spring源码依赖注入的核心方法populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper)分析:通过源码我们发现在分析这个方法之前,此对象已经创建完成实例,内存开辟了空间,比如:
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);但是对象类里面的参数和方法还没有真正赋值,真正的赋值在这里,doCreateBean的接口中:
//ioc di,依赖注入的核心方法
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);1、点击 populateBean
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
//这里很有意思,写接口可以让所有类都不能依赖注入
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
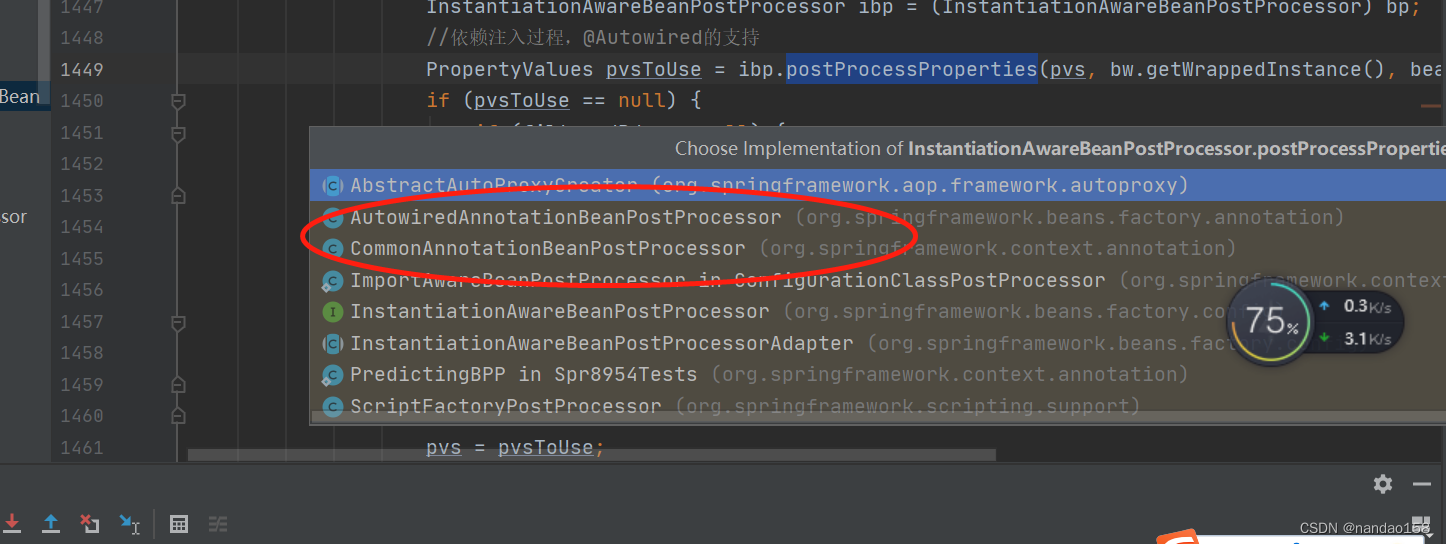
//重点看这个if代码块,重要程度 5
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
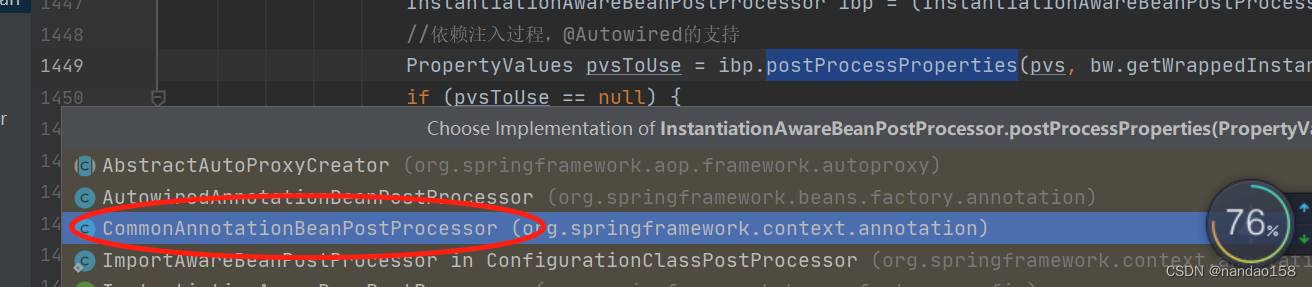
//依赖注入过程,@Autowired的支持
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
//老版本用这个完成依赖注入过程,@Autowired的支持
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
//这个方法很鸡肋了,建议不看,是老版本用<property name="username" value="Jack"/>
//标签做依赖注入的代码实现,复杂且无用
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}2、点击 postProcessProperties方法:
循环调用:我们以 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 为例进入:
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {//去缓存中取封装的类信息,在上篇的apply..方法中保存的,这里点开简单看一下
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {//反射调用,核心方法
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
点击findAutowiringMetadata方法:
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
//此处缓存中有数据,直接就返回了
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//这个重要方法上篇分享过了,这里就不说了
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}3、点击 metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);方法,来到 InjectionMetadata 类
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
//循环每个带有@Atowared注解的参数或者方法,依次通过反射赋值
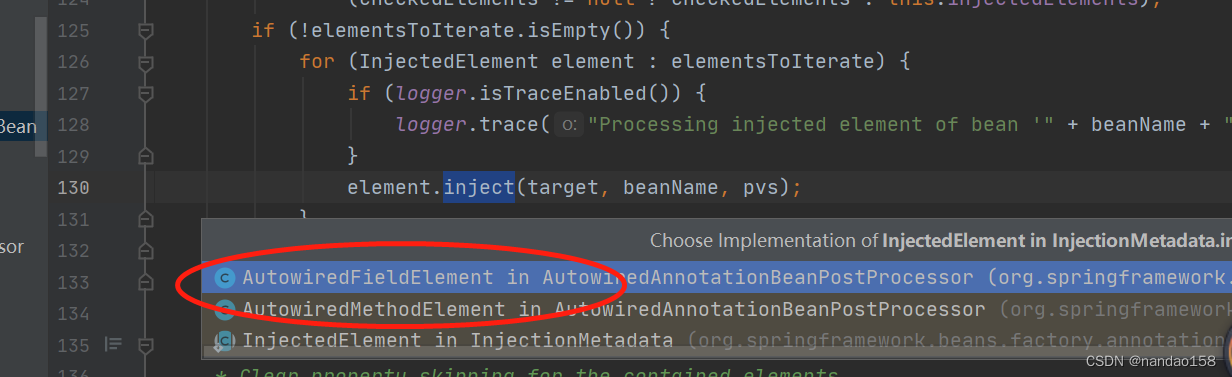
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}//反射核心方法,处理参数或者方法,点击
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}如图验证参数或者方法:
4、点击 element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);方法:参数赋值
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
//这里会触发依赖注入属性的getBean操作,前几篇分析过,此处省略
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
//最终通过反射赋值,参数如下。
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}
方法赋值进入:
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();
arguments = new Object[argumentCount];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[argumentCount];
Set<String> autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(argumentCount);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (arguments != null) {
DependencyDescriptor[] cachedMethodArguments = Arrays.copyOf(descriptors, arguments.length);
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeans);
if (autowiredBeans.size() == argumentCount) {
Iterator<String> it = autowiredBeans.iterator();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
String autowiredBeanName = it.next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i])) {
cachedMethodArguments[i] = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
descriptors[i], autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i]);
}
}
}
this.cachedMethodArguments = cachedMethodArguments;
}
else {
this.cachedMethodArguments = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);//方法执行
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
5、业务测试类:
import com.enjoy.jack.designPattern.strategy.CQ;
import com.enjoy.jack.designPattern.strategy.SC;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component
public class AutowiredConstructorBean {
@Autowired(required = false)
public AutowiredConstructorBean(SC sc,CQ cq) {
System.out.println(sc);
System.out.println(cq);
}
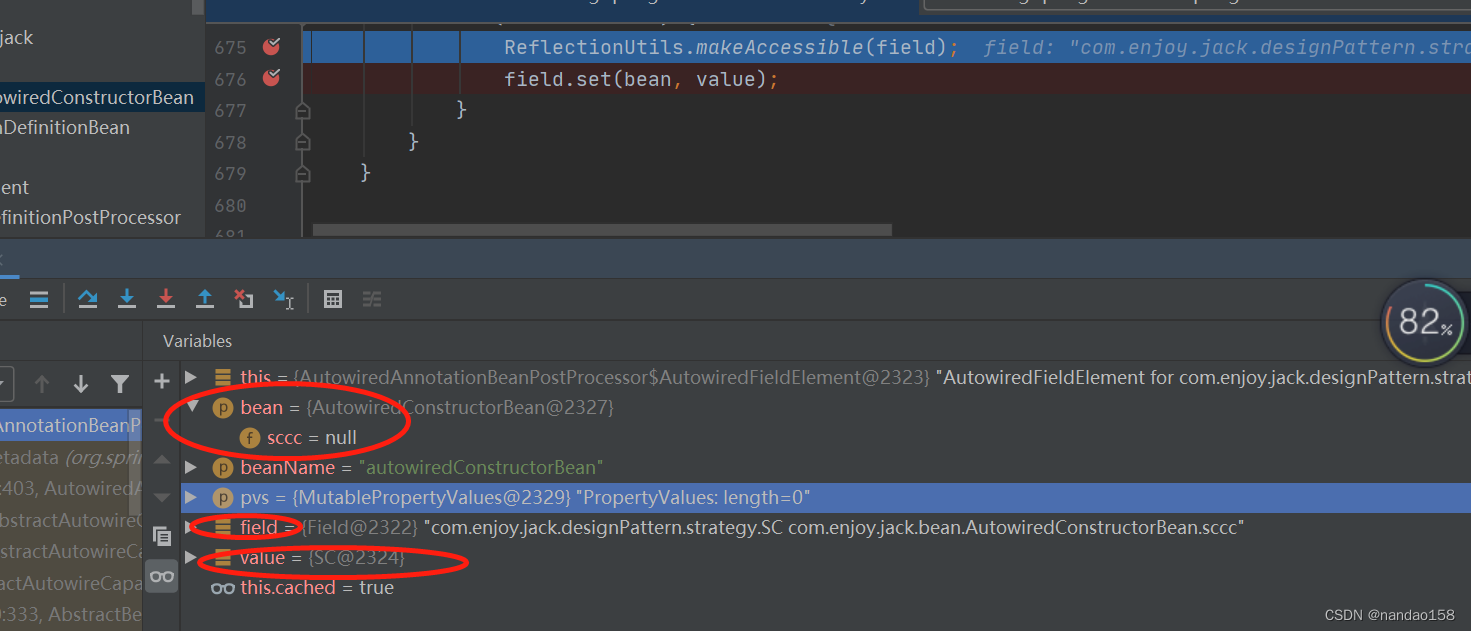
@Autowired
SC sccc;
}
参数:
package com.enjoy.jack.designPattern.strategy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SC implements Province{
private static String flag = "SC";
@Override
public boolean support(String flag) {
return SC.flag.equalsIgnoreCase(flag);
}
@Override
public String handler() {
System.out.println("======SC处理类处理");
return null;
}
}
执行如图:
6、当然注解的方法也是同样道理,比如进入:
点击进入:
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {//也是从缓存中取,同上道理
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}到此,注解参数赋值依赖注入分析结束,下篇分享依赖注入后的调用,敬请期待。