以前看过的关于RabbitMQ核心消息模式的文章都是基于Java API的,最近看了下官方文档,发现这些核心消息模式都可以通过Spring AMQP来实现。于是总结了下RabbitMQ的实用技巧,包括RabbitMQ在Windows和Linux下的安装、5种核心消息模式的Spring AMQP实现,相信对于想要学习和回顾RabbitMQ的朋友都会有所帮助。
简介
RabbitMQ是最受欢迎的开源消息中间件之一,在全球范围内被广泛应用。RabbitMQ是轻量级且易于部署的,能支持多种消息协议。RabbitMQ可以部署在分布式系统中,以满足大规模、高可用的要求。
相关概念
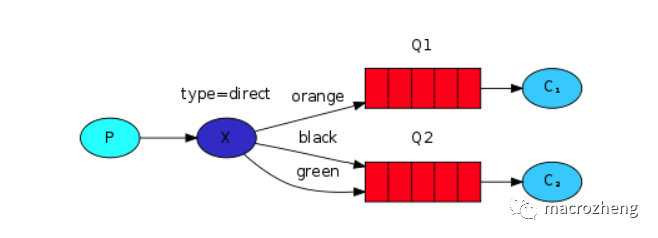
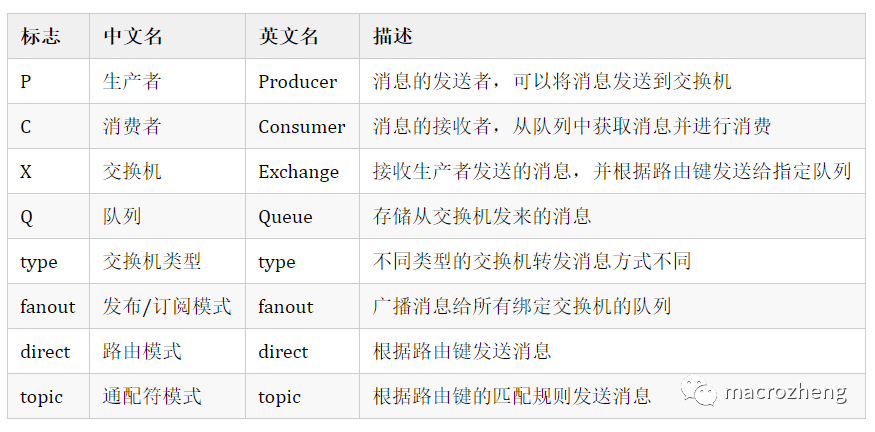
我们先来了解下RabbitMQ中的相关概念,这里以5种消息模式中的路由模式为例。
安装及配置
接下来我们介绍下RabbitMQ的安装和配置,提供Windows和Linux两种安装方式。
Windows下的安装
安装Erlang,下载地址:http://erlang.org/download/otp_win64_21.3.exe
安装RabbitMQ,下载地址:https://dl.bintray.com/rabbitmq/all/rabbitmq-server/3.7.14/rabbitmq-server-3.7.14.exe
安装完成后,进入RabbitMQ安装目录下的sbin目录;
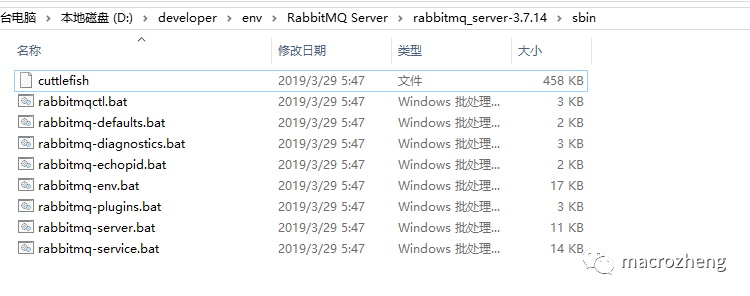
在地址栏输入cmd并回车启动命令行,然后输入以下命令启动管理功能。
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Linux下的安装
下载
rabbitmq 3.7.15的Docker镜像;
docker pull rabbitmq:3.7.15
使用Docker命令启动服务;
docker run -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 --name rabbitmq \
-d rabbitmq:3.7.15
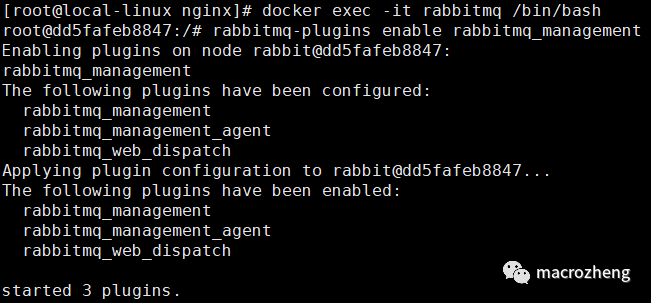
进入容器并开启管理功能;
docker exec -it rabbitmq /bin/bash
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
开启防火墙便于外网访问。
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=15672/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5672/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
访问及配置
访问RabbitMQ管理页面地址,查看是否安装成功(Linux下使用服务器IP访问即可):http://localhost:15672/
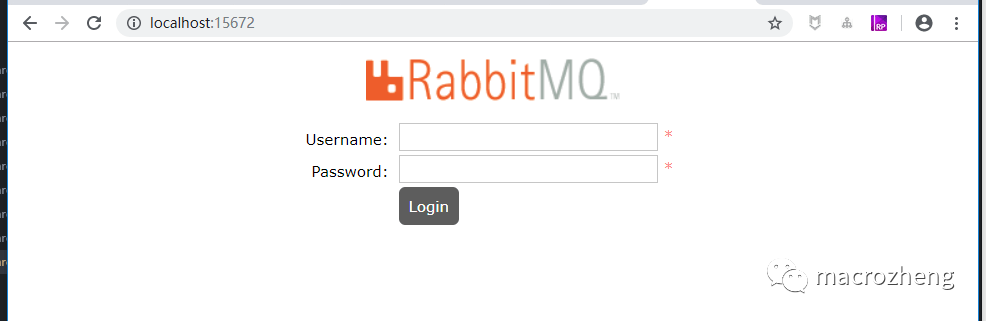
输入账号密码并登录,这里使用默认账号密码登录:guest guest
创建帐号并设置其角色为管理员:mall mall
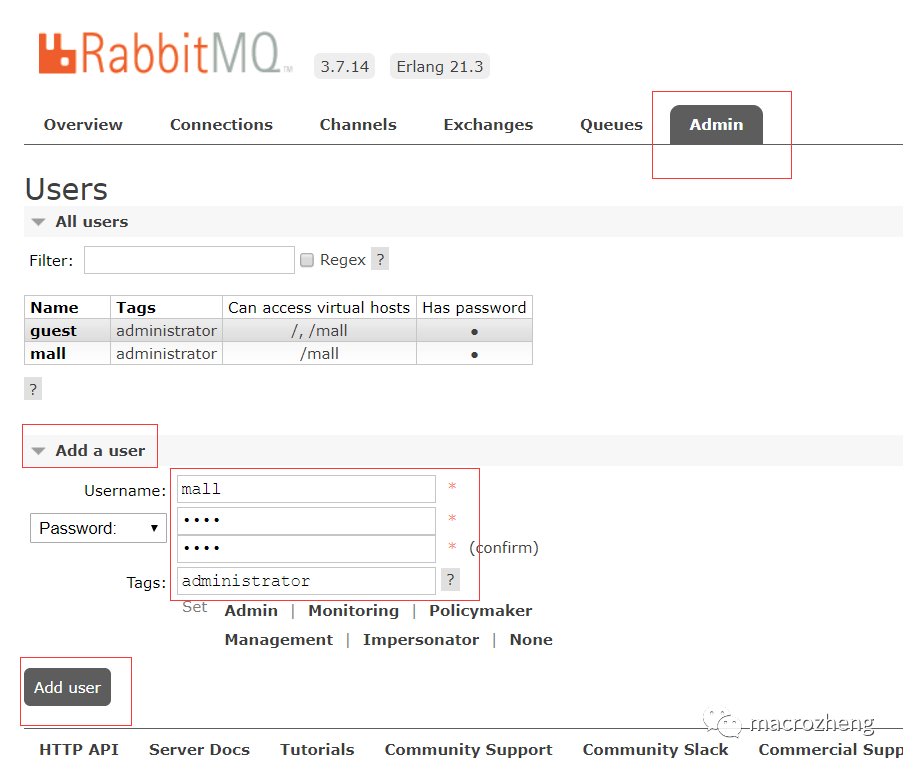
创建一个新的虚拟host为:/mall
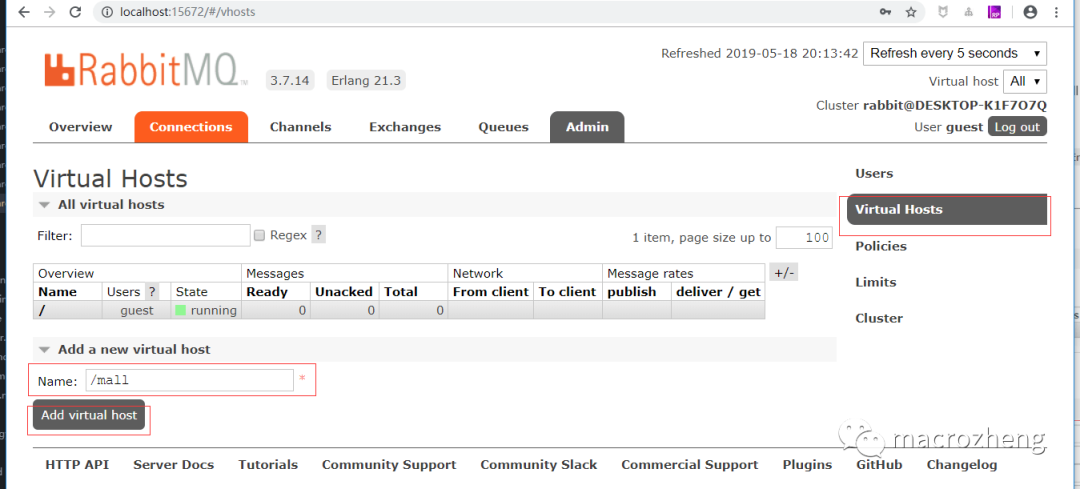
点击mall用户进入用户配置页面;
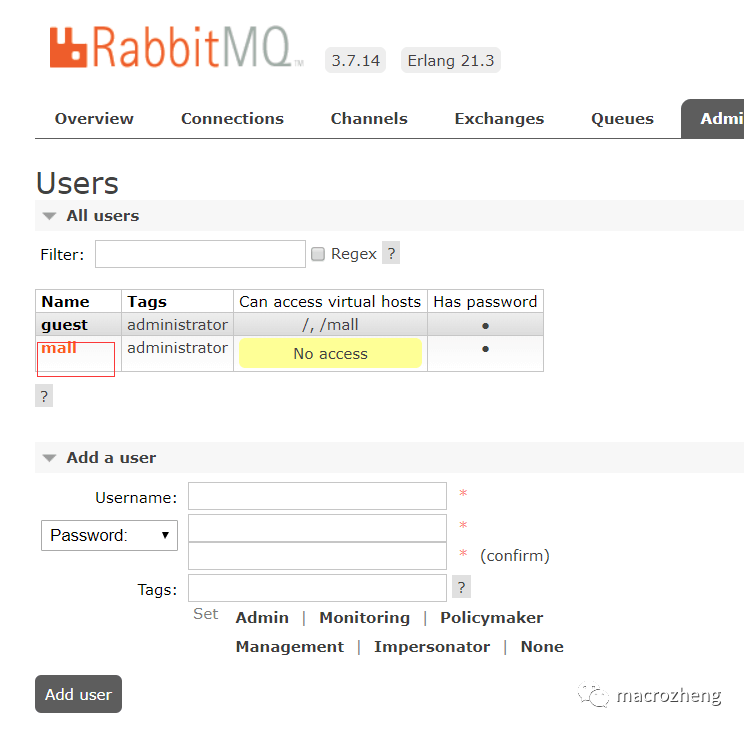
给mall用户配置该虚拟host的权限;
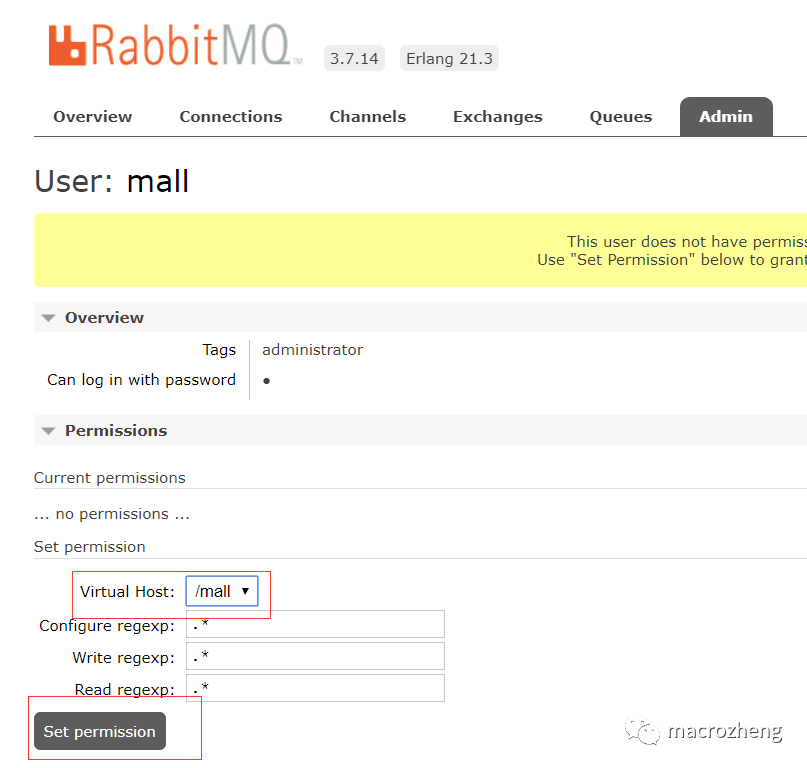
至此,RabbitMQ的配置完成。
5种消息模式
这5种消息模式是构建基于RabbitMQ的消息应用的基础,一定要牢牢掌握它们。学过RabbitMQ的朋友应该了解过这些消息模式的Java实现,这里我们使用Spring AMQP的形式来实现它们。
简单模式
简单模式是最简单的消息模式,它包含一个生产者、一个消费者和一个队列。生产者向队列里发送消息,消费者从队列中获取消息并消费。
模式示意图

Spring AMQP实现
首先需要在
pom.xml中添加Spring AMQP的相关依赖;
<!--Spring AMQP依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后修改
application.yml,添加RabbitMQ的相关配置;
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
virtual-host: /mall
username: mall
password: mall
publisher-confirms: true #消息发送到交换器确认
publisher-returns: true #消息发送到队列确认
添加
简单模式相关Java配置,创建一个名为simple.hello的队列、一个生产者和一个消费者;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Configuration
public class SimpleRabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Queue hello() {
return new Queue("simple.hello");
}
@Bean
public SimpleSender simpleSender(){
return new SimpleSender();
}
@Bean
public SimpleReceiver simpleReceiver(){
return new SimpleReceiver();
}
}
生产者通过
send方法向队列simple.hello中发送消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class SimpleSender {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SimpleSender.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
private static final String queueName="simple.hello";
public void send() {
String message = "Hello World!";
this.template.convertAndSend(queueName, message);
LOGGER.info(" [x] Sent '{}'", message);
}
}
消费者从队列
simple.hello中获取消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.hello")
public class SimpleReceiver {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SimpleReceiver.class);
@RabbitHandler
public void receive(String in) {
LOGGER.info(" [x] Received '{}'", in);
}
}
在controller中添加测试接口,调用该接口开始发送消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Api(tags = "RabbitController", description = "RabbitMQ功能测试")
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rabbit")
public class RabbitController {
@Autowired
private SimpleSender simpleSender;
@ApiOperation("简单模式")
@RequestMapping(value = "/simple", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult simpleTest() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
simpleSender.send();
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
return CommonResult.success(null);
}
}
运行后结果如下,可以发现生产者往队列中发送消息,消费者从队列中获取消息并消费。
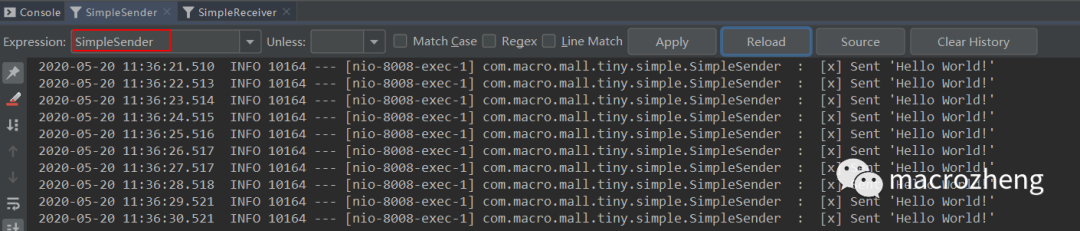
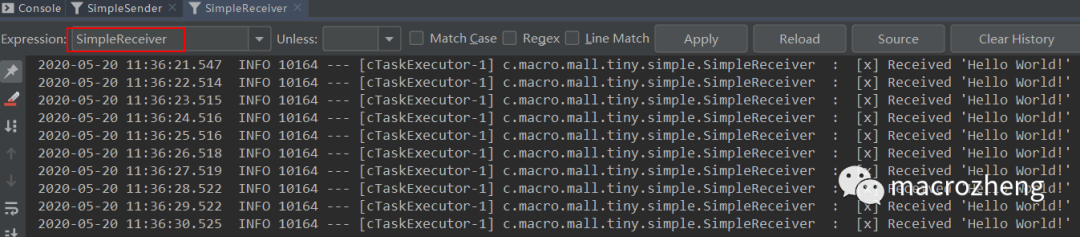
工作模式
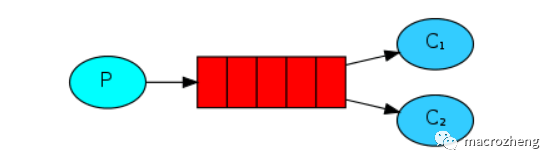
工作模式是指向多个互相竞争的消费者发送消息的模式,它包含一个生产者、两个消费者和一个队列。两个消费者同时绑定到一个队列上去,当消费者获取消息处理耗时任务时,空闲的消费者从队列中获取并消费消息。
模式示意图
Spring AMQP实现
添加
工作模式相关Java配置,创建一个名为work.hello的队列、一个生产者和两个消费者;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Configuration
public class WorkRabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Queue workQueue() {
return new Queue("work.hello");
}
@Bean
public WorkReceiver workReceiver1() {
return new WorkReceiver(1);
}
@Bean
public WorkReceiver workReceiver2() {
return new WorkReceiver(2);
}
@Bean
public WorkSender workSender() {
return new WorkSender();
}
}
生产者通过
send方法向队列work.hello中发送消息,消息中包含一定数量的.号;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class WorkSender {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WorkSender.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
private static final String queueName = "work.hello";
public void send(int index) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("Hello");
int limitIndex = index % 3+1;
for (int i = 0; i < limitIndex; i++) {
builder.append('.');
}
builder.append(index+1);
String message = builder.toString();
template.convertAndSend(queueName, message);
LOGGER.info(" [x] Sent '{}'", message);
}
}
两个消费者从队列
work.hello中获取消息,名称分别为instance 1和instance 2,消息中包含.号越多,耗时越长;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.hello")
public class WorkReceiver {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WorkReceiver.class);
private final int instance;
public WorkReceiver(int i) {
this.instance = i;
}
@RabbitHandler
public void receive(String in) {
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch();
watch.start();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Received '{}'", this.instance, in);
doWork(in);
watch.stop();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Done in {}s", this.instance, watch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
private void doWork(String in) {
for (char ch : in.toCharArray()) {
if (ch == '.') {
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
在controller中添加测试接口,调用该接口开始发送消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Api(tags = "RabbitController", description = "RabbitMQ功能测试")
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rabbit")
public class RabbitController {
@Autowired
private WorkSender workSender;
@ApiOperation("工作模式")
@RequestMapping(value = "/work", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult workTest() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
workSender.send(i);
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
return CommonResult.success(null);
}
}
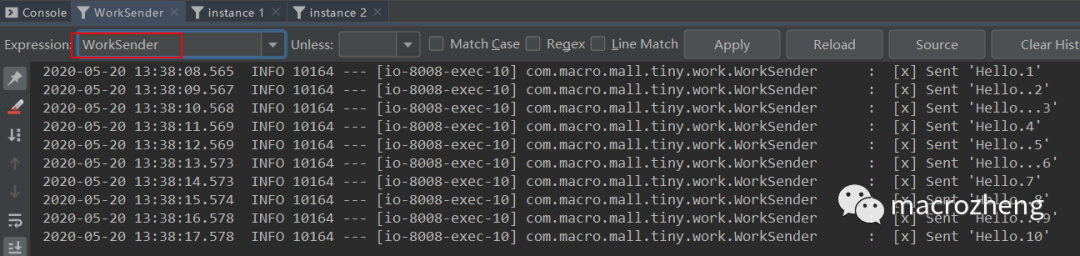
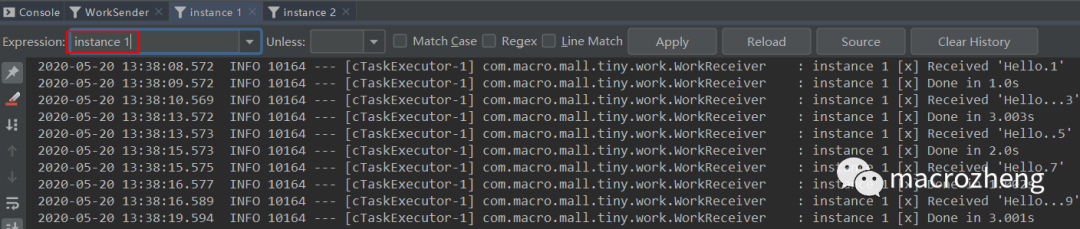
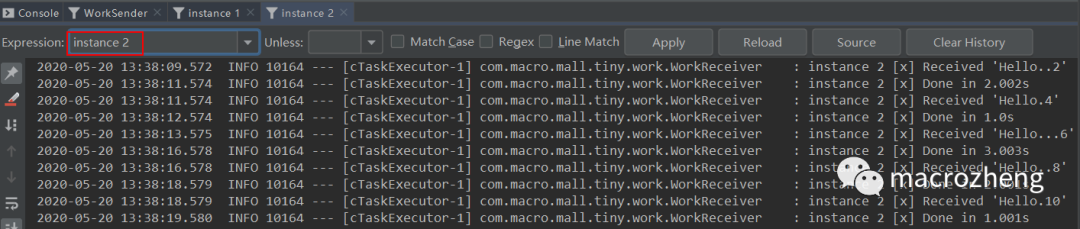
运行后结果如下,可以发现生产者往队列中发送包含不同数量
.号的消息,instance 1和instance 2消费者互相竞争,分别消费了一部分消息。
发布/订阅模式
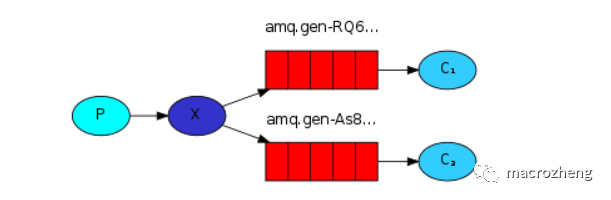
发布/订阅模式是指同时向多个消费者发送消息的模式(类似广播的形式),它包含一个生产者、两个消费者、两个队列和一个交换机。两个消费者同时绑定到不同的队列上去,两个队列绑定到交换机上去,生产者通过发送消息到交换机,所有消费者接收并消费消息。
模式示意图
Spring AMQP实现
添加
发布/订阅模式相关Java配置,创建一个名为exchange.fanout的交换机、一个生产者、两个消费者和两个匿名队列,将两个匿名队列都绑定到交换机;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Configuration
public class FanoutRabbitConfig {
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanout() {
return new FanoutExchange("exchange.fanout");
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1() {
return new AnonymousQueue();
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2() {
return new AnonymousQueue();
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding1(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue fanoutQueue1) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanout);
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue fanoutQueue2) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanout);
}
@Bean
public FanoutReceiver fanoutReceiver() {
return new FanoutReceiver();
}
@Bean
public FanoutSender fanoutSender() {
return new FanoutSender();
}
}
生产者通过
send方法向交换机exchange.fanout中发送消息,消息中包含一定数量的.号;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class FanoutSender {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FanoutSender.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
private static final String exchangeName = "exchange.fanout";
public void send(int index) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("Hello");
int limitIndex = index % 3 + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < limitIndex; i++) {
builder.append('.');
}
builder.append(index + 1);
String message = builder.toString();
template.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "", message);
LOGGER.info(" [x] Sent '{}'", message);
}
}
消费者从绑定的匿名队列中获取消息,消息中包含
.号越多,耗时越长,由于该消费者可以从两个队列中获取并消费消息,可以看做两个消费者,名称分别为instance 1和instance 2;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class FanoutReceiver {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FanoutReceiver.class);
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{fanoutQueue1.name}")
public void receive1(String in) {
receive(in, 1);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{fanoutQueue2.name}")
public void receive2(String in) {
receive(in, 2);
}
private void receive(String in, int receiver) {
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch();
watch.start();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Received '{}'", receiver, in);
doWork(in);
watch.stop();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Done in {}s", receiver, watch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
private void doWork(String in) {
for (char ch : in.toCharArray()) {
if (ch == '.') {
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
在controller中添加测试接口,调用该接口开始发送消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Api(tags = "RabbitController", description = "RabbitMQ功能测试")
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rabbit")
public class RabbitController {
@Autowired
private FanoutSender fanoutSender;
@ApiOperation("发布/订阅模式")
@RequestMapping(value = "/fanout", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult fanoutTest() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
fanoutSender.send(i);
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
return CommonResult.success(null);
}
}
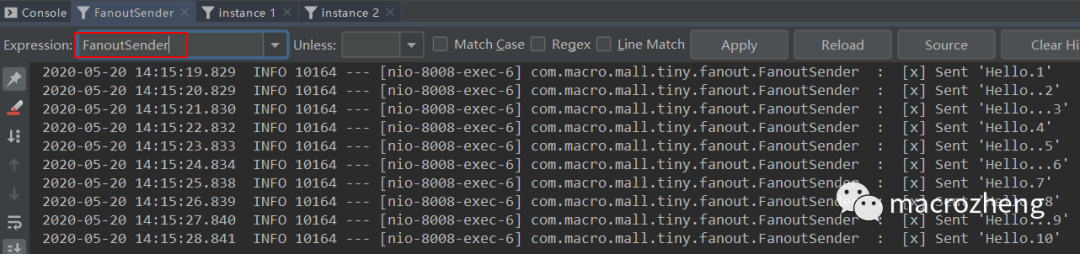
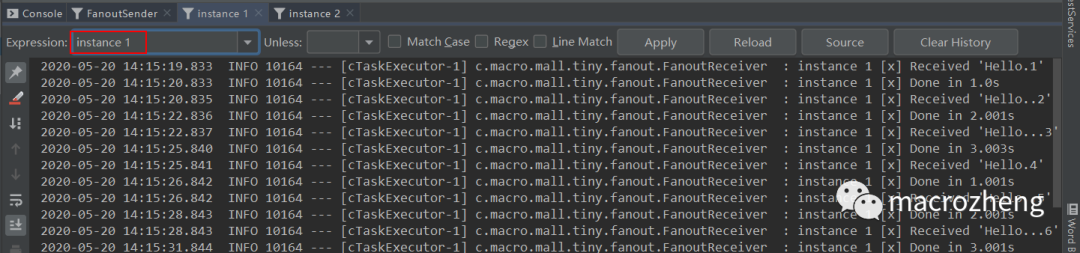
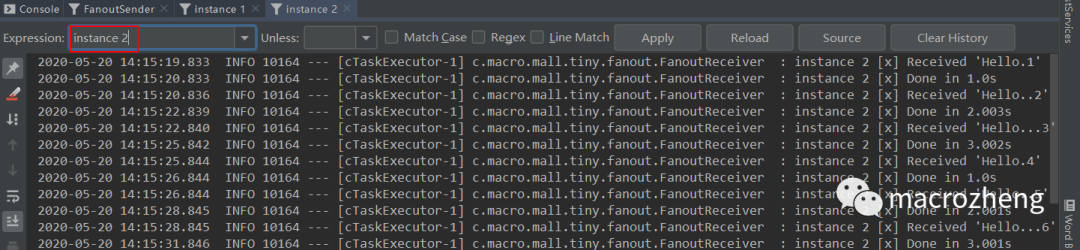
运行后结果如下,可以发现生产者往队列中发送包含不同数量
.号的消息,instance 1和instance 2同时获取并消费了消息。
路由模式
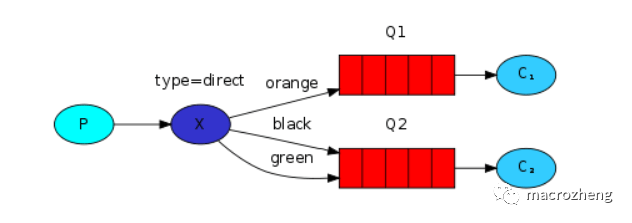
路由模式是可以根据
路由键选择性给多个消费者发送消息的模式,它包含一个生产者、两个消费者、两个队列和一个交换机。两个消费者同时绑定到不同的队列上去,两个队列通过路由键绑定到交换机上去,生产者发送消息到交换机,交换机通过路由键转发到不同队列,队列绑定的消费者接收并消费消息。
模式示意图
Spring AMQP实现
添加
路由模式相关Java配置,创建一个名为exchange.direct的交换机、一个生产者、两个消费者和两个匿名队列,队列通过路由键都绑定到交换机,队列1的路由键为orange和black,队列2的路由键为green和black;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Configuration
public class DirectRabbitConfig {
@Bean
public DirectExchange direct() {
return new DirectExchange("exchange.direct");
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue1() {
return new AnonymousQueue();
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue2() {
return new AnonymousQueue();
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding1a(DirectExchange direct, Queue directQueue1) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(direct).with("orange");
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding1b(DirectExchange direct, Queue directQueue1) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(direct).with("black");
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding2a(DirectExchange direct, Queue directQueue2) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(direct).with("green");
}
@Bean
public Binding directBinding2b(DirectExchange direct, Queue directQueue2) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(direct).with("black");
}
@Bean
public DirectReceiver receiver() {
return new DirectReceiver();
}
@Bean
public DirectSender directSender() {
return new DirectSender();
}
}
生产者通过
send方法向交换机exchange.direct中发送消息,发送时使用不同的路由键,根据路由键会被转发到不同的队列;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class DirectSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
private static final String exchangeName = "exchange.direct";
private final String[] keys = {"orange", "black", "green"};
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DirectSender.class);
public void send(int index) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("Hello to ");
int limitIndex = index % 3;
String key = keys[limitIndex];
builder.append(key).append(' ');
builder.append(index+1);
String message = builder.toString();
template.convertAndSend(exchangeName, key, message);
LOGGER.info(" [x] Sent '{}'", message);
}
}
消费者从自己绑定的匿名队列中获取消息,由于该消费者可以从两个队列中获取并消费消息,可以看做两个消费者,名称分别为
instance 1和instance 2;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class DirectReceiver {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DirectReceiver.class);
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{directQueue1.name}")
public void receive1(String in){
receive(in, 1);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{directQueue2.name}")
public void receive2(String in){
receive(in, 2);
}
private void receive(String in, int receiver){
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch();
watch.start();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Received '{}'", receiver, in);
doWork(in);
watch.stop();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Done in {}s", receiver, watch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
private void doWork(String in){
for (char ch : in.toCharArray()) {
if (ch == '.') {
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
在controller中添加测试接口,调用该接口开始发送消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Api(tags = "RabbitController", description = "RabbitMQ功能测试")
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rabbit")
public class RabbitController {
@Autowired
private DirectSender directSender;
@ApiOperation("路由模式")
@RequestMapping(value = "/direct", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult directTest() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
directSender.send(i);
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
return CommonResult.success(null);
}
}
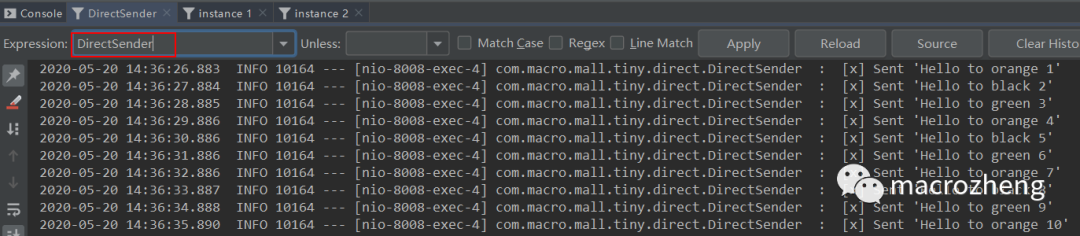
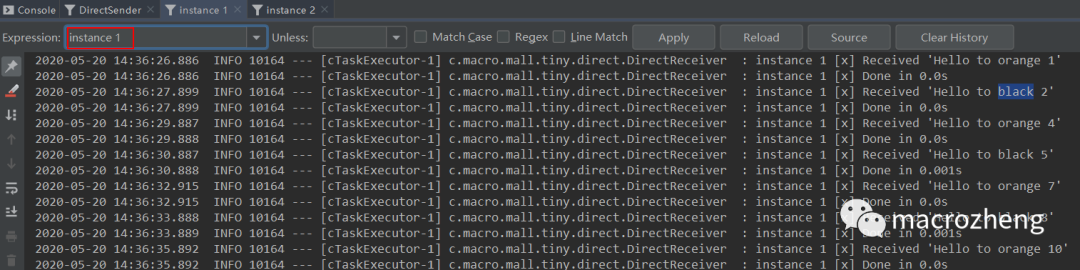
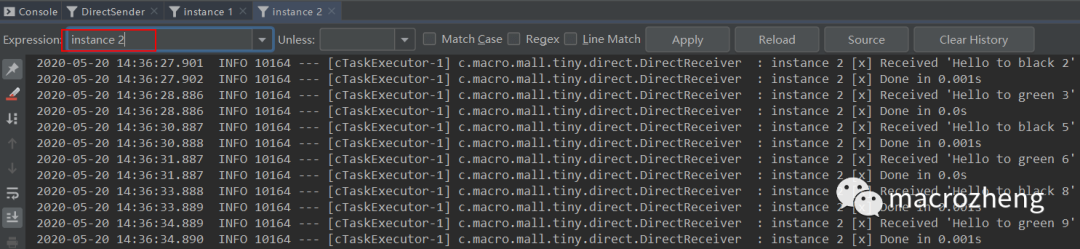
运行后结果如下,可以发现生产者往队列中发送包含不同
路由键的消息,instance 1获取到了orange和black消息,instance 2获取到了green和black消息。
通配符模式
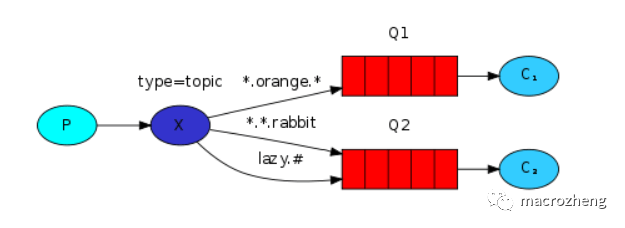
通配符模式是可以根据
路由键匹配规则选择性给多个消费者发送消息的模式,它包含一个生产者、两个消费者、两个队列和一个交换机。两个消费者同时绑定到不同的队列上去,两个队列通过路由键匹配规则绑定到交换机上去,生产者发送消息到交换机,交换机通过路由键匹配规则转发到不同队列,队列绑定的消费者接收并消费消息。
特殊匹配符号
*:只能匹配一个单词;#:可以匹配零个或多个单词。
模式示意图
Spring AMQP实现
添加
通配符模式相关Java配置,创建一个名为exchange.topic的交换机、一个生产者、两个消费者和两个匿名队列,匹配*.orange.*和*.*.rabbit发送到队列1,匹配lazy.#发送到队列2;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicRabbitConfig {
@Bean
public TopicExchange topic() {
return new TopicExchange("exchange.topic");
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new AnonymousQueue();
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new AnonymousQueue();
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding1a(TopicExchange topic, Queue topicQueue1) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1).to(topic).with("*.orange.*");
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding1b(TopicExchange topic, Queue topicQueue1) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1).to(topic).with("*.*.rabbit");
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding2a(TopicExchange topic, Queue topicQueue2) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2).to(topic).with("lazy.#");
}
@Bean
public TopicReceiver topicReceiver() {
return new TopicReceiver();
}
@Bean
public TopicSender topicSender() {
return new TopicSender();
}
}
生产者通过
send方法向交换机exchange.topic中发送消息,消息中包含不同的路由键;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class TopicSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
private static final String exchangeName = "exchange.topic";
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TopicSender.class);
private final String[] keys = {"quick.orange.rabbit", "lazy.orange.elephant", "quick.orange.fox",
"lazy.brown.fox", "lazy.pink.rabbit", "quick.brown.fox"};
public void send(int index) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("Hello to ");
int limitIndex = index%keys.length;
String key = keys[limitIndex];
builder.append(key).append(' ');
builder.append(index+1);
String message = builder.toString();
template.convertAndSend(exchangeName, key, message);
LOGGER.info(" [x] Sent '{}'",message);
System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + message + "'");
}
}
消费者从自己绑定的匿名队列中获取消息,由于该消费者可以从两个队列中获取并消费消息,可以看做两个消费者,名称分别为
instance 1和instance 2;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
public class TopicReceiver {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TopicReceiver.class);
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{topicQueue1.name}")
public void receive1(String in){
receive(in, 1);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{topicQueue2.name}")
public void receive2(String in){
receive(in, 2);
}
public void receive(String in, int receiver){
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch();
watch.start();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Received '{}'", receiver, in);
doWork(in);
watch.stop();
LOGGER.info("instance {} [x] Done in {}s", receiver, watch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
private void doWork(String in){
for (char ch : in.toCharArray()) {
if (ch == '.') {
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
在controller中添加测试接口,调用该接口开始发送消息;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/5/19.
*/
@Api(tags = "RabbitController", description = "RabbitMQ功能测试")
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rabbit")
public class RabbitController {
@Autowired
private TopicSender topicSender;
@ApiOperation("通配符模式")
@RequestMapping(value = "/topic", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult topicTest() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
topicSender.send(i);
ThreadUtil.sleep(1000);
}
return CommonResult.success(null);
}
}
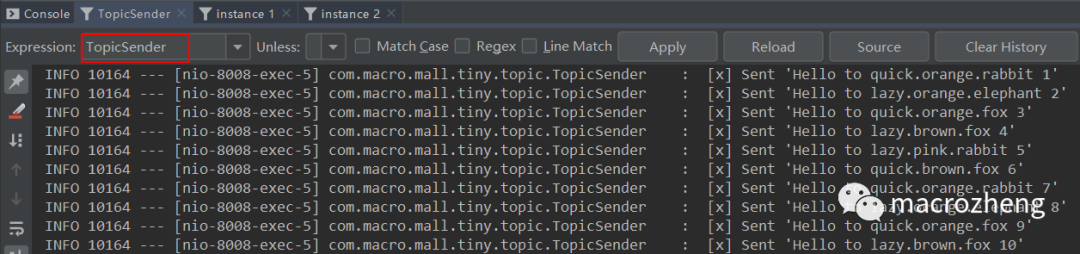
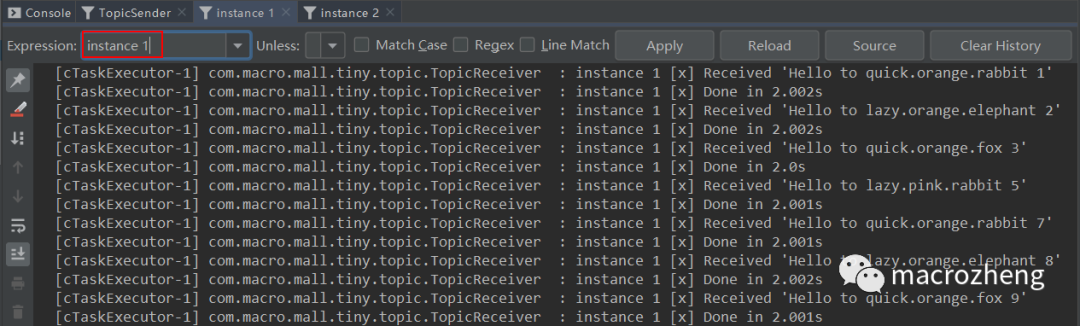
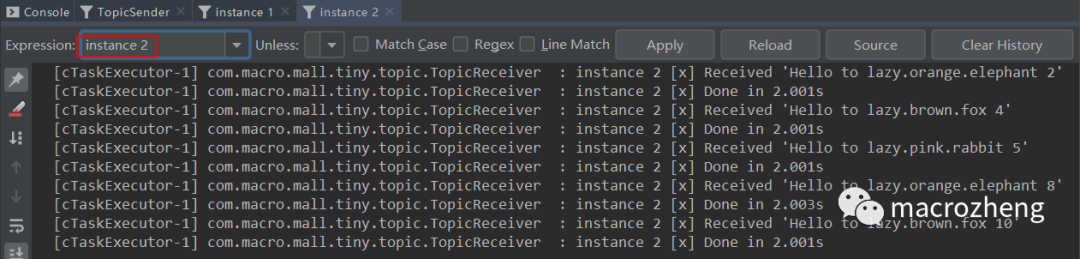
运行后结果如下,可以发现生产者往队列中发送包含不同
路由键的消息,instance 1和instance 2分别获取到了匹配的消息。
参考资料
RabbitMQ Tutorials:https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html
项目源码地址
https://github.com/macrozheng/mall-learning/tree/master/mall-tiny-rabbit
推荐阅读
欢迎关注,点个在看
