【数据结构与算法——TypeScript】
算法(Algorithm)的认识
-
解决问题的过程中,不仅仅 数据的存储方式会影响效率,算法的优劣也会影响效率
-
什么是算法?
- 定义:
🟢 一个有限指令集,每条指令的描述不依赖于言语 (编写指令:java/c++/ts/js)
🟢 接收一些输入(有些情况下不需要输入)(接收:排序:无序数组)
🟢 产生输出 (产出:有序数组)
🟢 一定在有限步骤之后终止
- 定义:
-
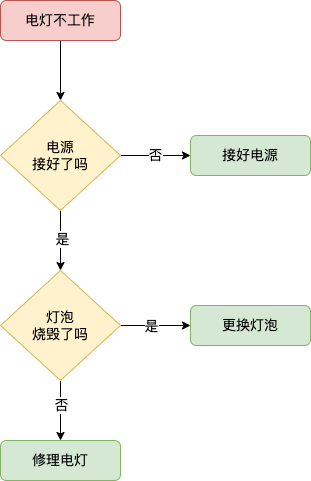
举例:电灯不工作的解决算法
-
算法的通俗理解
- Algorithm这个单词本意就是 解决问题的办法/步骤逻辑。
- 数据结构的实现,离不开算法。
线性结构(Linear List)
-
线性结构(Linear List)是由n(n≧0)个数据元素(结点)a[0],a[1],a[2],…,a[n-1]组成的有限序列。
-
其中:
- 【数据元素的个数 n 定义为表的长度】= “list”.length()(“list”.length() = 0 (表示没有一个元素) 时,称为空表)。
- 将非空的线性表 (n>=1),记作:(a[0],a[1],a[2],…,a[n-1])。
- 数据元素 a[i] (0 <= i <= n-1) 只是抽象符号,其具体含义在不同情况下可以不同。
-
常见线性结构:
💚 数组结构(Array)
💚 栈结构(Stack)
💚 队列结构(Queue)
💚 链表结构(LinkedList)
数组(Array)结构
-
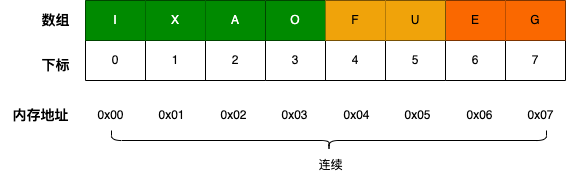
数组(Array)结构是一种重要的数据结构
- 几乎是每种编程语言都会提供的一种 原生数据结构(语言自带的);
- 并且我们 可以借助于数组结构来实现其他的数据结构,比如:栈(Stack)、队列(Queue)、堆(Heap);
-
通常数组的内存都是连续的,所以数组在知道下标值的情况下,访问效率是非常高的
-
TypeScript中数组的各种用法,和JavaScript是一致的:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array
栈结构(Stack)
认识栈结构和特性 ❤️
认识栈结构
-
栈 也是一种非常常见的数据结构,并且在程序中的应用非常广泛。
-
数组:
- 是一种 线性结构,可以在数组的 任意位置 插入和删除数据。
- 但,为了实现某些功能,必须对这种 任意性加入限制。
- 而 栈和队列 就是比较常见的 受限的线性结构。
-
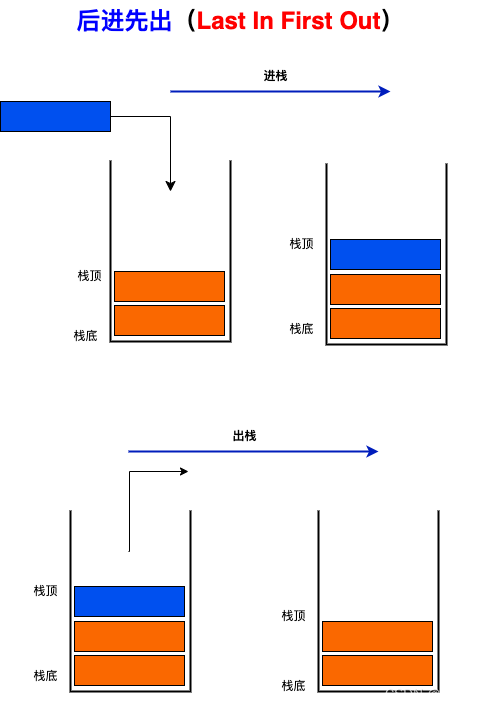
栈结构示意图
❤️ 后进先出/先进后出
栈结构特性
- 栈(Stack),它是一种受限的线性结构, 后进先出(LIFO)
- 其限制是仅允许在 表的一端 进行插入和删除运算。这一端被称为 栈顶,相对地,另一端就是 栈低。
- LIFO(last in first out)表示 后进入的元素,第一个弹出栈空间。类似于,自动餐托盘,最后放上的托盘,往往先拿出去使用。
- 向一个栈插入新元素,又叫 进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;
- 从一个栈删除元素又称之为 出栈 或者 退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
栈结构特性 —— 面试题
面试题目
-
❓题目:
🔖 有六个元素6,5,4,3,2,1顺序入栈,问下列哪一个不是合法的出栈序列?()
A. 5 4 3 6 1 2
B. 4 5 3 2 1 6
C. 3 4 6 5 2 1
D. 2 3 4 1 5 6 -
分析:
- A. 5 4 3 6 2 1
- 6,5进栈,5出栈,4进栈,4出栈,3进栈,3出栈,6出栈,2进栈,1进栈,1出栈,2出栈
- B. 4 5 3 2 1 6
- 6,5,4进栈,4出栈,5出栈,3进栈,3出栈,2进栈,2出栈,1入栈,1出栈,6出栈
- C. 3 4 6(x) 5 2 1 ❌
- 6,5,4,3进栈,3出栈,4出栈,5出栈
- D. 2 3 4 1 5 6
- 6,5,4,3,2进栈,2出栈,3出栈,4出栈,1进栈,1出栈,5出栈,6出栈
- 答案: C
- A. 5 4 3 6 2 1
实现栈结构的封装
- 常见的方式:
🔹 基于数组实现
🔹 基于链表实现
🔹 基于数组实现:创建栈的类
- 代码解析:
- 创建一个 Stack ,用户创建栈的类,可以定义一个泛型类。
- 在构造函数中,定义一个变量,存储当前栈对象中的所有元素。
- 这个变量是一个数组类型。
- 之后,无论是入栈还是出栈操作,都是从数组中添加和删除元素。
- 栈的一些操作方法,无论是什么语言,操作都是比较类似的。
栈结构常见的方法
🔸栈的常见操作
- push(element):添加一个新元素到栈顶。
- pop():删除栈顶元素,返回被移除的元素。
- peek():仅返回栈顶元素,不对栈做任何修改。
- isEmpty():判断栈里是否有元素。有,返回true,否,返回false。
- size():返回栈里的元素个数。这个方法和数组的length属性类型。
实现
import { IStack } from './IStack';
class ArrayStack<T = any> implements IStack<T> {
// 定义一个数组/链表,用于存储元素
private data: T[] = [];
// 实现栈中的操作方法
// push(element):添加一个新元素到栈顶
push(element: T): void {
this.data.push(element);
}
// pop():删除栈顶元素,返回被移除的元素。
pop(): T | undefined {
return this.data.pop();
}
// peek():仅返回栈顶元素,不对栈做任何修改。
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[this.data.length - 1];
}
// isEmpty():判断栈里是否有元素。有,返回true,否,返回false。
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.data.length === 0;
}
// size():返回栈里的元素个数。这个方法和数组的length属性类型。
size(): number {
return this.data.length;
}
}
export default ArrayStack;
export interface IStack<T> {
push(element: T): void;
pop(): T | undefined;
peek(): T | undefined;
isEmpty(): boolean;
size(): number;
}
栈面试题 —— 十进制转二进制
-
为什么需要十进制转二进制?
- 现实生活中,主要使用 十进制。
- 但,在计算机科学中, 二进制非常重要,因为 计算机里的所有内容都是用二进制数字表示的(0和1)。
- 没有十进制和二进制互相转换的能力,与计算机交流就很困难。
- 转换二进制是计算机科学和编程领域中经常使用的算法。
-
如何实现时十进制转二进制(整数)?
- 将十进制数字和2整除(二进制是满2进1),直到结果为0
- 把十进制数字35转为二进制的数字:
- 35/2 = 17…1, 余 1
- 17/2 = 8…1, 余 1
- 8/2 = 4…0,余 0
- 4/2 = 2…0,余 0
- 2/2 = 1…0,余 0
- 1/2 = 0…1,余 1
- 从后往前:100011
-
简单实现
import ArrayStack from './02_实现栈结构Stack(重构)'; function decimalToBinary(decimal: number): string { // 1. 创建一个栈,用于存储余数 const stack = new ArrayStack<number>(); // 2. 使用循环:while:不确定次数,只知道循环结束条件 while (decimal > 0) { const result = decimal % 2; stack.push(result); decimal = Math.floor(decimal / 2); } // 3.将所有的余数已放入到stack中,依次取出所有余数 let binary = ''; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { binary += stack.pop(); } return binary; } export {}; console.log('35:', decimalToBinary(35)); console.log('100:', decimalToBinary(100));
栈面试题 —— 有效括号
-
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ 的字符串
s,判断字符串是否有效。- ❗️有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号
- Leecode 20:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
- ❗️有效字符串需满足:
-
示例 1:
输入:s = “()”
输出:true -
示例 2:
输入:s = “()[]{}”
输出:true -
示例 3:
输入:s = “(]”
输出:false -
⚠️ 提示:
- 1 <= s.length <= 10的4次
- s 仅由括号 ‘()[]{}’ 组成
-
代码
import ArrayStack from './02_实现栈结构Stack(重构)';
function isValid(s: string): boolean {
// 1. 创建一个栈结构:
const stack = new ArrayStack<string>();
// 2. 遍历字符串
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
const c = s[i];
switch (c) {
case '(':
stack.push(')');
break;
case '{':
stack.push('}');
break;
case '[':
stack.push(']');
break;
default:
if (c !== stack.pop()) return false;
break;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
console.log(isValid('()'));
console.log(isValid('()[]{}'));
console.log(isValid('(]'));
console.log(isValid('([])'));
console.log(isValid('({[}])'));
队列结构(Queue)
认识队列和特性
-
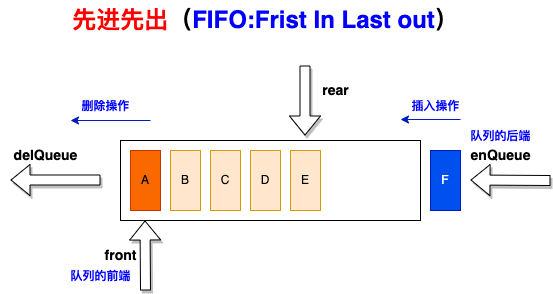
受限的线性结构
- 这种受限的线性结构对于解决某些 特别问题有特别的结果。
- 受限的数据结构:队列。
-
队列(Queue),它是一种受限的线性结构,先进先出(FILO:First In Last Out)
- 受限之处:只允许在队列的前端(front),进行删除操作;
- 在队列的 后端(rear) 进行插入操作;
实现队列结构封装
- 基于 数组实现(性能低)
- 基于 链表实现(更好)
队列结构常见方法
- enqueue(element):向队列尾部添加一个(或者多个)新的项。
- dequeue():移除队列的第一(即排在队列最前面的)项,也是最先移除的元素;
- front/peek():返回队列中第一个元素——最先被添加,也是最先被移除的元素。队列不做任何变动(不移除元素,只返回元素信息)
- isEmpty():如果队列中不包含任何元素,返回true,否则返回false
- size():返回队列包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似
基于数组实现
import { IQueue } from './IQueue';
class ArrayQueue<T = any> implements IQueue<T> {
// 内部通过数组保存
private data: T[] = [];
// 队列常见操作
/**
* enqueue(element):向队列尾部添加一个(或者多个)新的项。
* dequeue():移除队列的第一(即排在队列最前面的)项,也是最先移除的元素;
* front/peek():返回队列中第一个元素——最先被添加,也是最先被移除的元素。队列不做任何变动(不移除元素,只返回元素信息)
* isEmpty():如果队列中不包含任何元素,返回true,否则返回false;
* size():返回队列包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似
*/
enqueue(element: T): void {
this.data.push(element);
}
dequeue(): T | undefined {
return this.data.shift();
}
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.data.length === 0;
}
get size(): number {
return this.data.length;
}
}
export default ArrayQueue;
import type { IList } from '../types/IList';
export interface IQueue<T> extends IList<T> {
enqueue(element: T): void;
dequeue(): T | undefined;
}
export interface IList<T> {
peek(): T | undefined;
isEmpty(): boolean;
get size(): number;
}
面试题 —— 击鼓传花
-
击鼓传花,是一个常见的面试算法题:使用队列可以非常方便的实现最终的结果
-
原游戏规则
- 班级中玩一个游戏,所有同学围成一个圈,从某位同学手里开始向旁边的同学传一束花;
- 这个时候某个人(比如班长),在击鼓,鼓声停下的一刻,花落在谁的手里,谁就出来表演节目。
-
修改游戏规则
- 几个朋友一起玩一个游戏, 围成一圈,开始数数,数到某个数字的人自动淘汰;
- 最后 剩下的这个人获胜,请问最后剩下的人是原来在哪一个位置上的人?
-
封装一个基于队列的函数:
- 参数:所有参与人的姓名,基于的数字;
- 结果:最终剩下的一个人的姓名
-
分析:
- 假如数到3的人,淘汰;
- 那么,队列中 数的1,2的人,出队之后,又入队;
- 数到 3 的人,出队,不需要入队
- 直到,队列的size() 等于1 的时候,取到队列里的人
- 假如数到3的人,淘汰;
-
代码
import ArrayQueue from './01_基于数组的队列结构Queue';
function hotPatato(names: string[], num: number) {
if (names.length === 0) return -1;
// 1. 创建一个队列结构
const queue = new ArrayQueue<string>();
// 2. 将所有的name加入队列
for (const name of names) {
queue.enqueue(name);
}
// 3. 淘汰的规则
while (queue.size > 1) {
// 小于 num 的不淘汰
for (let i = 1; i < num; i++) {
const name = queue.dequeue();
if (name) queue.enqueue(name);
}
// num 淘汰
queue.dequeue();
}
// 取出最后一个人
const leftName = queue.dequeue()!;
// 取出最后一个人的原索引
const index = names.indexOf(leftName);
return index;
}
const leftIndex = hotPatato(['why', 'JIM', 'JANE', 'LENO', 'CURRY', 'TIM', 'TOM', 'JERRY', 'JENO', 'TIA'], 5);
console.log(leftIndex);
面试题 —— 约瑟夫环
-
什么是约瑟夫环问题(历史)?
-
阿乔问题(有时也称为约瑟夫斯置换),是一个出现在计算机科学和数学中的问题。在计算机编程的算法中,类似问题又称为约瑟夫环。
- 人们站在一个等待被处决的圈子里;
- 计数从圆圈中指定的点开始,并沿指定方向围绕圆圈进行;
- 在跳过指定数量的人之后,处刑下一个人;
- 对剩下的人重复该过程,从下一个人开始,朝同一方向跳过相同数量的人,直到只剩下一个人,并被释放;
- 在给定数量的情况下,站在第几个位置可以避免被处刑?
-
Leecode 剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
-
https://leetcode.cn/problems/yuan-quan-zhong-zui-hou-sheng-xia-de-shu-zi-lcof/
-
0,1,···,n-1这n个数字排成一个圆圈,从数字0开始,每次从这个圆圈里删除第m个数字(删除后从下一个数字开始计数)。
-
求出这个圆圈里剩下的最后一个数字。
-
例如,0、1、2、3、4这5个数字组成一个圆圈,从数字0开始每次删除第3个数字,则删除的前4个数字依次是2、0、4、1,因此最后剩下的数字是3。
-
示例 1:
输入: n = 5, m = 3
输出: 3 -
示例 2:
输入: n = 10, m = 17
输出: 2 -
代码
import ArrayQueue from './01_基于数组的队列结构Queue';
function lastRemaining(n: number, m: number): number {
const queue = new ArrayQueue<number>();
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.enqueue(i);
}
while (queue.size > 1) {
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue()!);
}
queue.dequeue();
}
return queue.dequeue()!;
}
console.log(lastRemaining(5, 3));
console.log(lastRemaining(10, 17));
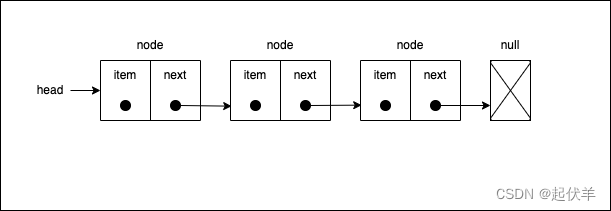
链表结构(LinkedList)
认识链表及特性
数组的缺点
- 链表和数组一样,可以用于 存储一系列的元素,但是链表和数组的 实现机制完全不同。
- 用于存储数据的线性结构:链表。
🥺
-
数组:
- 要存储多个元素,数组(或选择链表)可能是 最常用的数据结构
- 几乎每种语言都有默认实现 数组结构
-
💔 但是,数组有很多缺点
- 数组的创建通常需要申请一段 连续的内存空间(一整块的内存),并且大小是固定的(大多数编程语言数组都是固定的),所以当前数组 不能满足容量需求时,需要 扩容。(一般情况下时申请一个更大的数组,比如2倍。然后将原数组中的元素复制过去)
- 而且在 数组开头或者中间位置插入数据的成本很高,需要 进行大量元素的位移。
🥰 链表的优势
-
要存储多个元素,另外一个选择就是 链表
-
不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中 不必是连续的空间。
- 链表的每个元素由一个存储 元素本身的节点和 一个指向下一个元素的引用(有些语音称为指针或链接)组成。
-
❣️ 相对于数组,链表的优势有
- 🟩 内存空间不是必须连续的
- ✓ 可以充分利用计算机的内存,实现灵活的 内存动态管理。
- 🟩 链表不必在创建时就 确定大小,并且大小可以 无限延伸下去。
- 🟩 链表在 插入和删除数据时,时间复杂度可以达到O(1)
- ✔️ 相对数组效率高很多
- 🟩 内存空间不是必须连续的
-
💔 相对于数组,链表的缺点有
- ❌ 链表访问任何一个位置的元素时,都需要 从头开始访问(无法跳过第一个元素访问任何一个元素)。
- ❌ 无法通过下标直接访问元素,需要从头一个一个访问,直到找到对应的元素。
什么是链表?
- 链表是什么?
- 链表类似于火车:有一个火车头,火车头会连接一个节点,节点上有乘客(类似于数据),并且这个节点会连接下一个节点,以此类推。
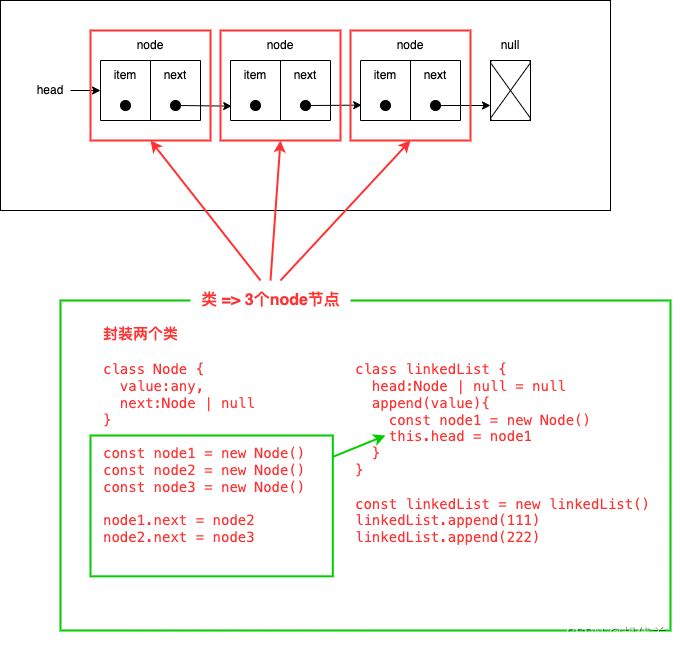
封装链表的类结构
分析代码
- 封装一个 Node类,用于封装每一个节点上的信息(包括值和指向下一个节点的引用),它是一个泛型。
- 封装一个 LinkedList类,用于表示我们的链表结构。
- 链表中保存两个属性:链表长度、链表的第一个节点。
// 1. 创建Node节点类
class Node<T> {
value: T;
next: Node<T> | null = null;
constructor(value: T) {
this.value = value;
}
}
// 2.创建LinkedList类
class LinkedList<T> {
head: Node<T> | null = null;
private size: number = 0;
get length() {
return this.size;
}
}
const linkedList = new LinkedList<string>();
console.log(linkedList.head);
export {};
封装链表的相关方法
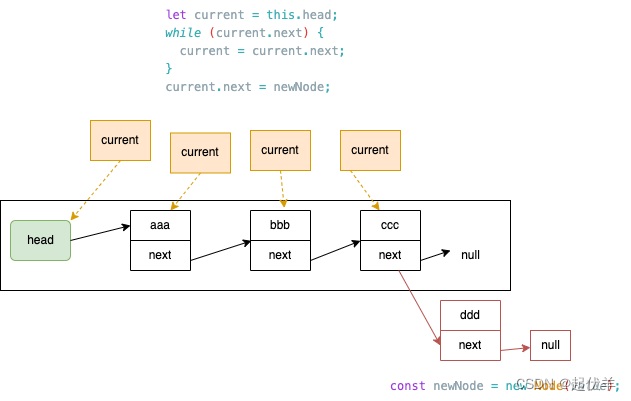
- append(element):向链尾添加一个新的项
-
- 链表本身为空,新添加数据时唯一的节点
-
- 链表本身不为空,需要向其他节点后面追加节点
-
// 追加节点
append(value: T) {
// 1.根据value创建一个新节点
const newNode = new Node(value);
// 1. 链表本身为空,新添加数据时唯一的节点
// 2. 链表本身不为空,需要向其他节点后面追加节点
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// current此时,肯定是指向最后一个节点
current.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
-
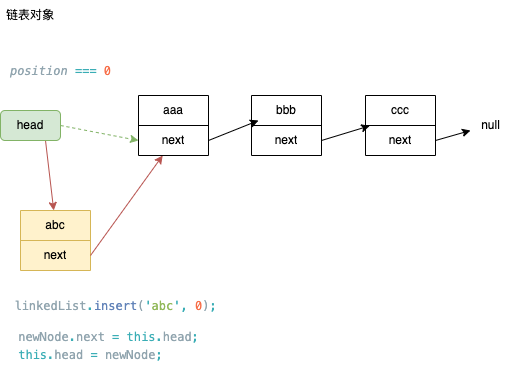
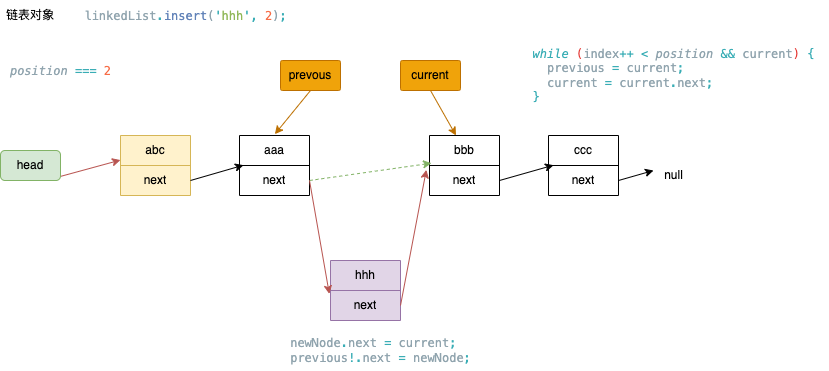
insert(position,element):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项
- 1.添加到第一个位置
- 添加到第一个位置,表示新添加的节点是头,就需要将原来的头节点,作为新的节点的next
- 这个时候的head应该指向新节点
-
- 其他位置
- 1.添加到第一个位置
-
//插入 insert(position, element): 向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项;
insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {
if (position < 0 || position > this.size) return false;
// 是否添加到第一个
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
let previous: Node<T> | null = null;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position && current) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// index === position
newNode.next = current;
previous!.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
return true;
}
- get(position):获取对应位置的元素
// 获取get
get(position: number): T | null {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return null;
// 查找元素
let index = 0;
let current = this.head;
while (index++ < position && current) {
current = current?.next;
}
// index === position
return current?.value ?? null;
}
- indexOf(element):返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素则返回 -1
// 获取索引
indexOf(value: T): number {
// 遍历
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index++;
}
return -1;
}
- update(position,element):修改某个位置的元素
// 更新
update(value: T, position: number): boolean {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return false;
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position && current) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
currentNode!.value = value;
return true;
}
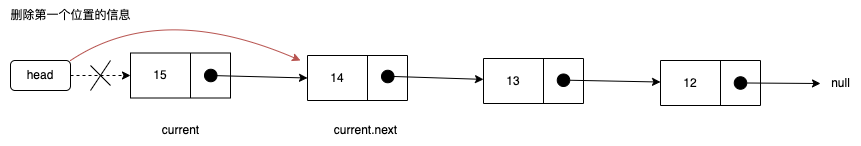
- removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项
-
常见两种
-
- 根据位置位移对应的数据
-
- 根据数据,先找到对应的位置,再移除数据
-
-
移除第一项:
- 移除第一项时,直接让head指向第二项信息
- 第一项信息没有引用指向,就在链表中不再有效,后面会被回收
-
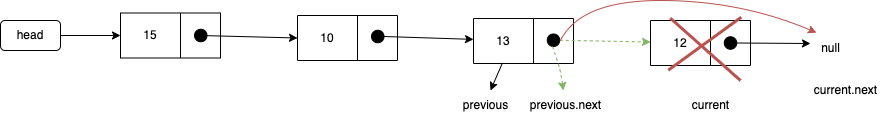
移除其他项:
- 首先,通过while循环,找到正确的位置
- 其次,直接将上一项的next指向current项的next,这样中间的项就没有引用指向它,也就不存于链表中,后面就会被回收
-
// 删除
removeAt(position: number): T | null {
// 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return null;
// 删除元素
// 判断是否是删除第一个节点
let current = this.head;
if (position === 0) {
this.head = this.head?.next ?? null;
} else {
let previous: Node<T> | null = null;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position && current) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// index === position
previous!.next = current?.next ?? null;
}
this.size--;
return current?.value ?? null;
}
- remove(element):从链表中移除一项
// 根据value删除
remove(value: T): T | null {
const index = this.indexOf(value);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
- isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false
// 链表是否为空
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.size === 0;
}
- size():返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似
完整代码
// 1. 创建Node节点类
class Node<T> {
value: T;
next: Node<T> | null = null;
constructor(value: T) {
this.value = value;
}
}
// 2.创建LinkedList类
class LinkedList<T> {
private head: Node<T> | null = null;
private size: number = 0;
get length() {
return this.size;
}
// 封装私有方法:
// 根据position 获取到当前节点(不是节点的value,而是获取节点)
private getNode(position: number): Node<T> | null {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position && current) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
// 追加节点
append(value: T) {
// 1.根据value创建一个新节点
const newNode = new Node(value);
// 1. 链表本身为空,新添加数据时唯一的节点
// 2. 链表本身不为空,需要向其他节点后面追加节点
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// current此时,肯定是指向最后一个节点
current.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// 遍历链表的方法
traverse() {
const values: T[] = [];
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
values.push(current.value);
current = current.next;
}
console.log(values.join(' -> '));
}
// 插入 insert(position, element): 向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项;
insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {
if (position < 0 || position > this.size) return false;
// 是否添加到第一个
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let previous = this.getNode(position - 1);
// index === position
newNode.next = previous?.next ?? null;
previous!.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
return true;
}
// 根据位置删除
removeAt(position: number): T | null {
// 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return null;
// 删除元素
// 判断是否是删除第一个节点
let current = this.head;
if (position === 0) {
this.head = this.head?.next ?? null;
} else {
// 重构
let previous = this.getNode(position - 1);
// index === position
previous!.next = previous?.next?.next ?? null;
}
this.size--;
return current?.value ?? null;
}
// 获取get
get(position: number): T | null {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return null;
// 查找元素
return this.getNode(position)?.value ?? null;
}
// 更新
update(value: T, position: number): boolean {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return false;
const currentNode = this.getNode(position);
currentNode!.value = value;
return true;
}
// 获取索引
indexOf(value: T): number {
// 遍历
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index++;
}
return -1;
}
// 根据value删除
remove(value: T): T | null {
const index = this.indexOf(value);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
// 链表是否为空
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.size === 0;
}
}
const linkedList = new LinkedList<string>();
linkedList.append('aaa');
linkedList.append('bbb');
linkedList.append('ccc');
linkedList.insert('abc', 0);
linkedList.insert('abcd', 0);
linkedList.insert('中间444', 2);
linkedList.insert('nba', 6);
linkedList.traverse();
linkedList.removeAt(0);
linkedList.traverse();
linkedList.removeAt(2);
linkedList.traverse();
console.log('-----测试get-----');
console.log(linkedList.get(0));
console.log(linkedList.get(1));
console.log(linkedList.get(2));
console.log('-----测试update-----');
console.log(linkedList.update('11111', 1));
linkedList.traverse();
console.log('-----测试indexOf-----');
console.log(linkedList.indexOf('11111'));
linkedList.traverse();
export {};
链表常见的面试题
-
-
你可以选择使用单链表或者双链表,设计并实现自己的链表。
-
单链表中的节点应该具备两个属性:val 和 next 。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。
-
如果是双向链表,则还需要属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点下标从 0 开始。
-
实现 MyLinkedList 类:
- MyLinkedList() 初始化 MyLinkedList 对象。
- int get(int index) 获取链表中下标为 index 的节点的值。如果下标无效,则返回 -1 。
- void addAtHead(int val) 将一个值为 val 的节点插入到链表中第一个元素之前。在插入完成后,新节点会成为链表的第一个节点。
- void addAtTail(int val) 将一个值为 val 的节点追加到链表中作为链表的最后一个元素。
- void addAtIndex(int index, int val) 将一个值为 val 的节点插入到链表中下标为 index 的节点之前。如果 index 等于链表的长度,那么该节点会被追加到链表的末尾。如果 index 比长度更大,该节点将 不会插入 到链表中。
- void deleteAtIndex(int index) 如果下标有效,则删除链表中下标为 index 的节点。
-
class Node<T> {
val: T;
next: Node<T> | null = null;
constructor(val: T) {
this.val = val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList<T> {
private head: Node<T> | null = null;
private size: number = 0;
private getNode(index: number): Node<T> | null {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
while (i++ < index && current) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
// int get(int index) 获取链表中下标为 index 的节点的值。如果下标无效,则返回 -1 。
get(index: number): any {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return -1;
}
return this.getNode(index)?.val ?? null;
}
addAtHead(val: T): void {
const newNode = new Node(val);
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.size++;
}
addAtTail(val: T): void {
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// current此时,肯定是指向最后一个节点
current.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
addAtIndex(index: number, val: T): boolean {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) return false;
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (index === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let previous = this.getNode(index - 1);
// index === position
newNode.next = previous?.next ?? null;
previous!.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
return true;
}
deleteAtIndex(index: number): T | null {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) return null;
// 删除元素
// 判断是否是删除第一个节点
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head?.next ?? null;
} else {
// 重构
let previous = this.getNode(index - 1);
// index === position
previous!.next = previous?.next?.next ?? null;
}
this.size--;
return current?.val ?? null;
}
}
export {};
-
- 删除链表中的节点
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
有一个单链表的head,我们想删除它其中的一个节点node。
给你一个需要删除的节点
node。你将 无法访问 第一个节点head。链表的所有值都是 唯一的,并且保证给定的节点
node不是链表中的最后一个节点。删除给定的节点。注意,删除节点并不是指从内存中删除它。这里的意思是:
- 给定节点的值不应该存在于链表中。
- 链表中的节点数应该减少 1。
node前面的所有值顺序相同。node后面的所有值顺序相同。
自定义测试:
- 对于输入,你应该提供整个链表
head和要给出的节点node。node不应该是链表的最后一个节点,而应该是链表中的一个实际节点。 - 我们将构建链表,并将节点传递给你的函数。
- 输出将是调用你函数后的整个链表。
class ListNode {
val: number;
next: ListNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;
}
}
function deleteNode(node: ListNode | null): void {
node!.val = node!.next!.val;
node!.next = node!.next!.next;
}
export {};
-
- 反转链表
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
- 给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
class ListNode {
val: number;
next: ListNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;
}
}
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
if (!head || !head.next) return head;
const newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}