8.13 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
8.13.1 题目描述
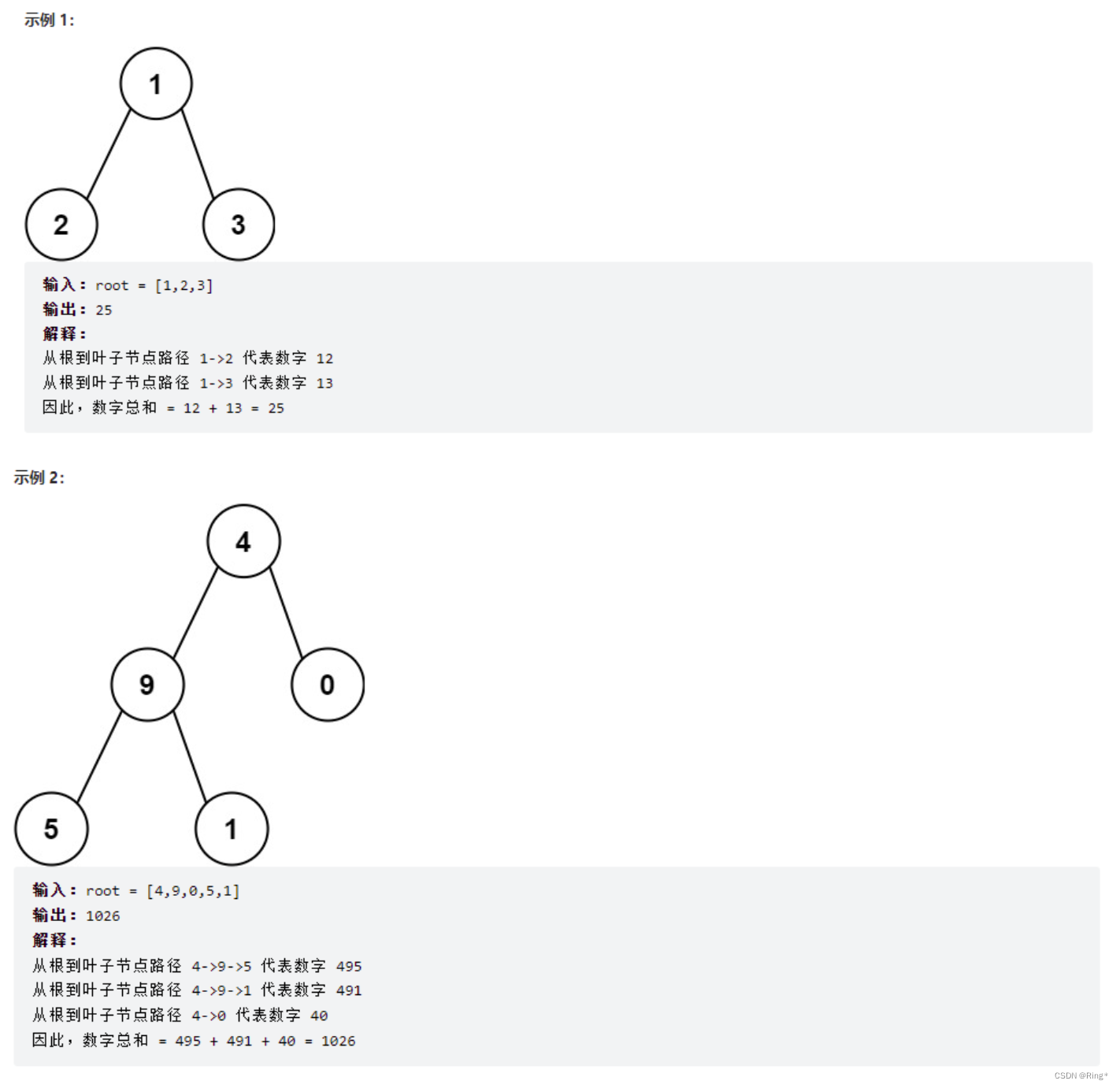
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。
每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径 1 -> 2 -> 3 表示数字 123 。
计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
前言
这道题中,二叉树的每条从根节点到叶子节点的路径都代表一个数字。其实,每个节点都对应一个数字,等于其父节点对应的数字乘以 10 再加上该节点的值(这里假设根节点的父节点对应的数字是 0)。只要计算出每个叶子节点对应的数字,然后计算所有叶子节点对应的数字之和,即可得到结果。可以通过深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索实现。
8.13.2 方法一:深度优先搜索
思路与算法
深度优先搜索是很直观的做法。从根节点开始,遍历每个节点,如果遇到叶子节点,则将叶子节点对应的数字加到数字之和。如果当前节点不是叶子节点,则计算其子节点对应的数字,然后对子节点递归遍历。
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int prevSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum;
} else {
return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum);
}
}
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间,递归栈的深度等于二叉树的高度,最坏情况下,二叉树的高度等于节点个数,空间复杂度为 O(n)。
8.13.3 方法二:广度优先搜索
思路与算法
使用广度优先搜索,需要维护两个队列,分别存储节点和节点对应的数字。
初始时,将根节点和根节点的值分别加入两个队列。每次从两个队列分别取出一个节点和一个数字,进行如下操作:
- 如果当前节点是叶子节点,则将该节点对应的数字加到数字之和;
- 如果当前节点不是叶子节点,则获得当前节点的非空子节点,并根据当前节点对应的数字和子节点的值计算子节点对应的数字,然后将子节点和子节点对应的数字分别加入两个队列。
搜索结束后,即可得到所有叶子节点对应的数字之和。
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int sum = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> numQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
numQueue.offer(root.val);
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
int num = numQueue.poll();
TreeNode left = node.left, right = node.right;
if (left == null && right == null) {
sum += num;
} else {
if (left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(left);
numQueue.offer(num * 10 + left.val);
}
if (right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(right);
numQueue.offer(num * 10 + right.val);
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列,每个队列中的元素个数不会超过 n。
8.13.4 my answer—广度优先搜索
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
Integer ans = 0;
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<String> pathQueue = new LinkedList<>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
pathQueue.offer(Integer.toString(root.val));
while(!nodeQueue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
String path = pathQueue.poll();
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
paths.add(path);
}else{
if(node.left != null){
nodeQueue.offer(node.left);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append(node.left.val).toString());
}
if(node.right != null){
nodeQueue.offer(node.right);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append(node.right.val).toString());
}
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<paths.size();i++){
ans += Integer.parseInt(paths.get(i));
}
return ans;
}
}