面向对象特性之——封装
封装——将实体特征的属性隐藏起来,对象和外界仅通过公共方法进行交流,这样可以提高程序的可读性,安全性,改善程序的可维护性。
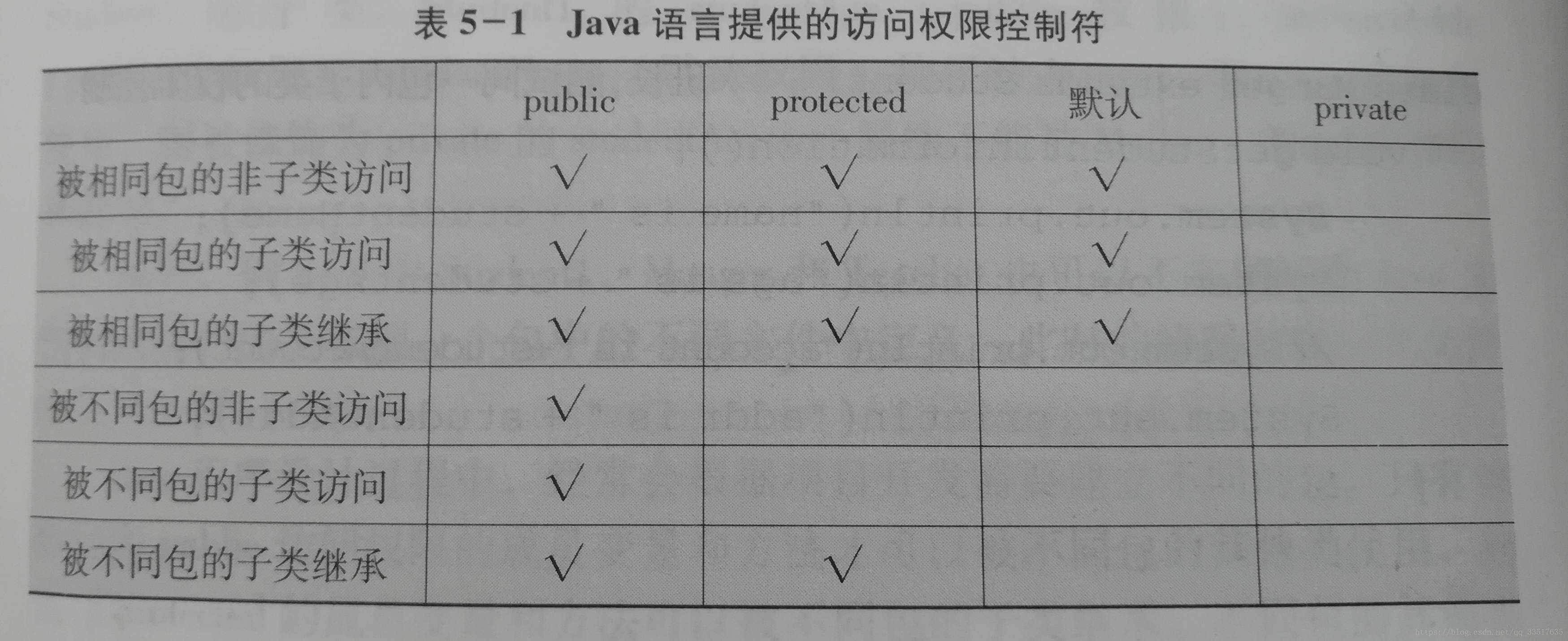
数据的隐藏于开放对外的接口可以提高访问权限控制符来实现,权限控制符可以用来设置类、成员变量、成员方法等的访问权限。
JAVA 提供public,protected,private和默认等4中访问控制符,在类、成员变量,成员方法的前面都可以使用这4种关键字。没有显示的使用,为默认控制类型。
1 public
public权限最具有开放性,可以用来修饰类、类与接口的成员(包括成员变量、成员方法)。由public修饰的类或类成员可以被任何类访问,他们既可以位于同一个包中,也可以位于不同的包中。修饰为public的类可以被任何类及成员方法访问或引用。修饰为public的类成员变量或方法,可以在其他类中无限制地访问该成员(变量或方法)。
为了保证数据的隐藏性和安全性,不建议把所有的而长远变量或方法全部设置为public,通常只将公共类或公共接口的成员方法指定为public。
2 protected
修饰类的成员变量或方法,具有protected访问特性的成员可以被本类、本包中的其他类访问,可以被其他包中的子类继承,它的可访问性低于public,高于默认。
3 默认
如果没有指定访问权限控制符,他们的权限即为默认权限。称为包权限。
4 private
私有访问控制符private用来声明类的私有成员,他提供了最高的保护级别。用private修饰的成员变量或方法只能被该类自身所访问和修改,而不能被其他类(包括该类的子类)来获取和引用。
【例5-9】同一包内访问权限控制符使用
```
package com.ch5;
public class Ex5_9_Student {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student1 zhangGang = new Student1(19,"山西太原","张刚",350);
Teacher missLiu = new Teacher(35,"北京","刘老师",2000,"102198");
missLiu.question(zhangGang);
}
}
class Student1{
public int studentAge;
protected String studentAddr;
String studentName;
private int studentAccount;
public Student1(int studentAge,String studentAddr,
String studentName,int studentAccount){
this.studentAccount = studentAccount;
this.studentAge = studentAge;
this.studentAddr = studentAddr;
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public Student1(){
this.studentAge = 18;
}
}
class Manager extends Student1{// 同一包内子类的权限控制
void getStudentInformation(){
System.out.println("name is " + studentName);
System.out.println("age is " + studentAge);
// System.out.println("account is " + studentAccount);
// 私有权限的studentAccount 不能被子类Manager访问
System.out.println("addr is " + studentAddr);
}
}
class Teacher{
public int age;
protected String addr;
String name;
private int account;
String teacherID;
public Teacher(int age,String addr,String name,
int account,String teacherID){
this.age = age;
this.addr = addr;
this.name = name;
this.account = account;
this.teacherID = teacherID;
}
public void SetInfo(String teacherID){
this.teacherID = teacherID;
}
public void question(Student1 s){
System.out.println(s.studentAddr + "\t" + s.studentAge + "\t" + s.studentName);// studentAddr保护权限 同一个包内 可以访问
// System.out.println("\t" + s.studentAccount);
// 私有权限
}
}
结果:山西太原 19 张刚
[例5-10]不同包内访问权限控制符的使用
package com.course;
public class Course {
public String courseID;
public float credit;
protected String courseCharacter;
String description; // 默认访问权限
private String term;
public Course(){
// 为空
}
public Course(String courseID,float credit,String courseCharacter,
String description,String term){
this.courseCharacter = courseCharacter;
this.courseID = courseID;
this.credit = credit;
this.description = description;
this.term = term;
}
}
// end
package com.ch5;
import com.course.*;// 为了使用此包里的Course类
public class Ex5_10_Assitanter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Examination exam;
Student1 zhangGang = new Student1(19,"山西太原","张刚",350);
Teacher missLiu = new Teacher(35,"beijing","刘老师",2000,"102198");
ComputerCourse c1 = new ComputerCourse(missLiu,"12345",3.5f,"必修","java语言程序设计","5");
c1.putInfo();
exam = new Examination(zhangGang,c1,55f);
exam.putCredit();
System.out.println();
}
}
class Examination{
Student1 student;
float score;
Course course;
public Examination(Student1 student,Course course,float score){ // 带参数的构造方法
this.student = student;
this.course = course;
this.score = score;
}
public float putCredit(){
float c = 0.0f;// c 实际学分
if(score >= 60){
c = course.credit;
System.out.println("通过考试,实际学分为 " + c);
}else{
c = 0;
System.out.println("未通过考试,实际学分为 " + c);
}
// System.out.println("课程性质" + courseCharacter);
// courseCharacter(Course类的成员)为protected权限,不可被不同包的非子类访问 Examination和 Course这两个类是不同包的类
return c;
}
}// class Examination类定义结束
class ComputerCourse extends Course{
Teacher teacher; // ComputerCourse 类比他的父类Course 多一个成员 Teacher
public ComputerCourse(Teacher teacher,String courseID,
float credit,String courseCharacter,String description,String term){// 子类的构造方法
/**
* 在构造方法中,可以调用当前类和父类的第一个构造方法,但必须是方法体的第一条语句。
* 使用当前类的构造方法用 this
* 使用其父类的构造方法用 super
*/
super(courseID,credit,courseCharacter,description,term);// 子类使用父类的构造方法
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public void putInfo(){
System.out.println("课程编号 " + courseID); // public
System.out.println("学分 " + credit); // public
System.out.println("课程性质 " + courseCharacter);
// courseCharacter protected 可以被相同包下的子类继承和访问 被不同包的子类继承
// System.out.println("开设学期 " + term); // term为private权限,不可被不同包的子类访问
// System.out.println("课程介绍 " + description); // description为默认权限,不可被不同包的子类访问
}
}结果:
课程编号 12345
学分 3.5
课程性质 必修
未通过考试,实际学分为 0.0
5.getInfo和setInfo的使用示例
出于系统安全性考虑,一般类的属性成员定义为private形式保护起来,而将类的成员方法定义为public对外公开,这是类封装特性的一个体现。
package com.ch5;
public class Ex5_11_setGet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student2 s1;
s1 = new Student2();
s1.setGpa(26.5f);
s1.setInfo("赵强", "2015006377", "山西太原");
s1.getInfo();
}
}
class Student2{
public String name;
public String studentID;
private String address; // 住址 private
public String mobilePhone;
protected String major; // 专业 protected
private float gpa; // 绩点 private
public float getGpa() {
return gpa;
}
public void setGpa(float gpa) {
this.gpa = gpa;
}
public void setInfo(String n,String ID,String add){
name = n;
studentID = ID;
address = add;
}
public void setInfo(float g,String ID){
gpa = g;
studentID = ID;
}
public void getInfo(){
System.out.println("学号:" + studentID + "\t姓名:" + name
+ "\t地址:" + address + "\t总学分绩点:" + gpa );
}
}结果:
学号:2015006377 姓名:赵强 地址:山西太原 总学分绩点:26.5