一. 认识字符串
字符串是 Python 中最常用的数据类型。我们一般使用引号来创建字符串。创建字符串很简单,只要为变量分配一个值即可。
a = 'hello world'
b = "abcdefg"
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
注意:控制台显示结果为
<class 'str'>, 即数据类型为str(字符串)。
1.1 字符串特征
- 一对引号字符串
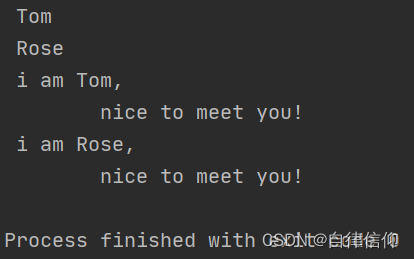
name1 = 'Tom'
name2 = "Rose"
- 三引号字符串
name3 = ''' Tom '''
name4 = """ Rose """
a = ''' i am Tom,
nice to meet you! '''
b = """ i am Rose,
nice to meet you! """
print(name3)
print(name4)
print(a)
print(b)
注意:三引号形式的字符串支持换行。
思考:如果创建一个字符串
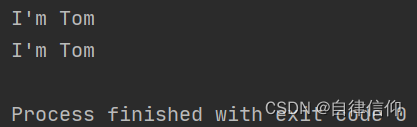
I'm Tom?
c = "I'm Tom"
d = 'I\'m Tom'
print(c)
print(d)
1.2 字符串输入
在Python中,使用input()接收用户输入。
- 代码
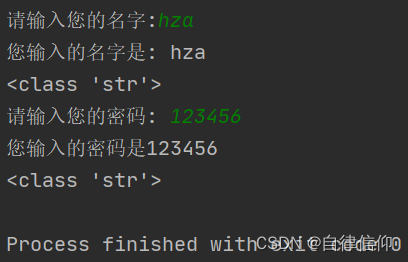
name = input('请输入您的名字:')
print(f'您输入的名字是: {name}')
print(type(name))
password = input('请输入您的密码: ')
print(f'您输入的密码是{password}')
print(type(password))
f’otherstrs {varname} otherstrs’
又学习一种方便的写法
二、下标
“下标”又叫“索引”,就是编号。比如火车座位号,座位号的作用:按照编号快速找到对应的座位。同理,下标的作用即是通过下标快速找到对应的数据。
2.1 快速体验
需求:字符串name = "abcdef",取到不同下标对应的数据。
- 代码
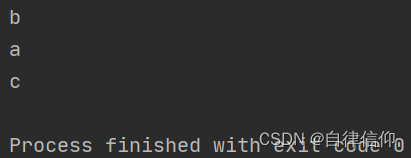
name = "abcdef"
print(name[1])
print(name[0])
print(name[2])
- 输出结果
注意:下标从0开始。
三、切片
切片是指对操作的对象截取其中一部分的操作。字符串、列表、元组都支持切片操作。
3.1 语法
序列[开始位置下标:结束位置下标:步长]
注意
1. 不包含结束位置下标对应的数据, 正负整数均可;
2. 步长是选取间隔,正负整数均可,默认步长为1。
3.2 体验
name = "abcdefg"
print(name[2:5:1]) # cde
print(name[2:5]) # cde
print(name[:5]) # abcde
print(name[1:]) # bcdefg
print(name[:]) # abcdefg
print(name[::2]) # aceg
print(name[:-1]) # abcdef, 负1表示倒数第一个数据
print(name[-4:-1]) # def
print(name[::-1]) # gfedcba
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g |
四、常用操作方法
字符串的常用操作方法有查找、修改和判断三大类。
4.1 查找
所谓字符串查找方法即是查找子串在字符串中的位置或出现的次数。
4.1.1 find() [找不到返回-1]
- find():检测某个子串是否包含在这个字符串中,如果在返回这个子串开始的位置下标,否则则返回-1。
- 语法
字符串序列.find(子串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
注意:开始和结束位置下标可以省略,表示在整个字符串序列中查找。
- 快速体验
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.find('and')) # 12
print(mystr.find('and', 15, 30)) # 23
print(mystr.find('ands')) # -1
4.1.2 index() [找不到直接报异常]
- index():检测某个子串是否包含在这个字符串中,如果在返回这个子串开始的位置下标,否则则报异常。
- 语法
字符串序列.index(子串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
注意:开始和结束位置下标可以省略,表示在整个字符串序列中查找。
- 快速体验
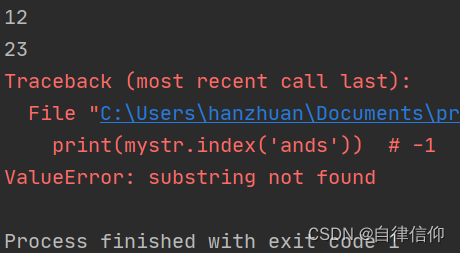
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.index('and')) # 12
print(mystr.index('and', 15, 30)) # 23
print(mystr.index('ands')) # 报错 ValueError
4.1.3 rfind() 、rindex() [反过来查找而已]
- rfind(): 和find()功能相同,但查找方向为右侧开始。
- rindex():和index()功能相同,但查找方向为右侧开始。
- 语法
字符串序列.count(子串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
注意:开始和结束位置下标可以省略,表示在整个字符串序列中查找。
- 快速体验1
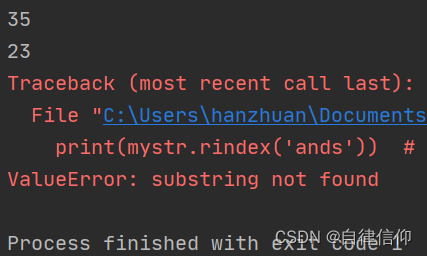
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.rindex('and')) # 35 (最后一个and)
print(mystr.rindex('and', 15, 30)) # 23 (指定区间内就一个and)
print(mystr.rindex('ands')) # ValueError
2. 快速体验2
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.rfind('and')) # 35 (最后一个and)
print(mystr.rfind('and', 15, 30)) # 23 (指定区间内就一个and)
print(mystr.rfind('ands')) # 找不到返回-1
4.1.4 count()
- count():返回某个子串在字符串中出现的次数
- 语法
字符串序列.count(子串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
注意:开始和结束位置下标可以省略,表示在整个字符串序列中查找。
- 快速体验
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.count('and')) # 3
print(mystr.count('ands')) # 0
print(mystr.count('and', 0, 20)) # 1 (指定区间内就出现过一次)
4.2 修改
所谓修改字符串,指的就是通过函数的形式修改字符串中的数据。
4.2.1 replace()
- replace():替换
- 语法
字符串序列.replace(旧子串, 新子串, 替换次数)
注意:替换次数如果超出子串出现次数,则替换次数为该子串出现次数。
不指定次数 默认全部替换
- 快速体验
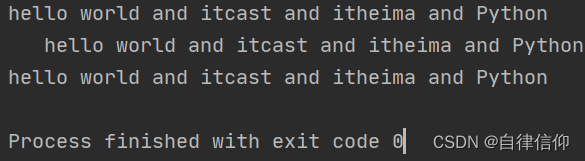
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.replace('and', 'he')) # 结果:hello world he itcast he itheima he Python
print(mystr.replace('and', 'he', 10)) # 结果:hello world he itcast he itheima he Python
print(mystr.replace('and', 'he', 1)) # 结果:hello world he itcast and itheima and Python 替换一次,就只替换了第一次找到的
print(mystr) # 结果:hello world and itcast and itheima and Python 并不会修改原字符串
注意:数据按照是否能直接修改分为可变类型和不可变类型两种。字符串类型的数据修改的时候不能改变原有字符串,属于不能直接修改数据的类型即是不可变类型。
可变类型: 直接修改原变量
不可变类型: 不修改原变量,修改结果以返回值形式返回
4.2.2 split()
- split():按照指定字符分割字符串。
- 语法
字符串序列.split(分割字符, num)
注意:num表示的是分割字符出现的次数,即将来返回数据个数为num+1个。
- 快速体验
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.split('and')) # ['hello world ', ' itcast ', ' itheima ', ' Python']
print(mystr.split('and', 2)) # ['hello world ', ' itcast ', ' itheima and Python'] 只分割2个and
print(mystr.split(' ')) # ['hello', 'world', 'and', 'itcast', 'and', 'itheima', 'and', 'Python']
print(mystr.split(' ', 2)) # ['hello', 'world', 'and itcast and itheima and Python'] 只分割两个空格
注意:如果分割字符是原有字符串中的子串,分割后则丢失该子串。
4.2.3 join()
- join():用一个字符或子串合并字符串,即是将多个字符串合并为一个新的字符串。
- 连接符.join(字符串1,字符串2,字符串3 …)
- 语法
字符或子串(连接符).join(多字符串组成的序列)
- 快速体验
list1 = ['chuan', 'zhi', 'bo', 'ke']
t1 = ('aa', 'b', 'cc', 'ddd')
print('_'.join(list1)) # chuan_zhi_bo_ke
print('...'.join(t1)) # aa...b...cc...ddd
print(''.join(list1)) # chuanzhiboke
print(' '.join(list1)) # chuan zhi bo ke
4.2.4 其他不重要的:capitalize()、title()、lower()、upper()、lstrip()、rstrip()、strip()、ljust()、rjust()
1. capitalize()
- capitalize():将字符串第一个字符转换成大写。其他字符全部改成小写
mystr = "hello world and itcast AND itheima and Python"
print(mystr.capitalize()) # Hello world and itcast and itheima and python
注意:capitalize()函数转换后,只字符串第一个字符大写,其他的字符全都改为小写。
2. title()
- title():将字符串每个单词首字母转换成大写。
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.title()) # Hello World And Itcast And Itheima And Python
3. lower()
- lower():将字符串中大写转小写。 转换后字符串全部变成小写
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.lower()) # hello world and itcast and itheima and python 全部变小写
4. upper()
- upper():将字符串中小写转大写。 转换后全部变大写
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.upper()) # HELLO WORLD AND ITCAST AND ITHEIMA AND PYTHON
5. lstrip()、rstrip()、strip()
- lstrip():删除字符串左侧空白字符。
- rstrip():删除字符串右侧空白字符。
- strip():删除字符串两侧空白字符。
mystr = " hello world and itcast and itheima and Python "
print(mystr.lstrip())
print(mystr.rstrip())
print(mystr.strip())
5.1 补
- strip(‘xyz’) 删除开头和结尾 所有指定匹配字符
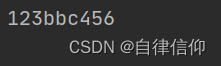
s = 'cbb123bbc456bcc'
print(s.strip('bc'))
s = '{1,2,3,4,5}'
print(s.strip('{}'))
6. ljust()
- ljust():返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用指定字符(默认空格)填充至对应长度 的新字符串。
- 语法
字符串序列.ljust(长度, 填充字符)
rjust()、center() 同上
- rjust():返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用指定字符(默认空格)填充至对应长度 的新字符串,语法和ljust()相同。
- center():返回一个原字符串居中对齐,并使用指定字符(默认空格)填充至对应长度 的新字符串,语法和ljust()相同。
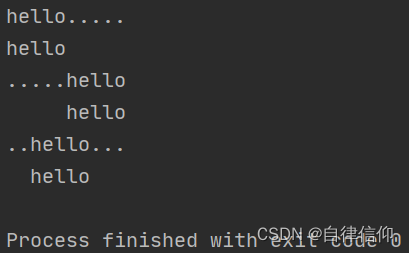
mystr = 'hello'
print(mystr.ljust(10, '.')) #'hello.....' [强制填充长度为10 并左对齐 空位补'.']
print(mystr.ljust(10)) #'hello ' [强制填充长度为10 并左对齐 空位默认补空格]
print(mystr.rjust(10, '.')) #'.....hello' [强制填充长度为10 并右对齐 空位补'.']
print(mystr.rjust(10)) #' hello' [强制填充长度为10 并右对齐 空位默认补空格]
print(mystr.center(10, '.')) #'..hello...' [强制填充长度为10 并居中对齐 空位补'.']
print(mystr.center(10)) #' hello ' [强制填充长度为10 并居中对齐 空位默认补空格]
4.3 判断
所谓判断即是判断真假,返回的结果是布尔型数据类型:True 或 False。
4.3.1 startswith()
- startswith():检查字符串是否是以指定子串开头,是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果设置开始和结束位置下标,则在指定范围内检查。
- 语法
字符串序列.startswith(子串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
- 快速体验
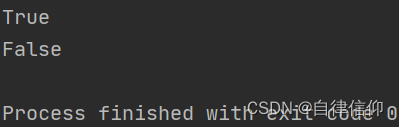
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python "
print(mystr.startswith('hello')) # True
print(mystr.startswith('hello', 5, 20)) # False
4.3.2 endswith()
- endswith()::检查字符串是否是以指定子串结尾,是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果设置开始和结束位置下标,则在指定范围内检查。
- 语法
字符串序列.endswith(子串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
- 快速体验
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.endswith('Python')) # True
print(mystr.endswith('python')) # False
print(mystr.endswith('Python', 2, 20)) # False
print(mystr.endswith('and', 0, 15)) # True
4.3.3 isalpha()
- isalpha():如果字符串至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母则返回 True, 否则返回 False。
- 全是字母返回True 否则返回False
mystr1 = 'hello'
mystr2 = 'hello12345'
print(mystr1.isalpha()) # True
print(mystr2.isalpha()) # False
4.3.4 isdigit()
- isdigit():如果字符串只包含数字则返回 True 否则返回 False。
mystr1 = 'aaa12345'
mystr2 = '12345'
print(mystr1.isdigit()) # False
print(mystr2.isdigit()) # True
4.3.4 isalnum()
- isalnum():如果字符串至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或数字则返 回 True,否则返回 False。
mystr1 = 'aaa'
mystr2 = '12345'
mystr3 = 'aaa12345'
mystr4 = '12345-'
print(mystr1.isalnum()) # True
print(mystr2.isalnum()) # True
print(mystr3.isalnum()) # True
print(mystr4.isalnum()) # False
4.3.5 isalnum()
- isspace():如果字符串中只包含空白,则返回 True,否则返回 False。
mystr1 = '1 2 3 4 5'
mystr2 = ' '
print(mystr1.isspace()) # False
print(mystr2.isspace()) # True