Android窗口机制(一)Window,PhoneWindow,DecorView,setContentView源码理解
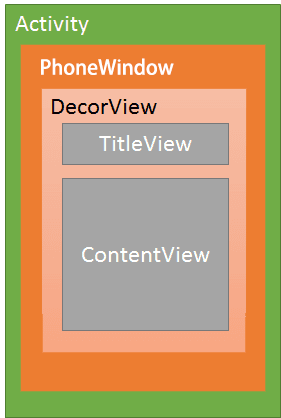
Activtiy 视图
Activity —> PhoneWindw —> DecorView —>(TitleView — ContentView)
1.Window
public abstract class Window {
...
@Nullable
public View findViewById(@IdRes int id) {
return getDecorView().findViewById(id);
}
public abstract void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID);
...
}
Window 是 顶级窗口外观和行为策略的抽象基类。应该将此类的实例用作添加到窗口管理器的顶级视图。它提供标准的UI策略,例如背景,标题*区域,默认密钥处理等,其本身是一个抽象类 PhoneWinodw 是其唯一一个实现类
2.PhoneWinodw
Window 的唯一实现类
public class PhoneWindow extends Window implements MenuBuilder.Callback {
private final static String TAG = "PhoneWindow";
// This is the top-level view of the window, containing the window decor.
private DecorView mDecor;
// This is the view in which the window contents are placed. It is either
// mDecor itself, or a child of mDecor where the contents go.
private ViewGroup mContentParent;
private ViewGroup mContentRoot;
...
}
在PhoneWindow中 有一个DecorView 内部类 DecorView 是窗口的顶层视图,包含窗口装饰
private final class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker {
/* package */int mDefaultOpacity = PixelFormat.OPAQUE;
/** The feature ID of the panel, or -1 if this is the application's DecorView */
private final int mFeatureId;
private final Rect mDrawingBounds = new Rect();
private final Rect mBackgroundPadding = new Rect();
private final Rect mFramePadding = new Rect();
private final Rect mFrameOffsets = new Rect();
....
}
DecorView 继承于FrameLayout 既然继承于FrameLayout ,我们就可以在DecorView 中添加布局 等等 而DecorView则是由PhoneWindow负责添加
那么两者又没什么关系,我们看到布局又是如何添加到 DecorView中
我们在初始化Activity时候,需要setContentView(xx); 设置Activity布局,那么两者应该有关系,我们先看看setContentView源码
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
源码中 调用了 getWindow().setContentView(xxx); 方法 getWIndow 获取的就是 当前Activtiy的 window
-----划重点
mContentParent 这是放置窗口内容的视图。它可以是// mDecor本身,也可以是内容的mDecor的子项。
整个PhoneWindw 中重点mContentParent 我们所有 获取到的 视图都赋值给 mContentParent,再由CallBack 通知界面刷新
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}
首先我们看看setContentView源码
在if判断中 先判断了mContentParent 是否为空 如果不为空 并且 当前是否加载过过场动画 加载过了 直接进行 remove
如果mContentParent 不为空 调用了 installDecor(); 方法
installDecor 方法 有点多 我们只看 核心代码
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
//在这里 判断了DecorView是否为空 为空则进行 进一步的创建
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
} else { // 否则设置当前DecorView
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
//当前mContentParent 不为空
if (mContentParent == null) {
//把当前的 decorView 添加到Window 绑定到 布局上
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
// Set up decor part of UI to ignore fitsSystemWindows if appropriate.
mDecor.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows();
//~~~~省略 加载 动画代码
}
}
DecorView的创建 通过generateDecor方法创建
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
Context context;
if (mUseDecorContext) {
Context applicationContext = getContext().getApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext == null) {
context = getContext();
} else {
context = new DecorContext(applicationContext, getContext().getResources());
if (mTheme != -1) {
context.setTheme(mTheme);
}
}
} else {
context = getContext();
}
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}
下面我们看 布局是如何进行绑定的generateLayout()
//返回值为ViewGroup
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
//设置主题 根据自己的设置的 主题来加载
TypedArray a = getWindowStyle();
if (false) { // 省略不看
System.out.println("From style:");
String s = "Attrs:";
for (int i = 0; i < R.styleable.Window.length; i++) {
s = s + " " + Integer.toHexString(R.styleable.Window[i]) + "="
+ a.getString(i);
}
System.out.println(s);
}
//是否全屏
mIsFloating = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowIsFloating, false);
int flagsToUpdate = (FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR)
& (~getForcedWindowFlags());
if (mIsFloating) {
setLayout(WRAP_CONTENT, WRAP_CONTENT);
setFlags(0, flagsToUpdate);
} else {
setFlags(FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR, flagsToUpdate);
}
//根据设置的的主题 来进行判断
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
} else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) {
// Don't allow an action bar if there is no title.
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
//以下大部分代码。都是 设置主题 资源等等 直接省略
// Inflate the window decor.
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
// 根据 用户设置的。主题 来设置 对应的features。在根据features 来加载对应的 布局文件
if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_SWIPE_TO_DISMISS)) != 0) {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_swipe_dismiss;
} else if(){
//省略
.........
}
mDecor.startChanging();
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
//吧当前的视图设置到 DecorView 中
// public static final int ID_ANDROID_CONTENT = com.android.internal.R.id.content;
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view");
}
return conentParent;
}
generateLayout 方法 主要 根据 用户设置的。主题 来设置 对应的features。在根据features 来加载对应的 布局文件
不同的布局 样子不同 比如没有 标题栏 等等 。 DecorView 布局 只有一个子元素为LinearLayout。代表整个Window界面,包含通知栏,标题栏,内容显示栏三块区域。其中我们的 内容都设置在了 id为 content 的 FrameLayout 中
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundInsidePadding="false"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</LinearLayout>
generateLayout 方法返回了 conentParent 也就回到了我们最开始的方法 setContentView();
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
//刷新 Callback 通知
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}
//callback 通知 callback Window下面的方法
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
implements LayoutInflater.Factory2,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks2,
Window.OnWindowDismissedCallback { ... }
小结:
1.Window是一个抽象类,提供了各种窗口操作的方法
2.PhoneWindow则是Window的唯一实现类,它里面实现了各种添加背景主题ContentView的方法,内部通过DecorView来添加顶级视图
3.DecorView,顶级视图,继承与FramentLayout,setContentView则是添加在它里面的@id/content里
4.setContentView里面创建了DecorView,根据Theme,Feature添加了对应的布局文件
5.当setContentView设置显示后会回调Activity的onContentChanged方法
本文部分内容来源于https://www.jianshu.com/p/e42b638944ae 感谢作者