常用工具
1.将现有集合按照指定的长度拆分为几个子集合
引入依赖包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>23.0</version>
</dependency>
public <T> List<List<T>> split(List<T> resList,int subListLength) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(resList) || subListLength <= 0) {
return Lists.newArrayList();
}
int listLength = resList.size();
List<List<T>> ansList = new ArrayList<>();
if (listLength <= subListLength) {
ansList.add(resList);
} else {
int pre = listLength / subListLength;
int last = listLength % subListLength;
for (int i = 0; i < pre;i++) {
ansList.add(resList.subList(subListLength * i,subListLength * (i + 1)));
}
if (last > 0) {
ansList.add(resList.subList(subListLength * pre,resList.size()));
}
}
return ansList;
}
public static <T> List<List<T>> split(List<T> list, long limit) {
long listCount = (list.size() % limit == 0) ? (list.size() / limit) : (list.size() / limit + 1);
final long listSize = limit;
List<List<T>> splitLists = Stream.iterate(0, n -> n + 1).limit(listCount).parallel().map(i -> {
List<T> subList = list.stream().skip(i * listSize).limit(listSize).parallel().collect(Collectors.toList());
return subList;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return splitLists;
}
2.两个时间进行比较
比较两个时间间间隔几天:
// compareIntevalDays_1("2021-12-21","2021-12-22"); 打印结果为1
public void compareIntevalDays_1(String startTime,String endTime) {
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd");
LocalDate startDate = LocalDate.parse(startTime, pattern);
LocalDate endDate = LocalDate.parse(endTime, pattern);
Period period = Period.between(startDate, endDate);
System.out.println(period.getDays());
}
// compareIntevalDays_2("2021-12-21 00:00:00","2021-12-22 01:00:00");打印结果为1。
// 转化为LocalDate后,时分秒均为00:00:00,所以相差天数为1。但是在实际业务中如果两个时间只能间隔1天,此时这两个时间实际间隔1天1个小时,所以需要使用LocalDateTime
public void compareIntevalDays_2(String startTime,String endTime) {
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDate startDate = LocalDate.parse(startTime, pattern);
LocalDate endDate = LocalDate.parse(endTime, pattern);
Period period = Period.between(startDate, endDate);
System.out.println(period.getDays());
}
// compareIntevalDays_3("2021-12-21 00:00:00","2021-12-22 01:00:00");打印结果为1。
public void compareIntevalDays_3(String startTime,String endTime) {
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime startDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(startTime, pattern);
LocalDateTime endDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(endTime, pattern);
Period period = Period.between(startDateTime.toLocalDate(), endDateTime.toLocalDate()); // 这种和compareIntevalDays_2的情况一样
System.out.println(period.getDays());
Duration duration = Duration.between(startDateTime, endDateTime);
long millis = duration.toMillis();//相差毫秒数
if (millis > 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000) {
System.out.println("开始创建时间和结束创建时间差不能超过1天"); // 控制台打印此信息
}
}
比较两个时间的大小:
// compareTime("2021-12-23 00:00:00","2021-12-22 01:00:00");
public void compareTime(String startTime,String endTime) {
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime startDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(startTime, pattern);
LocalDateTime endDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(endTime, pattern);
if (startDateTime.compareTo(endDateTime) > 0) {
System.out.println("开始创建时间不能大于截止创建时间");// 控制台打印此信息
}
}
3.if判断的改写(在代码中不宜出现大量的if)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ThrowCustomException {
void throwCustomException(String message);
}
public class CompareUtil {
public static ThrowCustomException isTrue(boolean check) {
return ((message) -> {
if (check) {
throw new RuntimeException(message);
}
});
}
}
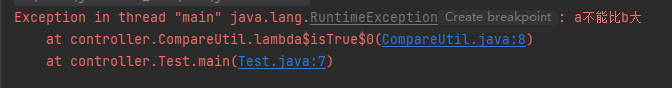
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1,b = 0;
CompareUtil.isTrue(a > b).throwCustomException("a不能比b大");
}
}
4.校验对象取值(校验对象取值的时候,如果对象本身为null就会出现空指针的问题,该方法避免出现空指针报错)
例如:
package controller;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
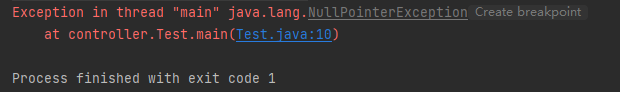
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = null;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(user.getUserName())) {
System.out.println(111);
}
}
}
运行结果为:
需要修改为:if (user!= null && StringUtils.isEmpty(user.getUserName())) {
System.out.println(111);
}
更好的方法如下:
package controller;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class AvoidNullPointUtil {
public static <T> Optional<T> resolve(Supplier<T> resolve) {
try {
T result = resolve.get();
return Optional.ofNullable(result);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = null;
if (AvoidNullPointUtil.resolve(() -> user.getUserName()).isPresent()) {
System.out.println(111);
}
}
5.非空校验
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.14.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
1.判断对象是否为null
Assert.notNull(endpoint, "endpoint must not be null");
2.判断字符串是否为空
Assert.hasText(id, "id must not be empty");
3.集合中是否包含该对象
Assert.state(!map.containsKey(id),
"map is already registered with id '" + id + "'");