SpringBoot创建系统应用上下文是在run方法,第301行。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
private ApplicationContextFactory applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.applicationContextFactory.createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType);
if (environment == null && this.applicationContextFactory != ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT) {
environment = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT.createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType);
}
return (environment != null) ? environment : new ApplicationEnvironment();
}
ApplicationContextFactory DEFAULT = new DefaultApplicationContextFactory();
最后具体的加载逻辑在
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return getFromSpringFactories(webApplicationType, ApplicationContextFactory::createEnvironment, null);
}
仍然是一个工厂类:ApplicationContextFactory
这个工厂类有两个实现。
# Application Context Factories
org.springframework.boot.ApplicationContextFactory=\
org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext.Factory,\
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.Factory
算上默认的ApplicationEnvironment,有三个上下文环境类型,刚好对应了WebApplicationType的三个枚举值。
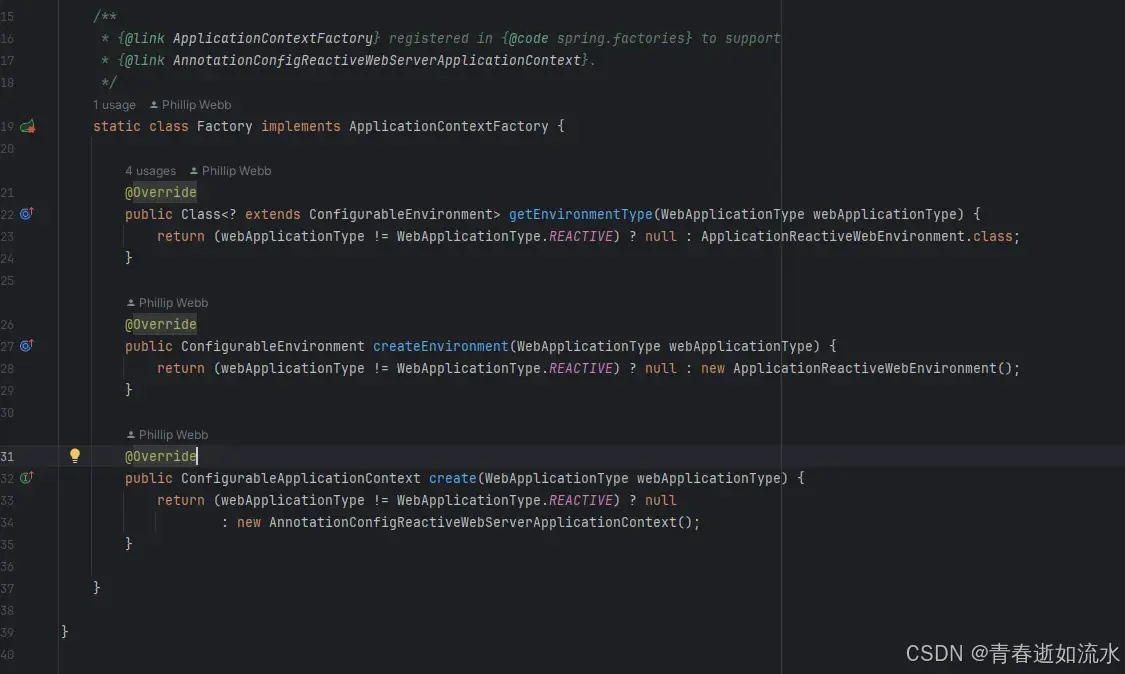
AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext.Factory
注释:
接受带注释类作为输入的ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext,特别是@Configuration带注释类,还接受使用javax.inject注释的普通@Component类和JSR-330兼容类。允许一个接一个地注册类(将类名指定为配置位置)以及类路径扫描(将基本包指定为配置地点)。
注意:如果有多个@Configuration类,稍后的@Bean定义将覆盖先前加载的文件中定义的定义。这可以用来通过一个额外的Configuration类故意覆盖某些bean定义。
如果是REACTIVE类型,就创建一个ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment类。
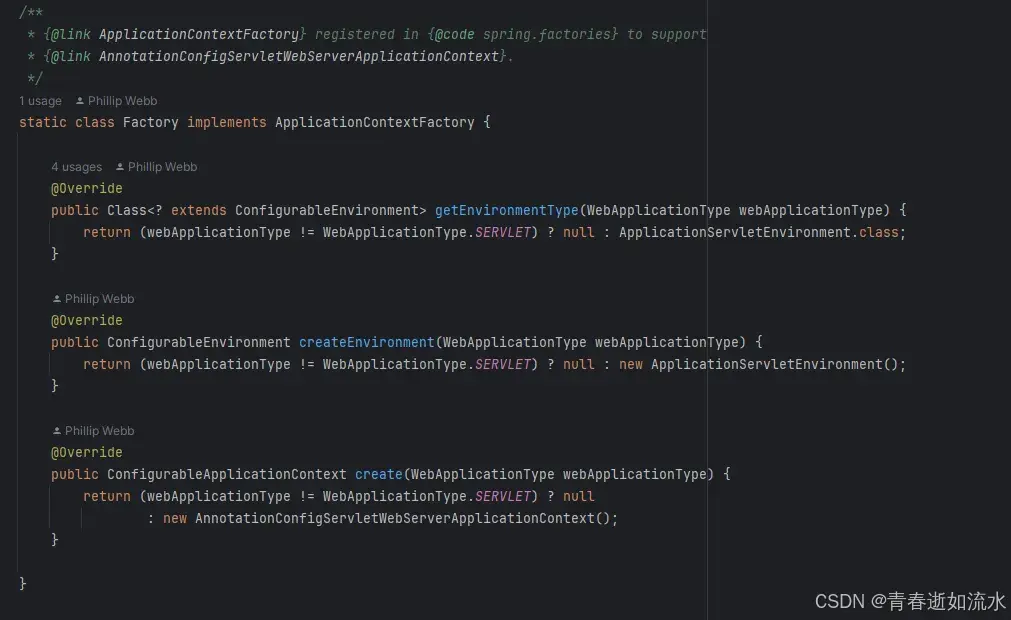
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.Factory
注释:
ServletWebServerApplicationContext,它接受带注释的类作为输入,特别是@Configuration注释的类,也接受普通的@Component类和使用javax.inject注释的JSR-330兼容类。允许一个接一个地注册类(将类名指定为配置位置)以及类路径扫描(将基本包指定为配置地点)
注意:如果有多个@Configuration类,稍后的@Bean定义将覆盖先前加载的文件中定义的定义。这可以用来通过一个额外的Configuration类故意覆盖某些bean定义。
如果应用类型是SERVLET,就创建一个ApplicationServletEnvironment类。
java中实例化一个类,会同时调用父类的构造方法。
ApplicationServletEnvironment
继承关系:StandardServletEnvironment、StandardEnvironment、AbstractEnvironment
在AbstractEnvironment抽象类中,创建了一个类。
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this(new MutablePropertySources());
}
protected AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
this.propertyResolver = createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
最终,propertySources是一个MutablePropertySources 类型。
propertyResolver则是被使用子类createPropertyResolver方法返回的值。
@Override
protected ConfigurablePropertyResolver createPropertyResolver(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
return ConfigurationPropertySources.createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
}
创建了一个ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertyResolver类,再创建一个DefaultResolver,持有propertySources。
然后调用子类customizePropertySources方法。
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletContextInitParams";
public static final String SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletConfigInitParams";
public static final String JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "jndiProperties";
private static final boolean jndiPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent(
"javax.naming.InitialContext", StandardServletEnvironment.class.getClassLoader());
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (jndiPresent && JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
把servlet上下文参数和servlet配置参数放入propertySources,占位。
然后调用父类方法
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
把系统环境变量和JVM环境变量添加到propertySources中。