08 Button 组件
Button 组件是 tkinter 中用于创建可交互按钮的组件,它允许用户通过点击按钮来触发特定的事件或执行命令。Button 组件是构建交互式图形用户界面的基础。
基本用法与可选属性
基本用法
创建 Button 组件的基本语法如下:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
button = tk.Button(root, text="Click Me!", command=lambda: print("Button clicked"))
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
import tkinter as tk: 导入 tkinter 库,并给它一个简短的别名tk。root = tk.Tk(): 创建一个主窗口实例。button = tk.Button(root, text="Click Me!", command=lambda: print("Button clicked")): 创建一个 Button 组件,root是这个 Button 的父容器,text参数定义了 Button 上显示的文本,command参数定义了按钮被点击时执行的函数。button.pack(): 使用 pack 布局管理器将 Button 添加到窗口中。root.mainloop(): 进入主事件循环,等待用户操作。
可选属性
Button 组件支持多种可选属性,用于定制其外观和行为:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| text | 按钮上显示的文本 |
| font | 设置文本的字体和大小 |
| fg (foreground) | 文本颜色 |
| bg (background) | 按钮的背景色 |
| width | 按钮的宽度(以字符为单位) |
| height | 按钮的高度(以字符为单位) |
| cursor | 鼠标的样式 |
| command | 绑定事件 |
| padx | 文字到边框的距离,水平方向 |
| pady | 文字到边框的距离,垂直方向 |
| bd (borderwidth) | 边框的宽度 |
| relief | 边框的样式 |
| justify | 文本对齐方式 |
| image | 图片 |
| compound | 图片与文字的混搭 |
| anchor | 方位 |
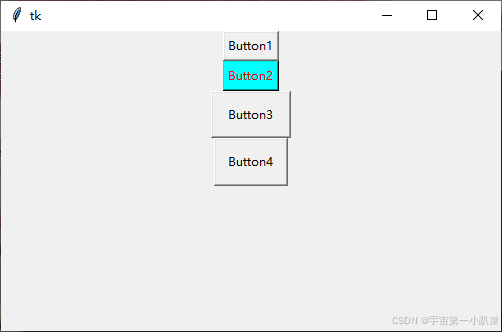
示例:使用可选属性
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
# 普通按钮
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="Button1")
button1.pack()
# 背景与前景色
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="Button2", bg="#00ffff", fg="red")
button2.pack()
# 宽度与高度
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="Button3", width=10, height=2)
button3.pack()
# 边距
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="Button4", padx=10, pady=10)
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()
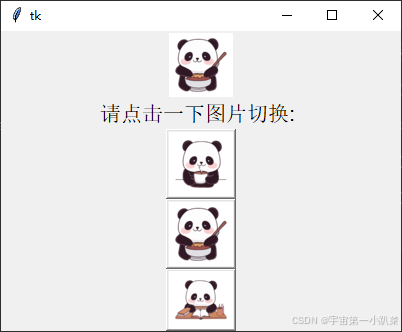
图片按钮
Button 组件可以包含图片,与 Label 组件类似,可以使用 image 属性添加图片,并通过 compound 属性设置图片与文本的相对位置。
import tkinter as tk
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
# 创建主窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("400x300+150+150") # 设置窗口大小和位置
# 加载图片
image1 = ImageTk.PhotoImage(Image.open("1.png"))
image2 = ImageTk.PhotoImage(Image.open("2.png"))
image3 = ImageTk.PhotoImage(Image.open("3.png"))
# 定义按钮点击事件处理函数
def on_button_click(image):
# 更新 Label 显示的图片
label_image.config(image=image)
# 创建 Label 显示图片和文字
label_image = tk.Label(root, image=image1)
label_image.pack()
label_text = tk.Label(root, text="请点击一下图片切换: ", font=("Arial", 16))
label_text.pack()
# 创建图片按钮
button_image1 = tk.Button(root, image=image1, command=lambda: on_button_click(image1))
button_image1.pack()
button_image2 = tk.Button(root, image=image2, command=lambda: on_button_click(image2))
button_image2.pack()
button_image3 = tk.Button(root, image=image3, command=lambda: on_button_click(image3))
button_image3.pack()
# 进入主事件循环
root.mainloop()
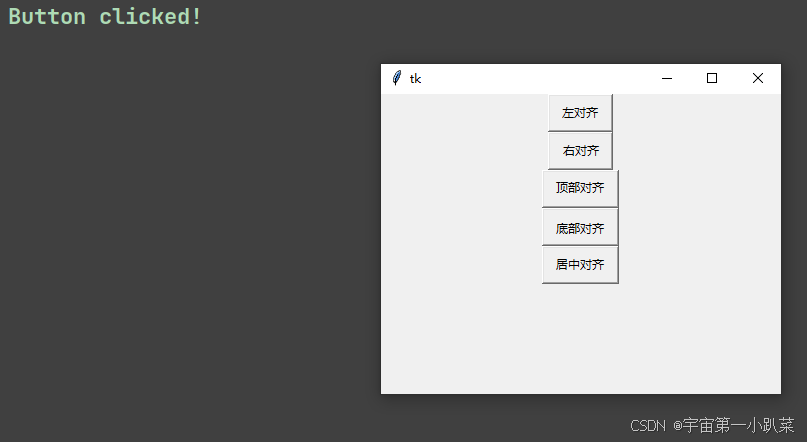
边距与对齐方式
Button 组件可以设置边距和文本对齐方式,与 Label 组件的用法相同。
import tkinter as tk
# 创建主窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("400x300+150+150") # 设置窗口大小和位置
# 定义按钮点击事件处理函数
def on_button_click():
print("Button clicked!")
# 创建具有不同边距和对齐方式的按钮
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="左对齐", command=on_button_click, padx=10, pady=5, anchor=tk.W)
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="右对齐", command=on_button_click, padx=10, pady=5, anchor=tk.E)
button2.pack()
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="顶部对齐", command=on_button_click, padx=10, pady=5, anchor=tk.N)
button3.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="底部对齐", command=on_button_click, padx=10, pady=5, anchor=tk.S)
button4.pack()
button5 = tk.Button(root, text="居中对齐", command=on_button_click, padx=10, pady=5, anchor=tk.CENTER)
button5.pack()
# 进入主事件循环
root.mainloop()
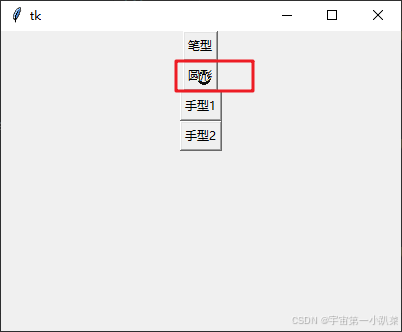
鼠标样式
Button 组件允许设置鼠标悬停时的样式,这可以通过 cursor 属性实现。
import tkinter as tk
# 创建主窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("400x300+150+150") # 设置窗口大小和位置
# 定义按钮点击事件处理函数
def on_button_click():
print("Button clicked!")
# 创建具有不同鼠标样式的按钮
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="笔型", command=on_button_click, cursor="pencil")
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="圆形", command=on_button_click, cursor="circle")
button2.pack()
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="手型1", command=on_button_click, cursor="hand1")
button3.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="手型2", command=on_button_click, cursor="hand2")
button4.pack()
# 进入主事件循环
root.mainloop()
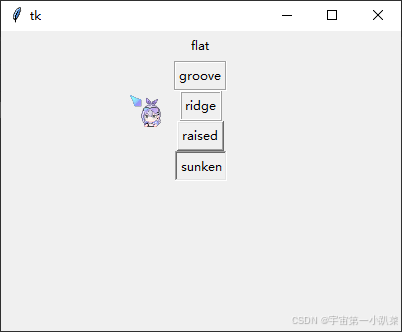
边框样式与宽度
Button 组件可以设置边框样式和宽度,这通过 relief 和 bd 属性来实现。
import tkinter as tk
# 创建主窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("400x300+150+150") # 设置窗口大小和位置
# 定义按钮点击事件处理函数
def on_button_click():
print("Button clicked!")
# 创建具有不同边框样式和宽度的按钮
button_flat = tk.Button(root, text="flat", command=on_button_click, relief="flat", bd=2)
button_flat.pack()
button_groove = tk.Button(root, text="groove", command=on_button_click, relief="groove", bd=2)
button_groove.pack()
button_ridge = tk.Button(root, text="ridge", command=on_button_click, relief="ridge", bd=2)
button_ridge.pack()
button_raised = tk.Button(root, text="raised", command=on_button_click, relief="raised", bd=2)
button_raised.pack()
button_sunken = tk.Button(root, text="sunken", command=on_button_click, relief="sunken", bd=2)
button_sunken.pack()
# 进入主事件循环
root.mainloop()
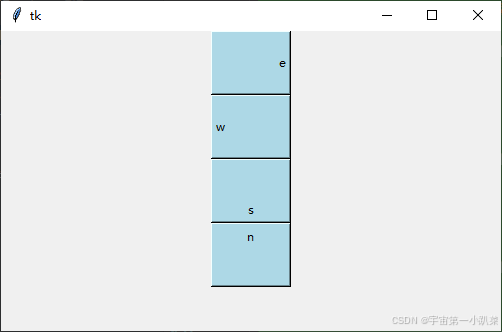
文字对齐方式
Button 组件可以设置文本的对齐方式,这通过 anchor 属性来实现。
import tkinter as tk
def on_button_click(e):
print(f"Button is clicked!")
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
# 创建具有不同文本对齐方式的按钮
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="e", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.E, relief="raised", bg="lightblue", command=lambda: on_button_click(button1))
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="w", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.W, relief="raised", bg="lightblue", command=lambda: on_button_click(button2))
button2.pack()
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="s", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.S, relief="raised", bg="lightblue", command=lambda: on_button_click(button3))
button3.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="n", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.N, relief="raised", bg="lightblue", command=lambda: on_button_click(button4))
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()