目录
一 beans包的层次结构
main.java包下是beans的核心类,resources是beans中的配置文件。
二 核心类介绍
1 DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分,是spring注册及加载bean的默认实现,而对于XmlBeanFactory与DefaultListableBeanFactory不同的地方是XmlBeanFactory使用了自定义的Xml读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了个性化的BeanDefinitionReader读取。DefaultListableBeanFactory继承了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,并实现了ConfigurableListableBeanFactory以及BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。
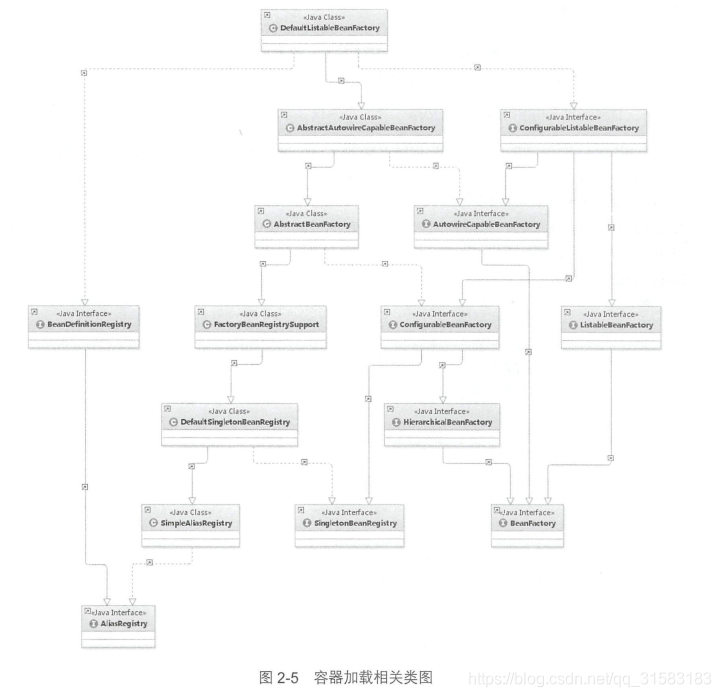
上面的类图显示了DefaultListableBeanFactory的结构:
- AliasRegistry:定义对alias的简单增删改等操作;
- SimpleAliasRegistry:主要使用map作为alias的缓存,并对接口AliasRegistry进行实现;
- SingletonBeanRegistry:定义对单例的注册及获取;
- BeanFactory:定义获取bean及bean的各种属性;
- DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:对接口SingletonBeanRegistry的实现;
- HiearchicalBeanFactory:继承BeanFactory,也就是在BeanFactory定义的功能的基础上增加了对parentFactory的支持;
- BeanDefinitionRegistry:定义对BeanDefinition的各种增删改操作;
- FactoryBeanRegistrySupport:在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry基础上增加了对FactoryBean的特殊处理功能;
- ConfigurableBeanFactory:提供配置Factory的各种方法;
- ListableBeanFactory:根据各种条件获取bean的配置清单;
- AbstractBeanFactory:综合FactoryBeanRegistrySupport和ConfigurableFactory的功能;
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory:提供创建bean、自动注入、初始化以及应用bean的后处理器;
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory:综合AbstractBeanFactory并对接口AutowireCapableBeanFactory进行实现;
- ConfigurableListableBeanFactory:BeanFactory配置清单,指定忽略类型及接口等;
- DefaultListableBeanFactory:综合上面所有功能,主要是对bean注册后的处理。
XmlBeanFactory继承DefaultListableBeanFactory并对其进行了扩展,主要用于XML文件中读取BeanDefinition,对于注册及获取bean都是使用从父类DefaultListableBeanFactory继承的方法去实现,而唯独和父类不同的个性化实现是增加了XmlBeanDefinitionReader类型的reader属性,在XmlBeanFactory中用于对资源文件进行读取和注册。
2 XmlBeanDefinitionReader
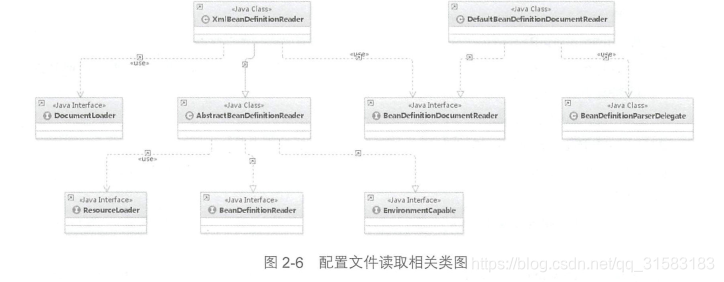
XML文件的读取是spring中重要的功能,因为spring的大部分功能都是以配置为切入点。以下是XmlBeanDefinitionReader类的结构。
整个XML配置文件的读取流程如下:
- 1>:通过继承AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的方法,来使用Resource将资源文件路径转换为对应的Resource文件;
- 2>:通过DocumentLoader对Resource文件进行转换,将Resource文件转换为Document文件;
- 3>:通过实现接口BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类对Document进行解析,并使用BeanDefinitionParserDelegate对Element进行解析。
三 容器的基础XmlBeanFactory
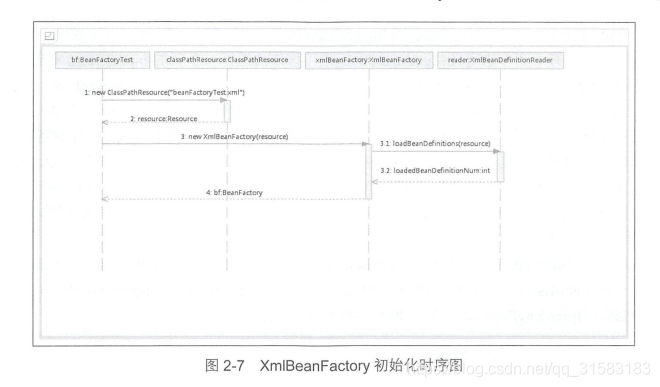
public static void main(String[] args) {
XmlBeanFactory xmf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactory.xml"));
}通过XmlBeanFactory初始化时序图如下:
1 配置文件封装
spring的配置文件读取是通过ClassPathResource进行封装的。
在java中,将不同来源的资源抽象成URL,通过注册不同的handler(URLStreamHandler)来处理不同来源的资源读取逻辑。
一般handler的类型使用不同前缀等资源的handler,虽然可以注册自己的URLStreamHandler来解析特定的URL前缀,比如“classpath”,但这需要了解URL的实现机制,而且URL也没有提供基本的方法,比如检查当前资源是否存在、检查当前资源是否可读等方法。因而Spring对其内部使用到的资源实现了自己的抽象结构:Resource接口封装底层资源。
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* Return an {@link InputStream}.
* <p>It is expected that each call creates a <i>fresh</i> stream.
* <p>This requirement is particularly important when you consider an API such
* as JavaMail, which needs to be able to read the stream multiple times when
* creating mail attachments. For such a use case, it is <i>required</i>
* that each {@code getInputStream()} call returns a fresh stream.
* @return the input stream for the underlying resource (must not be {@code null})
* @throws IOException if the stream could not be opened
* @see org.springframework.mail.javamail.MimeMessageHelper#addAttachment(String, InputStreamSource)
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* Return whether this resource actually exists in physical form.
* <p>This method performs a definitive existence check, whereas the
* existence of a {@code Resource} handle only guarantees a
* valid descriptor handle.
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* Return whether the contents of this resource can be read,
* e.g. via {@link #getInputStream()} or {@link #getFile()}.
* <p>Will be {@code true} for typical resource descriptors;
* note that actual content reading may still fail when attempted.
* However, a value of {@code false} is a definitive indication
* that the resource content cannot be read.
* @see #getInputStream()
*/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* Return whether this resource represents a handle with an open
* stream. If true, the InputStream cannot be read multiple times,
* and must be read and closed to avoid resource leaks.
* <p>Will be {@code false} for typical resource descriptors.
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* Return a URL handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URL,
* i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a URI handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URI,
* i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a File handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as absolute
* file path, i.e. if the resource is not available in a file system
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* Determine the content length for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* Determine the last-modified timestamp for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* Create a resource relative to this resource.
* @param relativePath the relative path (relative to this resource)
* @return the resource handle for the relative resource
* @throws IOException if the relative resource cannot be determined
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* Determine a filename for this resource, i.e. typically the last
* part of the path: for example, "myfile.txt".
* <p>Returns {@code null} if this type of resource does not
* have a filename.
*/
String getFilename();
/**
* Return a description for this resource,
* to be used for error output when working with the resource.
* <p>Implementations are also encouraged to return this value
* from their {@code toString} method.
* @see Object#toString()
*/
String getDescription();
}
2 加载Bean
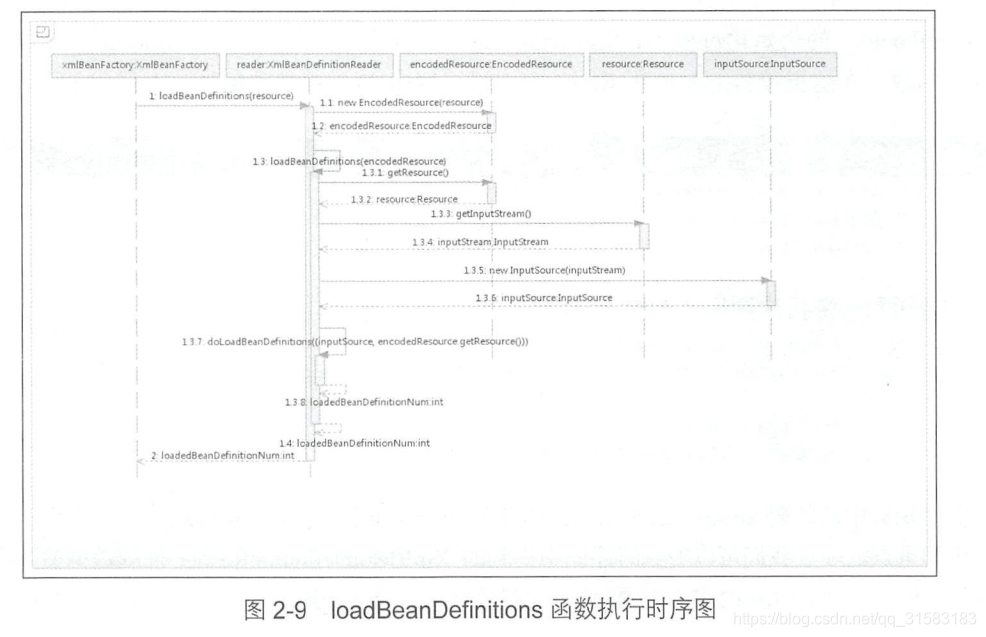
在XmlBeanFactory构造函数中调用了XmlBeanDefinitionReader类型的reader属性提供的方法this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource),它是整个资源加载的切入点,如下图可看整个处理流程:
- 封装资源文件。当进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader后首先对参数Resource使用EncodedResource进行封装;
- 获取输入流。从Resource中获取对应的InputStream并构造InputSource;
- 通过构造的InputSource和Resource继续调用函数doLoadBeanDefinitions。
下面是loadBeanDefinitions的代码:
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}有上可以看出,loadBeanDefinitions中产生了一个EncodedResource实例作为参数,它的作用主要是用于对资源文件的编码进行处理的。它的主要逻辑体现在getReader()方法中,当设置了编码的时候spring会使用响应的编码作为输入流的编码。
public Reader getReader() throws IOException {
if (this.charset != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.charset);
}
else if (this.encoding != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.encoding);
}
else {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream());
}
}getReader构造好一个有编码(encoding)的InputStramReader。当构造好EncodedResource对象后再转入可复用方法loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource))。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}由上代码可知,对传入resource参数做了封装,目的是Resource可能存在编码要求的情况。其次通过SAX读取XML文件的方式准备InputSource对象,最后将InpuSource对象作为参数传入真正的核心处理部分doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())。
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}上述代码做了三件事:
- 获取XML文件的验证模式;
- 加载XML文件,并得到对应的Document;
- 根据返回的Document注册Bean信息。
这三个步骤支撑着整个Spring容器部分的实现,尤其是第3步对配置文件的解析。下面依次来说这三个步骤。
四 获取XML的验证模式
XML文件的验证模式有两种:DTD和XSD。
1 DTD和XSD的区别
DTD即文档类型定义,是一种XML约束模式语言,是XML文件的验证机制,属于XML文件组成的一部分。DTD 是一种保证XML文档格式正确的有效方法,可以通过比较XML文档和DTD文件来看文档是否符合规范,元素和标签使用是否正确。
一个 DTD文档包含:元素的定义规则,元素间关系的定义规则,元素可使用的属性,可使用的实体或符号规则。 DTD和XSD相比:DTD 是使用非 XML 语法编写的。 DTD 不可扩展,不支持命名空间,只提供非常有限的数据类型 .
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN"
"http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd">XML Schema语言也就是XSD。XML Schema描述了XML文档的结构。 可以用一个指定的XML Schema来验证某个XML文档,以检查该XML文档是否符合其要求。文档设计者可以通过XML Schema指定一个XML文档所允许的结构和内容,并可据此检查一个XML文档是否是有效的。XML Schema本身是一个XML文档,它符合XML语法结构。可以用通用的XML解析器解析它。 一个XML Schema会定义:文档中出现的元素、文档中出现的属性、子元素、子元素的数量、子元素的顺序、元素是否为空、元素和属性的数据类型、元素或属性的默认 和固定值。
XSD是DTD替代者的原因,一是据将来的条件可扩展,二是比DTD丰富和有用,三是用XML书写,四是支持数据类型,五是支持命名空间。
XML Schema的优点:
- XML Schema基于XML,没有专门的语法;
- XML Schema可以象其他XML文件一样解析和处理;
- XML Schema比DTD提供了更丰富的数据类型;
- XML Schema提供可扩充的数据模型;
- XML Schema支持综合命名空间;
- XML Schema支持属性组。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd> 2 验证模式的读取
spring通过getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource)方法来获取对应资源的验证模式。
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) {
int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode();
if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return validationModeToUse;
}
int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource);
if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return detectedMode;
}
// Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD,
// since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until
// detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag).
return VALIDATION_XSD;
}通过上述代码可知,spring如果设定了验证模式则使用设定的验证模式(可以通过对调用XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的setValidationMode()方法进行设定),否则使用自动检测的方式。而自动检测验证模式的功能是在函数detectValidationMode()方法中实现的,在detectValidationMode()方法中又将自动检测验证模式的工作交给了专门处理的类XmlValidationModeDetector,调用了它自己的detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream)方法,具体如下;
XmlBeanFactory的detectValidationMode()方法:
protected int detectValidationMode(Resource resource) {
if (resource.isOpen()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Passed-in Resource [" + resource + "] contains an open stream: " +
"cannot determine validation mode automatically. Either pass in a Resource " +
"that is able to create fresh streams, or explicitly specify the validationMode " +
"on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance.");
}
InputStream inputStream;
try {
inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Unable to determine validation mode for [" + resource + "]: cannot open InputStream. " +
"Did you attempt to load directly from a SAX InputSource without specifying the " +
"validationMode on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance?", ex);
}
try {
return this.validationModeDetector.detectValidationMode(inputStream);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unable to determine validation mode for [" +
resource + "]: an error occurred whilst reading from the InputStream.", ex);
}
}XmlValidationModeDetector的detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream)方法:
public int detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// Peek into the file to look for DOCTYPE.
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
try {
boolean isDtdValidated = false;
String content;
while ((content = reader.readLine()) != null) {
content = consumeCommentTokens(content);
if (this.inComment || !StringUtils.hasText(content)) {
continue;
}
if (hasDoctype(content)) {
isDtdValidated = true;
break;
}
if (hasOpeningTag(content)) {
// End of meaningful data...
break;
}
}
return (isDtdValidated ? VALIDATION_DTD : VALIDATION_XSD);
}
catch (CharConversionException ex) {
// Choked on some character encoding...
// Leave the decision up to the caller.
return VALIDATION_AUTO;
}
finally {
reader.close();
}
}
private boolean hasDoctype(String content) {
return content.contains(DOCTYPE);
}spring用来检测验证模式的办法就是判断是否包含DOCTYPE,如果包含就是DTD,否则就是XSD。
五 获取Document
经过验证模式准备的步骤就可以进行Document加载了,XmlBeanFactoryReader将加载Document委托给DocumentLoader执行,DocumentLoader只是接口,真正的调用者是DefaultDocumentLoader()。
private DocumentLoader documentLoader = new DefaultDocumentLoader();
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}DefaultDocumentLoader的loadDocument()方法如下:
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}由上面代码可知,spring通过创建DocumentBuilderFactory,再通过DocumentBuilderFactory创建DocumentBuilder,进而解析inputSource来返回Document对象。
对与createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler)中的entityResolver参数,它是通过getEntityResolver()函数获取的返回值。
XmlBeanDefinitionReader的getEntityResolver()函数:
protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() {
if (this.entityResolver == null) {
// Determine default EntityResolver to use.
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader != null) {
this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader);
}
else {
this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader());
}
}
return this.entityResolver;
}1 EntityResolver的作用
在loadDocument方法中涉及一个参数EntityResolver,如果SAX应用程序需要实现自定义处理外部实体,则必须实现此接口并使用setEntityResolver()方法向SAX驱动器注册一个实例。也就是说,对于解析一个XML,SAX首先读取该XML文档的声明,根据声明去寻找对应的DTD定义,以便对文档进行一个验证,默认的寻找规则即通过网络来下载相应的DTD声明,并进行认证。
EntityResolver的作用是项目本身就可以提供一个如何寻找DTD声明的方法,即由程序来实现寻找DTD声明的过程,比如我们将DTD文件放在项目某处,在实现时直接将此文档读取并返回给SAX即可。这样就避免了通过网络来寻找相应的声明。
EntityResolver接口的resolveEntity方法:这个方法接收publicId,systemId两个参数,并返回InputSource对象。
public abstract InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId,
String systemId)
throws SAXException, IOException;
}在验证模式为XSD的配置文件中,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.2.xsd">- publicId:null;
- systemId:http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd;
验证文件默认的加载方式是通过网络下载,但是这种方式在网络状况不好时容易出现错误,一般可以将验证文件放在自己的工程中。
DelegatingEntityResolver类的resolveEntity,Spring使用DelegatingEntityResolver作为EntityResolver的实现类。
@Override
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException {
if (systemId != null) {
if (systemId.endsWith(DTD_SUFFIX)) {
return this.dtdResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId);
}
else if (systemId.endsWith(XSD_SUFFIX)) {
return this.schemaResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId);
}
}
return null;
}由上述代码可以看出不同的验证模式使用不同的resolveEntity()方法:它使用的是PluggableSchemaResolver的resolveEntity()方法,下面是代码。
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public id [" + publicId +
"] and system id [" + systemId + "]");
}
if (systemId != null) {
String resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get(systemId);
if (resourceLocation != null) {
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(resourceLocation, this.classLoader);
try {
InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream());
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found XML schema [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + resourceLocation);
}
return source;
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Couldn't find XML schema [" + systemId + "]: " + resource, ex);
}
}
}
}
return null;
}六 解析及注册BeanDefinitions
当文件转换为Document后,下面就是提取及注册bean的过程。当获得Document对象后,就开始转入提取注册bean的流程,它会进入下面的方法:
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//获取Document对象
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 通过doc和resource注册Bean
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//实例化BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
//统计BeanDefinitions加载个数
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//记录本次加载的BeanDefinitions个数
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}通过获得的doc对象并将它交给BeanDefinitionDocumentReader(它是一个接口,它的默认实现类为DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader,由下面代码可以看出)。
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
.........
...........
private Class<?> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class;
protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() {
return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass));
}
...............
......
}当进入到documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource))方法,它提取出root对象,然后将root对象作为参数继续BeanDefinitions的注册。
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}registerBeanDefinitions()方法中继续调用了doRegisterBeanDefinitions()方法开始进行解析,
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
//用于处理解析
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//对profile进行处理
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
//解析前处理,留给子类实现
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
//解析后处理,留给子类实现
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}上述代码可以看出,先对profile进行了处理,然后调用了preProcessXml(root)和postProcessXml(root)方法,然而这两个方法是空的,这个类是面向继承设计的,未来让子类对Bean解析前后进行处理,继承的子类只需重写这两个方法就可以。
/**
* Allow the XML to be extensible by processing any custom element types first,
* before we start to process the bean definitions. This method is a natural
* extension point for any other custom pre-processing of the XML.
* <p>The default implementation is empty. Subclasses can override this method to
* convert custom elements into standard Spring bean definitions, for example.
* Implementors have access to the parser's bean definition reader and the
* underlying XML resource, through the corresponding accessors.
* @see #getReaderContext()
*/
protected void preProcessXml(Element root) {
}
/**
* Allow the XML to be extensible by processing any custom element types last,
* after we finished processing the bean definitions. This method is a natural
* extension point for any other custom post-processing of the XML.
* <p>The default implementation is empty. Subclasses can override this method to
* convert custom elements into standard Spring bean definitions, for example.
* Implementors have access to the parser's bean definition reader and the
* underlying XML resource, through the corresponding accessors.
* @see #getReaderContext()
*/
protected void postProcessXml(Element root) {
}七 Profile属性
在注册bean的开始是对PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE(即profile)属性的解析。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.2.xsd">
<beans profile="dev"></beans>
</beans>这个属性定义了程序的运行环境,它可以是开发环境或者生产环境,可以在配置文件中同时配置两个环境,在需要时可以进行切换,部署环境。其中最常用就是部署数据库。
在web.xml声明下列配置,声明当前的运行环境。
八 解析并注册BeanDefinition
处理了profile后就可以进行XML读取了,下面是DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的parseBeanDefinitions方法
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}默认配置文件方式:
<bean id="userService" class="UserServiceImpl"/>
自定义方式:
<tx:annotation-driven/>
Spring中注册Bean可以通过XML配置文件方式和自定义方式,如果是注解方式,需要用户实现一些接口和配置。
对于根节点或者子节点如果是默认命名空间的话采用parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)方法解析,否则使用parseCustomElement(ele)方法解析对自定义方式进行解析。
判断命名空间的方法是delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele),它其实调用的是getNamespaceURI()方法,并与http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans比对,如果一致则为默认,否则是自定义。
public boolean isDefaultNamespace(String namespaceUri) {
return (!StringUtils.hasLength(namespaceUri) || BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI.equals(namespaceUri));
}
public boolean isDefaultNamespace(Node node) {
return isDefaultNamespace(getNamespaceURI(node));
}