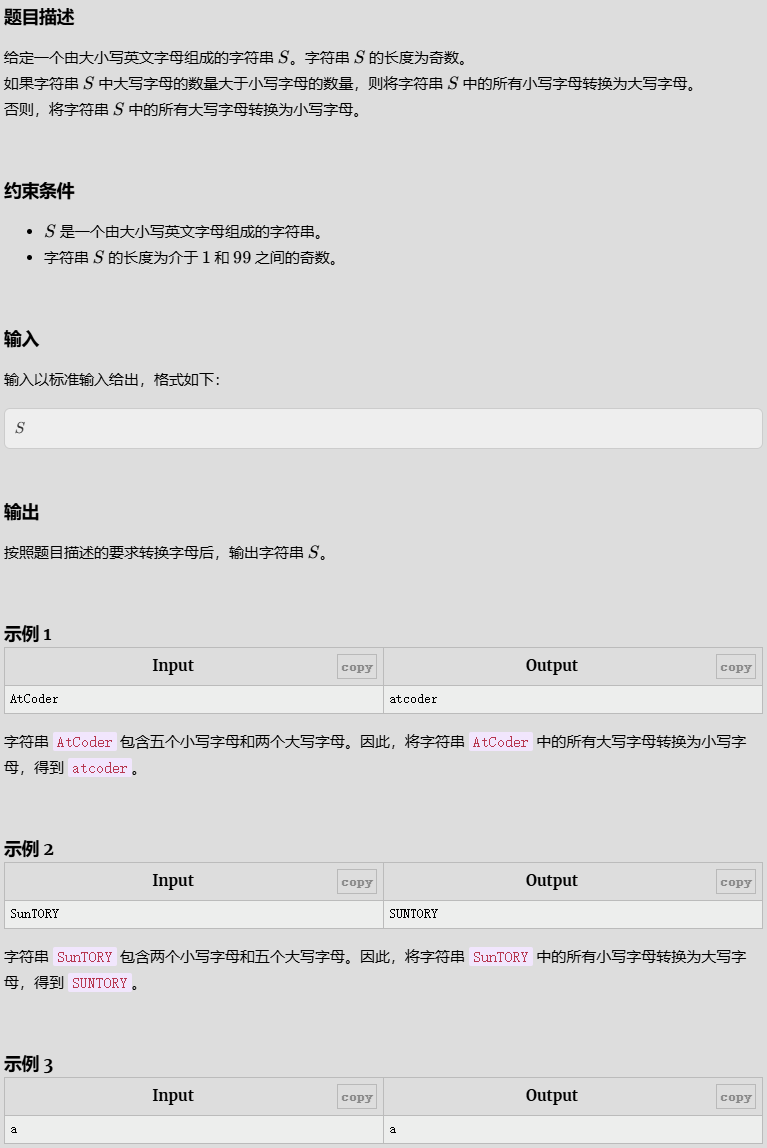
Uppercase and Lowercase
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10; // 注意这个常量在代码中没有直接使用,但定义也没问题
const double eps = 1e-7; // 这个常量同样在代码中没有使用
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
string s, sx = "", sk = ""; // 初始化 sx 和 sk 为空字符串
cin >> s;
int a = 0, b = 0;
for(char x : s){
if(x >= 'a' && x <= 'z'){
a++;
sx += x;
sk += (x - 'a' + 'A'); // 将小写转换为大写并添加到 sk
}
else if(x >= 'A' && x <= 'Z'){ // 确保只处理大写字母
b++;
sx += (x - 'A' + 'a'); // 将大写转换为小写并添加到 sx
sk += x;
}
}
if(a > b){
cout << sx << endl; // 输出小写字母组成的字符串
}
else{
cout << sk << endl; // 输出大写字母组成的字符串
}
return 0;
}
Nutrients
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
int a[1000],x[1000][1000],sum[1000];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
cin >> x[i][j];
sum[j] += x[i][j];
}
}
for (int z = 1; z <= m;z++){
if(a[z]>sum[z]){
cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "Yes" << endl;
return 0;
}
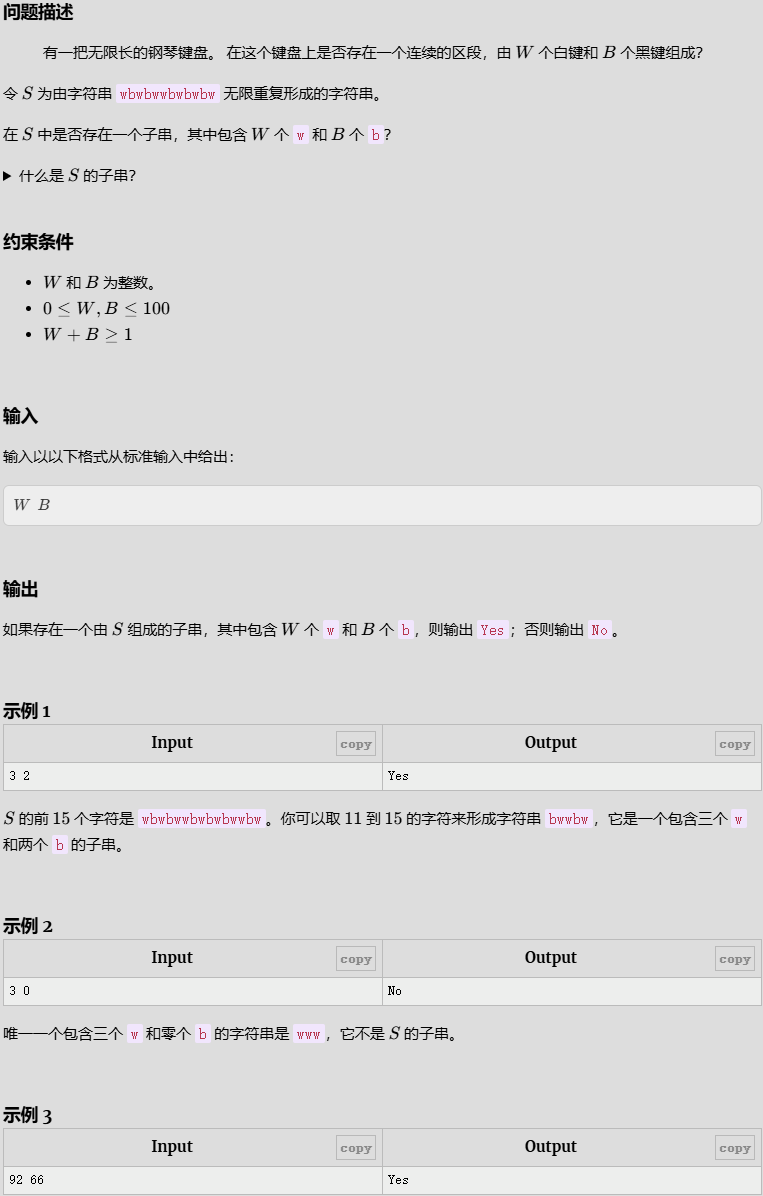
Piano
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int w, b;
cin >> w >> b;
string s = "wbwbwwbwbwbw";
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
int numw = 0, numb = 0;//w的数量,b的数量
//以i,j为双指针,j移动w+b的长度;
for (int j = 0; j < w + b; j++) {
if (s[(i + j) % 12] == 'w') numw++;
else numb++;
}
//ij子集若满足条件则yes
if (w == numw and b == numb) {
cout << "Yes" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "No" << endl;
}
Sierpinski carpet
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int n,l=1;
char a[729][730];
for(int i=0;i<729;i++)for(int j=0;j<730;j++)a[i][j]=0;
cin>>n;
a[0][0]='#';
for(int k=0;k<n;k++){
for(int x=0;x<3;x++){
for(int y=0;y<3;y++){
if((x==0)&&(y==0))continue;
if((x==1)&&(y==1)){
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)for(int j=0;j<l;j++)a[x*l+i][y*l+j]='.';
}
else{
for(int i=0;i<l;i++){
for(int j=0;j<l;j++){
a[x*l+i][y*l+j]=a[i][j];
}
}
}
}
}
l*=3;
}
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)cout<<a[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int x;
char s[2005][2005];
void fill(int x, int y, int k) {
if (k == 0) return s[x][y] = 1, void();
int t = k / 3;
fill(x, y, t);
fill(x + t, y, t);
fill(x + t * 2, y, t);
fill(x, y + t, t);
fill(x, y + t * 2, t);
fill(x + t, y + t * 2, t);
fill(x + t * 2, y + t, t);
fill(x + t * 2, y + t * 2, t);
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> x;
if (x == 0) return cout << "#", 0;
int t = pow(3, x);
fill(1, 1, t);
for (int i = 1; i <= t; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= t; j++) cout << (s[i][j] == 0 ? '.' : '#');
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Rudolf and the Ugly String
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const double eps =1e-7;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
int cnt=0;
for (int x = 0; x < n-2;x++){
if(s[x]=='m'&&s[x+1]=='a'&&s[x+2]=='p'){
cnt++;
x += 2;
}
else if(s[x]=='p'&&s[x+1]=='i'&&s[x+2]=='e'){
cnt++;
x += 2;
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
return 0;
}