前言
2009年9月Spring 3.0 RC1发布后,Spring就引入了SpEL(Spring Expression Language)。对于开发者而言,引入新的工具显然是令人兴奋的,但是对于运维人员,也许是噩耗的开始。类比Struts 2框架,会发现绝大部分的安全漏洞都和ognl脱不了干系。尤其是远程命令执行漏洞,占据了多少甲方乙方工程师的夜晚/周末,这导致Struts 2越来越不受待见。
因此,我们有理由相信Spring引入SpEL必然增加安全风险。事实上,过去多个Spring CVE都与其相关,如CVE-2017-8039、CVE-2017-4971、CVE-2016-5007、CVE-2016-4977等。
本文分析的CVE-2017-8046同样也与SpEL有关。如果急于查看自己的应用是否受影响和修复建议,请查看官方公告,或者跳至0x07漏洞修复。
Spring Data REST简介
Spring Data REST是Spring Data的一个子项目。关于Spring Data,引用官方介绍如下: > Spring Data’s mission is to provide a familiar and consistent, Spring-based programming model for data access while still retaining the special traits of the underlying data store.
It makes it easy to use data access technologies, relational and non-relational databases, map-reduce frameworks, and cloud-based data services. This is an umbrella project which contains many subprojects that are specific to a given database. The projects are developed by working together with many of the companies and developers that are behind these exciting technologies.
一句话概括:Spring Data是对数据访问的更高抽象。通过它,开发者进一步从数据层解放出来,更专注于业务逻辑。不管是关系型数据还是非关系型数据,利用相应接口,开发者可以使用非常简单的代码构建对数据的访问(当然,Spring Data还有很多特性和功能,感兴趣的可参考官方文档)。
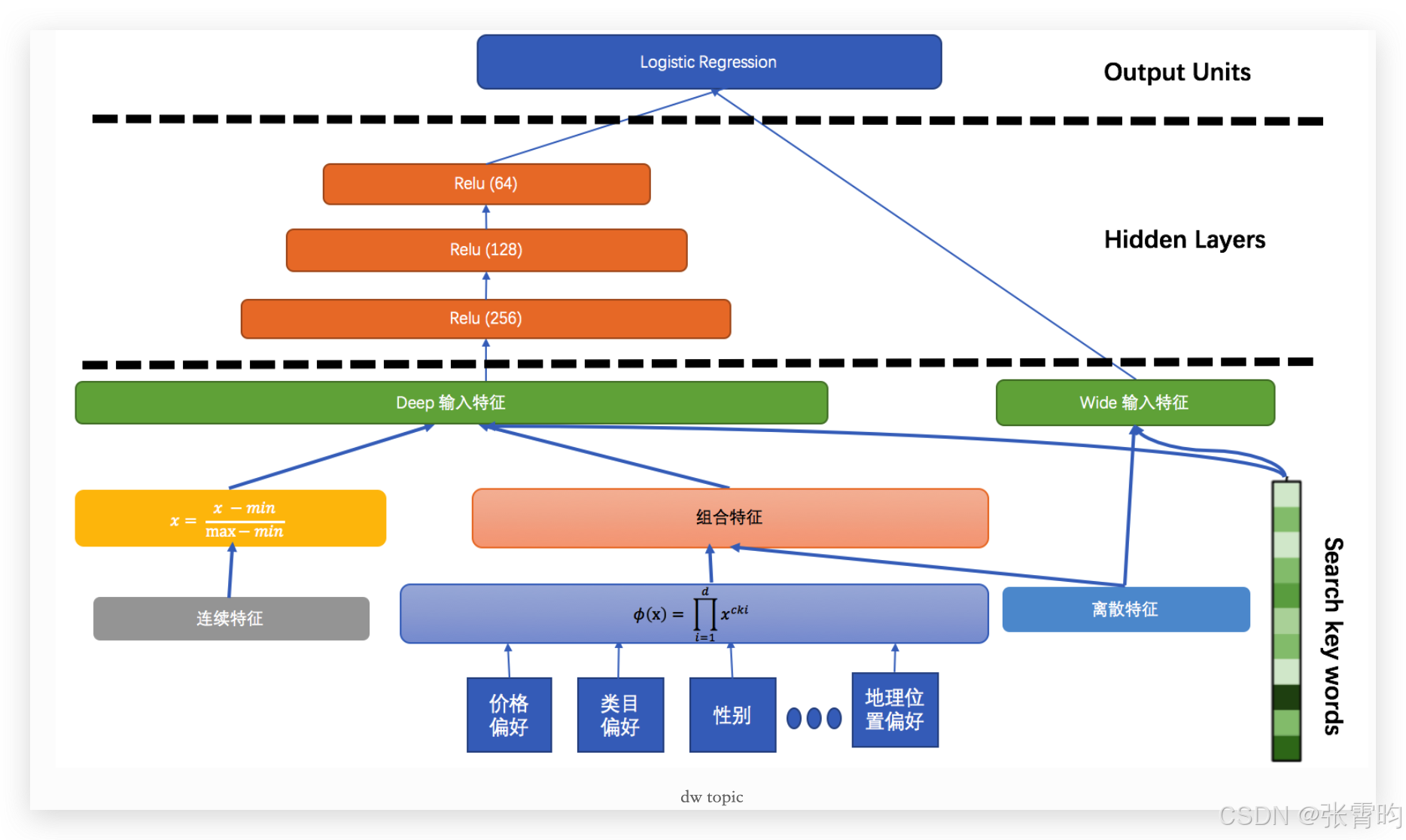
回过头看Spring Data REST,它是一个构建在Spring Data之上,为了帮助开发者更加容易地开发REST风格的Web服务,官方声称完成demo只需15分钟。
官方提供的Demo
参照官方文档,笔者使用Maven构建Spring-boot应用,数据库为H2 Database。
1) 添加依赖,pom.xml内容来自官方示例文档。 2) 编写实体类Person。
//import 省略
@Entity
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private long id; //自增主健
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
//getter setter省略
}
3) 编写接口。
//import 省略
//在/people处创建RESTful入口点
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "people", path = "people")
public interface PersonRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Person, Long> {
//接口继承了PagingAndSortingRepository,此接口封装了对Person实体类的CURD,并且具备分页和排序
}
4) Spring Boot执行入口。
//import 省略
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
5) 编译运行。
编译运行
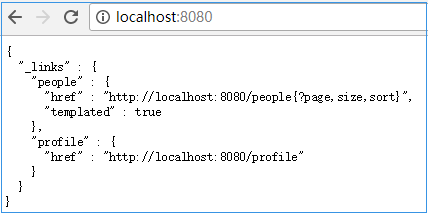
数据操作测试
1)测试是否成功
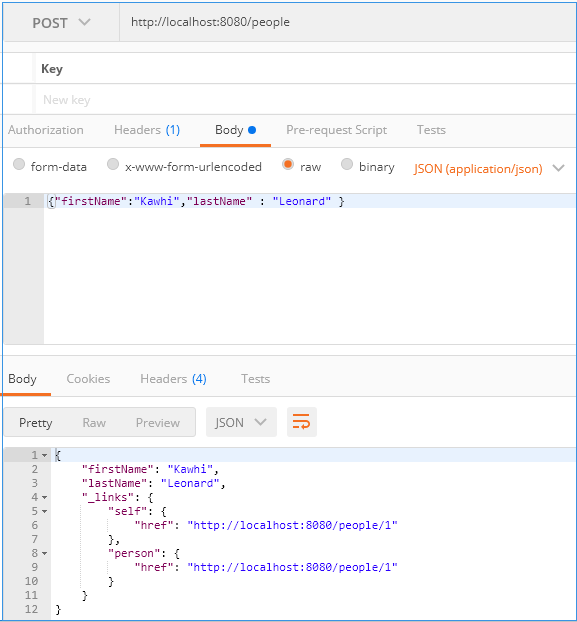
数据操作测试
2)使用POST方法添加一个数据
数据操作测试
3)查看新加入的数据
数据操作测试
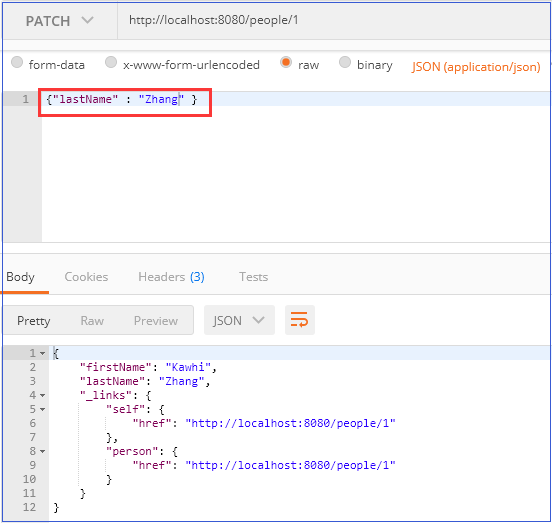
4)使用PATCH请求方法更新数据
数据操作测试
对于JSON Patch请求方法IETF制定了标准RFC6902。JSON Patch方法提交的数据必须包含一个path成员,用于定位数据,同时还必须包含op成员,可选值如下:
| op | 含义 |
|---|---|
| add | 添加数据 |
| remove | 删除数据 |
| replace | 修改数据 |
| move | 移动数据 |
| copy | 拷贝数据 |
| test | 测试给定数据与指定位置数据是否相等 |
比如对于上面添加的Person数据,修改其lastName属性,请求数据如下: > [{ “op”: “replace”, “path”: “/lastName”, “value”: “Zhang” }]
有两点需要注意:
① 必须将Content-Type指定为application/json-patch+json。 ② 请求数据必须是json数组。
漏洞分析
漏洞分析涉及的源码比较多,为了减少歧义和减小篇幅,约定两点: ① 代码以片段[a-z]标识; ② 提到某个方法不会包含完整的方法签名,仅提供方法名,需联系上下文识别。
1)根据官方公告,结合GitHub 的commit,猜测漏洞出在path参数值的处理上。尝试提交非法的path参数值,查看异常堆栈信息:
at org.springframework.expression.spel.ast.MethodReference$MethodValueRef.setValue(MethodReference.java:355) ~[spring-expression-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.expression.spel.ast.CompoundExpression.setValue(CompoundExpression.java:95) ~[spring-expression-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpression.setValue(SpelExpression.java:438) ~[spring-expression-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.json.patch.PatchOperation.setValueOnTarget(PatchOperation.java:167) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.json.patch.ReplaceOperation.perform(ReplaceOperation.java:41) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.json.patch.Patch.apply(Patch.java:64) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.JsonPatchHandler.applyPatch(JsonPatchHandler.java:91) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.JsonPatchHandler.apply(JsonPatchHandler.java:83) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.PersistentEntityResourceHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.readPatch(PersistentEntityResourceHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.java:206) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.PersistentEntityResourceHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.read(PersistentEntityResourceHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.java:184) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.PersistentEntityResourceHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.resolveArgument(PersistentEntityResourceHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.java:141) ~[spring-data-rest-webmvc-2.6.6.RELEASE.jar:na]
at org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite.resolveArgument(HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite.java:121) ~[spring-web-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.getMethodArgumentValues(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:158) ~[spring-web-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:128) ~[spring-web-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.java:97) ~[spring-webmvc-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:827) ~[spring-webmvc-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:738) ~[spring-webmvc-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handle(AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.java:85) ~[spring-webmvc-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:967) ~[spring-webmvc-4.3.10.RELEASE.jar:4.3.10.RELEASE]
//省略部分堆栈信息
2)既然是Patch请求方法,我们从org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.JsonPatchHandler.apply(JsonPatchHandler.java:83)入手分析。
//片段a:
public <T> T apply(IncomingRequest request, T target) throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(request, "Request must not be null!");
Assert.isTrue(request.isPatchRequest(), "Cannot handle non-PATCH request!");
Assert.notNull(target, "Target must not be null!");
if (request.isJsonPatchRequest()) {//
return applyPatch(request.getBody(), target);
} else {
return applyMergePatch(request.getBody(), target);
}
}
片段a中的if判断决定了请求Content-Type须指定application/json-patch+json。
//片段b:
public boolean isJsonPatchRequest() {
return isPatchRequest() //是否是PATCH请求方法
//Content-Type是否与application/json-patch+json兼容
&& RestMediaTypes.JSON_PATCH_JSON.isCompatibleWith(contentType);
}
片段a中的if判断为true的话,进入applyPatch方法:
//片段c:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
<T> T applyPatch(InputStream source, T target) throws Exception {
return getPatchOperations(source).apply(target, (Class<T>) target.getClass());
}
跟进getPatchOperations方法:
//片段d:
private Patch getPatchOperations(InputStream source) {
try {
return new JsonPatchPatchConverter(mapper).convert(mapper.readTree(source));//通过Jackson 生成对应的对象实例
} catch (Exception o_O) {
throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException(
String.format("Could not read PATCH operations! Expected %s!", RestMediaTypes.JSON_PATCH_JSON), o_O);
}
}
片段d通过Jackson实例化对象,我们看看相关构造函数:
//片段e:
public Patch(List<PatchOperation> operations) {
this.operations = operations;
}
//片段f:
public PatchOperation(String op, String path, Object value) {
this.op = op;
this.path = path;
this.value = value;
this.spelExpression = pathToExpression(path);
}
对于PatchOperation对象,成员spelExpression根据path转化而来,这一点对于PoC构造非常重要,笔者一开始就坑在这里。 pathToExpression完整的调用链比较长,影响PoC的构造关键在于下面两个方法。
//片段g:
private static String pathToSpEL(String path) {
return pathNodesToSpEL(path.split("\\/"));//跟据斜杠分割成字符数组
}
//片段h:
private static String pathNodesToSpEL(String[] pathNodes) {
StringBuilder spelBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < pathNodes.length; i++) {
String pathNode = pathNodes[i];
if (pathNode.length() == 0) {
continue;
}
if (APPEND_CHARACTERS.contains(pathNode)) {
if (spelBuilder.length() > 0) {
spelBuilder.append(".");
}
spelBuilder.append("$[true]");
continue;
}
try {
int index = Integer.parseInt(pathNode);
spelBuilder.append('[').append(index).append(']');
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
if (spelBuilder.length() > 0) {//使用.拼接字符数组
//如笔者尝试执行touch /tmp/file,
spelBuilder.append('.'); //并未在/tmp中发现file文件,后来发现应用目录中多了隐藏文件,
} //原因就在此处
spelBuilder.append(pathNode);
}
}
String spel = spelBuilder.toString();
if (spel.length() == 0) {
spel = "#this";
}
return spel;
}
回到片段C,继续看apply:
//片段i:
public <T> T apply(T in, Class<T> type) throws PatchException {
for (PatchOperation operation : operations) {
operation.perform(in, type);
}
return in;
}
在RFC6902的标准中,一次PATCH请求允许多个操作,比如:
[
{ "op": "test", "path": "/a/b/c", "value": "foo" },
{ "op": "remove", "path": "/a/b/c" },
{ "op": "add", "path": "/a/b/c", "value": [ "foo", "bar" ] }
]
对于上面的请求数据,将会顺序执行test、remove、add操作(当前操作的”文档”为上一次操作更新后的”文档”)。
因此,在代码片段i中循环每一个”操作”。假设我们提交了一个PATCH请求op为replace,我们接着看PatchOperation子类ReplaceOperation的perform方法:
//片段j:
<T> void perform(Object target, Class<T> type) {
setValueOnTarget(target, evaluateValueFromTarget(target, type));
}
调用父类PatchOperation的evaluateValueFromTarget方法:
//片段k:
protected <T> Object evaluateValueFromTarget(Object targetObject, Class<T> entityType) {
return value instanceof LateObjectEvaluator
? ((LateObjectEvaluator) value).evaluate(spelExpression.getValueType(targetObject)) : value;
}
官方在evaluateValueFromTarget方法中打了补丁,补丁的修复逻辑是检查路径是否合法,如果不合法则会抛出PatchException。完整的补丁信息可以从GitHub看对应commit。
//片段l:
protected <T> Object evaluateValueFromTarget(Object targetObject, Class<T> entityType) {
- return value instanceof LateObjectEvaluator
- ? ((LateObjectEvaluator) value).evaluate(spelExpression.getValueType(targetObject)) : value;
+ verifyPath(entityType);
+
+ return evaluate(spelExpression.getValueType(targetObject));
+ }
+
+ protected final <T> Object evaluate(Class<T> type) {
+ return value instanceof LateObjectEvaluator ? ((LateObjectEvaluator) value).evaluate(type) : value;
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Verifies that the current path is available on the given type.
+ *
+ * @param type must not be {@literal null}.
+ * @return the {@link PropertyPath} representing the path. Empty if the path only consists of index lookups or append
+ * characters.
+ */
+ protected final Optional<PropertyPath> verifyPath(Class<?> type) {
+
+ String pathSource = Arrays.stream(path.split("/"))//
+ .filter(it -> !it.matches("\\d")) // no digits
+ .filter(it -> !it.equals("-")) // no "last element"s
+ .filter(it -> !it.isEmpty()) //
+ .collect(Collectors.joining("."));
+
+ if (pathSource.isEmpty()) {
+ return Optional.empty();
+ }
+
+ try {
+ return Optional.of(PropertyPath.from(pathSource, type)); //根据对象和路径获取PropertyPath
+ } catch (PropertyReferenceException o_O) {
+ throw new PatchException(String.format(INVALID_PATH_REFERENCE, pathSource, type, path), o_O);
+ }
}
回过头看代码片段j,setValueOnTarget再往后走就是SpEL解析了。由于SpEL非该漏洞核心,本文不再深入。
漏洞复现
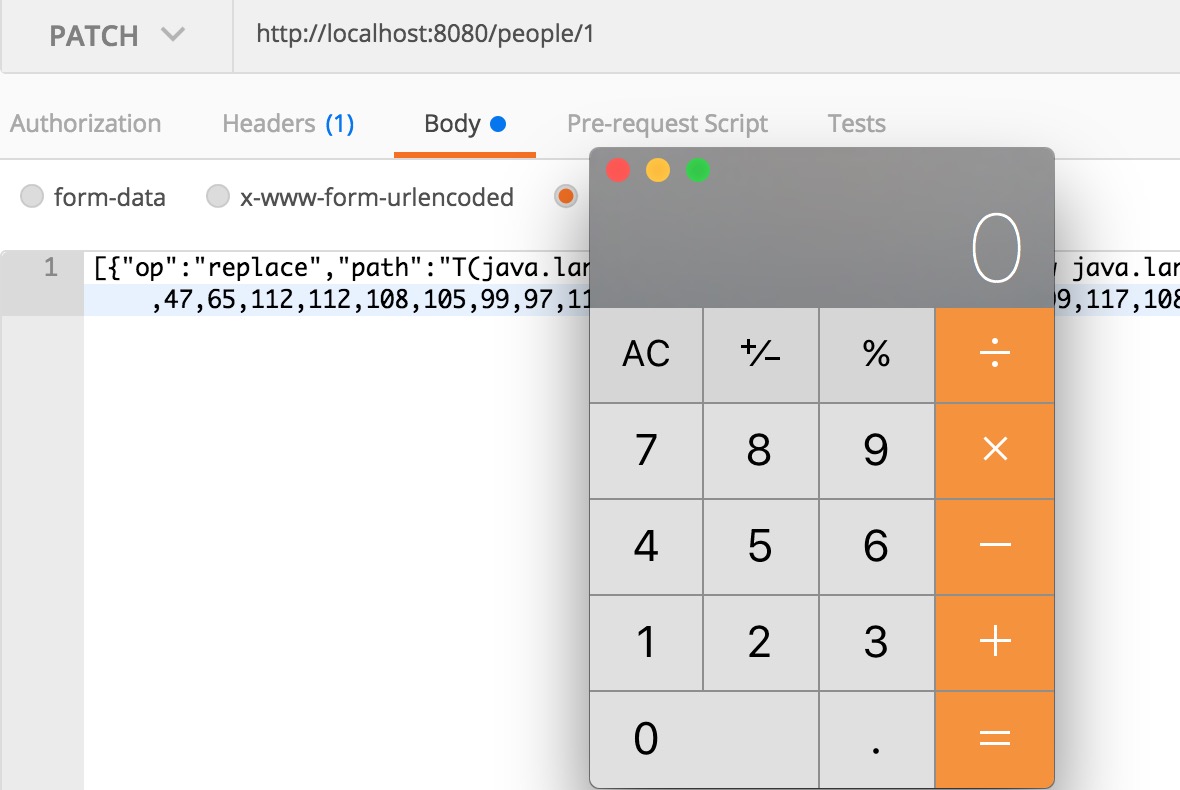
明白了漏洞原理之后,复现就非常简单了。注入表达式没有太多限制。
漏洞复现
漏洞修复
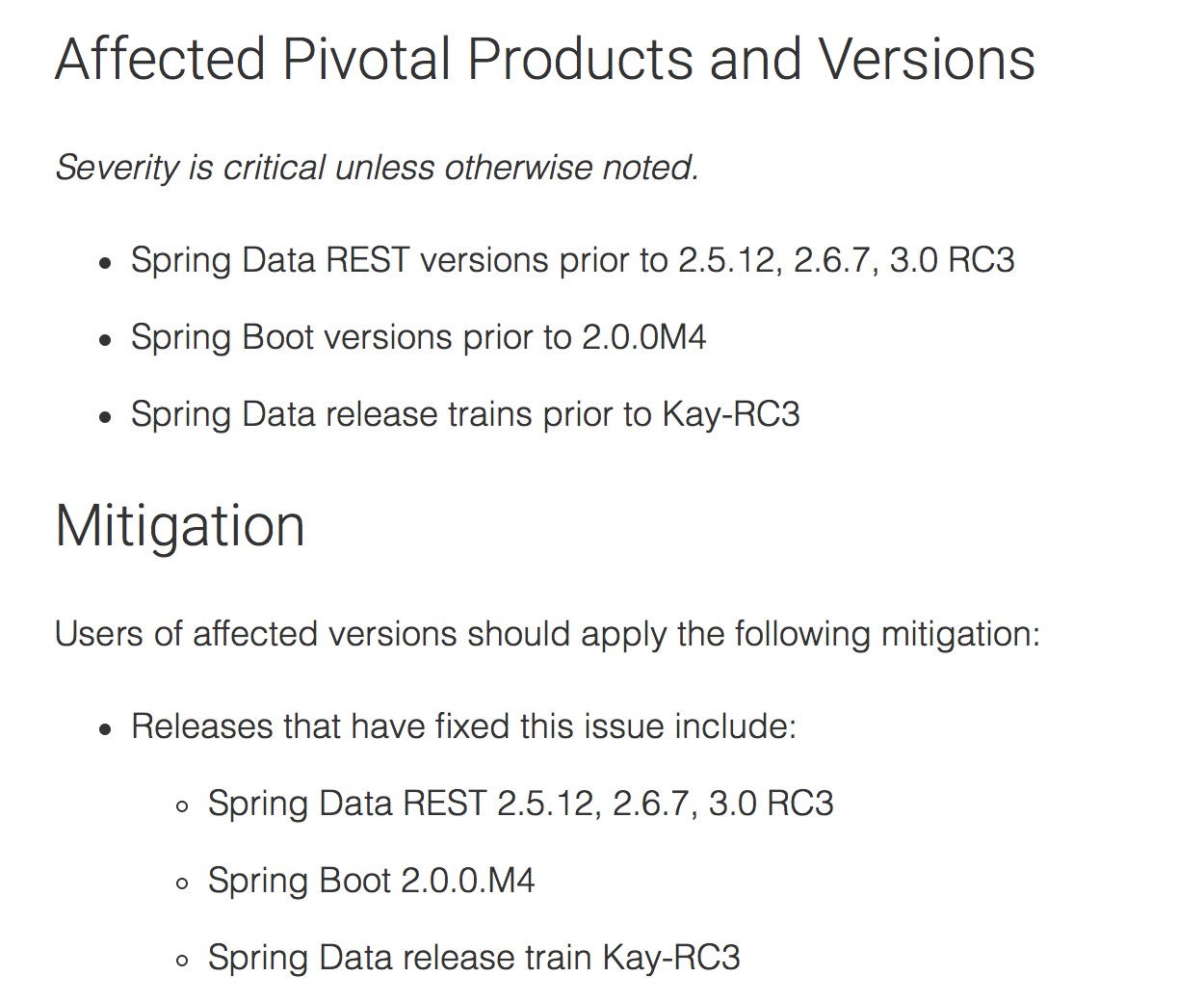
漏洞在9月21日披露,虽然定位为严重。但是笔者持续跟踪,并未发现国内哪些站点在跟进,不排除攻击者利用此漏洞攻击未打补丁的受影响应用。
漏洞信息来源于官方公告。
漏洞修复
值得注意的是,本次漏洞问题出现在 spring-data-rest-webmvc中。由于Spring 提供内建的依赖解决,因此可能并不会在依赖配置文件(如Maven的pom.xml)显式看到 spring-data-rest-webmv的依赖配置,这就是为什么官方公告还提及Spring Boot和Spring Data的缘故。
漏洞触发条件:网站使用Spring Data REST提供REST Web服务,版本在受影响范围内。
修复建议:及时升级。
from :
Spring Data REST 远程代码执行漏洞(CVE-2017-8046)分析与复现 - 美团技术团队
LruCache在美团DSP系统中的应用演进 - 美团技术团队
iOS 覆盖率检测原理与增量代码测试覆盖率工具实现 - 美团技术团队
日常开发Guava提效工具库核心实用指南梳理_guava string转list-CSDN博客