由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
注:本文的例子项目结构
src
/store
index.js
goods.js
todos.js
App.vue
main.js
模块的局部状态管理
这部分主要讲的是,子模块中的getter,mutation,action,都默认给我们提供了哪些参数
以下内容来自官网: Module-模块的局部状态 | Vuex (vuejs.org)
-
对于模块内部的
mutation和getter,接收的第一个参数是模块的局部状态对象state。 -
对于模块内部的
action,接受的第一个参数为context,局部状态通过context.state暴露出来,根节点状态则为context.rootState: -
对于模块内部的
getter,根节点状态会作为第三个参数暴露出来:
命名空间
一定要使用命名空间吗?
首先,先思考一个问题,如果想要使用vuex的module模块化,子模块一定要配置命名空间(namespace: true)吗?
答:不一定,子模块不配置namespace仍然可以正常使用;但是正如官网所说,如果不给子模块配置命名空间,那么开发时需要注意以下问题
默认情况下,模块内部的 action 和 mutation 仍然是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一个 action 或 mutation 作出响应。Getter 同样也默认注册在全局命名空间,但是目前这并非出于功能上的目的(仅仅是维持现状来避免非兼容性变更)。必须注意,不要在不同的、无命名空间的模块中定义两个相同的 getter 从而导致错误这句话什么意思呢?看下面的例子
举例:
- vuex入口文件,只配置了modules子模块
// src/store/index.js
import Goods from './goods'
import Todos from './todos'
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
Goods,
Todos
}
})
- 子模块goods
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
testState: 'goods',
},
mutations: {
testMutation(state) {
console.log('goodsMutation');
}
},
actions: {
testAction({ commit }) {
console.log('goodsAction');
}
},
getters: {
testGetters(state) {
return 'goods'
}
}
}
- 子模块todos
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
testState: 'todos',
},
mutations: {
testMutation(state) {
console.log('todosMutation');
}
},
actions: {
testAction({ commit }) {
console.log('testAction');
}
},
getters: {
testGetters() {
return 'todos'
}
}
}
- 测试页面App.vue
<template>
<div>
{{ testState }}
{{ testGetters }}
<button @click="testMutation">测试testMutation</button>
<button @click="testAction">测试testAction</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations, mapGetters, mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
...mapMutations(["testMutation"]),
...mapActions(["testAction"]),
},
computed: {
...mapGetters(["testGetters"]),
...mapState(["testState"])
}
};
</script>
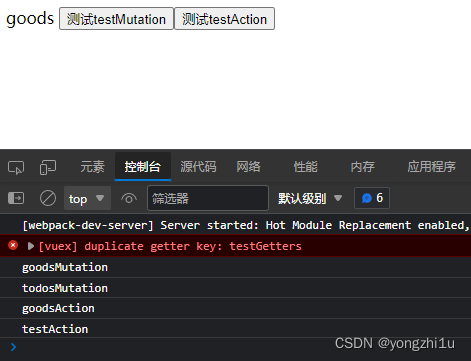
- 结果
看到下面结果可以发现
①对于相同名字state,src/store/index中,哪个模块在上面,使用哪个模块state的数据(已测验,如果Todos在上面,页面显示结果为Todos)
②对于相同方法名getters,直接报错,重复定义
③对于相同方法名mutation,两个都执行
④对于相同方法名action,两个都执行
结论:如果vuex想要使用子模块开发,又不想为命名重复问题考虑过多,我们需要开启namespaced
结果:
使用命名空间管理子模块
启用了命名空间的 getter 和 action 会收到局部化的
getter,dispatch和commit。换言之,你在使用模块内容(module assets)时不需要在同一模块内额外添加空间名前缀。
如果你希望使用全局 state 和 getter,
rootState和rootGetters会作为第三和第四参数传入 getter,也会通过context对象的属性传入 action。若需要在全局命名空间内分发 action 或提交 mutation,将
{ root: true }作为第三参数传给dispatch或commit即可。
- 访问子模块Goods中的属性
对于mutation,Getters,需要添加前缀Goods
对于state,通过state上的Goods对象访问Goods模块内部的属性
注:前缀值为store/index.js中modules注册模块时的名字
注:需要把 src/store/goods.js和 src/store/todos.js中添加namespaced: true,这里代码省略,只列出App.vue代码
<template>
<div>
{{ testState }}
{{ testGetters }}
<button @click="testMutation">测试testMutation</button>
<button @click="testAction">测试testAction</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations, mapGetters, mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
...mapMutations({
testMutation: 'Goods/testMutation',
}),
...mapActions({
testAction: 'Goods/testAction'
})
},
computed: {
...mapGetters({
testGetters: 'Goods/testGetters'
}),
...mapState({
testState: state => state.Goods.testState
}),
}
};
</script>
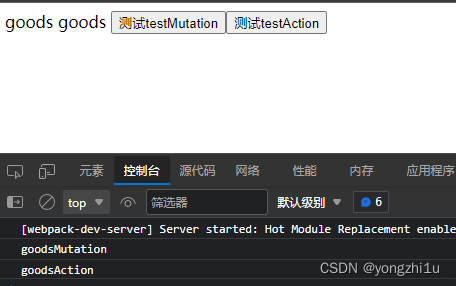
结果:可以看到 ①getter没有报错,②控制台也只输出了goods的mutation和action ③页面上显示的是goods的state和getter
子模块使用全局模块的内容
getters
goods模块getter访问全局getter
goods模块getter访问全局state
goods模块getter访问todos的getter
goods模块getter访问todos的state
goods模块访问本模块goods
// src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Goods from './goods'
import Todos from './todos'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters: {
getCount: state => state.count
},
modules: {
Goods,
Todos,
}
})
// src/store/goods.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
goods: [
{ id: 1, type: "apple" },
{ id: 2, type: "banana" },
]
},
getters: {
getGoodsState(state) {
return state.goods[0]
},
getGlobalGetter(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return rootGetters.getCount
},
getGlobalState(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return rootState.count
},
getTodosGetter(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return rootGetters["Todos/getTodosCount"]
},
getTodosState(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return rootState.Todos.todos[0]
},
getGoodsGetter(state, getters) {
return getters.getGoodsState
}
}
}
// src/store/todos.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, do: "do homework" },
{ id: 2, do: "do exercise" },
]
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
getters: {
getTodosCount: (state) => state.todos[0]
}
}
// App.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li>{{ getGlobalGetter }}</li>
<li>{{ getGlobalState }}</li>
<li>{{ getTodosGetter }}</li>
<li>{{ getTodosState }}</li>
<li>{{ getGoodsGetter }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations, mapGetters, mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
},
computed: {
...mapGetters({
getGlobalGetter: 'Goods/getGlobalGetter', // goods模块getter访问全局getter
getGlobalState: 'Goods/getGlobalState', // goods模块getter访问全局state
getTodosGetter: 'Goods/getTodosGetter', // goods模块getter访问Todos的getter
getTodosState: 'Goods/getTodosState', // goods模块getter访问Todos的state
getGoodsGetter: 'Goods/getGoodsGetter' // goods模块getter访问Goods的getter
}),
}
};
</script>
结果:
action
goods模块action调用全局mutation
goods模块action调用Todos的mutation
// src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Goods from './goods'
import Todos from './todos'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
addCount(state) {
state.count++;
}
},
actions: {
addCount2({ commit }) {
commit('addCount')
}
},
getters: {
getCount: state => state.count
},
modules: {
Goods,
Todos,
}
})
// src/store/goods.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
goods: [
{ id: 1, type: "apple" },
{ id: 2, type: "banana" },
]
},
actions: {
addTodos({ dispatch, commit, getters, rootGetters }, playload) {
commit('addCount', null, { root: true })
},
addCount({ dispatch, commit, getters, rootGetters }, playload) {
commit('Todos/addTodos', null, { root: true })
}
},
mutations: {
addGoods(state) {
state.goods.push(
{id: 3, type: "orange"}
)
}
}
}
// src/store/todos.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, do: "do homework" },
{ id: 2, do: "do exercise" },
]
},
actions: {
addTodos2({ commit }) {
commit('addTodos')
}
},
mutations: {
addTodos(state) {
state.todos.push({
id: 3,
do: "play games"
})
}
},
getters: {
getTodosCount: (state) => state.todos[0]
}
}
// App.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li>{{ count }}</li>
<li>{{ goods }}</li>
<li>{{ todos }}</li>
</ul>
<button @click="addTodos">addTodos</button>
<button @click="addCount">addCount</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { createNamespacedHelpers, mapState } from 'vuex';
const { mapActions: mapGoodsActions, mapState: mapGoodsState } = createNamespacedHelpers('Goods')
const { mapState: mapTodosState } = createNamespacedHelpers('Todos')
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState(["count"]),
...mapGoodsState(["goods"]),
...mapTodosState(["todos"]),
},
methods: {
...mapGoodsActions(["addTodos", "addCount"])
},
};
</script>
总结
跨模块访问,主要是前缀的配置以及{root: true}的配置
带命名空间的绑定函数
简而言之,可以对模块名进行提取,避免重复写过长的模块前缀,如
some/nested/module/someOtherGetter
例如:改写上述getter访问其他模块内容的代码
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
},
computed: {
...mapGetters({
getGlobalGetter: 'Goods/getGlobalGetter', // goods模块getter访问全局getter
getGlobalState: 'Goods/getGlobalState', // goods模块getter访问全局state
getTodosGetter: 'Goods/getTodosGetter', // goods模块getter访问Todos的getter
getTodosState: 'Goods/getTodosState', // goods模块getter访问Todos的state
getGoodsGetter: 'Goods/getGoodsGetter' // goods模块getter访问Goods的getter
}),
}
};
// 方式一,mapGetters添加前缀
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
},
computed: {
...mapGetters('Goods',{
getGlobalGetter: 'getGlobalGetter',
getGlobalState: 'getGlobalState',
getTodosGetter: 'getTodosGetter',
getTodosState: 'getTodosState',
getGoodsGetter: 'getGoodsGetter'
}),
}
};
// 方式二,使用createNamespacedHelpers
// 注:这里重命名 mapGetters->mapGoodsGetters ,防止再引入其他模块,都叫mapGetters冲突
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapGetters: mapGoodsGetters } = createNamespacedHelpers('Goods')
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
},
computed: {
...mapGoodsGetters({
getGlobalGetter: 'getGlobalGetter',
getGlobalState: 'getGlobalState',
getTodosGetter: 'getTodosGetter',
getTodosState: 'getTodosState',
getGoodsGetter: 'getGoodsGetter'
}),
}
};
以上就是vuex开启module的内容总结,如果有哪里不明确的地方,欢迎一起交流~~