目录
Collection
可以保存任意多个数据(数组长度在定义时固定,不能改变)
集合主要有两组:Collection单列集合(List和Set接口继承Collection)和Map多列集合
Collection继承关系图
Collection常用方法
package com.lili.collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
public class CollectionMethod {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
//add 添加单个元素
list.add("hello");
list.add(88);
list.add("java");
list.add(true);
//remove 删除指定元素
//list.remove("hello"); //返回boolean
list.remove(0); //返回被删除的对象
System.out.println(list);
//contains 查找元素是否存在,返回boolean
System.out.println(list.contains(88));
//size 获取元素个数
System.out.println(list.size());
//isEmpty 判断是否为空
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
//clear 清空
list.clear();
System.out.println(list);
//addAll 添加多个元素
List list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add(8);
list2.add(true);
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println(list);
//containAll 查找多个元素是否都存在
System.out.println(list.containsAll(list2));
//removeAll 一次删除多个元素
list.add(888);
list.removeAll(list2);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
iterator迭代器
1. 先得到集合的迭代器 Iterator iterator = col.iterator();
2. while循环遍历,iterator.hasNext()判断是否还有未遍历元素,next()返回下一个元素
3. 若需重新遍历,需要更新迭代器
package com.lili.collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionIterator {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 65.5));
col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 87.5));
col.add(100);
//遍历col集合
//1. 得到col的迭代器
Iterator iterator = col.iterator();
//2. while循环遍历
int count = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) { //hasNext()判断是否还有未遍历元素
Object obj = iterator.next(); //next()获取元素
System.out.println("第" + (++count) + "个元素:" + obj);
}
//若需重新遍历,需要重置迭代器
iterator = col.iterator();
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + ' ' + author + ' ' + price;
}
}
增强for循环-可以替代迭代器
只能用于遍历集合或数组
增强for遍历集合的本质其实也是迭代器
package com.lili.collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 65.5));
col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 87.5));
col.add(100);
//增强for遍历集合,快捷键I
//增强for遍历集合的本质其实也是迭代器
for (Object obj : col) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
//增强for也可遍历数组
// int[] nums = {10, 20, 30};
// for (int i : nums) {
// System.out.println(i);
// }
}
}List接口
List常用方法
- List集合类中元素有序(先进先出),且可重复
- add(Object obj)直接添加对象
- add(int index, Object obj)在index处加入对象
- addAll(int index, Collection col)从index位置处开始多个添加对象
- get(int index)获取指定index位置的元素
- indexOf(Object obj)返回对象在集合中首次出现的位置
- lastIndexOf(Object obj)返回对象在集合中末次出现的位置
- remove(int index)移除指定位置的对象
- set(int index, Object obj)设置指定位置(index必须小于集合大小)的元素为obj,相当于替换
- subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)返回[fromIndex, toIndex)的子集合
package com.lili.list_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
//add(Object obj)直接添加对象
list.add("hello");
list.add("consistant");
list.add(true);
//add(int index, Object obj)在index处加入对象
list.add(1, 99);
//List集合类中元素有序(先进先出),且可重复
list.add(2, '.');
System.out.println(list);
List list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add(1);
list2.add('.');
//addAll(int index, Collection col)从index位置处开始多个添加对象
list.addAll(3, list2);
//addAll(Collection col)无index默认加在最后
//list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println(list);
//get(int index)获取指定index位置的元素
System.out.println(list.get(0));
//indexOf(Object obj)返回对象在集合中首次出现的位置
System.out.println(list.indexOf('.'));
//lastIndexOf(Object obj)返回对象在集合中末次出现的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf('.'));
//remove(int index)移除指定位置的对象
list.remove(4);
System.out.println(list);
//set(int index, Object obj)设置指定位置(index必须小于集合大小)的元素为obj,相当于替换
list.set(1, 88);
System.out.println(list);
//subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)返回[fromIndex, toIndex)的子集合
List returnList = list.subList(1, 5);
System.out.println(returnList);
}
}
List接口练习1
- 实例化List对象,并添加10个对象
- 在第2个位置插入元素
- 获取第5个元素
- 删除第6个元素
- 修改第7个元素
- 使用迭代器遍历集合
package com.lili.list_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class ListExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化List对象,并添加10个对象
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("pump");
list.add(21);
list.add("hi");
list.add("lucky");
list.add("stick");
list.add("10");
list.add('@');
list.add("again");
list.add("jennie");
list.add("young");
//在第2个位置插入元素
list.add(1,"lili");
System.out.println(list);
//获得第5个元素
System.out.println(list.get(4));
//删除第6个元素
list.remove(5);
System.out.println(list);
//修改第7个元素
list.set(6, '.');
System.out.println(list);
//使用迭代器遍历集合
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
List 3种遍历方式
List接口的实现子类ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector都适用
1. 迭代器
2. 增强for循环
3. 普通for循环,List底层也是一个数组
package com.lili.list_;
import java.util.*;
public class ListFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List list = new ArrayList();
// List list = new LinkedList();
List list = new Vector();
list.add("你好");
list.add("北京");
list.add("!");
list.add(21);
System.out.println("====迭代器遍历====");
//1. 迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
System.out.println("====增强for遍历====");
//2. 增强for遍历
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("====普通for遍历====");
//3. 普通for遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
List接口练习2
- 使用List的实现类添加3本图书,并遍历
- 冒泡法按价格降序排序
- 使用ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector三种集合实现
package com.lili.list_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
public class ListExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用List的实现类添加3本图书,并遍历
//冒泡法按价格降序排序
//使用ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector三种集合实现
//List list = new ArrayList();
List list = new LinkedList();
//List list = new Vector();
list.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 86.5));
list.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 112));
list.add(new Book("西游记", "吴承恩", 78));
list.add(new Book("水浒传", "施耐庵", 89));
//价格降序
sort(list);
//遍历集合
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
public static void sort(List list) {
int listSize = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < listSize - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < listSize - 1 - i; j++) {
Book book1 = (Book) list.get(j);
Book book2 = (Book) list.get(j + 1);
if (book1.getPrice() < book2.getPrice()) {
list.set(j, book2);
list.set(j+1, book1);
}
}
}
}
}
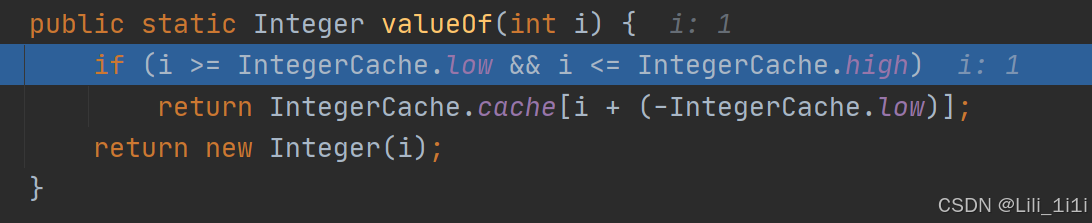
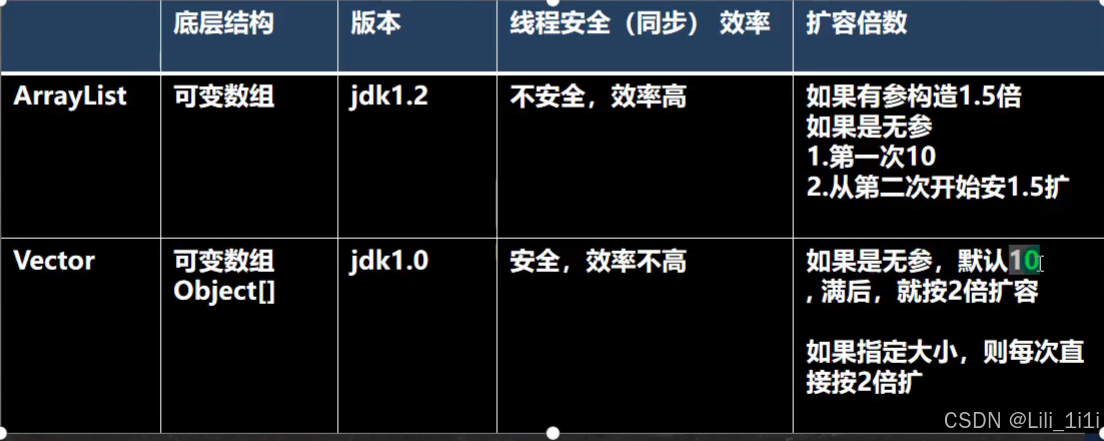
ArrayList细节
- ArrayList可以加入任意元素,包括空null
- ArrayList是由数组来实现数据存储的
- ArrayList基本等同于Vector,但ArrayList是线程不安全的 (看源码)
package com.lili.collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add(null);
arrayList.add("lucy");
arrayList.add(null);
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}ArrayList里的方法没有synchronized修饰,所以是线程不安全的
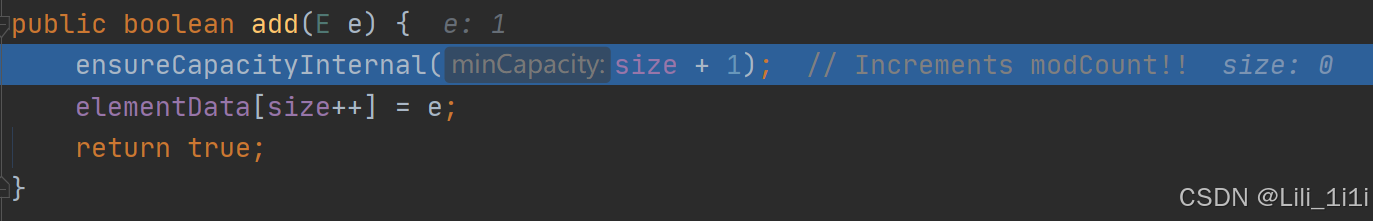
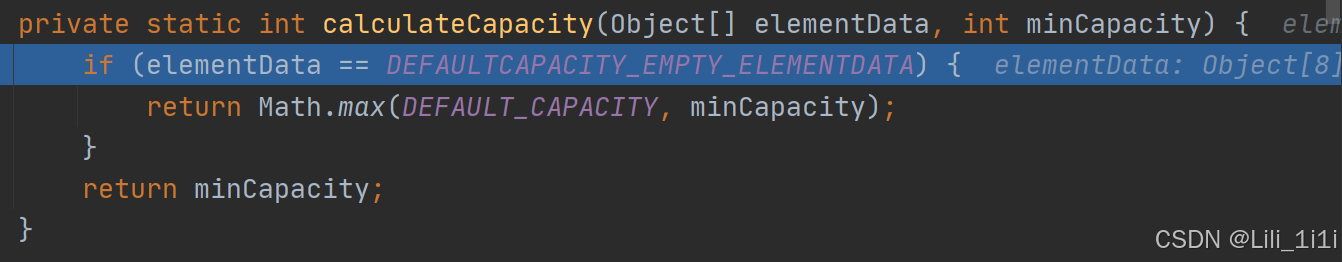
ArrayList底层结构和源码
- ArrayList中维护了一个Object类型的数组,transient Object[] elementData; transient表示瞬间的、短暂的,表示该属性不会被序列化
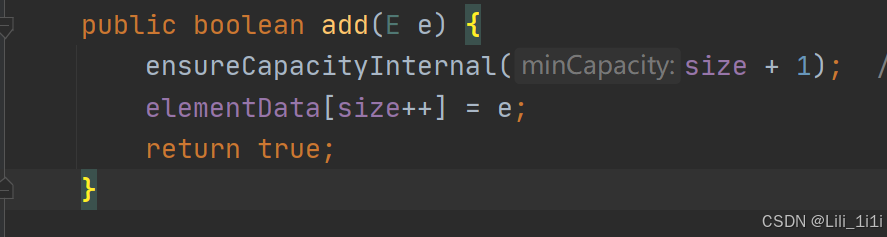
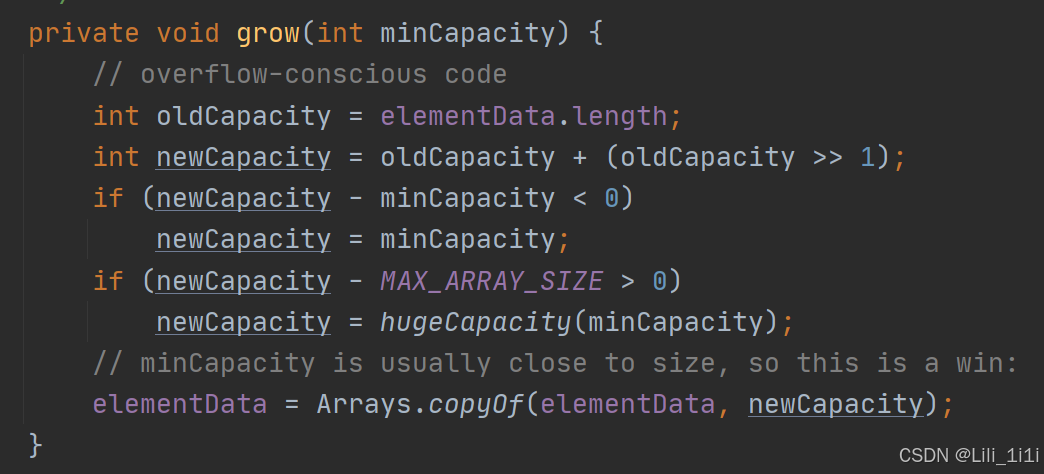
- 当创建ArrayList对象时,如果使用的是无参构造器,则初始elementData容量为0,第一次添加扩容为10,如需再次扩容,就扩容为当前倍数的1.5倍
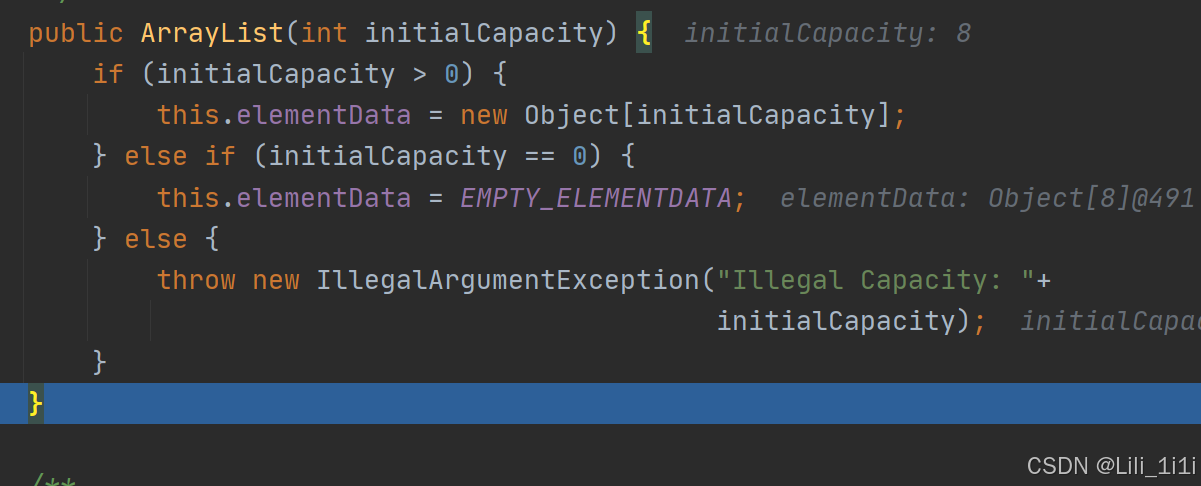
- 如果使用的是指定大小的构造器,则初始elementData容量为指定大小,再次扩容,就扩容为当前倍数的1.5倍
第一次容量为10;
第二次及以后扩容1.5倍;
扩容底层用的是Arrays.copyOf(),会保留原数组元素并扩容。
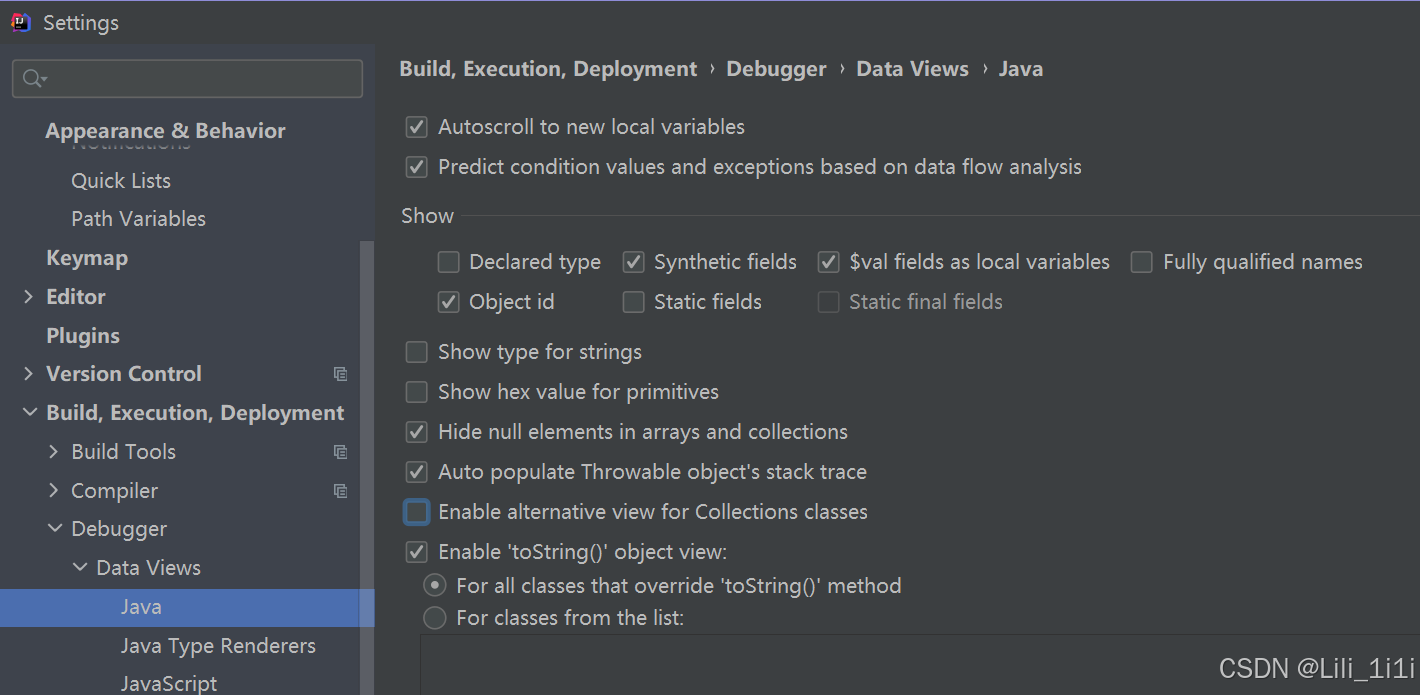
注意,使用idea进行debug时,默认显示的数据是简化后的,想看到所有数据需要设置(取消勾选下图中的篮色小方框)
创建指定大小的ArrayList
初始容量为指定大小
添加对象,进行装箱并添加
Vector 与ArrayList比较
- Vector底层也是一个对象数组,protected Object[] elementData;
- Vector是线程安全的,Vector的方法都有synchronized修饰
调用Vector无参构造器创建Vector,初始容量为10,每次扩容2倍
若是指定大小,直接每次扩容2倍
package com.lili.list_;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Vector_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vector = new Vector();
/*
Vector的无参构造器
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
*/
}
}
LinkedList
- LinkedList底层实现了双向链表和双端队列的特点
- 可以添加任意元素,包括null
- 线程不安全,没有实现同步
LinkedList底层结构
- LinkedList底层维护了一个双向链表
- LinkedList维护了两个属性,first和last分别指向首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点里面又维护了prev, next, item 三个属性
- LinkedList添加和删除效率高(修改指针即可)
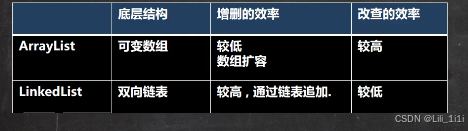
ArrayList和LinkedList比较与选择
- 如果改查操作多,选择ArrayList
- 如果增删操作多,选择LinkedList
- 在程序中80%是查找操作,因此大多数情况使用ArrayList
Set接口
- Set实现类的对象,不能存放重复元素
- Set实现类的对象,可以添加任意元素,包括null
- Set是无序的(添加时无序),但每次输出时顺序一样
public class SetMethod {
public static void main(String []args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add("john");
set.add("lucy");
set.add("john");
set.add("jack");
set.add(null);
set.add(null);
System.out.println(set);
}
}Set遍历
1. 使用迭代器
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}2. 增强for (增强for的底层就是迭代器)
for(Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o);
}注意:不能用普通for循环,因为Set接口对象不能通过索引获取,它是无序的
Set接口实现类-HashSet
- HashSet实现了Set接口
- HashSet底层实际上是HashMap(看源码,HashSet的构造器)
小练习:看看下面添加操作能否成功?
public class SetMethod {
public static void main(String []args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add("lucy"); //1
set.add("lucy"); //2
set.add(new Dog("大黄")); //3
set.add(new Dog("大黄")); //4
System.out.println(set);
}
}
class Dog {
private String name;
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}answer:
set集合不能有重复元素
1 添加成功
2 添加失败
3 添加成功
4 添加成功
经典面试题
看看下面代码添加能否成功?
public class SetMethod {
public static void main(String []args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(new String("tom")); //1
set.add(new String("tom")); //2
System.out.println(set);
}
}answer:
查看Set的 add() 源码,弄清什么情况算同一个元素
1 添加成功
2 添加失败
HashSet扩容机制
HashSet底层是HashMap
- 添加1个元素时,先得到这个元素的hash值,将hash值转成索引值
- 找到存储数据表table,再看这个索引处是否已存储别的元素
- 如果没有,直接加入
- 如果有,调用equals比较,如果是同一个元素,放弃添加,不相同添加到该索引的链表最后
- 在java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数到达TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小>=MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
HashSet练习1
定义1个Employee类,该类包含:private成员属性name, age
1. 创建3个Employee对象放入HashSet中
2. 当name和age相同时,认为是相同员工,不能添加到HashSet中
public class HashSetExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("judy", 21));
hashSet.add(new Employee("kiki", 19));
hashSet.add(new Employee("judy", 21));
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//Generate equals() 和 hashCode()
//name 和 age 相同时,equals()返回true,且hashCode()返回相同的hashCode值
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}HashSet练习2
定义1个Employee类,该类包含:private成员属性name, sal, birthday,其中birthday为MyDate类型(属性包括:year, month, day)
1. 创建3个Employee对象放入HashSet中
2. 当name和birthday相同时,认为是相同员工,不能添加到HashSet中
public class HashSetExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("judy", 6500, 20000101));
hashSet.add(new Employee("kiki", 10000, 20030605));
hashSet.add(new Employee("judy", 8000, 20011112));
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private int sal;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee(String name, int sal, MyDate birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getSal() {
return this.sal;
}
public void setSal(int sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return this.birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
//Generate equals() 和 hashCode()
//name 和 birthday 相同时,equals()返回true,且hashCode()返回相同的hashCode值
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, birthday);
}
}
class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
}Set接口实现类-LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类,实现了Set接口
- LinkedHashSet底层是一个LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个数组+双向链表(head和tail),加入和取出元素顺序一致
- LinkedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的
- LinkedHashSet不允许添加重复元素
LinkedHashSet练习
Car类(属性:name, price),如果name和price一样,就认为是相同元素
public class LinkedHashSetExercise {
LinkedHashSet linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet();
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("迪奥", 1000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("法拉利", 1000000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000)); //加入不了
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("保时捷", 20000000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000)); //加入不了
}
class Car {
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
//Generate equals() 和 hashCode()
//name 和 price 相同时,equals()返回true,且hashCode()返回相同的hashCode值
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, price);
}
}TreeSet
- 当使用TreeSet无参构造器创建TreeSet 时,集合仍是无序的
- 使用TreeSet 提供的一个带参构造器,可以传入一个比较器compare,指定排序规则
public class TreeSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o2).compareTo((String) o1);
}
});
treeSet.add("tom");
treeSet.add("rose");
treeSet.add("kuku");
}
}Map接口(很实用)
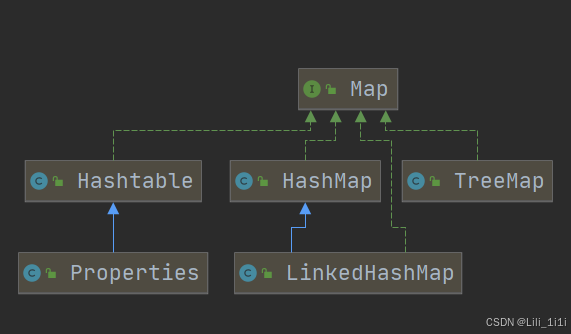
Map继承关系图
Map接口特点
- Map用于保存具有映射关系的数据key-value键值对
- Map中可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到HashMap$Node对象中
- Map中的key不能重复,若重复,会替换掉key对应的value
- Map中的value可以重复
- Map中的key可以为null(任意类型),但只能有一个key为null(不能重复),value为 null,可以有多个null的value
public class MapMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("no1", "kiki");
map.put("no2", "kiki"); //value可以重复
map.put("no1", "kuku"); //key不能重复,会覆盖掉原来的no1
map.put(null, null); //key为null
map.put(null, "abc") //替换
map.put("noo3", null); //value为null可以有多个
//get方法,传入key,返回对应的value
System.out.println(map.get("no1")); //kuku
}
}1. 一对k-v 是封装为一个HashMap$Node对象,HashMap$Node node = new Node(hash, key, value, null);
2. 为了方便遍历,会创建EntrySet集合,该集合存放的元素类型是Entry,而一个Entry对象就有 k, v,EntrySet<Entry<k, v>>
3. entrySet中,定义的类型是Map.Entry,但实际上存放的还是HashMap$Node(Node实现了Entry接口)
4. Entry提供了2个方法便于遍历,getKey()和getValue()
Set set = map.entrySet();
for(Object obj: set) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue);
}Map接口常用方法
- put 添加
- remove 根据key删除映射关系
- get 根据键获取值
- size 获取元素个数
- isEmpty 判断个数是否为0
- containsKey 查找键是否存在
- containsValue 查找值是否存在
- clear 清除
public class MapMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
//1 put 添加
map.put(1, "jerry");
map.put(2, "jimi");
map.put(3, "lucy");
//2 remove 根据key删除映射关系
map.remove(3);;
//3 get 根据键获取值
System.out.println(map.get(1));
//4 size 获取元素个数
System.out.println(map.size());
//5 isEmpty 判断个数是否为0
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//6 containsKey 查找键是否存在
System.out.println(map.containsKey(2)));
//7 containsValue 查找值是否存在
System.out.println(map.containsValue("刘亦菲")));
//8 clear 清除
System.out.println(map.clear());
}
}Map六大遍历方式
public class MapFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(1, "jerry");
map.put(2, "jimi");
map.put(3, "lucy");
//把所有的key取出
Set keyset = map.keySet();
//1 增强for
for(Object key : keyset) {
System.out.println(key + " : " + map.get(key));
}
//2 迭代器
Iterator iterator = keyset.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + " : " + map.get(key));
}
//把所偶的value取出
Collection values = map.values;
//3 增强for
for(Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
//4 迭代器
Iterator iterator2 = values.iterator();
while(iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object value = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
//通过EntrySet来获取k-v
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
//5 增强for
for(Object entry : entrySet) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + " : " + m.getValue());
}
// 6 迭代器
Iterator iterator3 = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator3.hasNext()) {
Object entry = iterator3.next();
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + " : " + m.getValue());
}
}
}Map接口小练习
使用HashMap添加3个员工对象,要求:
1. 键-员工id,值-员工对象
2. 遍历显示工资>18000的员工,员工类:姓名、工资、员工id
public class MapExercise {
public static void main() {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(1, new Employee(1, "kidy", 18500));
map.put(2, new Employee(2, "cuku", 19000));
map.put(3, new Employee(3, "lucy", 10000));
//1 使用keySet
Set keySet = map.keySet();
for(Object key : keySet) {
Employee emp = (Employee)map.get(key);
if(emp.getSal() > 18000) {
System.out.println(emp));
}
}
//2 使用entrySet
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
Employee emp = (Employee)entry.getValue();
if(emp.getSal() > 18000) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
}
}
class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private double sal;
public Employee(int id, String name, double sal) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
}
}HashMap底层机制
- HashMap底层维护了Node类型的数组table,默认为null
- 当创建对象时,将加载因子(loadfactor)初始化为0.75
- 当添加k-v时,通过key的哈希值得到在table的索引,然后判断该索引处是否已存放元素,如果没有直接添加;如果有且为相同元素,则不添加,否则添加在链表末尾
- 第一次添加,需要扩容table容量为16,临界值(threshold)为12
- 以后再扩容,则需要扩容为原来的2倍
- 在java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数 >= THREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小 >= MINI_THREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认是64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
HashTable
- 存放的元素是键值对
- HashTable的键和值都不能为null
- HashTable的键不能重复,否则会覆盖
- HashTable使用方法和HashMap基本一样
- HashTable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的
- HashTable底层是一个数组HashTale$Entry类型的table,初始大小为11
- 临界值threshold 8 = 11 * 0.75(到了临界值就会扩容,,临界值=当前大小*加载因子)
- 到了临界值扩容为原来大小的2倍+1
Properties
- Properties 是HashTable的子类
- Properties主要用于从xxx.properties文件中,加载数据到Properties类对象,并进行读取和修改(xxx.properties文件通常为配置文件)
TreeMap
- 当使用TreeMap无参构造器创建TreeMap时,集合仍是无序的
- 使用TreeMap提供的一个带参构造器,可以传入一个比较器compare,指定排序规则
public class TreeMap_ {
public staic void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o2).compareTo((String) o1);
}
});
treeMap.put("n1", "lily");
treeMap.put("n2", "qiqi");
treeMap.put("n3", "ferry");
}
}开发中如何选择集合实现类?
1. 先判断存储的类型是单列还是双列
2.
若为一组对象(单列),就用Collection接口对象
1) 允许重复:List
增删多:LinkedList(底层维护一个双向链表)
改查多:ArrayList(底层维护Object类型的可变数组)
2) 不能重复:Set
无序:HashSet(底层是HashMap,维护了一个哈希表,即数组+链表+红黑树)
排序:TreeSet
插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashSet(维护数组+双向链表)
若为一组键值对(双列),就用Map接口对象
键无序:HashMap(底层是:jdk8:数组+链表+红黑树,jdk7:数组+链表)
键排序:TreeMap
键插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashMap
读取文件:Properties
Collections工具类
排序方法(全是静态的)
public class Collections_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("kidy");
list.add("lary");
//reverse 反转
Collections.reverse(list);
//shuffle 随机排序
Collections.shuffle(list);
//sort(List) 升序排序
Collections.sort(list);
//sort(List, Comparator) 自定义排序规则
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o2).length() - ((String) o1).length();
}
});
//swap(List, int, int) 将指定两个下标交换
Collections.swap(list, 1, 0);
}
}查找、替换
public class Collections2_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("kidy");
list.add("lary");
//max(Collection) 根据元素的自然顺序,返回集合的最大元素
Collections.max(list);
//max(Collection, Comparator) 根据Comparator指定顺序,返回集合的最大元素
Collections.max(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
});
//min(Collection) 根据元素的自然顺序,返回集合的最小元素
Collections.min(list);
//min(Collection, Comparator) 根据Comparator指定顺序,返回集合的最小元素
Collections.min(list, Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
});
//frequency(Collection, Object) 返回指定集合中元素的出现次数
Collections.frequency(list);
//copy(List dest, List src) 将src中的内容复制到dest中
List dest = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
dest.add("");
}
Collections.copy(dest, list);
//replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal) 使用新值替换list中的所有旧值
Collections.replaceAll(list, "tom", "汤姆");
}
}练习1
1.封装1个新闻类,包含标题和内容属性,提供get和set方法,重写toString方法,只打印标题
2.只提供一个带参的构造器,实例化时,只初始化标题,并实例化2个对象
新闻一:博鳌亚洲论坛全球健康论坛第三届大会新闻发布会举行
新闻二:机票价格“跳水”后能否“买低退高” 调查:部分航司可操作
3.将新闻对象添加到ArrayList中,并进行倒序遍历
4.在遍历集合过程中,对新闻标题进行处理,超过15字的只保留15个,然后在后边加“...”
5.在控制台打印遍历出经过处理的新闻标题
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new News("博鳌亚洲论坛全球健康论坛第三届大会新闻发布会举行"));
list.add(new News("机票价格\"跳水\"后能否\"买低退高\" 调查\:部分航司可操作"));
//倒序遍历
for(int i = list.size() - 1; i>=0; i--) {
News news = (News) list.get(i);
System.out.println(processTitle(news.getTitle()));
}
}
public static String processTitle(String title) {
if(title.length() > 15) {
return title.subString(0,15) + "...";
}
return title;
}
}
class News {
private String title;
private String content;
public News(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getTitle() {
return this.title;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getContent() {
return this.content;
}
@Override
public int toString() {
return "title = " + this.title;
}
}练习2
1.使用HashMap类实例化一个Map类型的对象,键(String)和 值(int)分别用于存储员工的姓名和工资,存入数据:jack-4000, tom-7500, smith-10000;
2.将jack的工资改为5000
3.为所有员工加薪500
4.遍历集合中所有员工
5.遍历集合中所有工资
public class Homework02 {
pblic static void main(Strig[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("jack", 4000);
map.put("tom", 7500);
map.put("smith", 10000);
//修改jack的工资
map.put("jack", 5000);
Set keySet = map.keySet();
for(Object key : keySet) {
map.put(key,(Integer) m.get(key) + 100);
}
Set entrySet = map.EntrySet();
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}练习3
分析HashSet和TreeSet是如何实现去重的?
1) HashSet去重:hashCode() + equals(),先得到这个元素的hash值,将hash值转成索引值;找到存储数据表table,看这个索引处是否已存储别的元素;如果没有,直接添加;如果有,调用equals逐一比较,如果是同一个元素,放弃添加,全不相同则添加到该索引的链表最后
2) TreeSet去重:如果传入了Comparator匿名对象,使用实现的compare方法进行比较,如果返回0,就认为是相同元素,不添加,如果未传入Comparator匿名对象,就一添加的Compareable接口的compareTo去重
练习4
已知:Person类按照id和name重写了hashCode和equals方法,问下面代码输出什么?
public class Homework04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
Person p1 = new Person(1001, "AA");
Person p2 = new Person(1002, "BB");
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
p1.name = "CC";
set.remove(p1); //删除的时候也会根据哈希值确定索引位置来删除,删除失败
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001, "CC"));
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001, "AA"));
System.out.println(set);
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int id;
public Person(int id, String name) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(this == o) return true;
if(o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return id == person.id && Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, id);
}
}注意:删除的时候也会根据哈希值确定索引位置来删除,删除p1失败