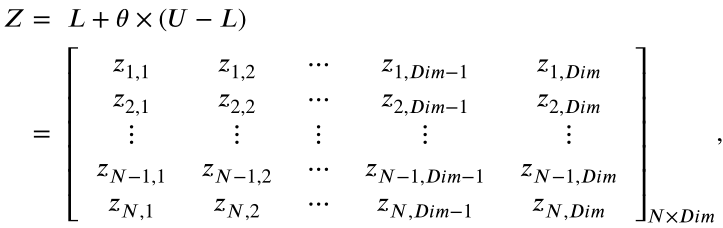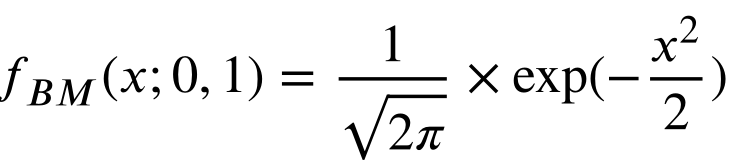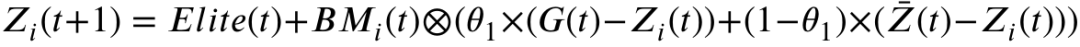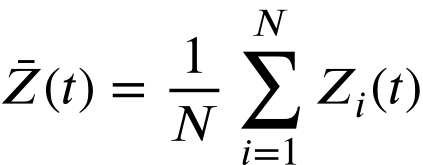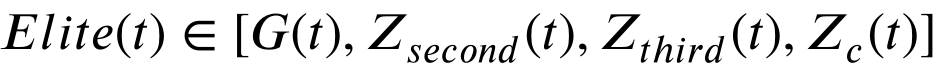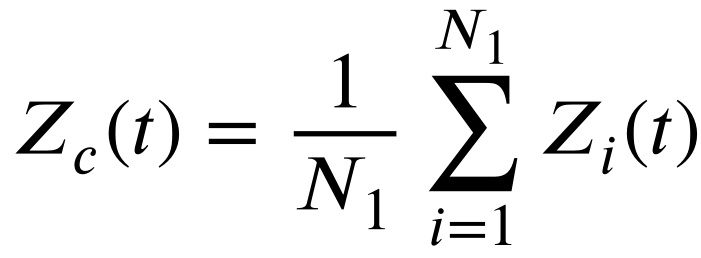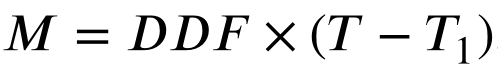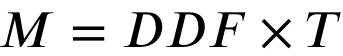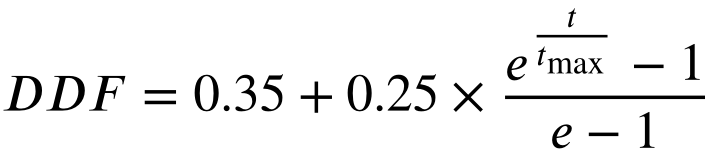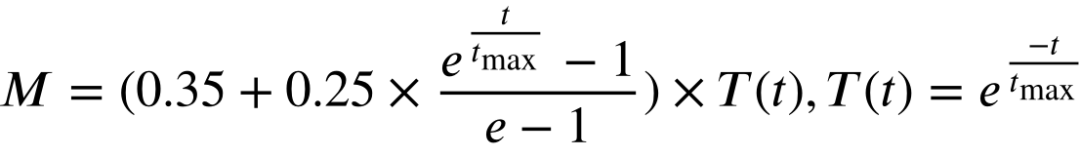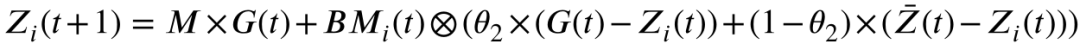今天为大家带来一期雪消融优化器(Snow ablation optimizer,SAO)。该算法发表于2023年6月1号。趁热乎,大家赶紧拿下!
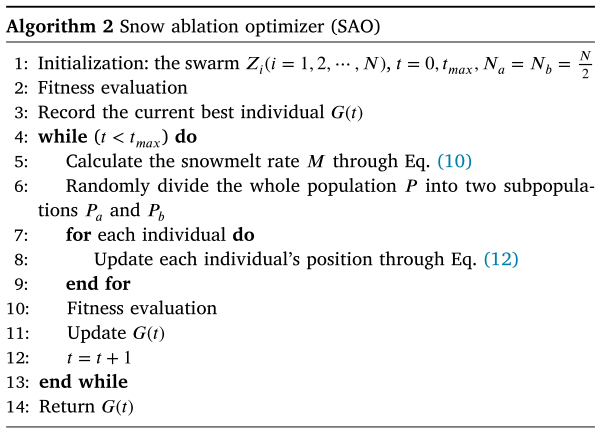
雪消融优化器( SAO) 是受自然界中雪的升华和融化行为的启发,开发了一种新的基于物理的雪消融优化器(SAO)算法,模拟雪的升华和融化行为。
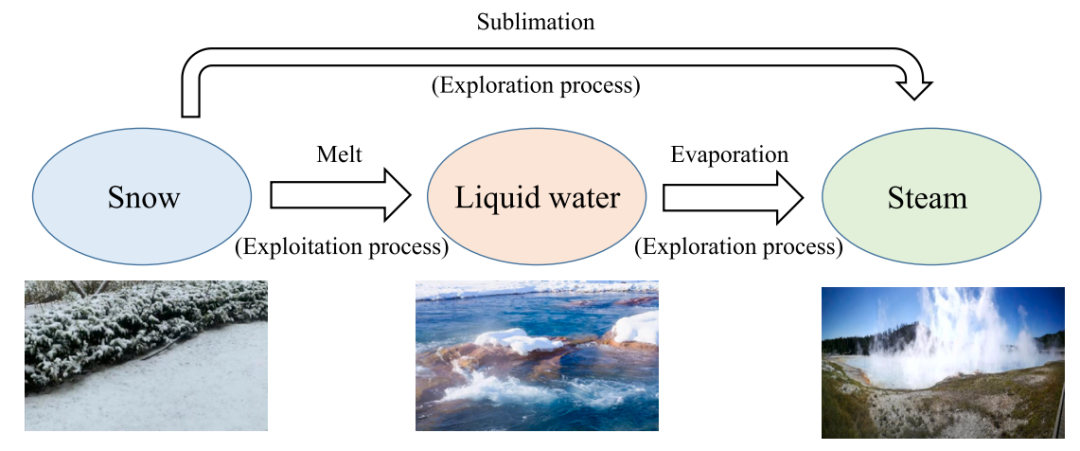
如下图所示:在融化的过程中,雪会转化为液态水,而它可以通过升华直接转化为蒸汽。同时,需要注意的是,融雪转化的液态水也可以通过蒸发转化为蒸汽。
本期在CEC2022函数集上进行测试,经过测试发现效果还是很不错的。
原理详解
①初始化阶段:
与大多数智能算法相似,就是随机生成一批粒子:
②探索阶段
当雪或由雪转化的液态水转化为蒸汽时,由于不规则的运动,搜索代理呈现出高度分散的特征。在这项研究中,布朗运动被用来模拟这种情况。作为一个随机过程,布朗运动被广泛应用于模拟动物的觅食行为,粒子的无休止和不规则运动、股票价格的波动行为等。对于标准布朗运动,步长是通过基于均值为零、方差为一的正态分布的概率密度函数来获得的。相关的数学表示如下:
布朗运动能够探索搜索空间中的一些潜在区域。因此,它可以很好地反映蒸汽在搜索空间中扩散的情况。勘探过程中的位置计算公式如下:
③开采阶段
当雪通过融化行为转化为液态水时,鼓励搜索代理围绕当前最佳解决方案开发高质量的解决方案,而不是在解决方案空间中以高度分散的特征进行扩展。作为最经典的融雪模型之一,degree-day法被用来反映融雪过程。该方法的一般形式如下所示:
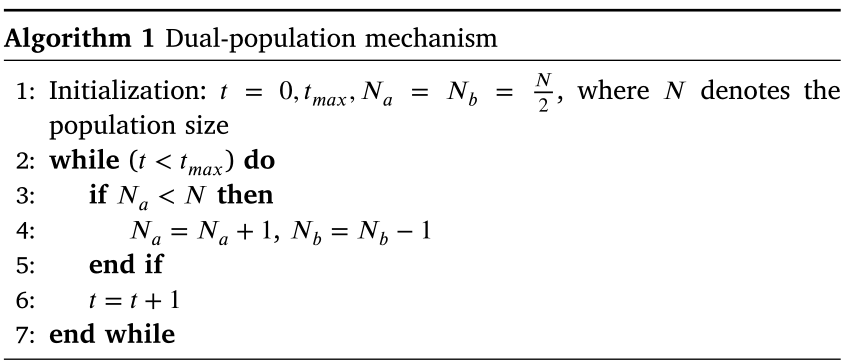
④双种群机制
一些从雪中转化的液态水也可以转化为蒸汽来进行勘探过程。也就是说,随着时间的推移,个体进行具有高度分散特征的不规则运动的可能性增加。然后算法逐渐有了探索解空间的趋势。在我们的研究中,二元种群机制是为了反映这种情况并保持开发和探索。如算法1所示,在迭代的早期阶段,将整个种群随机划分为两个大小相等的子种群。称之为双种群机制。
SAO算法的伪代码:
结果展示
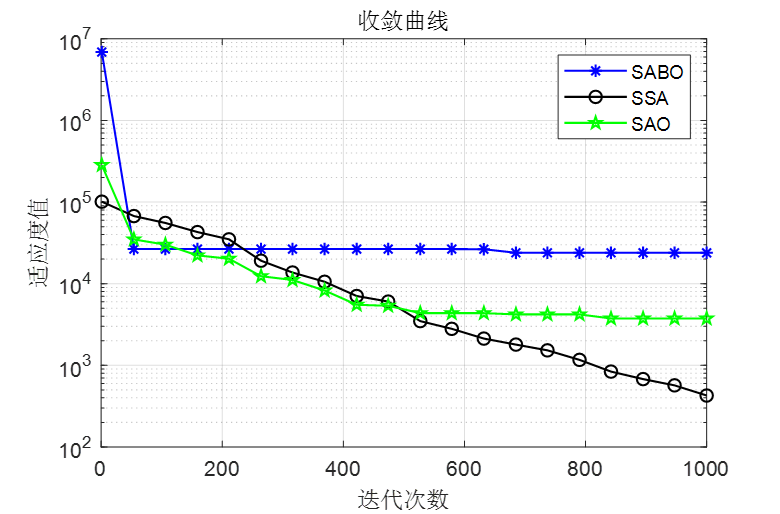
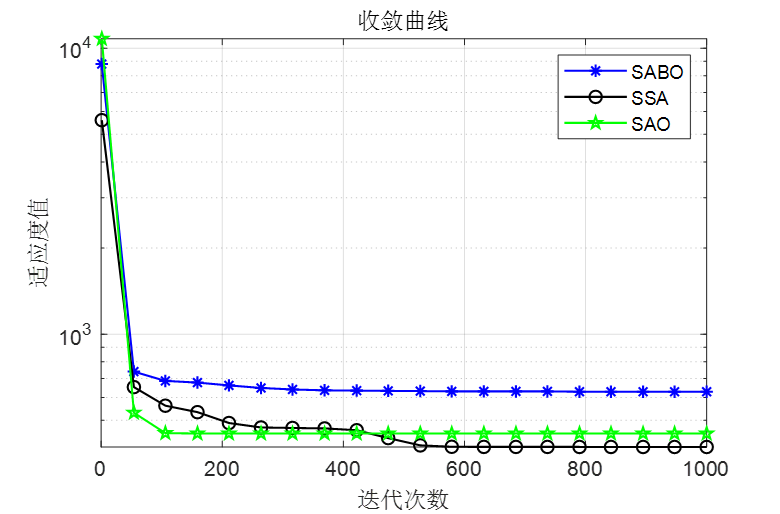
CEC2022测试结果:
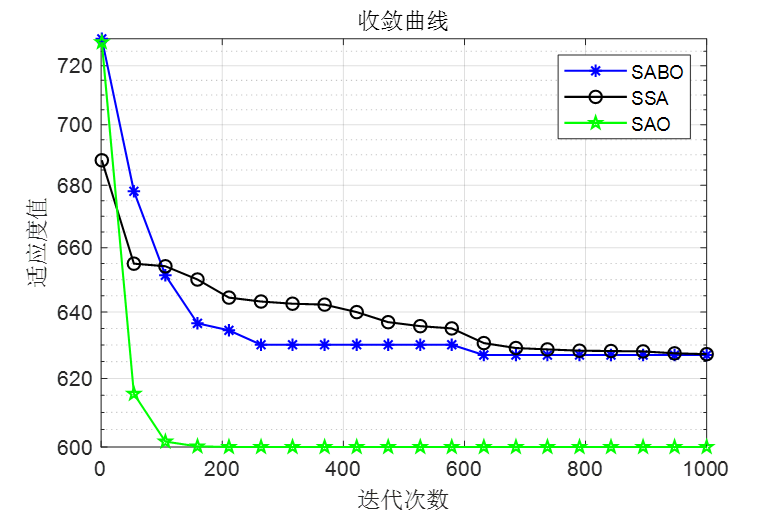
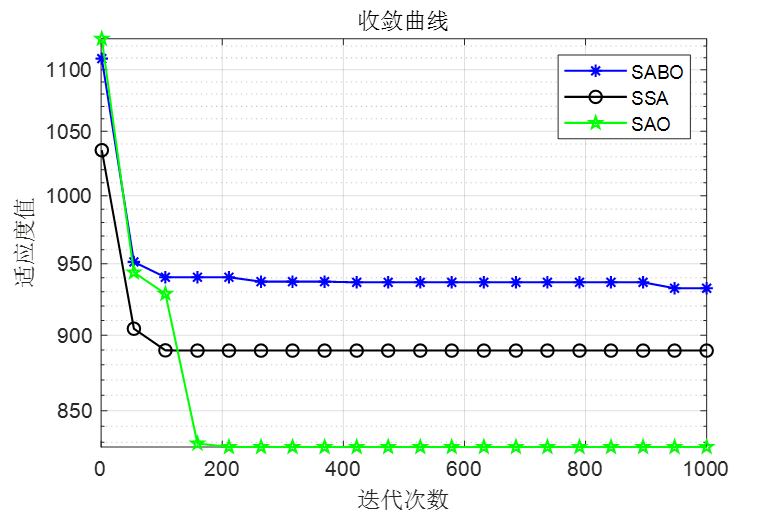
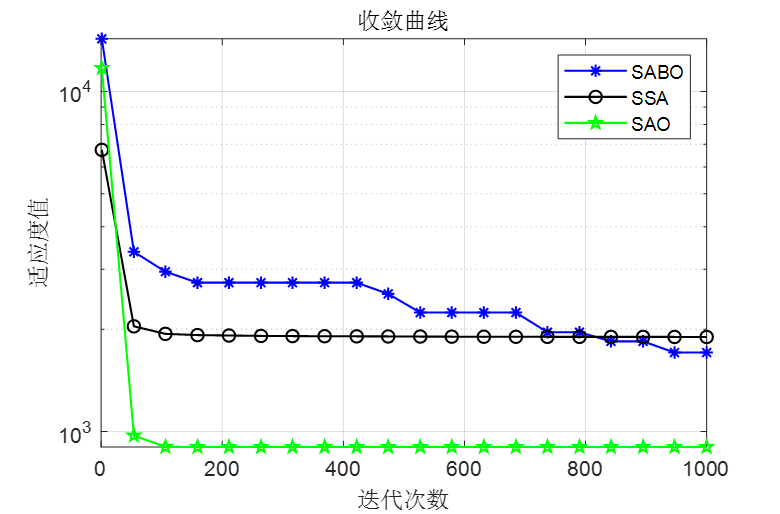
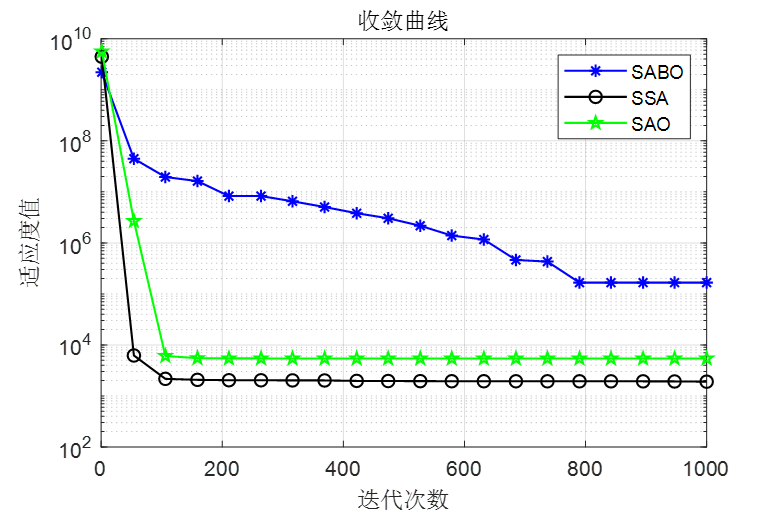
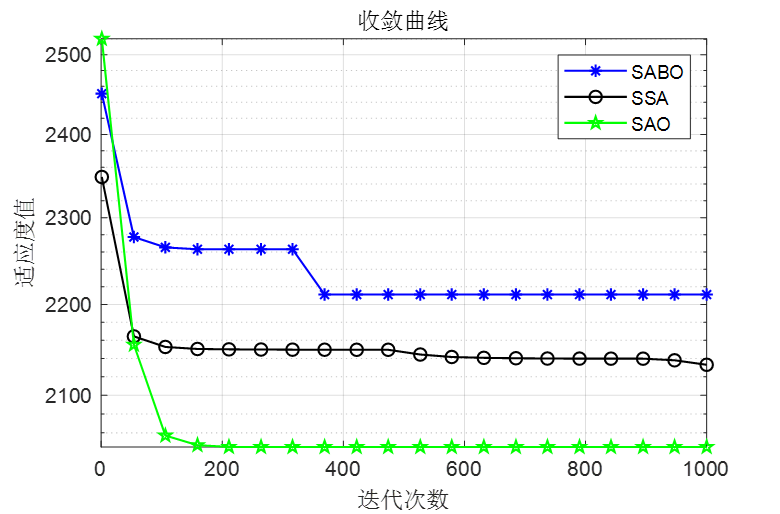
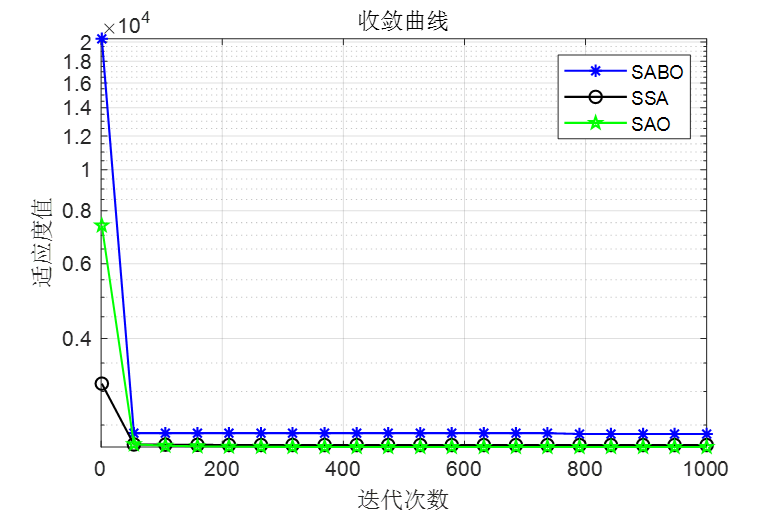
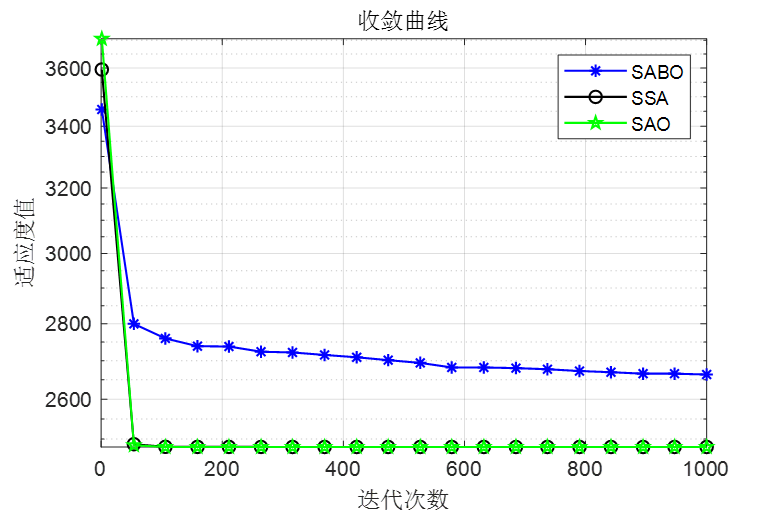
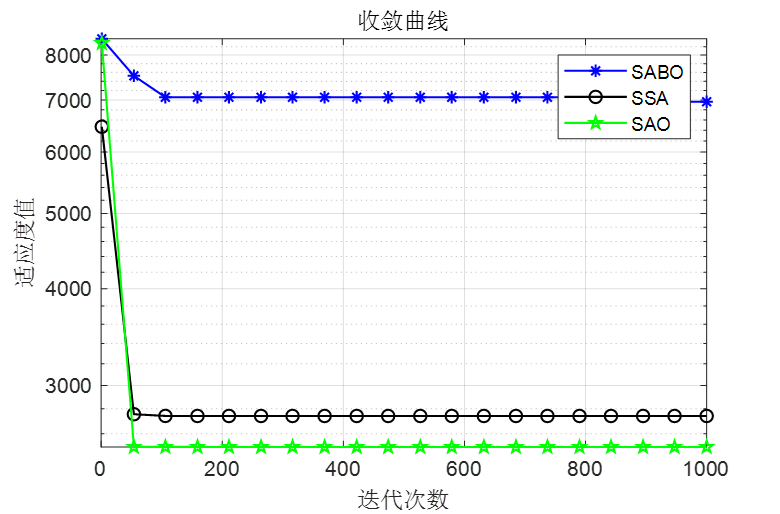
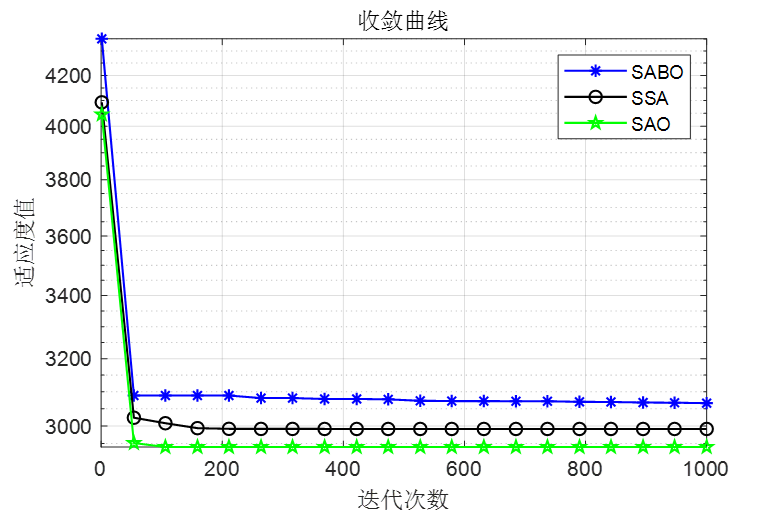
做了个简单对比,SABO是减法优化器算法,SSA是麻雀优化算法,SAO是本文的雪消融优化器
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
F11
F12
可以看到,SAO算法效果还是非常不错的!整体效果比麻雀和SABO算法都要好!接下来直接上代码!
代码展示
function [Best_pos,Best_score,Convergence_curve]=SAO(N,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
if(max(size(ub)) == 1)
ub = ub.*ones(1,dim);
lb = lb.*ones(1,dim);
end
%Initialize the set of random solutions
X=initialization(N,dim,ub,lb);
Best_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Best_score=inf;
Objective_values = zeros(1,size(X,1));
Convergence_curve=[];
N1=floor(N*0.5);
Elite_pool=[];
% Calculate the fitness of the first set and find the best one
for i=1:size(X,1)
Objective_values(1,i)=fobj(X(i,:));
if i==1
Best_pos=X(i,:);
Best_score=Objective_values(1,i);
elseif Objective_values(1,i)<Best_score
Best_pos=X(i,:);
Best_score=Objective_values(1,i);
end
All_objective_values(1,i)=Objective_values(1,i);
end
[~,idx1]=sort(Objective_values);
second_best=X(idx1(2),:);
third_best=X(idx1(3),:);
sum1=0;
for i=1:N1
sum1=sum1+X(idx1(i),:);
end
half_best_mean=sum1/N1;
Elite_pool(1,:)=Best_pos;
Elite_pool(2,:)=second_best;
Elite_pool(3,:)=third_best;
Elite_pool(4,:)=half_best_mean;
Convergence_curve(1) = Best_score;
for i=1:N
index(i)=i;
end
Na=N/2;
Nb=N/2;
%Main loop
l=2; % start from the second iteration since the first iteration was dedicated to calculating the fitness
while l<=Max_iter
RB=randn(N,dim); %Brownian random number vector
T=exp(-l/Max_iter);
k=1;
DDF=0.35*(1+(5/7)*(exp(l/Max_iter)-1)^k/(exp(1)-1)^k);
M=DDF*T;
%% Calculate the centroid position of the entire population
for j=1:dim
sum1=0;
for i=1:N
sum1=sum1+X(i,j);
end
X_centroid(j)=sum1/N;
end
%% Select individuals randomly to construct pop1 and pop2
index1=randperm(N,Na);
index2=setdiff(index,index1);
for i=1:Na
r1=rand;
k1=randperm(4,1);
for j=1:size(X,2) % in j-th dimension
X(index1(i),j)= Elite_pool(k1,j)+RB(index1(i),j)*(r1*(Best_pos(j)-X(index1(i),j))+(1-r1)*(X_centroid(j)-X(index1(i),j)));
end
end
if Na<N
Na=Na+1;
Nb=Nb-1;
end
if Nb>=1
for i=1:Nb
r2=2*rand-1;
for j=1:size(X,2) % in j-th dimension
X(index2(i),j)= M*Best_pos(j)+RB(index2(i),j)*(r2*(Best_pos(j)-X(index2(i),j))+(1-r2)*(X_centroid(j)-X(index2(i),j)));
end
end
end
% Check if solutions go outside the search spaceand bring them back
for i=1:size(X,1)
for j=1:dim
if X(i,j)>ub(j)
X(i,j)=ub(j);
end
if X(i,j)<lb(j)
X(i,j)=lb(j);
end
end
% Calculate the objective values
Objective_values(1,i)=fobj(X(i,:));
% Update the destination if there is a better solution
if Objective_values(1,i)<Best_score
Best_pos=X(i,:);
Best_score=Objective_values(1,i);
end
end
%% Update the elite pool
[~,idx1]=sort(Objective_values);
second_best=X(idx1(2),:);
third_best=X(idx1(3),:);
sum1=0;
for i=1:N1
sum1=sum1+X(idx1(i),:);
end
half_best_mean=sum1/N1;
Elite_pool(1,:)=Best_pos;
Elite_pool(2,:)=second_best;
Elite_pool(3,:)=third_best;
Elite_pool(4,:)=half_best_mean;
Convergence_curve(l)=Best_score;
l=l+1;
end参考文献:
Lingyun Deng, Sanyang Liu. Snow ablation optimizer: A novel metaheuristic technique for numerical optimization and engineering design,Expert Systems with Applications,Volume 225,2023.
文献原文已经放在代码压缩包里了。
2023智能算法合集代码免费获取方式
完整代码获取方式:后台回复关键字,不区分大小写。关键字:
2023