Python基础入门(四)
一、本课目标
- 理解并掌握 “元组” 的概念及使用
- 理解并掌握 “字典” 的概念及使用
- 理解并掌握 “集合” 的概念及使用
二、元组
-
元组与列表类似,不同之处在于元组的元素不能修改
-
元组使用小括号(),列表使用方括号[ ]
-
元组创建很简单,只需要在括号中添加元素,并使用逗号隔开即可
-
元组中只包含一个元素时,需要在元素后面添加逗号
-
元组与字符串类似,下标索引从0开始,可以进行截取,组合等
l = ['a', 'b', 'c'] t = ('a', 'b', 'c') l += 'd' l += ['b'] t += ('b', ) del l[0] print(l, t) t1 = (1, 2, 3) t2 = (4, 5, 6) t3 = t1 + t2 print(t3) t1 = (1, 2, 3) t1 += (4, 5, 6) t2 = t1 print(t1) print(t2) a = '12' print(id(a[0]), id(a[1]), id(a)) a = a.replace('1', '2') print(id(a[0]), id(a[1]), id(a)) b = [1, 2] print(id(b[0]), id(b[1]), id(b)) b[0] = 2 print(id(b[0]), id(b[1]), id(b)) for i in ('a', 'b', 'c'): print(i) t = ('12', '012', '21') print(max(t), min(t)) t = (16, 78, 89) print(max(t), min(t)) l = [1,2,3] t = tuple(l) print(t) -
练习一:
tupe1 = ('Google', 'Apache', '1997', 2000) tupe2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) print("tup1[0]:", tupe1[0]) print("tup2[1:5]:", tupe2[1:5]) tup1 = (12, 34.56) tup2 = ('abc', 'xyz') tup3 = tup1 + tup2 print(tup3) print(len((1, 2, 3))) a = (1, 2, 3) b = (4, 5, 6) c = a + b print(c) a += b print(a) print(('Hi!,' * 4)) print(3 in (1, 2, 3)) for x in (1, 2, 3): print(x, end='') -
练习二:
tup = ('Google', 'Apache', 'Taobao', 'Wiki', 'Weibo', 'Weixin') print(tup[1]) print(tup[-2]) print(tup[1:]) print(tup[1:4]) tuple1 = ('Google', 'Apache', 'Taobao') print(len(tuple1)) tuple2 = ('5', '4', '8') print(max(tuple2)) print(min(tuple2)) list1 = ['Google', 'Apache', 'Taobao', 'Baidu'] tuple1 = tuple(list1) print(tuple1)
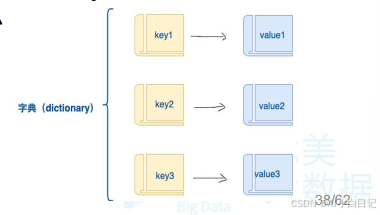
三、字典的概念
- 字典是另一种可变容器模型,且可存储任意类型对象
- 字典的每个键值key = >value对用冒号:分隔,每个对之间用逗号(,)分隔,整个字典包括在花括号{}中,格式如下所示:
- d = {key1: value1, key2 : value2, key3 : value3}
- 键必须是唯一的,但值则不必
四、字典操作
-
创建空字典
- 使用大括号{ }
- 使用函数dict()
-
访问字典里的值
- 通过[键]
- 通过 for in
-
修改字典
- 通过字典[值] = 值 添加或更新
- 通过del字典[键]删除
#字典
d = {}
print(tuple(d))
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
print(d)
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3, 'a':7, 5:6}
print(d)
d = dict(a=1, b=2, c=3)
print(d)
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3, 'd':4, 'e':5}
print(d['c'])
print(d['f']) # error
for i in d.items():
print(i)
for k,v in d.items():
print(k, v)
for k in d:
print(k)
for k in d.keys():
print(k)
for v in d.values():
print(v)
for k in d:
print(k, d[k])
d= {'apple':100, ' banana':200, 'orange':300}
print(d)
d['egg'] = 400
print(d)
d['egg'] = 500
print(d)
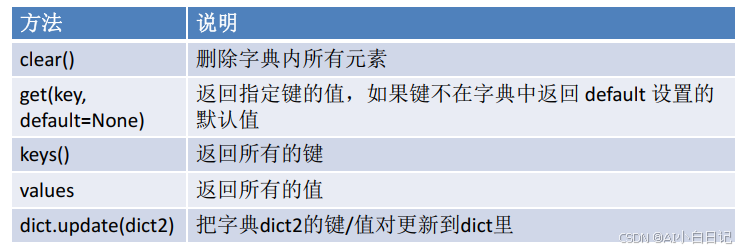
五、字典函数
d= {'apple':100, ' banana':200, 'orange':300}
print(d.get('banana', 400))
print(d)
d.clear()
print(d)
d1 = {'a':1, 'b':2}
d2 = {'a':3, 'c':4}
d1.update(d2)
print(d1)
print(d2)
d1 = {'a':1, 'b':2}
print(type(d1), d1)
print(str(d1), d1)
d1 = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
d2 = {'b':2, 'c':3, 'a':1}
print(d1 == d2)
print(d1, d2)
d = {'name':'Tom', 'age':22, 'sex':'male'}
print(d)
d = {}
r = d.fromkeys(('name', 'age', 'sex'))
r['name'] = 'Tom'
r['age'] = 22
r['sex'] = 'male'
print(r)
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
if 2.0 in d.values():
print("ok")
print(d.items(), type(d.items()), d)
for k, v in d.items():
print(k, v)
print(d.keys(), type(d.keys()))
print(d.values(), type(d.values()))
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
keys = d.keys()
print(list(keys))
del d['a']
del d['b']
d['b'] = 4
print(list(keys))
print(list(d.values()))
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
print(d.get('d',4))
print(d)
print(d.setdefault('d', 4))
print(d)
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
r = d.pop('b')
print(r)
print(d)
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
r = d.pop('d', 4)
print(r)
print(d)
d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
r = d.popitem()
print(r)
print(d)
d['f'] = 6
print(d)
六、字典案例
- 实现用户注册功能
- 输入用户名和密码
- 不允许用户名重复
- 不允许密码为空,默认为nopwd
- 遍历输出所有用户名和密码
# 实现用户名注册功能
# 输入应户名和密码
# 不允许用户名重复
# 不允许密码为空,默认为nopwd
# 遍历输出所有用户名和密码
users = {}
for i in range(3):
name = input("请输入用户名:")
if name not in users:
pwd = input("请输入密码:")
if pwd !='':
users[name] = pwd
else:
users[name] = 'nopwd'
users[name] = pwd
else:
print("对不起,应户名已存在!")
for k, v in users.items():
print(f"用户名:{k},密码:{v}")
dict1 = {'users':'google', 'num':[1,2,3]}
dict2 = dict1
dict3 = dict1.copy()
print(dict1 is dict2, dict1 is dict3)
dict1['users'] = 'root'
print(dict1, dict2, dict3)
dict1['num'].remove(1)
print(dict1, dict2, dict3)
- 案例1
# 字典
tinydict = {'Name': 'Google', 'Age':7, 'Class':'First'}
print(len(tinydict))
print(str(tinydict))
print(tinydict['Name'])
print(tinydict['Age'])
tinydict['Age'] = 8
tinydict['School'] = "北京大学"
print(tinydict['Age'])
print(tinydict['School'])
print(tinydict)
del tinydict['Name']
tinydict.clear()
del tinydict
print(tinydict)
print(tinydict['Age'])
print(tinydict['School'])
- 案例2
dict = {}
seq = ('name', 'age', 'sex')
tindict = dict.fromkeys(seq)
print("新的字典为:%s" % str(tindict))
tindict = dict.fromkeys(seq, 10)
print("新的字典为:%s" % str(tindict))
x = ('key1', 'value1', 'key2')
thisdict = dict.fromkeys(x)
print(thisdict)
tindict = {'Name': 'John', 'Age':7}
print("字典长度:%d" % len(tindict))
tindict.clesr()
print("字典清空后长度:%d" % len(tindict))
- 案例3
dict1 = {'user':'google', 'num':[1,2,3]}
dict2 = dict1
dict3 = dict1.copy()
dict1['user'] = 'root'
dict1['num'].remove(1)
print(dict1)
print(dict2)
print(dict3)
tinydict = {'Name':'Google', 'Age':27}
print("Age:", tinydict.get('Age'))
print("Sex:",tinydict.get('Sex'))
print("salary:", tinydict.get('Salary', 0.0))
- 案例4
google = {}
print('URL:', google.get('url'))
print(google(['url']))
tinydict = {'GOOGLE':{'url':'www.google.com'}}
res = tinydict.get('GOOGLE', {}).get('url')
print("GOOGLE url为:", str(res))
thisdict = {'Name':'Google', 'Age':7}
if 'Age'in thisdict:
print("键Age存在")
else :
print("键Age不存在")
if 'Sex' in thisdict:
print("键Sex存在")
else:
print("键Sex不存在")
if 'Age' not in thisdict:
print("键Age不存在")
else:
print("键Age存在")
tinydict = {'Name': 'Google', 'Age': 7}
print("Value:%s" % tinydict.items())
- 案例5
dishes = {'eggs':2, 'sausage':1, 'bacon':1, 'spam':500}
keys = dishes.keys()
values = dishes.values()
n = 0
for val in values:
n += val
print(n)
print(list(keys))
print(list(values))
del dishes['eggs']
del dishes['sausage']
print(list(keys))
tinydict = {'Name':'Google', 'Age':7}
print("Age 键的值为:%s"% tinydict.setdefault('Age', None))
print("Sex键的值为:%s")% tinydict.setdefault('Sex',None)
print("新字典为:", tinydict)
- 案例6
tinydict = {'Name':'Google', 'Age':7}
tinydict2 = {'Sex':'female'}
tinydict.update(tinydict2)
print("更新字典tinydict:", tinydict)
site = {'name': '阿蛮', 'alexa':10000, 'url':'http://google.com'}
element = site.pop('name')
print('删除的元素为:',element)
print('字典为:',site)
element = site.pop('nickname')
print("删除的元素为:",element)
print('字典为:', site)
element = site.pop('nickname', '不存在的key')
print('删除的元素为:',element)
print('字典为:',site)
- 案例7
site = {'name':'zhangsan', 'alexa':10000, 'url':'www.baidu.com'}
result = site.popitem()
print('返回值=', result)
print('site=',site)
site['nickname'] = 'Google'
print('site =', site)
result = site.popitem()
print('返回值 = ',result)
print('site=',site)
七、集合概念
- 集合(set)是一个无序的不重复元素序列
- 集合中的元素不会重复,并且可以进行交集、并集、差集等常见的集合操作
- 可以使用大括号{ }创建集合,元素之间用逗号,分隔,或者也可以使用set()函数创建集合
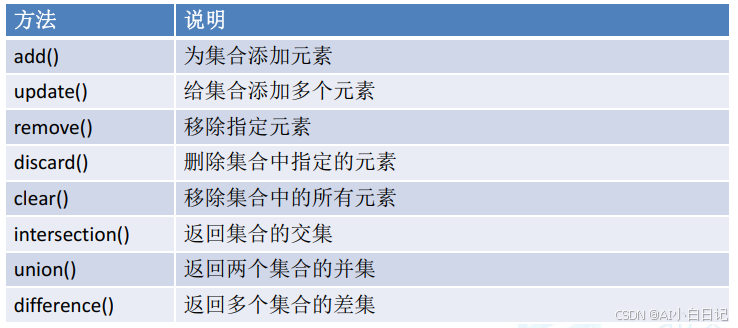
八、集合函数
#集合set
e = {1}
e = set()
print(type(e))
e = set()
e.add(1)
e.add(2)
e.update((1,2,3,4))
print(e)
e.remove(4)
print(e)
# e.remove(5) # Error
# print(e)
e.discard(5)
print(e)
e.clear()
print(e)
e1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
e2 = {3,4,5,6,7}
e3 = e1.intersection(e2)
print(e3)
e4 = e1.union(e2)
print(e4)
e5 = e1.difference(e2)
print(e5)
e6 = e2.difference(e1)
print(e6)
e7 = e1.difference(e1)
print(e7)
e = set([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
print(e)
e = set((1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9))
print(e)
e = set('2134')
print(e)
e = set({1:2, 3:3, 4:4, 5:5, 6:6})
print(e)
e1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}
e2 = {3,4,5,6}
print(e1 - e2)
print(e1 & e2)
e = {x for x in 'abcrrdadaradafrfsr' if x not in 'abc' }
print(e)
e = {1,2,3}
e.update([4,5],[6,7])
e.add((4,5))
print(e)
e = {1,2,3}
e.pop()
e.pop()
print(e)
e1 = {1,2,3}
e2 = {2,3,4,5}
e3 = e1.difference(e2)
print(e3)
print(e1)
e1.difference_update(e2)
print(e1)
e1 = {1,2,3}
e2 = {2,3,4,5}
e3 = e1.isdisjoint(e2)
print(e3)
r = e2.pop()
print(e2,r)
- 练习一
basket = {'apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'pear', 'orange', 'banana'}
print(basket)
print('orange' in basket)
print('crabgrass' in basket)
a = set('abracadabra')
b = set('alacazam')
print(a)
print(a - b)
print(a|b)
print(a & b)
print(a ^ b)
for x in 'abracadabra':
if x not in 'abc':
a = x
print(a)
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
thisset.add("Facebook")
print(thisset)
- 练习二
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
thisset.update({1, 3})
print(thisset)
thisset.update([1, 4],[5, 6])
print(thisset)
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
thisset.remove("Taobao")
print(thisset)
thisset.remove("Facebook")
print(thisset)
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
thisset.discard("Facebook")
print(thisset)
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache","Taobao","Facebook"))
x = thisset.pop()
print(x)
- 练习三
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
print(len(thisset))
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
thisset.clear()
print(thisset)
thisset = set(("Google", "Apache", "Taobao"))
print("Apache" in thisset)
print("Facebook" in thisset)
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
fruits.add("orange")
fruits.add("apple")
print(fruits)
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
fruits.claer()
print(fruits)
- 练习四
sites = {"Google", "Apache", "Taobao"}
x = sites.copy()
print(x)
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "microsoft", "apple"}
z = x.difference(y)
print(z)
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "microsoft", "apple"}
x.difference_update(y)
print(x)
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
fruits.discard("banana")
print(fruits)
- 练习五
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "apache", "apple"}
z = x.intersection(y)
print(z)
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
y = {"c", "d", "e"}
z = {"f", "g", "c"}
result = x.intersection(y, z)
print(result)
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "apache", "apple"}
x.intersection(y)
print(x)
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
y = {"c", "d", "e"}
z = {"f", "g", "c"}
x.intersection_update(y, z)
print(x)
- 练习六
x = {"f", "e", "d", "c", "b", "a"}
y = {"a", "b", "c"}
z = x.issubset(y)
print(z)
x = {"f", "e", "d", "c", "b"}
y = {"a", "b", "c"}
z = x.issubset(y)
print(z)
x = {"f", "e", "d", "c", "b", "a"}
y = {"a", "b", "c"}
z = y.issubset(x)
print(z)
x = {"f", "e", "d", "c", "b"}
y = {"a", "b", "c"}
z = y.issubset(x)
print(z)
- 练习七
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google","apache", "facebook"}
z = x.isdisjoint(y)
print(z)
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google","apache", "apple"}
z = x.isdisjoint(y)
print(z)
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
fruits.pop()
print(fruits)
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
x = fruits.pop()
print(x)
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
fruits.remove("banana")
print(fruits)
- 练习八
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "apache", "apple"}
z = x.symmetric_difference(y)
print(z)
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "apache", "apple"}
z = x.symmetric_difference_update(y)
print(z)
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"google", "apache", "apple"}
z = x.union(y)
print(z)
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
y = {"c", "d", "e"}
z = {"f", "g", "c"}
result = x.union(y, z)
print(result)
- 练习九
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
y = {"apple", "apache", "apple"}
x.update(y)
print(x)
text = "Hello, World"
length = len(text)
print(length)
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4,5]
length = len(my_list)
print(length)
my_tuple = (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60)
length = len(my_tuple)
print(length)
my_dict = {5, 10, 20}
length = len(my_dict)
print(length)
my_dict = {"apple":3, "banana":2, "cherry":4}
length = len(my_dict)
print(length)
九、集合案例
- 创建以下两个集合
- {1, 2, 3, 4, 5},{3, 4, 5,6, 7 }
- 计算集合之间的交集
- 计算集合之间的并集
- 计算集合之间的差集,注意有两种结果
# 创建两个集合
set_a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
set_b = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
# 计算交集
intersection = set_a.intersection(set_b)
print("交集:", intersection)
# 计算并集
union = set_a.union(set_b)
print("并集:", union)
# 计算差集,set_a - set_b
difference_a_minus_b = set_a.difference(set_b)
print("set_a 减去 set_b 的差集:", difference_a_minus_b)
# 计算差集,set_b - set_a
difference_b_minus_a = set_b.difference(set_a)
print("set_b 减去 set_a 的差集:", difference_b_minus_a)
十、总结
- 掌握元组的创建和操作方法
- 掌握字典的创建和操作方法
- 掌握集合的创建和操作方法