搜索引擎网页url : 链接
项目已上传gitee : 链接
一 : 项目相关背景
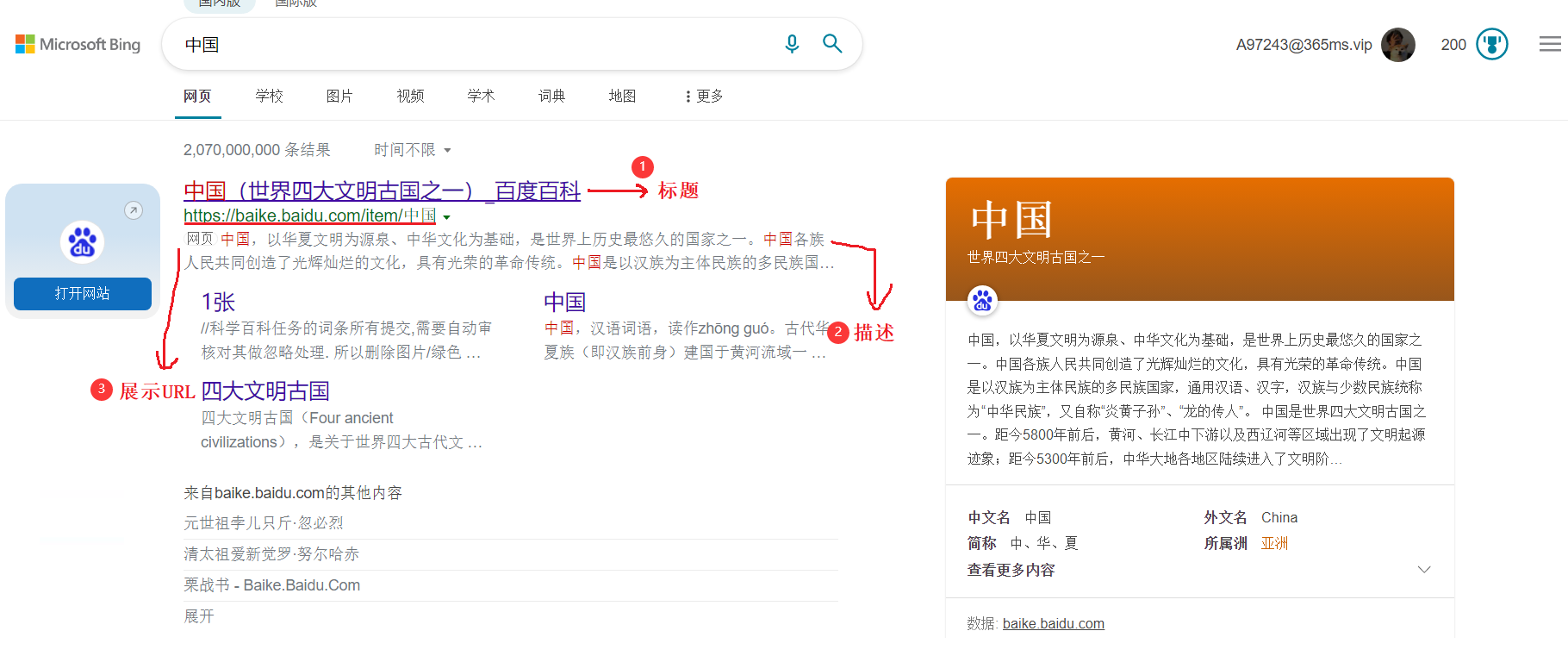
当我们输入搜索内容后,会展示出搜索结果页面:
搜索引擎获取页面的方式主要涉及“爬虫”这样的程序。当用户输入查询词后,如何让查询词和当前的网页内容进行匹配呢?如果直接进行暴力搜索是非常低效的,为了高效地获取结果,需要使用“倒排索引”。
倒排索引源于实际应用中需要根据属性的值来查找记录。
二 : 项目介绍
2.1 项目目标
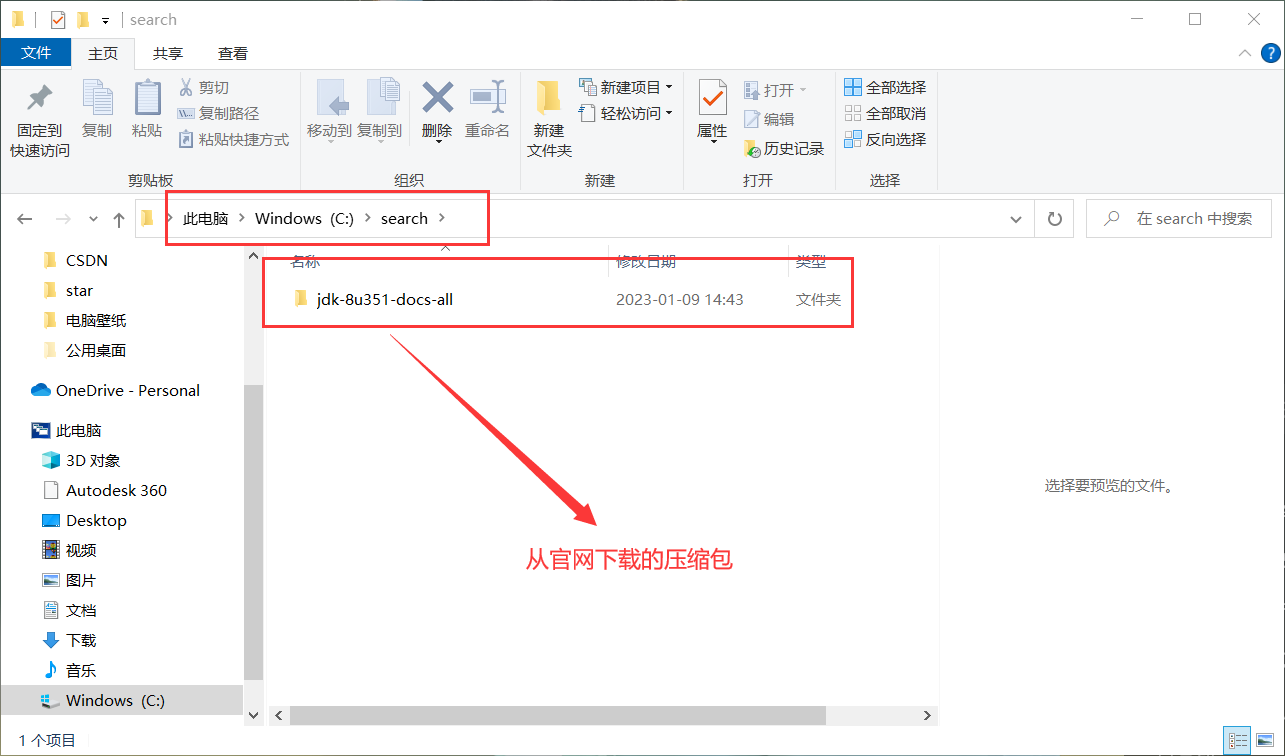
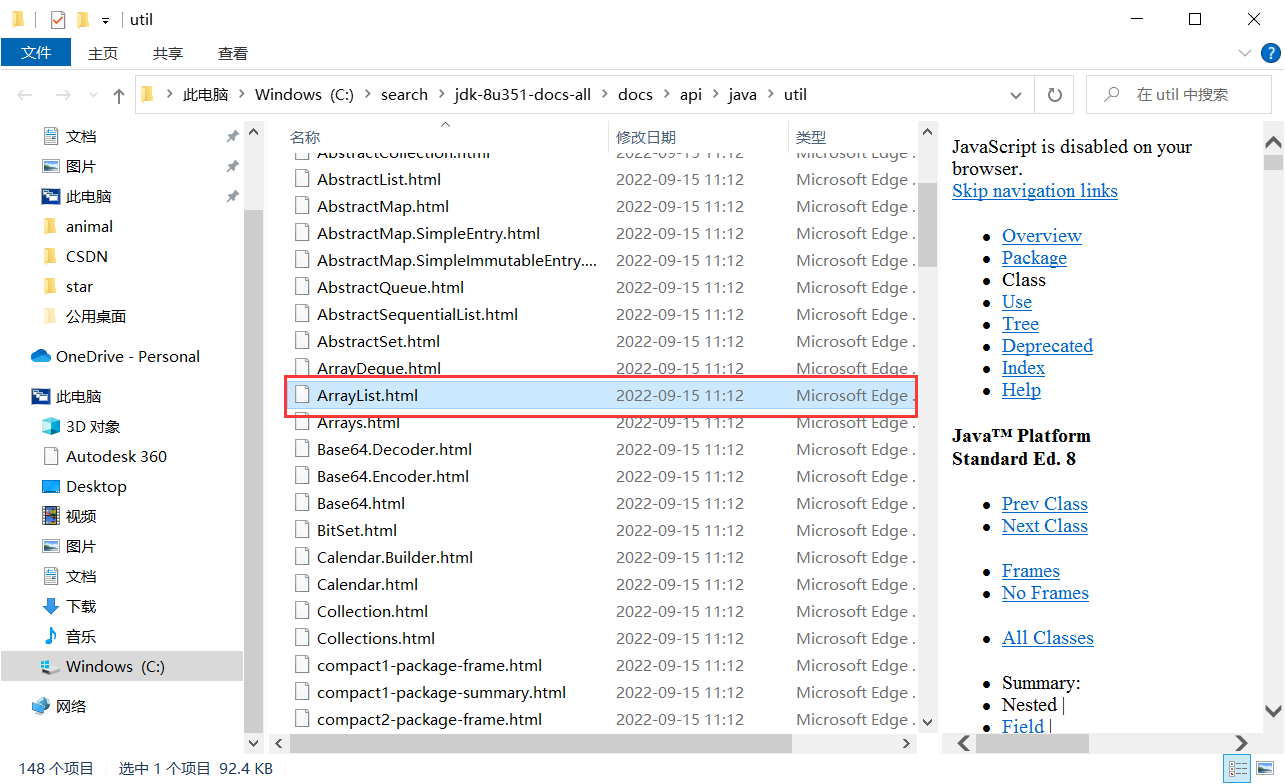
实现一个针对Java文档的搜索引擎。像百度,搜狗,bing等搜索引擎,都是属于“全站搜索”,即搜索整个互联网上所有的网站。还有一类搜索引擎,称为“站内搜索”,只针对某个网站内部的内容进行搜索。我们可以通过“爬虫”技术获取到一个网站的页面,但针对Java文档来说,我们有更简单的方案,直接从官网下载文档的压缩包。
我先将下载好的压缩包解压并放在C盘search目录下 , 如下图所示 :
2.2 项目模块划分
1.索引模块
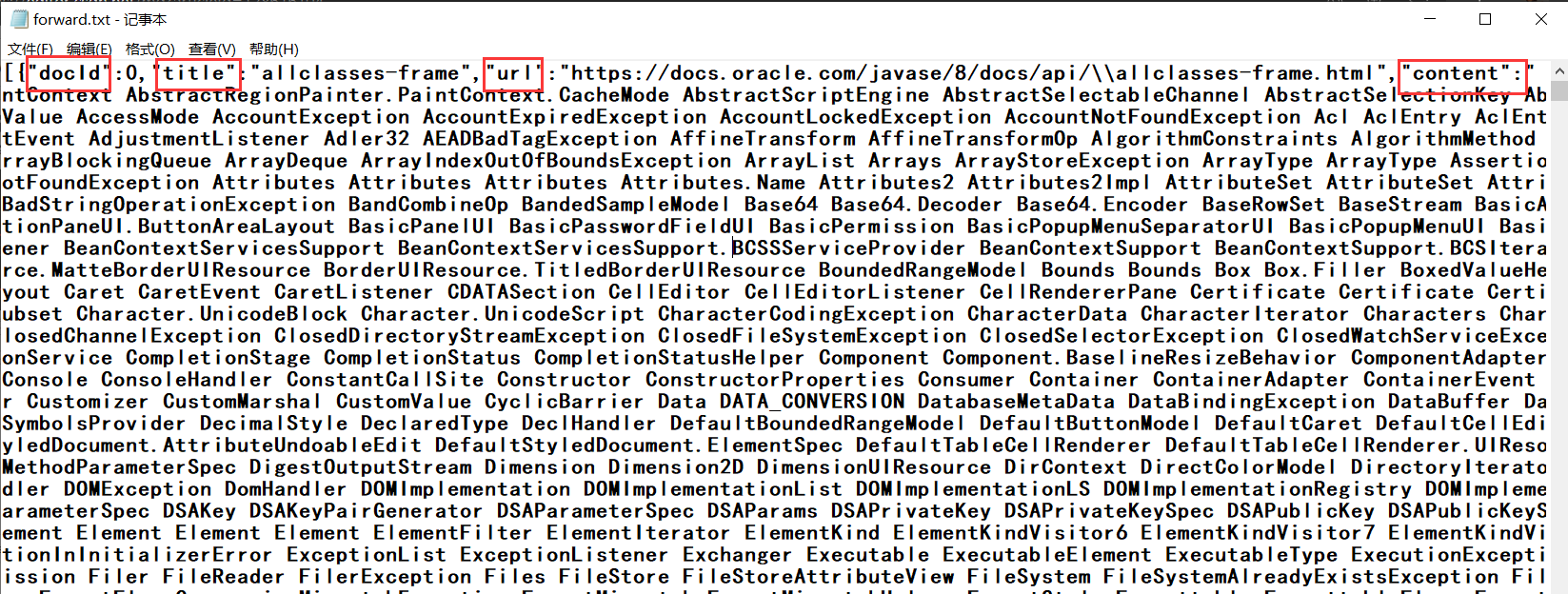
1)扫描下载到的文档。分析文档的内容 , 构建出正排索引+倒排索引 . 并且把索引内容保存到文件中 .
2)加载制作好的索引 . 并提供一些API实现查正排和查倒排这样的功能 .
2.搜索模块
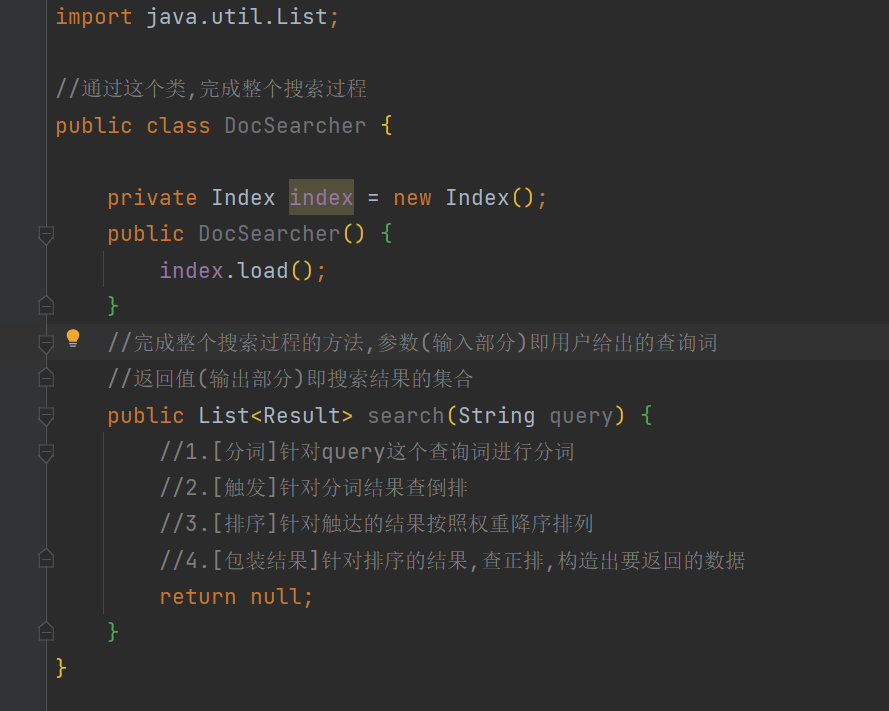
调用索引模块,实现一个搜索的完整过程 .
输入:用户的查询词;
输出:完整的搜索结果(包含了很多条记录,每个记录就有标题,描述,展示URL,并且点击能够跳转)。
3.web模块
需要实现一个简单的web程序,能够通过网页的形式来和用户进行交互。包含了前端和后端。
三 : 分词功能
用户在搜索引擎中输入的查询词很可能是一句话,那么此时就需要进行分词。
分词原理大体分为两种:
- 基于词库,尝试把所有的词都进行穷举,把穷举结果放到词典文件里,然后就可以依次取句子中的内容,每隔一个字,就在词典里查一下。
- 基于统计,收集到很多的“语料库”–>人工标注/直接统计,也就知道了哪些字在一起的概率比较大。
所谓分词的实现,属于“人工智能”的范畴。
Java中也有许多基于分词的第三方库,此处使用ansj。从maven中央仓库下载相关依赖到pom.xml中。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.ansj/ansj_seg -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ansj</groupId>
<artifactId>ansj_seg</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
测试分词功能:
import org.ansj.domain.Term;
import org.ansj.splitWord.analysis.ToAnalysis;
import java.util.List;
public class Testansj {
public static void main(String[] args) {
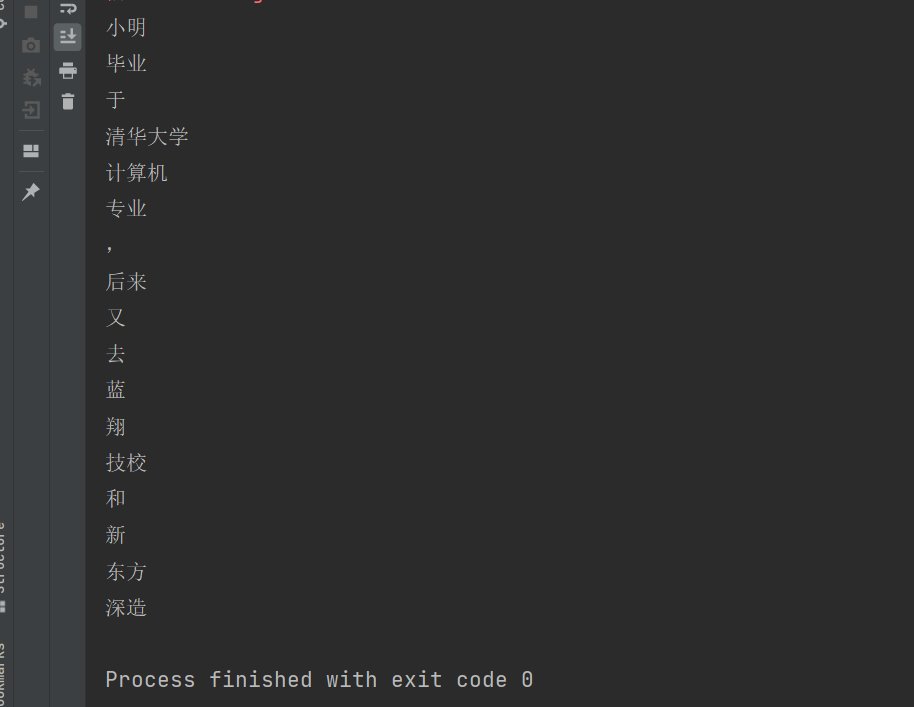
String str = "小明毕业于清华大学计算机专业,后来又去蓝翔技校和新东方深造";
//Term就表示一个分词结果
List<Term> terms = ToAnalysis.parse(str).getTerms();
for (Term t : terms) {
System.out.println(t.getName());
}
}
}
import org.ansj.domain.Term;
import org.ansj.splitWord.analysis.ToAnalysis;
import java.util.List;
public class Testansj {
public static void main(String[] args) {
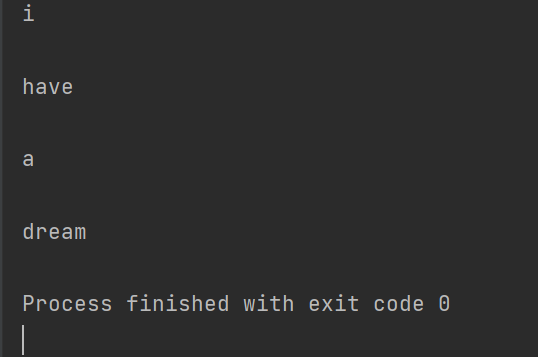
String str = "I have a dream";
//Term就表示一个分词结果
List<Term> terms = ToAnalysis.parse(str).getTerms();
for (Term t : terms) {
System.out.println(t.getName());
}
}
}
四 : 索引模块
4.1 目标
整个索引模块主要涉及Parser类和Index类 . Parser类主要负责解析文件 , Index类主要负责把在内存中构造好的索引数据结构,保存到指定的文件中 .
4.2 具体代码
Parser类
package com.example.demo.searcher;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class Parser {
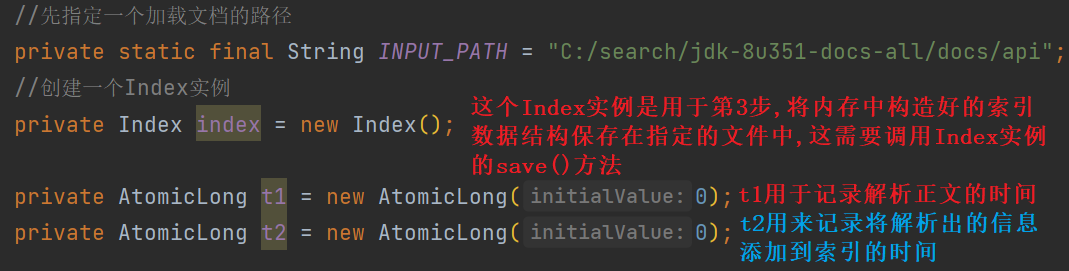
//先指定一个加载文档的路径
private static final String INPUT_PATH = "C:/search/jdk-8u351-docs-all/docs/api";
//创建一个Index实例
private Index index = new Index();
private AtomicLong t1 = new AtomicLong(0);
private AtomicLong t2 = new AtomicLong(0);
/**
* 实现单线程制作索引
* @throws IOException
*/
public void run() throws IOException {//整个Parser类的入口
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作开始!");
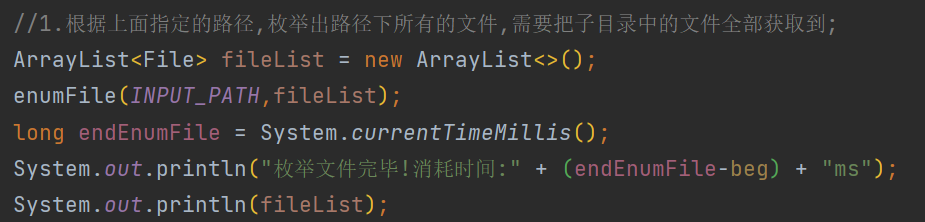
//1.根据上面指定的路径,枚举出路径下所有的文件,需要把子目录中的文件全部获取到
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
//fileList中已经得到所有以.html结尾的文件名
long endEnumFile = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("枚举文件完毕!消耗时间:" + (endEnumFile-beg) + "ms");
//展示输出部分文件名
if(25 <= fileList.size()) {
for (int i = 25; i >= 0; i++) {
System.out.println(fileList.get(i));
}
} else {
for (int i = fileList.size(); i >= 0; i++) {
System.out.println(fileList.get(i));
}
}
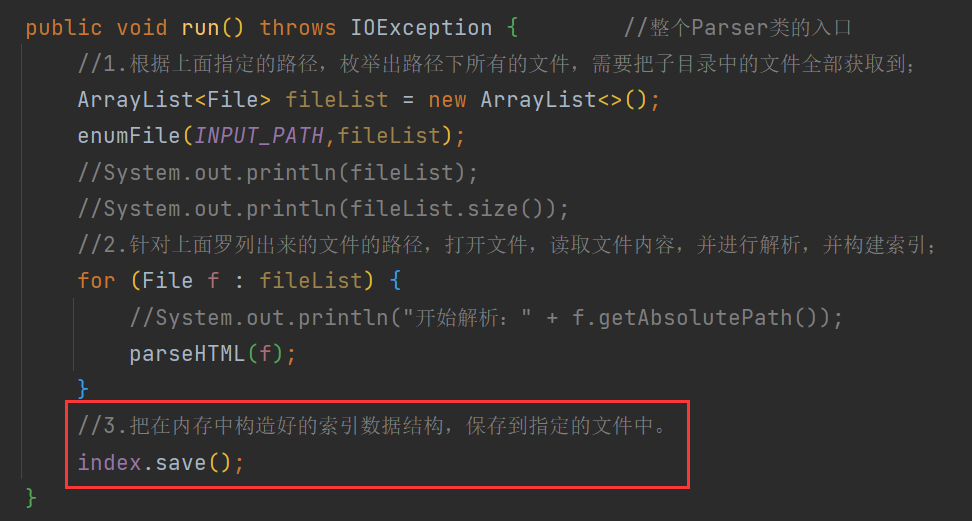
//2.针对上面罗列出来的文件的路径,打开文件,读取文件内容,并进行解析,并构建索引
for (File f : fileList) {
parseHTML(f);
}
long endFor = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("循环遍历文件并构建索引完毕!消耗时间:" + (endFor-endEnumFile) + "ms");
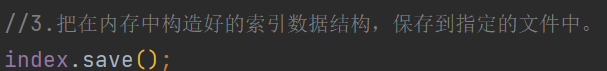
//3.把在内存中构造好的索引数据结构,保存到指定的文件中。
index.save();
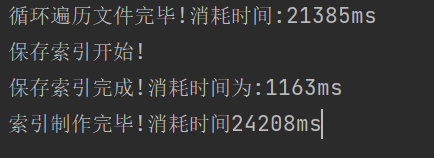
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作完毕!消耗时间" + (end-beg) + "ms");
}
/**
* 实现多线程制作索引
*/
public void runByThread() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作开始!");
//1.根据上面指定的路径,枚举出路径下所有的文件,需要把子目录中的文件全部获取到;
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
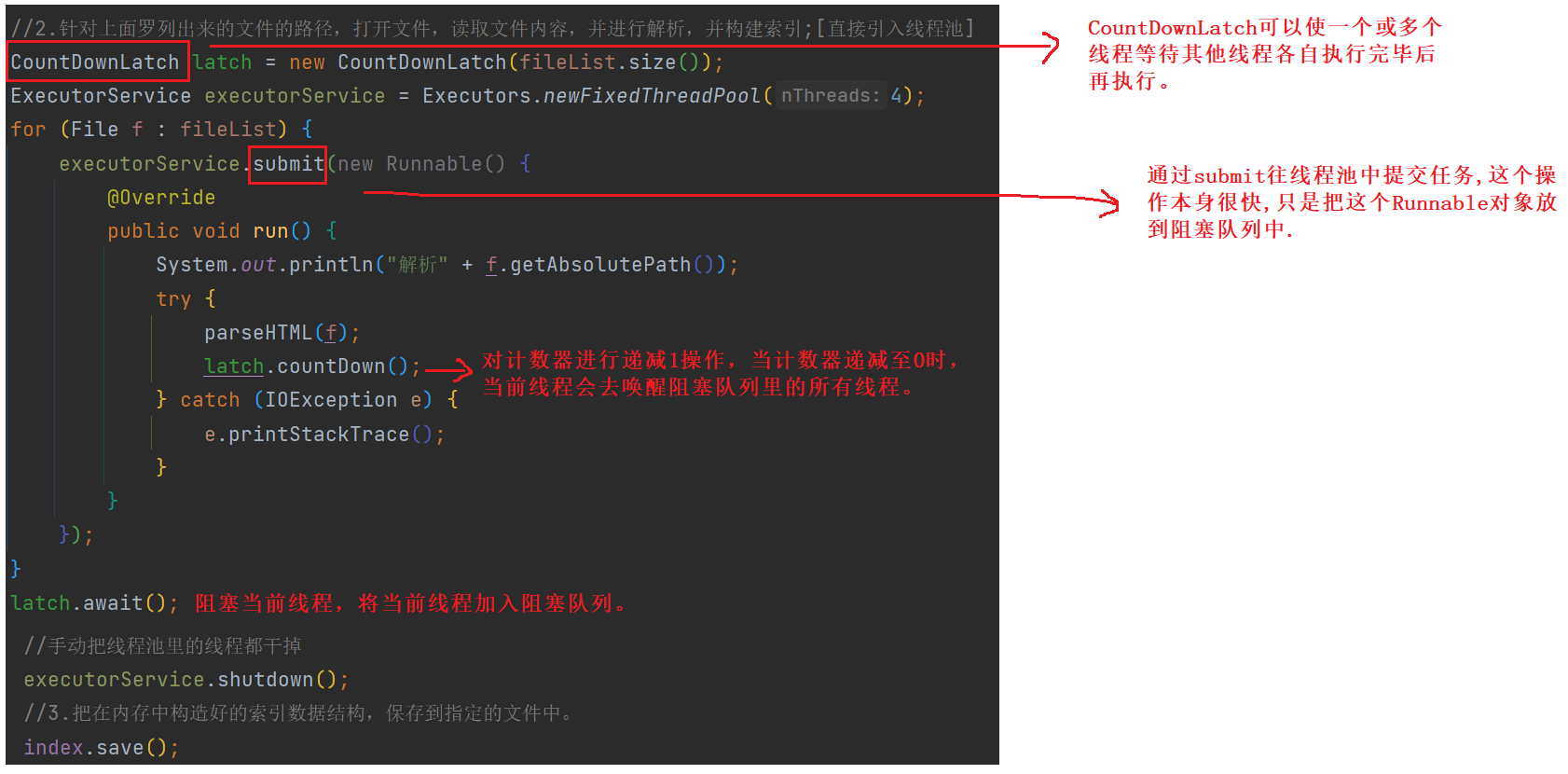
//2.针对上面罗列出来的文件的路径,打开文件,读取文件内容,并进行解析,并构建索引;[直接引入线程池]
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(fileList.size());
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
for (File f : fileList) {
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//System.out.println("解析" + f.getAbsolutePath());
try {
parseHTML(f);
latch.countDown();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
latch.await();
//手动把线程池里的线程都干掉
executorService.shutdown();
//3.把在内存中构造好的索引数据结构,保存到指定的文件中。
index.save();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作完毕!消耗时间" + (end-beg) + "ms");
System.out.println("解析正文的时间t1:" + t1 + " 将正文添加到索引的时间t2:" + t2);
}
//解析文件
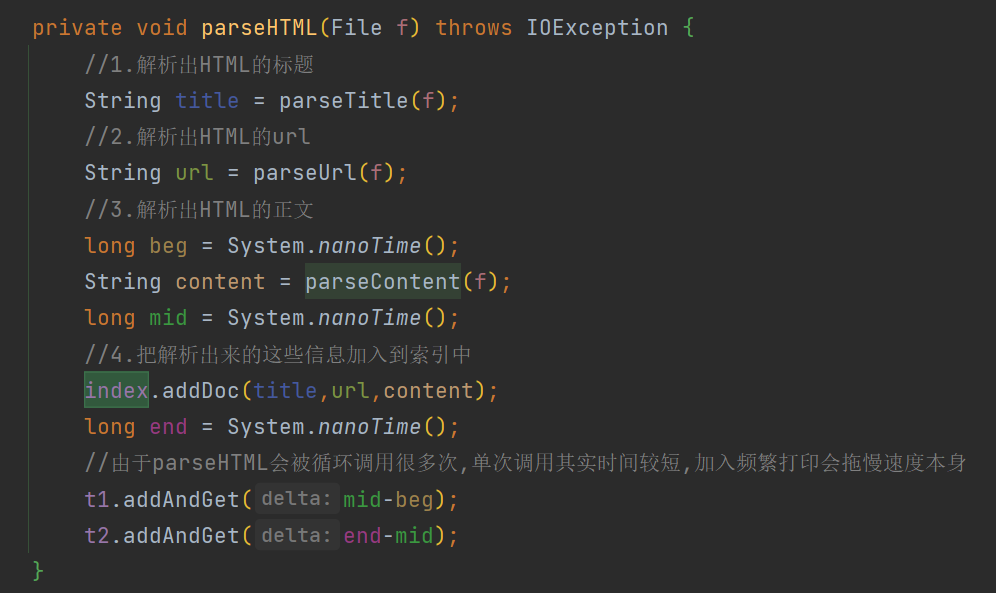
private void parseHTML(File f) throws IOException {
//1.解析出HTML的标题
String title = parseTitle(f);
//2.解析出HTML的url
String url = parseUrl(f);
//3.解析出HTML的正文
long beg = System.nanoTime();
String content = parseContentByRegex(f);
long mid = System.nanoTime();
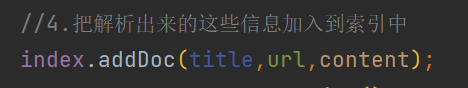
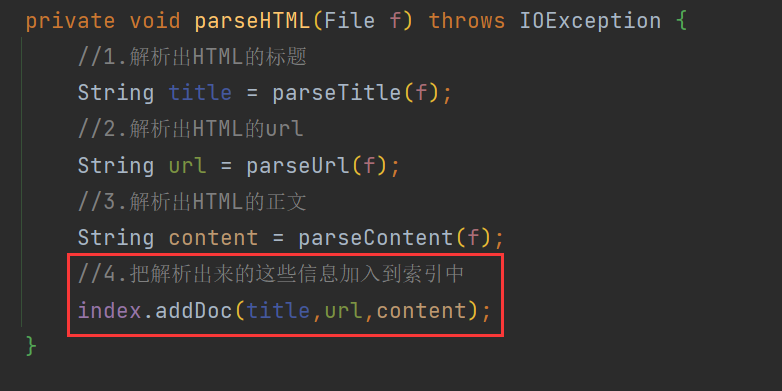
//4.把解析出来的这些信息加入到索引中
index.addDoc(title,url,content);
long end = System.nanoTime();
//由于parseHTML会被循环调用很多次,单次调用其实时间较短,加入频繁打印会拖慢速度本身
t1.addAndGet(mid-beg);
t2.addAndGet(end-mid);
}
//解析url
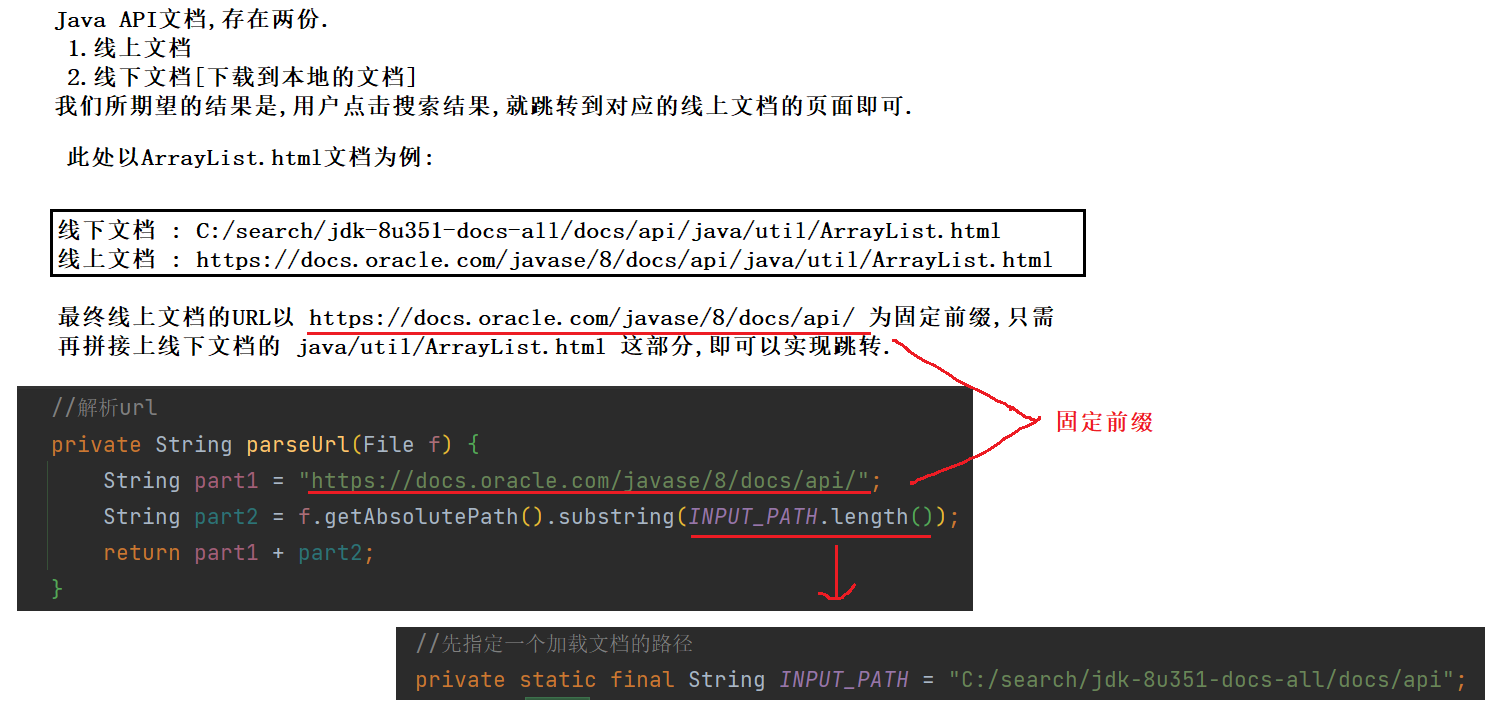
private String parseUrl(File f) {
String part1 = "https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/";
String part2 = f.getAbsolutePath().substring(INPUT_PATH.length());
return part1 + part2;
}
//解析标题
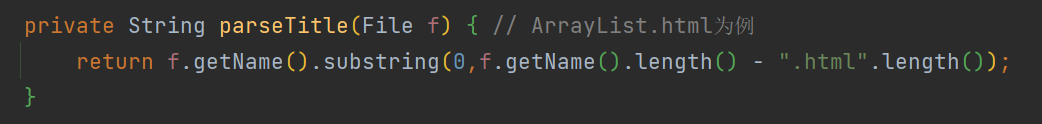
private String parseTitle(File f) { // ArrayList.html为例
return f.getName().substring(0,f.getName().length() - ".html".length());
}
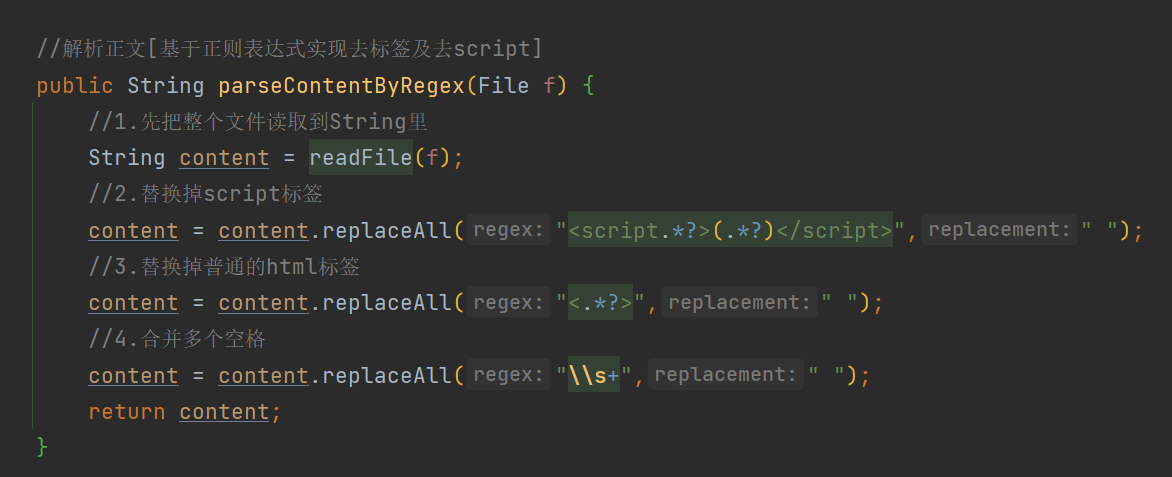
//解析正文[基于正则表达式实现去标签及去script]
public String parseContentByRegex(File f) {
//1.先把整个文件读取到String里
String content = readFile(f);
//2.替换掉script标签
content = content.replaceAll("<script.*?>(.*?)</script>"," ");
//3.替换掉普通的html标签
content = content.replaceAll("<.*?>"," ");
//4.合并多个空格
content = content.replaceAll("\\s+"," ");
return content;
}
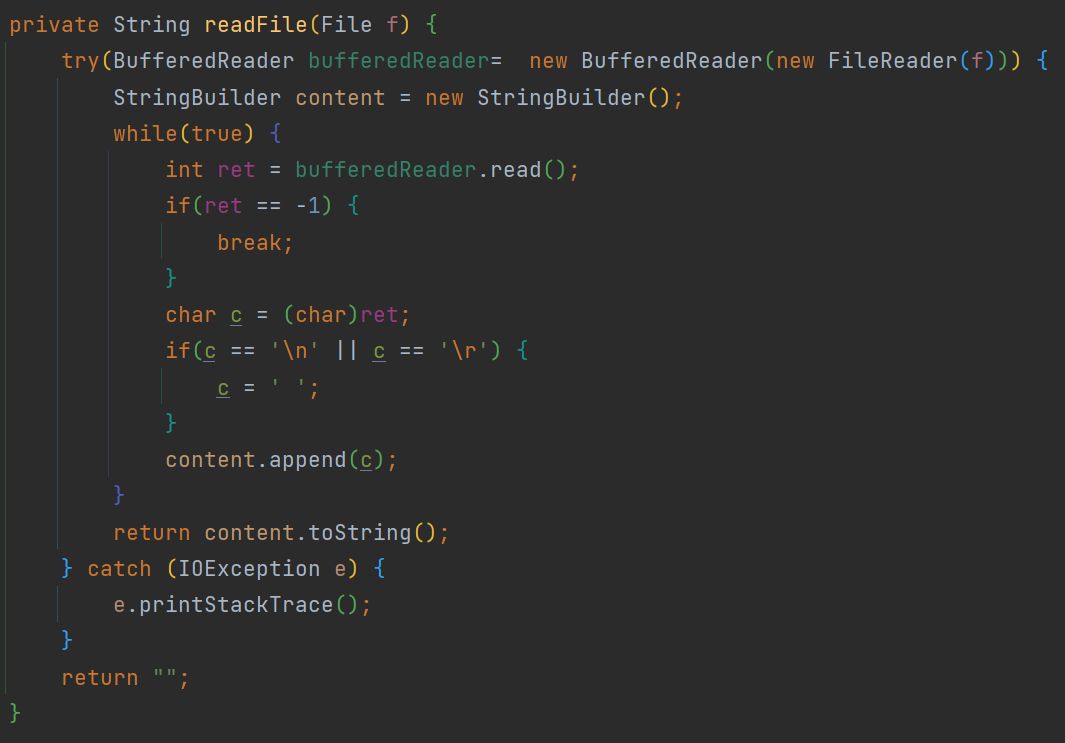
//把整个文件读取到String里
private String readFile(File f) {
try(BufferedReader bufferedReader= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f))) {
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
while(true) {
int ret = bufferedReader.read();
if(ret == -1) {
break;
}
char c = (char)ret;
if(c == '\n' || c == '\r') {// 将换行符解析为空格
c = ' ';
}
content.append(c);
}
return content.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
//获取路径下所有文件
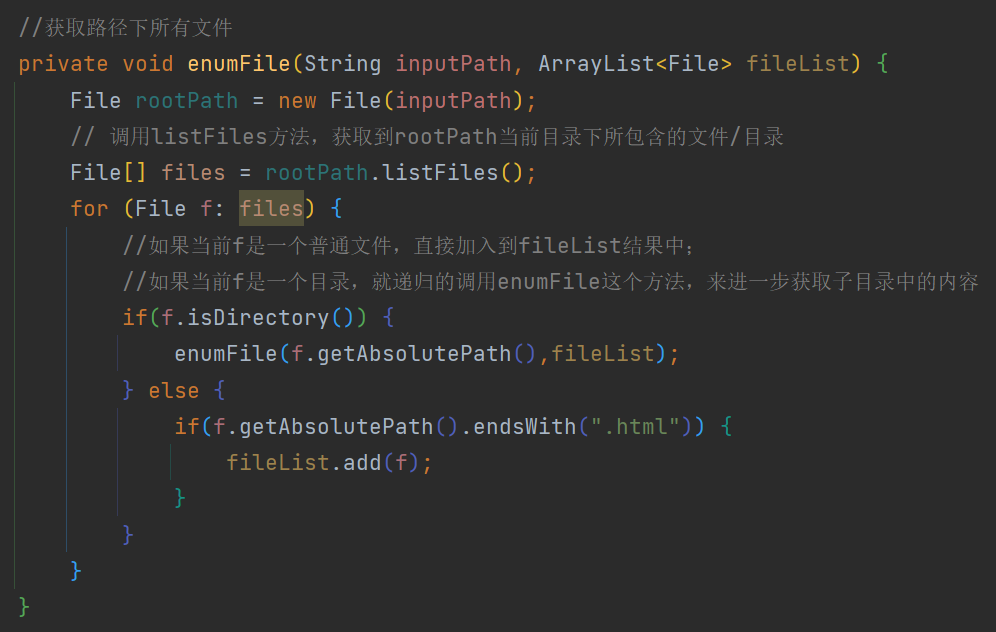
private void enumFile(String inputPath, ArrayList<File> fileList) {
File rootPath = new File(inputPath);
// 调用listFiles方法,获取到rootPath当前目录下所包含的文件/目录
File[] files = rootPath.listFiles();
for (File f: files) {
//如果当前f是一个普通文件且以.html结尾,直接加入到fileList结果中;
//如果当前f是一个目录,就递归的调用enumFile这个方法,来进一步获取子目录中的内容
if(f.isDirectory()) {
enumFile(f.getAbsolutePath(),fileList);
} else {
if(f.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".html")) {
fileList.add(f);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//通过main方法来实现整个制作索引的过程
Parser parser = new Parser();
//parser.run();
parser.runByThread();
}
}
Index类
package com.example.demo.searcher;
import com.example.demo.model.DocInfo;
import com.example.demo.model.Weight;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.ansj.domain.Term;
import org.ansj.splitWord.analysis.ToAnalysis;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 把在内存中构造好的索引数据结构,保存在文件中
*/
public class Index {
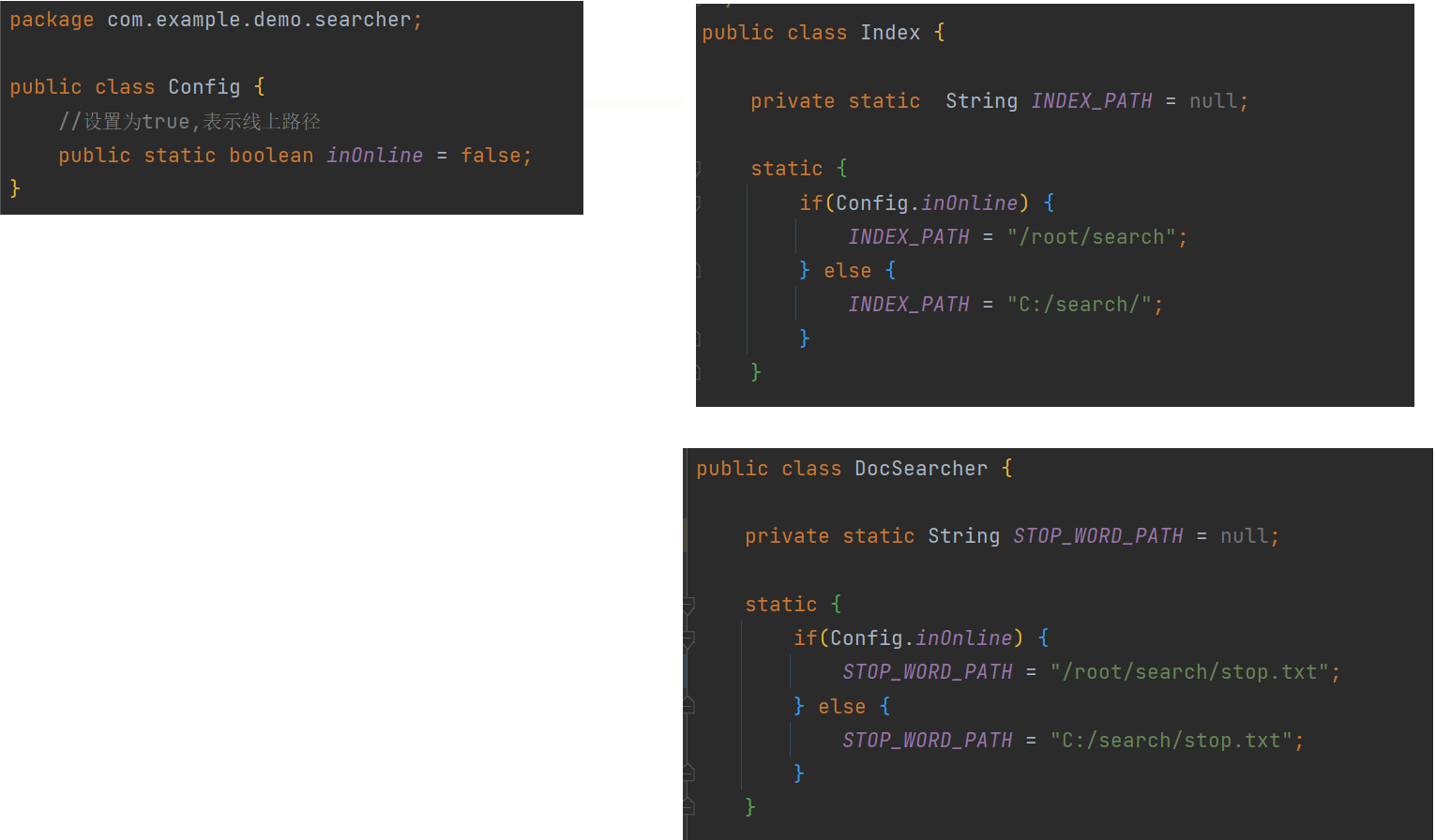
private static String INDEX_PATH = null;
static {
if(Config.inOnline) {
INDEX_PATH = "/root/search/";
} else {
INDEX_PATH = "C:/search/";
}
}
//将java对象和json对象相互转化
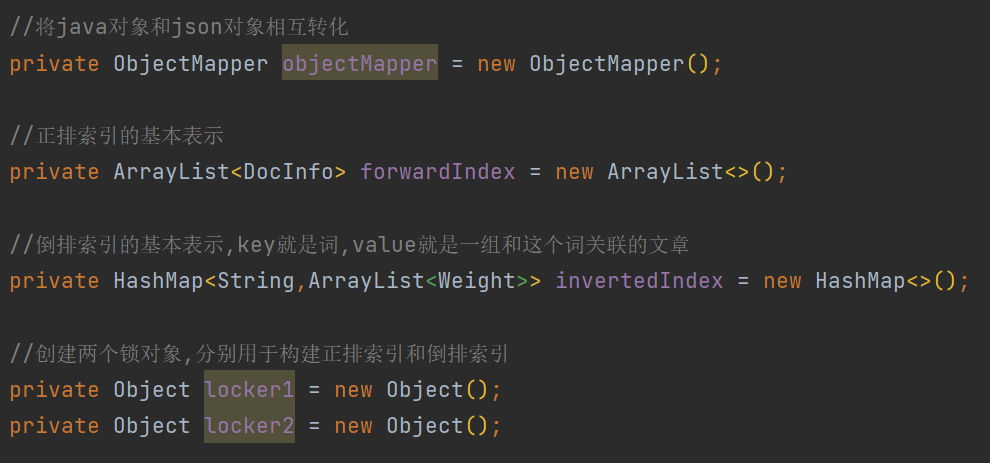
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//正排索引的基本表示
private ArrayList<DocInfo> forwardIndex = new ArrayList<>();
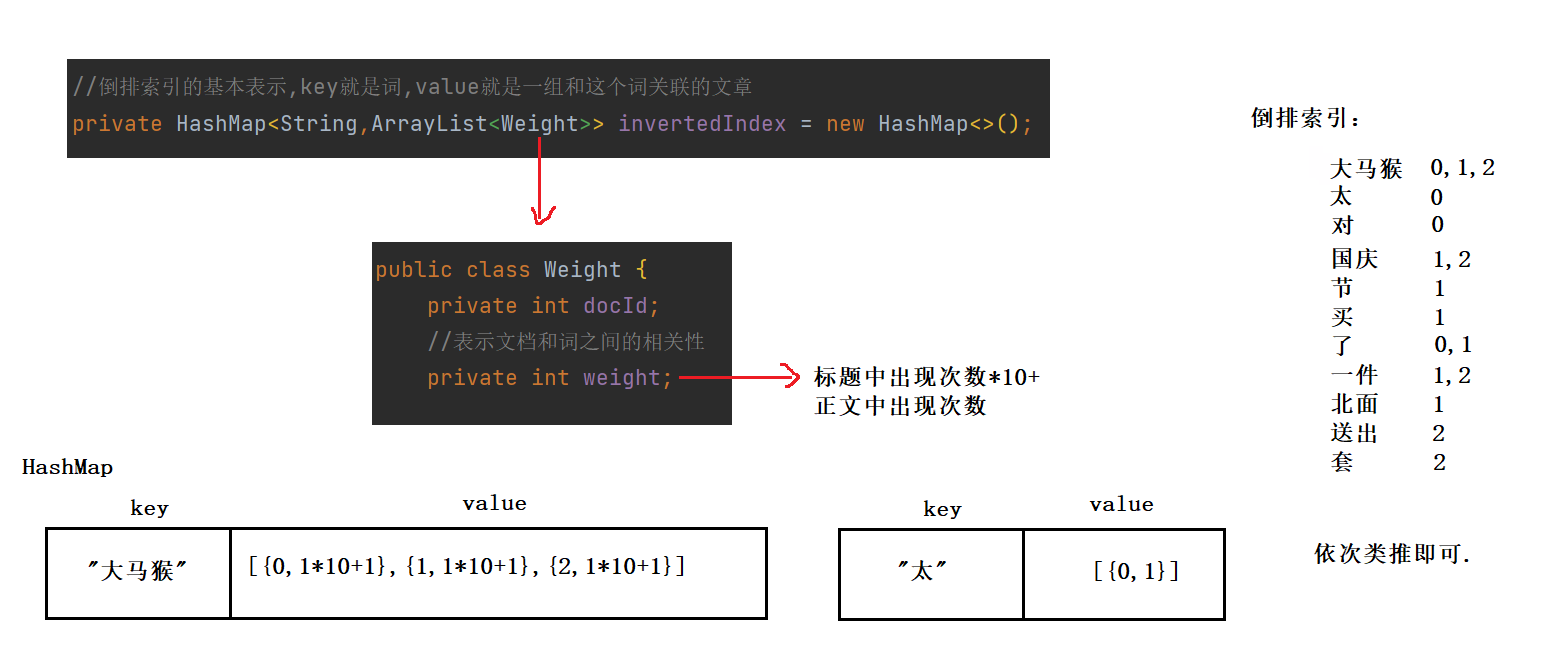
//倒排索引的基本表示,key就是词,value就是一组和这个词关联的文章
private HashMap<String,ArrayList<Weight>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();
//创建两个锁对象,分别用于构建正排索引和倒排索引
private Object locker1 = new Object();
private Object locker2 = new Object();
//1.给定一个docId,在正排索引中查询文档的详细信息
public DocInfo getDocInfo(int docId){
return forwardIndex.get(docId);
}
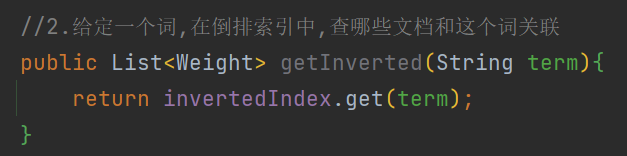
//2.给定一个词,在倒排索引中,查哪些文档和这个词关联
public List<Weight> getInverted(String term){
return invertedIndex.get(term);
}
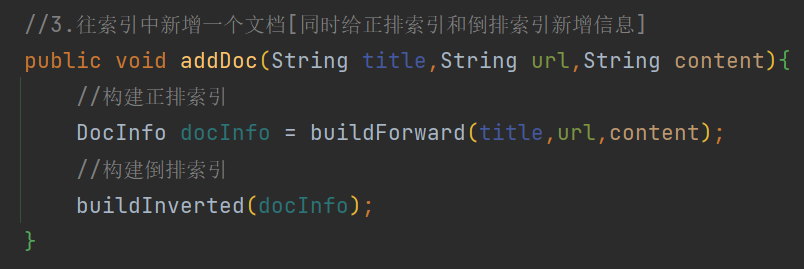
//3.往索引中新增一个文档[同时给正排索引和倒排索引新增信息]
public void addDoc(String title,String url,String content){
//构建正排索引
DocInfo docInfo = buildForward(title,url,content);
//构建倒排索引
buildInverted(docInfo);
}
//构建倒排索引
private void buildInverted(DocInfo docInfo) {
class WordCnt{
public int titleCount;
public int contentCount;
}
HashMap<String,WordCnt> wordCountHashMap = new HashMap<>();
//1.针对文档标题进行分词
List<Term> terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getTitle()).getTerms();
//2.遍历分词结果,统计每词出现的次数
for (Term term : terms) {
String word = term.getName();
WordCnt wordCnt = wordCountHashMap.get(word);
if(wordCnt == null) {
WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();
newWordCnt.contentCount = 0;
newWordCnt.titleCount = 1;
wordCountHashMap.put(word,newWordCnt);
} else {
wordCnt.titleCount += 1;
}
}
//3.针对正文进行分词
terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getContent()).getTerms();
//4.统计每词出现的次数
for (Term term : terms) {
String word = term.getName();
WordCnt wordCnt = wordCountHashMap.get(word);
if(wordCnt == null) {
WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();
newWordCnt.titleCount = 0;
newWordCnt.contentCount = 1;
wordCountHashMap.put(word,newWordCnt);
} else {
wordCnt.contentCount += 1;
}
}
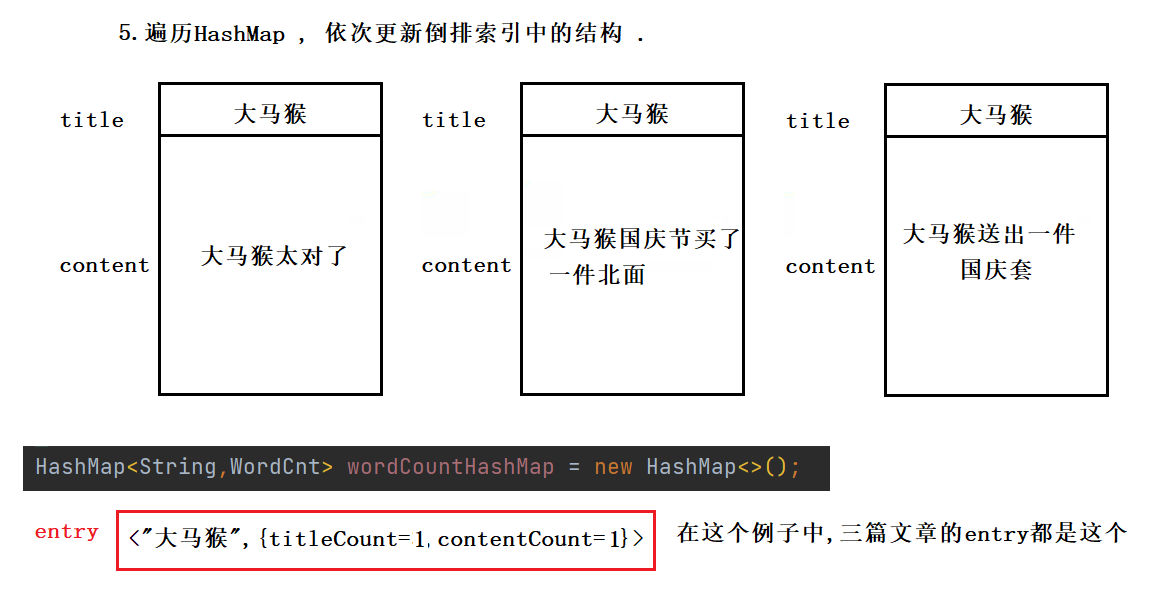
//5.遍历HashMap,依次更新倒排索引中的结构
//[最终文档的权重:设置成标题中出现的次数 * 10 + 正文中出现的次数]
synchronized (locker1) {
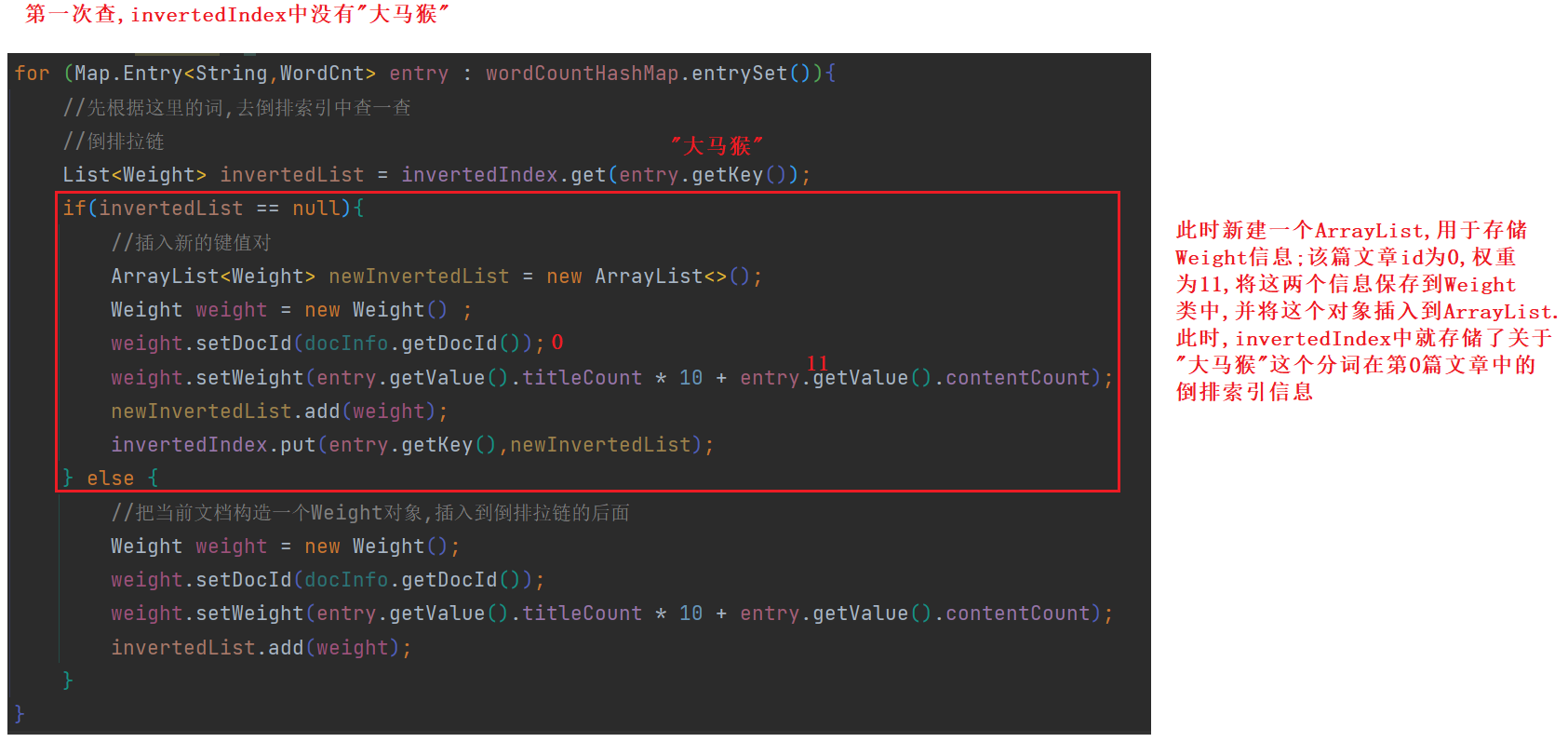
for (Map.Entry<String,WordCnt> entry : wordCountHashMap.entrySet()){
//先根据这里的词,去倒排索引中查一查
//倒排拉链
List<Weight> invertedList = invertedIndex.get(entry.getKey());
if(invertedList == null){
//插入新的键值对
ArrayList<Weight> newInvertedList = new ArrayList<>();
Weight weight = new Weight() ;
weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());
weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount * 10 + entry.getValue().contentCount);
newInvertedList.add(weight);
invertedIndex.put(entry.getKey(),newInvertedList);
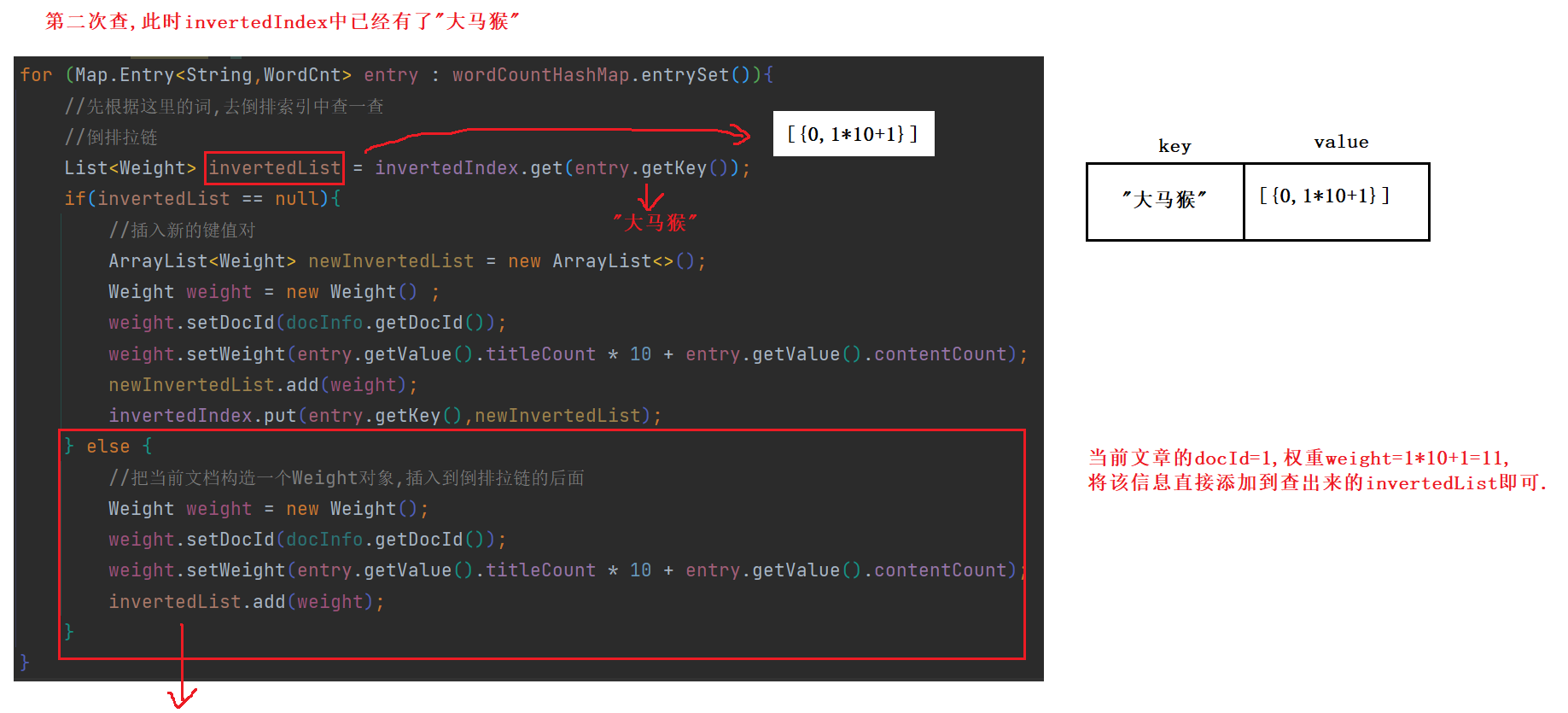
} else {
//把当前文档构造一个Weight对象,插入到倒排拉链的后面
Weight weight = new Weight();
weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());
weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount * 10 + entry.getValue().contentCount);
invertedList.add(weight);
}
}
}
}
//构建正排索引
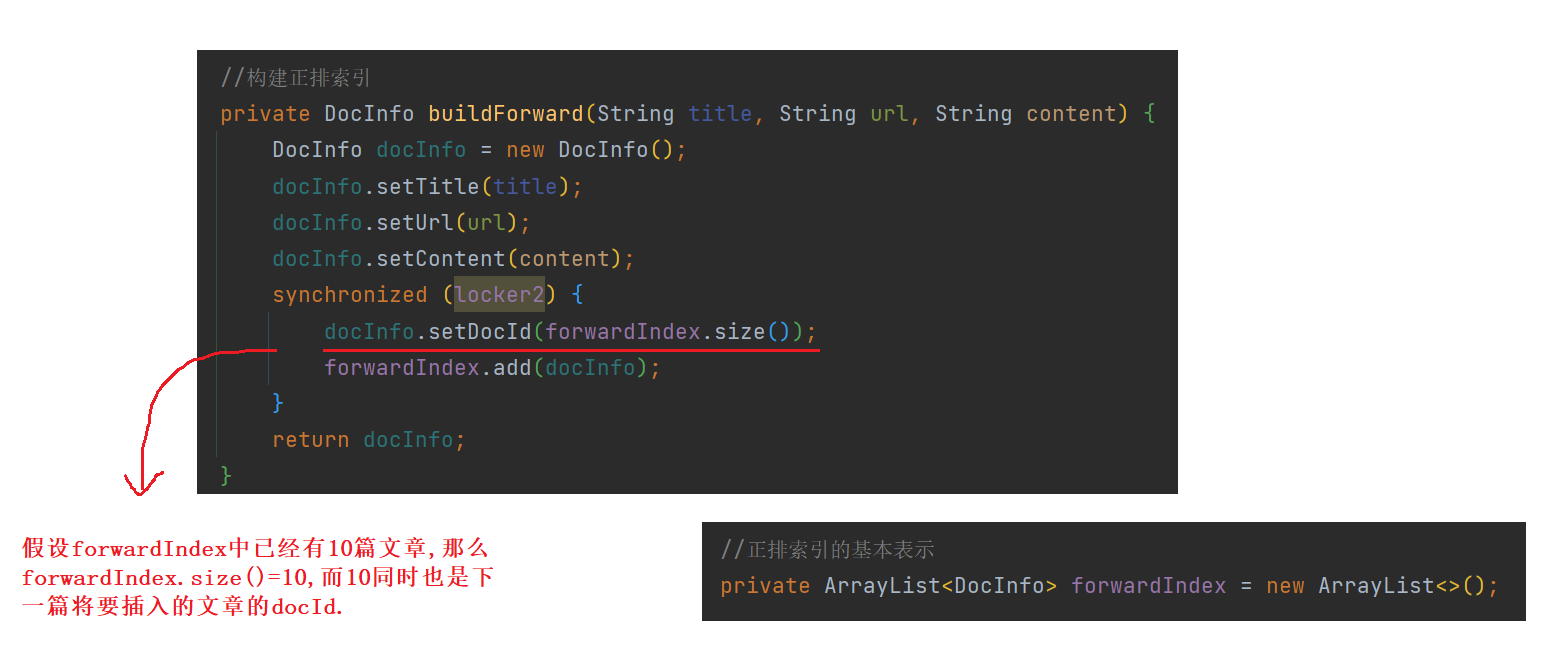
private DocInfo buildForward(String title, String url, String content) {
DocInfo docInfo = new DocInfo();
docInfo.setTitle(title);
docInfo.setUrl(url);
docInfo.setContent(content);
synchronized (locker2) {
docInfo.setDocId(forwardIndex.size());// docInfo从0开始
forwardIndex.add(docInfo);
}
return docInfo;
}
//4.把内存中的索引结构保存到磁盘中
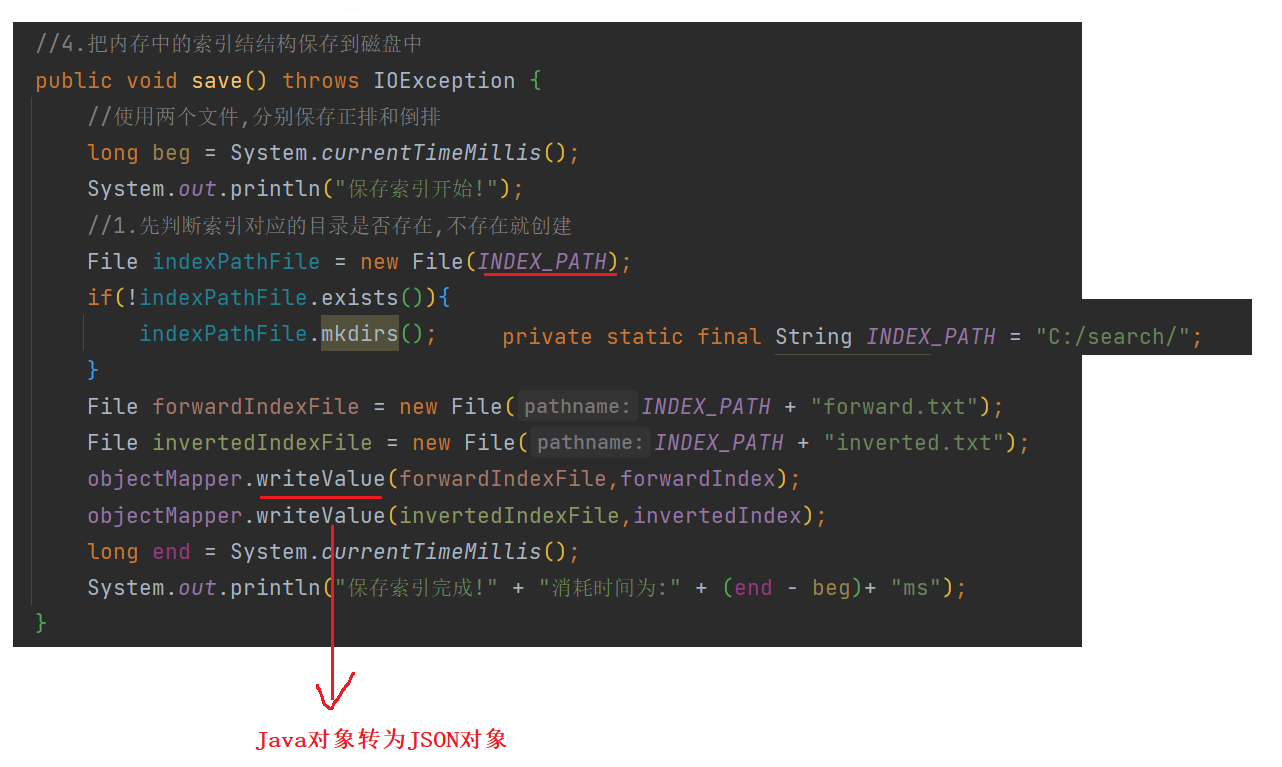
public void save() throws IOException {
//使用两个文件,分别保存正排和倒排
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("保存索引开始!");
//1.先判断索引对应的目录是否存在,不存在就创建
File indexPathFile = new File(INDEX_PATH);
if(!indexPathFile.exists()){
indexPathFile.mkdirs();
}
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "inverted.txt");
objectMapper.writeValue(forwardIndexFile,forwardIndex);
objectMapper.writeValue(invertedIndexFile,invertedIndex);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("保存索引完成!" + "消耗时间为:" + (end - beg)+ "ms");
}
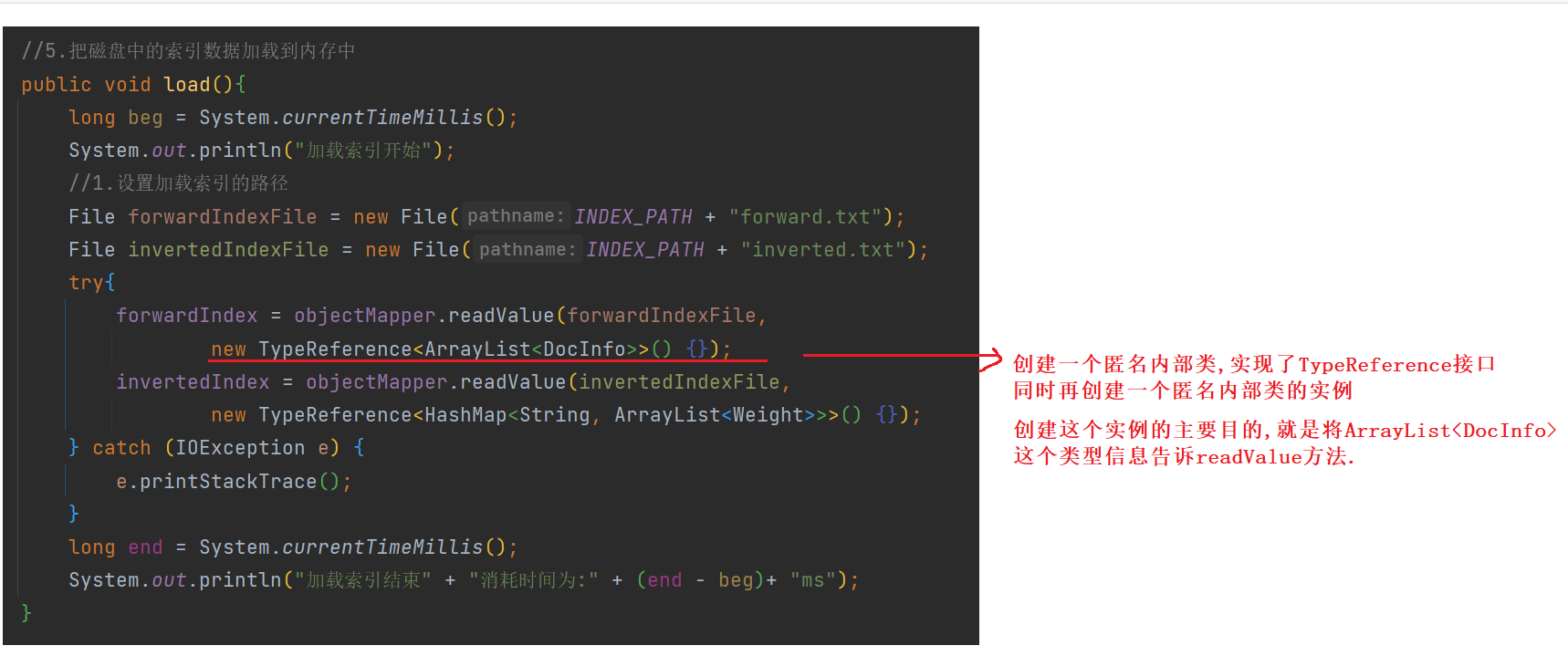
//5.把磁盘中的索引数据加载到内存中
public void load(){
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("加载索引开始");
//1.设置加载索引的路径
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "inverted.txt");
try{
forwardIndex = objectMapper.readValue(forwardIndexFile,
new TypeReference<ArrayList<DocInfo>>() {});
invertedIndex = objectMapper.readValue(invertedIndexFile,
new TypeReference<HashMap<String, ArrayList<Weight>>>() {});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("加载索引结束" + "消耗时间为:" + (end - beg)+ "ms");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Index index = new Index();
index.load();
System.out.println("索引加载完成!");
}
}
4.3 分步骤解析
Parser类
1 前置工作
2 获取路径下所有文件
3 开始解析
在解析过程中, 最开始为追求代码和逻辑的简洁性 , 使用了单线程的方式 , 直接进行for循环遍历每一个文件并进行解析 :
3.1 解析title
以ArrayList.html为例 , 其标题只需在文件名中截取.html之前的部分即可 . 代码如下所示 :
3.2 解析url
3.3 解析content
解析正文 , 本质上是去除HTML标签 , 以及script标签所包裹的内容 , 这些内容是js代码 , 不应该包含在正文部分 .
3.4 把解析出来的这些信息加入到索引中
到这里直接调用index中的addDoc方法 , 即可实现把解析出来的这些信息加入到索引中 . 关于Index类 , 后面详细介绍 .
4 将构造好的索引数据结构保存在文件中
要实现上面的功能 , 就不得不提到索引模块的另一大核心类 —>Index类 !
Index类
该类的主要功能如下 :
1.前置工作
正排和倒排的数据结构分别设计如下 :
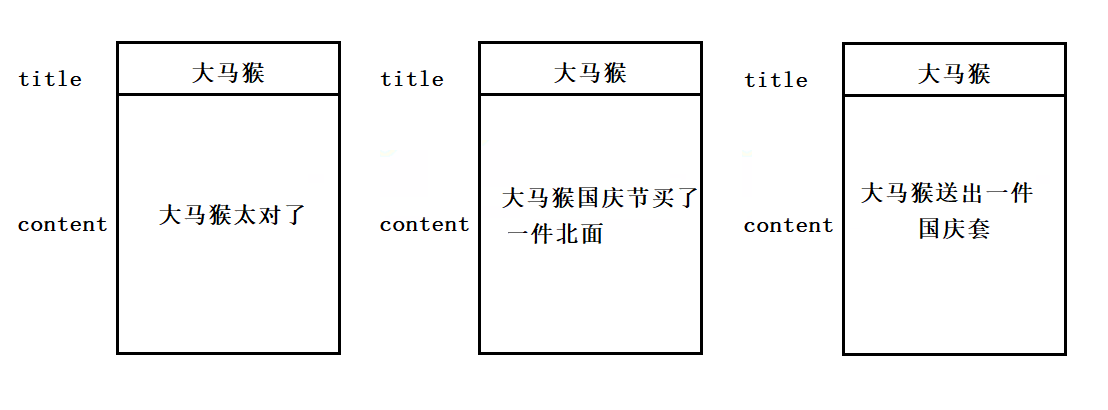
以这三篇文章为例 :
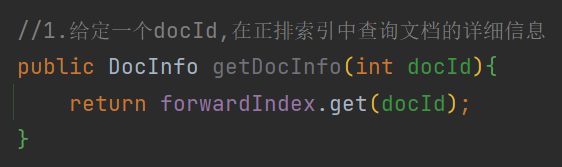
2 查正排
因为我们在存放正排索引时 , 已经将文章按照顺序保存在ArrayList中 , 所以可以直接根据get(i)方法获取到文章信息 .
3 查倒排
直接通过key获取value , 返回Weight数组 , 每个Weight存放该词所在的文章及在这篇文章中的权重(或者说与这篇文章的关联性) .
4 添加文档
4.1 构建正排索引
4.2 构建倒排索引
1.定义WordCnt类 , 统计每一个词在标题和正文中分别出现的次数 ;
2.针对文档标题进行分词 ;
3.遍历分词结果 , 统计每词出现的次数 ;
4.针对文档正文进行分词 ;
5.遍历分词结果 , 统计每词出现的次数 ;
5.遍历HashMap , 依次更新倒排索引中的结构 .
以"大马猴"为例 , 它在三篇文章的标题和正文中都出现过 . 第5步如下 :
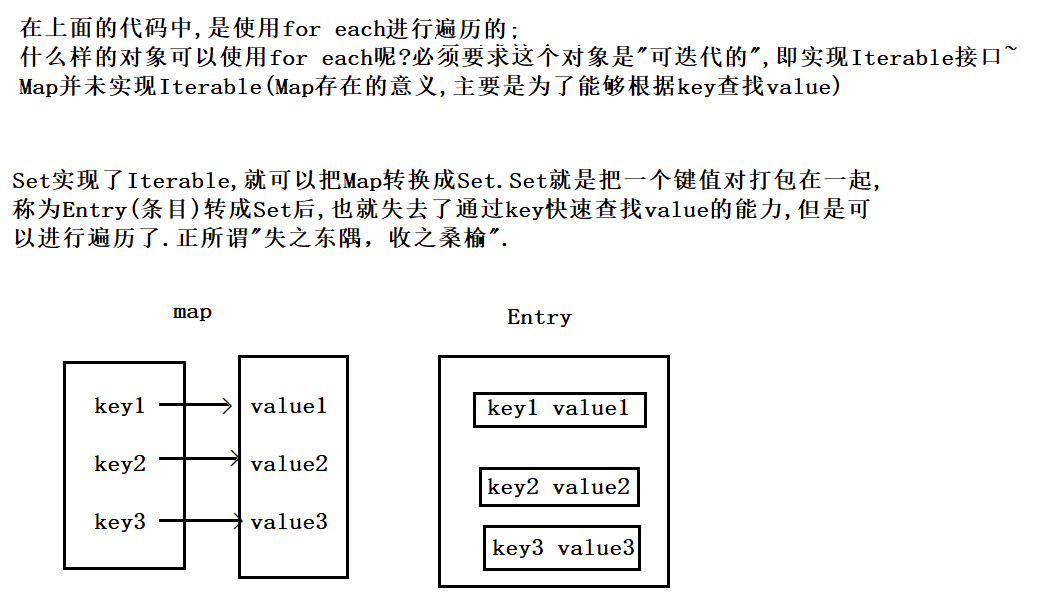
Q : 此处为什么使用entry这样的结构 ?
A :
5 保存索引
6 加载索引
4.4 检验成果
4.4.1 验证索引制作
在Parser中有两处调用了index :
运行结果 :
正排索引 :
倒排索引 :
4.4.2 性能优化
要想优化一段程序的性能 , 先需要通过测试的手段 , 找到其中的"性能瓶颈" .
通过刚才的测试 , 我们发现当前主要的性能瓶颈就在循环遍历文件上 . 每次循环都要针对一个文件进行解析 , 即读文件 + 分词 + 解析内容 (这里主要还是卡在CPU运算上) . 在单线程环境下 , 这些任务都是串行执行的 ; 多个线程 , 这些任务就可以并发执行了 .
4.4.3 实现多线程制作索引
/**
* 实现多线程制作索引
*/
public void runByThread() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作开始!");
//1.根据上面指定的路径,枚举出路径下所有的文件,需要把子目录中的文件全部获取到;
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
//2.针对上面罗列出来的文件的路径,打开文件,读取文件内容,并进行解析,并构建索引;[直接引入线程池]
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(fileList.size());
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
for (File f : fileList) {
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//System.out.println("解析" + f.getAbsolutePath());
try {
parseHTML(f);
latch.countDown();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
latch.await();
//手动把线程池里的线程都干掉
executorService.shutdown();
//3.把在内存中构造好的索引数据结构,保存到指定的文件中。
index.save();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作完毕!消耗时间" + (end-beg) + "ms");
}
验证多线程的效果 :
五 : 搜索模块
调用索引模块,来完成搜索的核心过程.
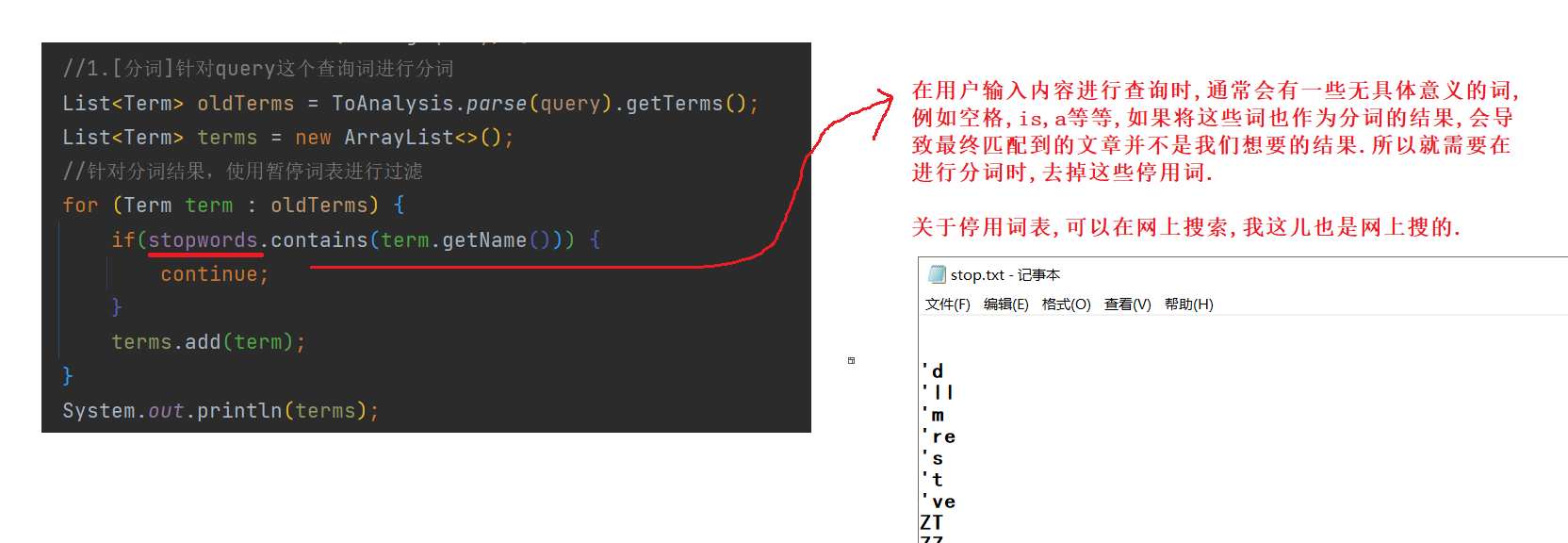
5.1 分词
针对用户输入的查询词进行分词(用户输入的查询词 , 可能是一个词 , 也可能是一句话)
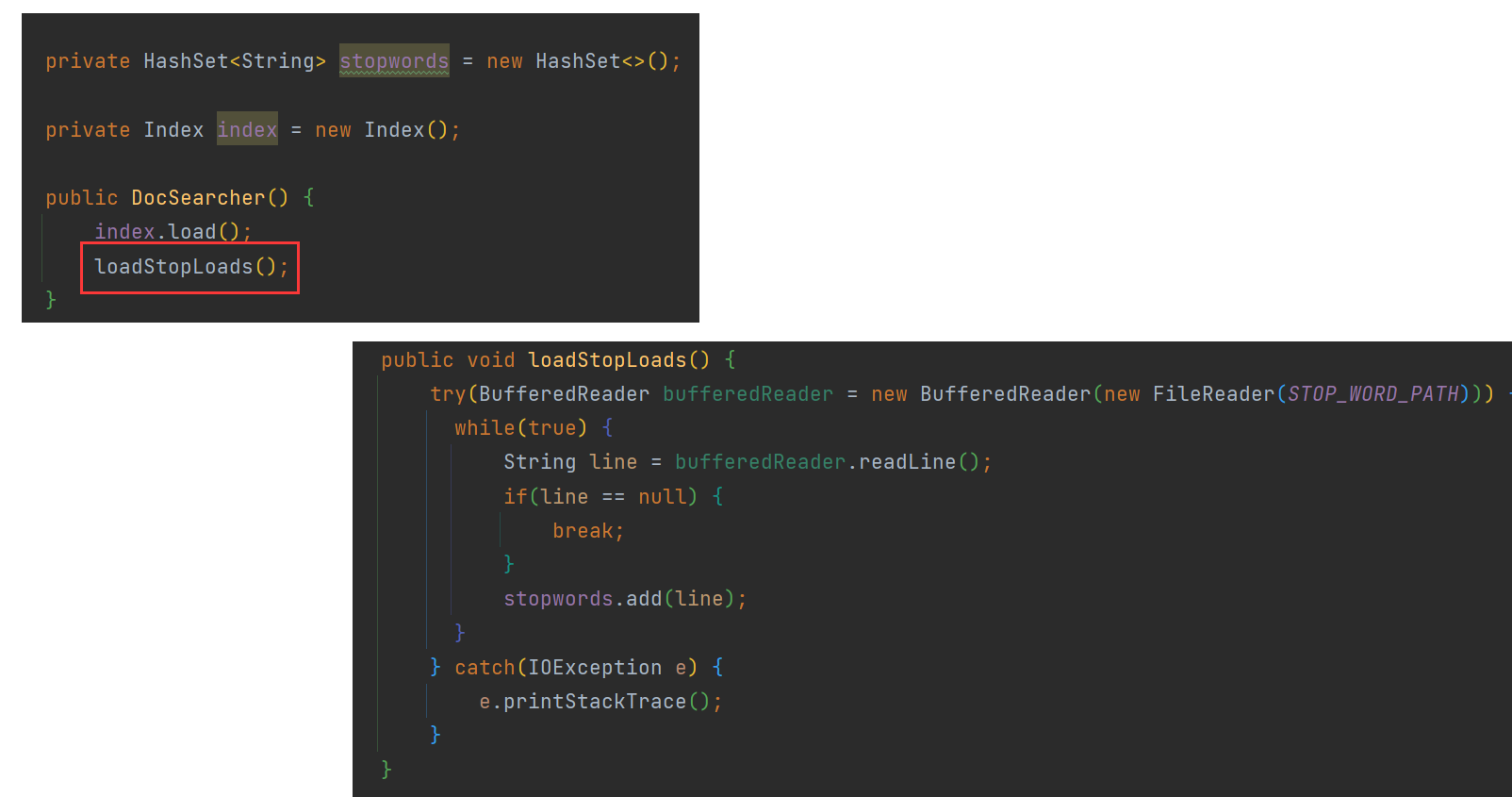
停用词可以在构造方法中进行加载 :
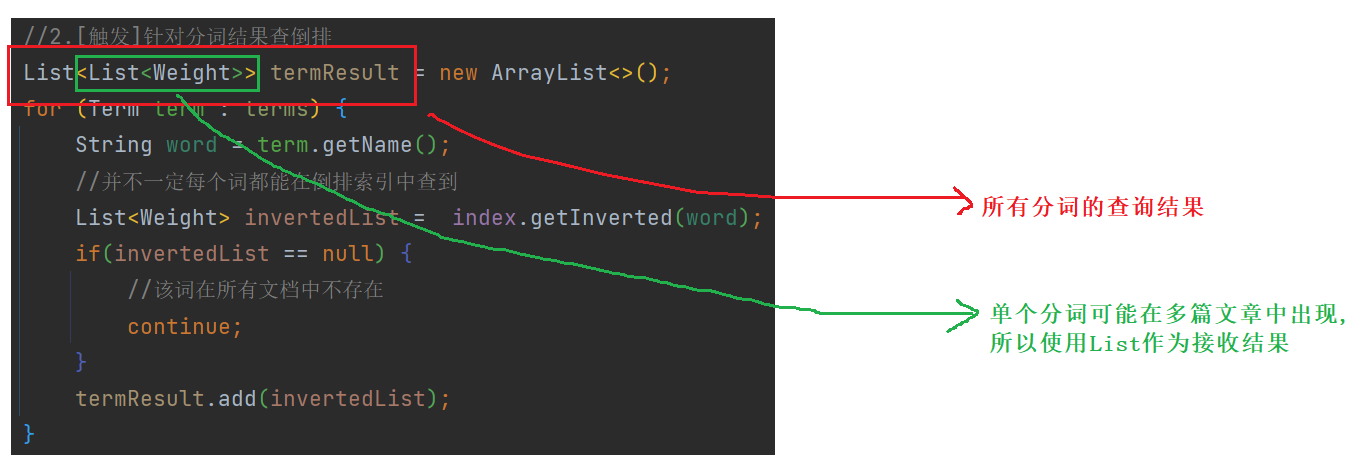
5.2 触发
拿着分词结果 , 查倒排索引 , 找到具有相关性的文档 .
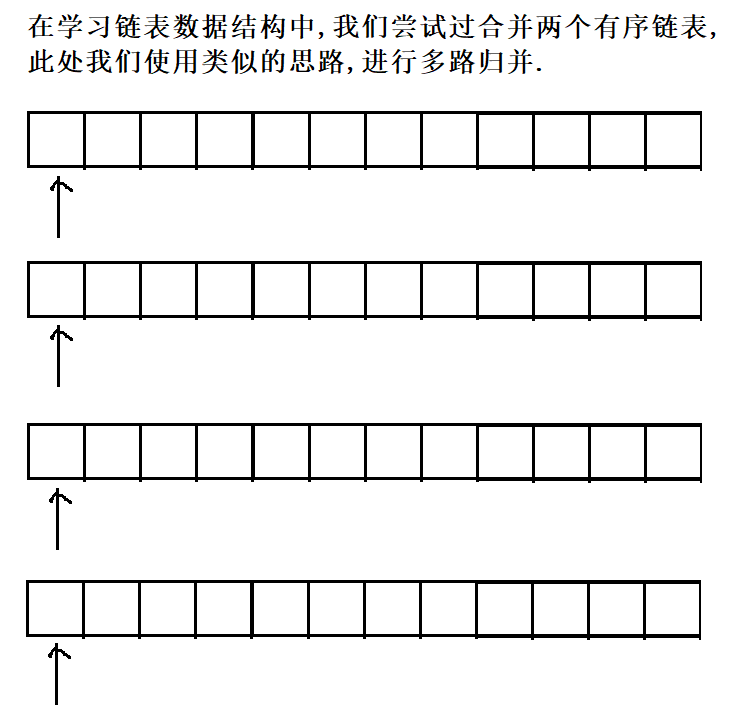
5.3 合并
//描述一个元素在二维数组中的位置
static class Pos {
public int row;
public int col;
public Pos(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
//合并权重
private List<Weight> mergeResult(List<List<Weight>> source) {
//是把多个行合并成一行,确定二维数组中的一个元素,需要行和列
//1.针对每一行,进行排序(按照id进行升序排序)
for (List<Weight> curRow : source) {
curRow.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() {
@Override
public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {
return o1.getDocId() - o2.getDocId();
}
});
}
//2.借助优先级队列,针对这些"行"进行合并
List<Weight> target = new ArrayList<>();// 表示合并结果
// 2.1创建优先级队列并按照Weight的docId,取小的优先
PriorityQueue<Pos> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Pos>() {
@Override
public int compare(Pos o1, Pos o2) {
Weight w1 = source.get(o1.row).get(o1.col);
Weight w2 = source.get(o2.row).get(o2.col);
return w1.getDocId() - w2.getDocId();
}
});
// 2.2初始化队列,把每行的第一个元素放到队列中
for (int row = 0; row < source.size(); row++) {
queue.offer(new Pos(row,0));// 初始插入的元素的列就是0
}
// 2.3循环取队元素,也就是当前若干行中最小的元素
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pos minPos = queue.poll();
Weight curWeight = source.get(minPos.row).get(minPos.col);
// 2.4看这个Weight是否和前一个插入到target的结果的docId相同
if(target.size() > 0) {
Weight lastWeight = target.get(target.size()-1);
if(lastWeight.getDocId() == curWeight.getDocId()) {
lastWeight.setWeight(lastWeight.getWeight() + curWeight.getWeight());
} else {
target.add(curWeight);
}
} else {// target当前为空,直接插入
target.add(curWeight);
}
// 2.5把对应这个元素的光标后移,取下一个元素
Pos newPos = new Pos(minPos.row, minPos.col+1);
if(newPos.col >= source.get(newPos.row).size()) {// 移动光标后,超出了这一行的列数
continue;
}
queue.offer(newPos);
}
return target;
}
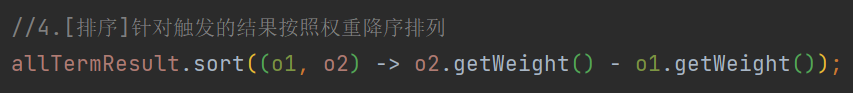
5.4 排序
排序很简单 , 权重高的排前面 , 在进行页面展示时 , 位置靠前 .
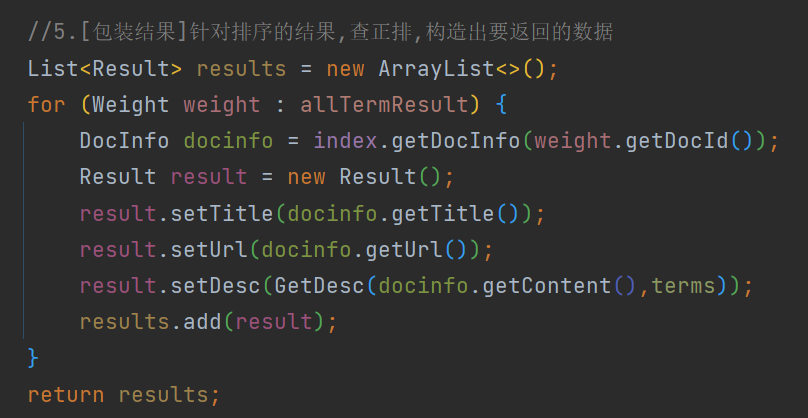
5.5 包装结果
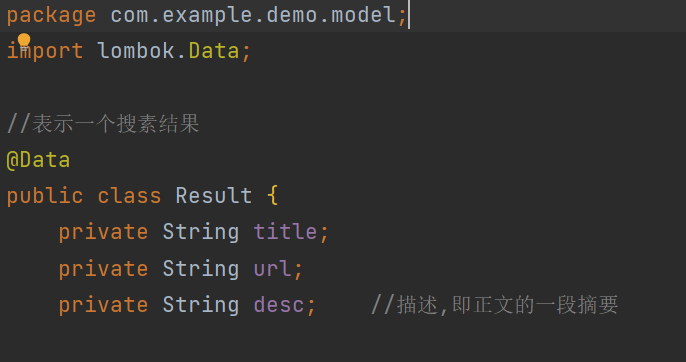
最终展示时 , 需要得到页面的id , url , 摘要 , 所以需要根据排序结果再查正排 , 构造出要返回的数据 .
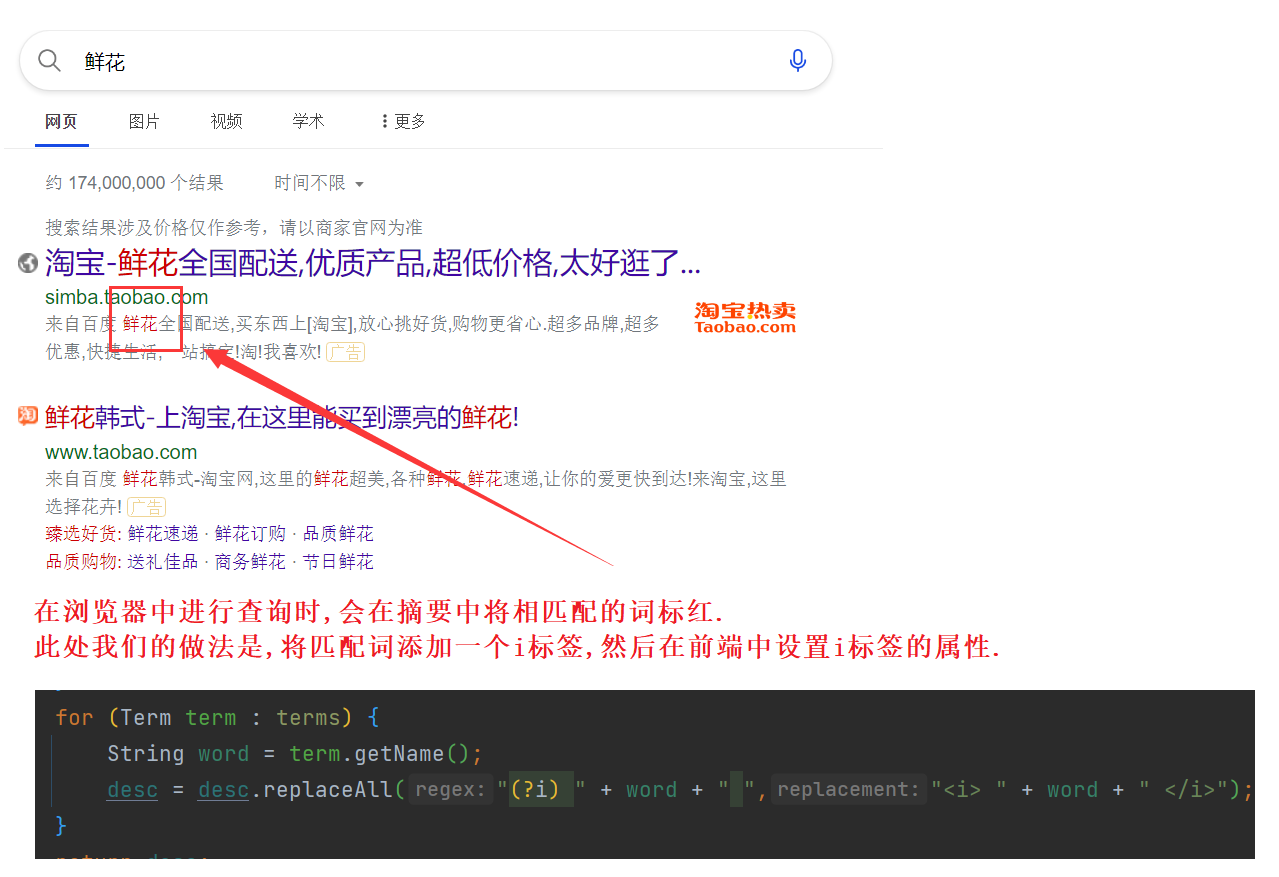
从正文中提取摘要 . 思路也很简单 , 首先判断是哪个分词结果在正文中出现了 , 如果找到该位置 , 将该位置向前截取60个字符 , 向后截取100个字符 , 整体作为摘要 ; 如果向前不足60个字符 , 从头开始截取 ; 如果向后不足100个字符 , 截取该字符后的全部内容 .
private String GetDesc(String content, List<Term> terms) {
//1.遍历分词结果,看看哪个结果是在content中存在
int firstPos = -1;
for (Term term : terms) {
String word = term.getName();
//严谨做法 : 正则表达式
content = content.toLowerCase().replaceAll("\\b" + word + "\\b", " " + word + " ");
firstPos = content.indexOf(" " + word + " ");
if(firstPos >= 0) {
//找到了
break;
}
}
if(firstPos == -1) {// 所有分词结果都不在正文中存在,可能性很小
if(content.length() > 160) {
return content.substring(0,160) + "...";
} else {
return content;
}
}
String desc = "";
int beg = firstPos < 60 ? 0 : firstPos - 60;
if(beg + 160 > content.length()) {
desc = content.substring(beg);
} else {
desc = content.substring(beg,beg+160) + "...";
}
for (Term term : terms) {
String word = term.getName();
desc = desc.replaceAll("(?i) " + word + " ","<i> " + word + " </i>");//(?i)表示不区分大小写进行替换
}
return desc;
}
细节分析 :
搜索模块到此就告一段落了 !
六 : web模块
后端代码 :
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.searcher.DocSearcher;
import com.example.demo.model.Result;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class DocSearcherController {
private static DocSearcher searcher = new DocSearcher();
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@RequestMapping(value = "/searcher",produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8")
@ResponseBody
public String search(@RequestParam("query") String query) throws JsonProcessingException {
//参数是查询词,返回值是响应内容
List<Result> results = searcher.search(query);
return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(results);
}
}
构建前端页面 :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Java文档搜索</title>
<script src="js/jQuery.js"></script>
<link rel="icon" href="image/tubiao.jpg">
</head>
<body>
<!--1.搜索框 + 搜索按钮-->
<!--2.搜索结果 -->
<div class="container">
<div class="header">
<input type="text">
<button id="search-btn">搜索</button>
</div>
<div class="result">
<!--包含很多记录-->
<!-- <div class="item">
<a href="#">我是标题</a>
<div class="desc">我是一段描述Lorem ipsum, dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Cum ipsum, voluptatibus assumenda sed facere nam ab tempore voluptas, perferendis sequi veritatis eveniet fuga cumque in aliquid dolor hic praesentium iusto.</div>
<div class="url">http://www.baidu.com</div>
</div> -->
</div>
</div>
<style>
/*样式*/
/*先去除浏览器的默认样式*/
* {
margin: 0;
padding:0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/*给整体页面指定一个高度*/
html, body {
height: 100%;
background-image: url(image/beijing.jpg);
/*设置背景图不平铺*/
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/*设置背景图位置*/
background-position: center center;
/*设置背景图大小*/
background-size: cover;
}
/*针对.container设置样式*/
.container {
/*也可设置为百分数形式*/
width: 1200px;
height: 100%;
/*设置水平居中*/
margin:0 auto;
/*设置背景色,让版心和背景图能够区分开*/
background-color: rgba(255,255,255,0.8);
/*设置圆角矩形*/
border-radius: 10px;
/*设置内边距,避免文字内容紧贴边界*/
padding: 20px;
overflow: auto;
}
.result .count {
color:grey;
margin-top:10px;
}
.header {
width:100%;
height: 50px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
.header>input {
width: 1050px;
height:50px;
font-size: 22px;
line-height: 50px;
padding-left: 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
.header>button {
width: 100px;
height:50px;
background-color: rgb(79, 121, 183);
color: fff;
font-size: 22px;
line-height: 50px;
border-radius: 10px;
border:none;
}
.header>button:active {
background: grey;
}
.item {
width: 100%;
margin-top: 20px;
}
.item a {
display: block;
height: 40px;
font-size: 22px;
line-height: 40px;
font-weight: 700;
color:rgb(79, 121, 183);
}
.item .desc {
font-size: 19px;
}
.item .url {
font-size: 19px;
color: rgb(69, 221, 69);
}
.item .desc i {
color:red;
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
<!--放置js代码-->
<script>
let button = document.querySelector("#search-btn");
button.onclick = function() {
let input = document.querySelector(".header input");
let query = input.value;
jQuery.ajax({
type:"GET",
url:"searcher?query=" + query,
data:"",
success: function(data,status) {
//data表示拿到的的结果数据
//status表示HTTP状态码
//根据收到的数据结果,构造页面内容
//console.log(data);
buildResult(data);
}
});
}
function buildResult(data) {
// 遍历data中的每个元素,针对每个元素都创建一个
// div.item,再把这个div.item加入div.result中
let result = document.querySelector('.result');
//清空上次结果
result.innerHTML="";
//构造div,用于显示结果的个数
let countDiv = document.createElement('div');
countDiv.innerHTML = '当前找到' + data.length + "条搜索结果";
countDiv.className = 'count';
result.appendChild(countDiv);
for(let item of data) {
let itemDiv = document.createElement('div');
itemDiv.className = 'item';
//构造标题
let title = document.createElement('a');
title.innerHTML = item.title;
title.href = item.url;
title.target = '_blank';
itemDiv.appendChild(title);
//构造描述
let desc = document.createElement('div');
desc.className = 'desc';
desc.innerHTML = item.desc;
itemDiv.appendChild(desc);
//构造url
let url = document.createElement('div');
url.className = 'url';
url.innerHTML = item.url;
itemDiv.appendChild(url);
result.appendChild(itemDiv);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
验证效果 :
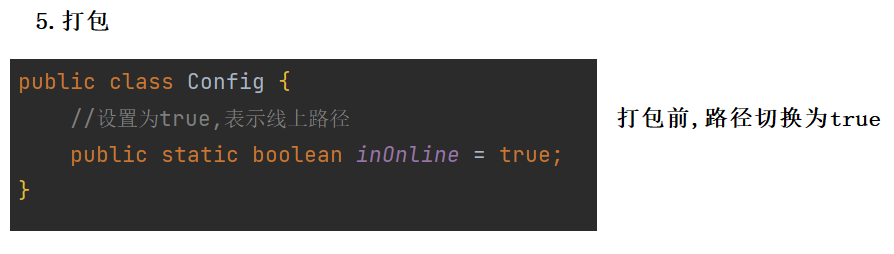
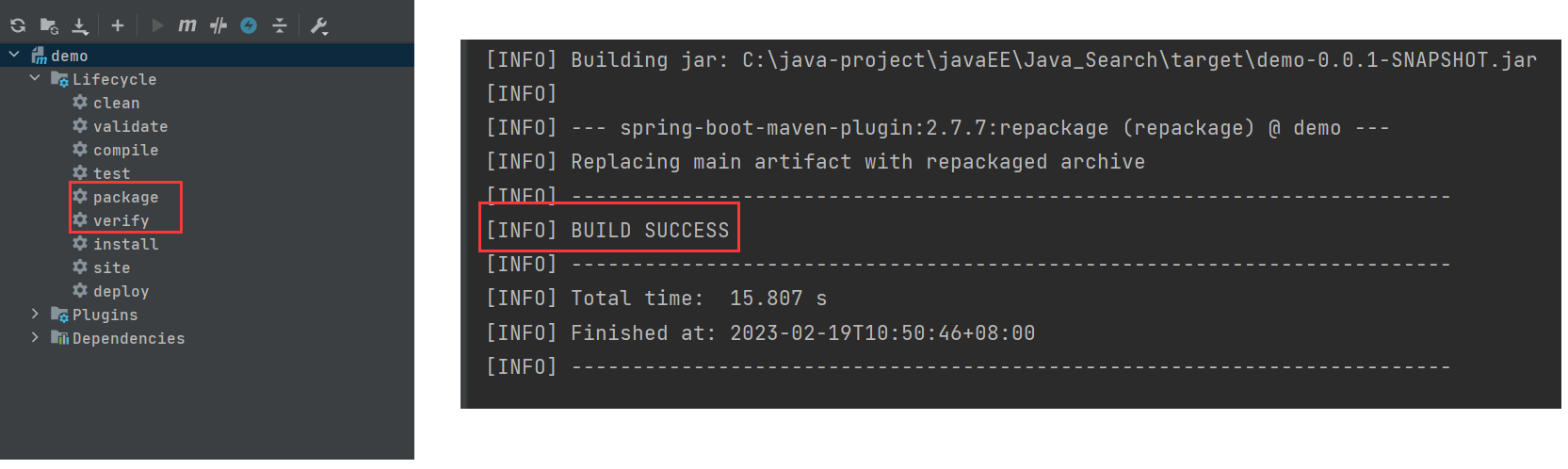
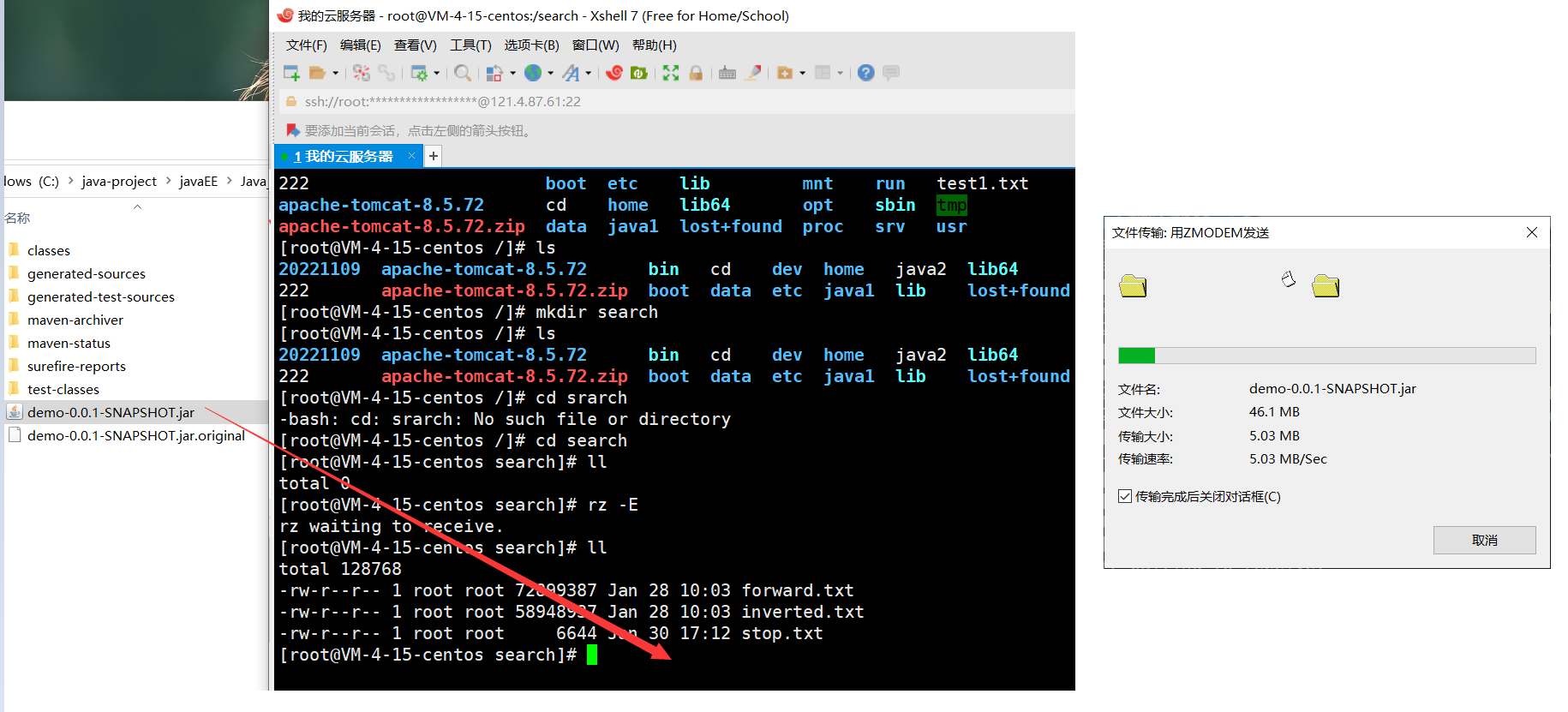
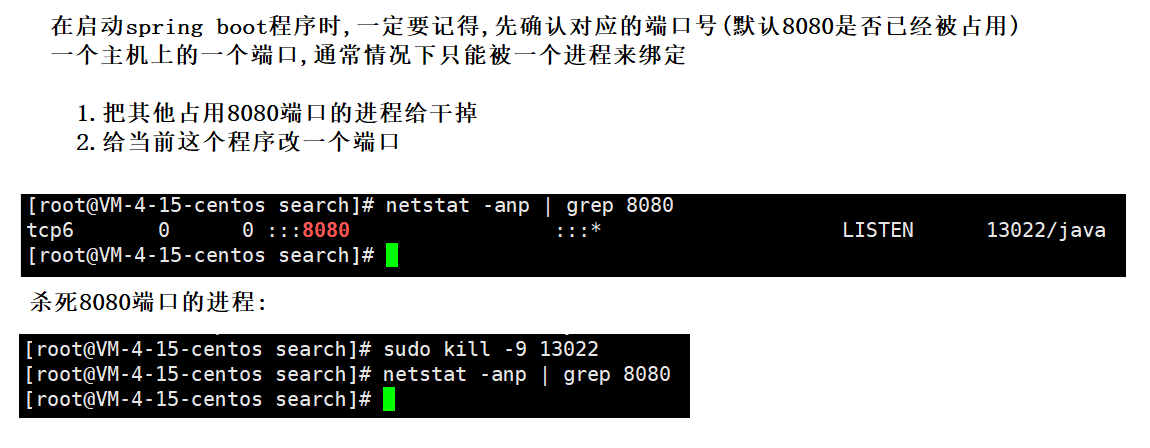
七 : 部署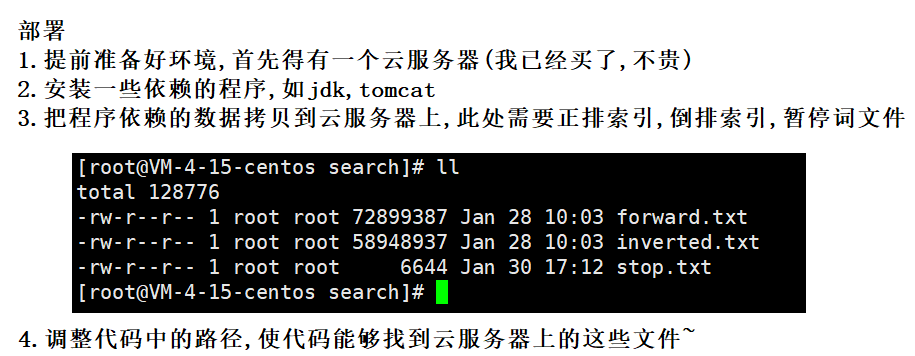
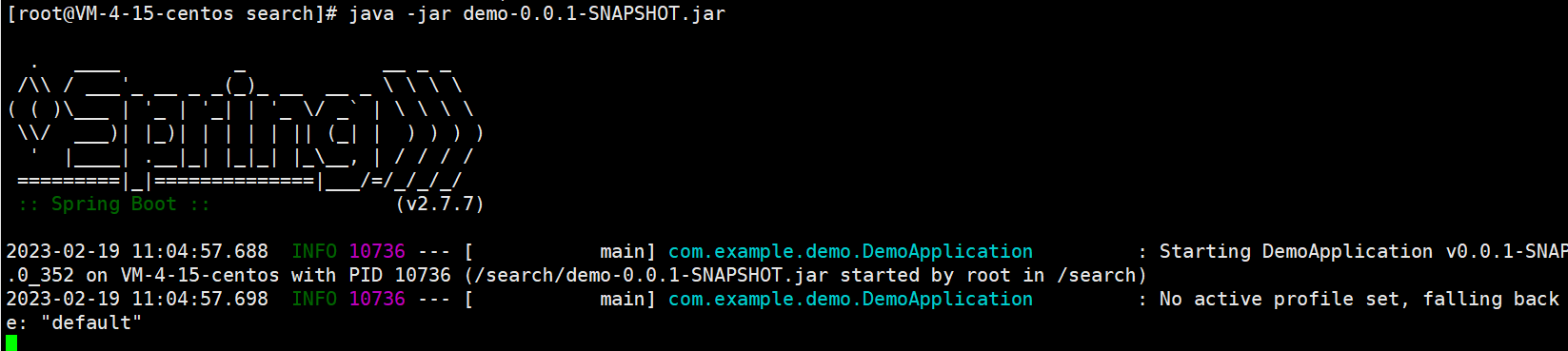
然后就可以运行了 :
linux涉及到一个概念 , 即前台线程 vs 后台线程 , 直接输入一个命令来产生的进程 , 就是"前台线程" ; 前台线程会随着终端的关闭被杀死 . 为了解决这个问题 , 需要把前台线程转换成后台线程 , 如下 :
nohup java -jar demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar &
断开XShell连接 :
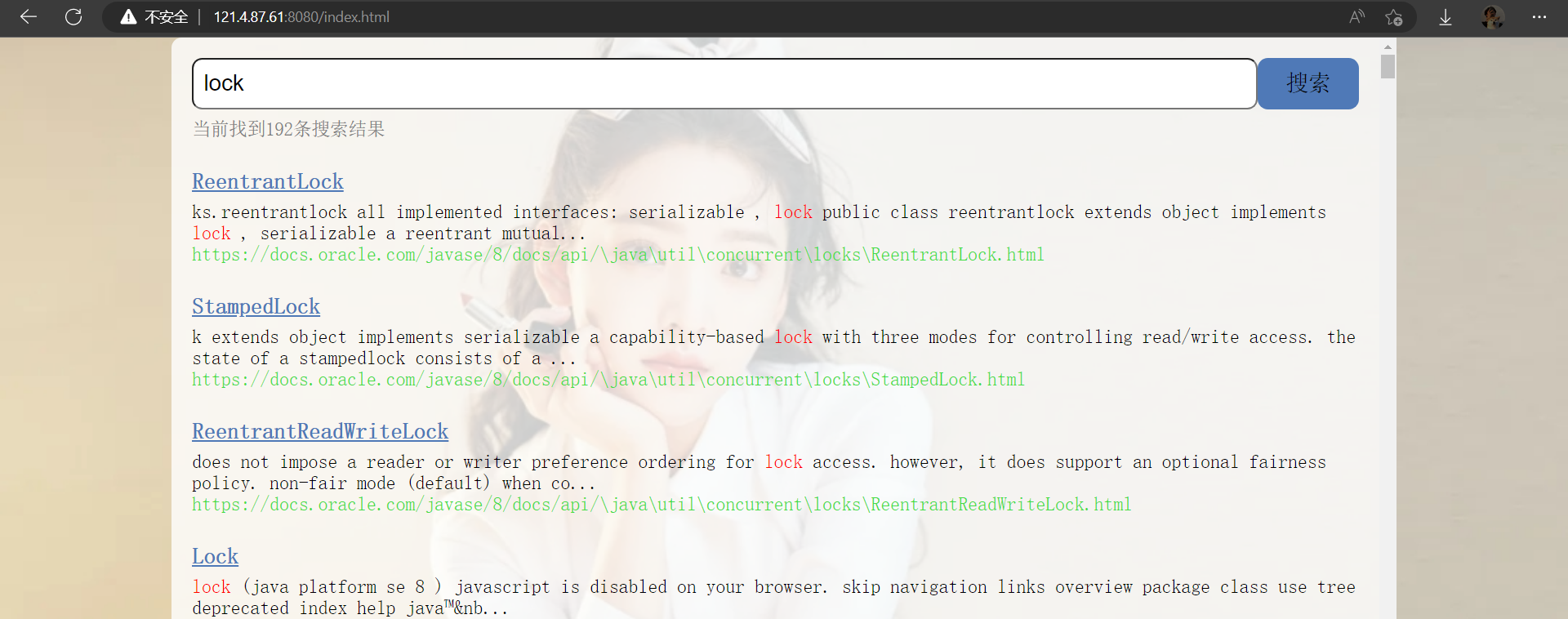
可以成功访问 !
搜索引擎网页url : 链接