1.前言
缓存(Cache)
缓存的作用:通过减少 IO 的方式,来提高程序的执行效率 。
MyBatis 的缓存:将 Select 语句的查询结果放到缓存(内存)当中,下一次还是这条 Select 语句的话,直接就从缓存当中取了,不再查询数据库。这样一方面减少了 IO,另一方面不再执行繁琐的查找算法。效率大大提升。
MyBatis 缓存包括:
- 一级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSession 中
- 二级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSessionFactory 中
- 或者是集成其它第三方的缓存:比如 EhCache(Java语言开发的),Memcache(C语言开发的)等。
注意:缓存只针对于 DQL(查询)语句,也就是说缓存机制只对应 Select 语句。
一旦你执行了,insert 或者delete或者 update 更新语句,无论是否是更新修改删除那个数据表中的记录,都会清空缓存,所以,这样就不会导致 缓存当中的 select 语句的数据是:旧的无用的数据了。
2. 准备工作
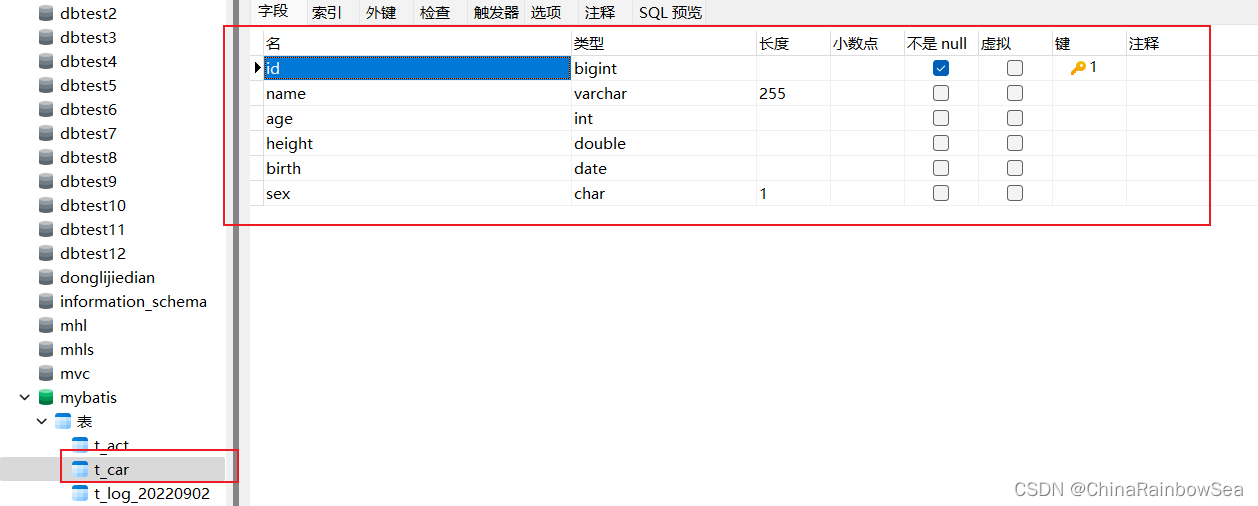
数据表结构的设计,数据表名为:t_car
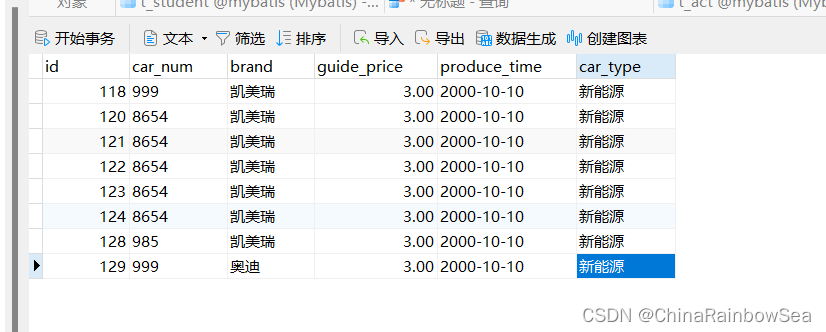
t_car 表中的数据信息:
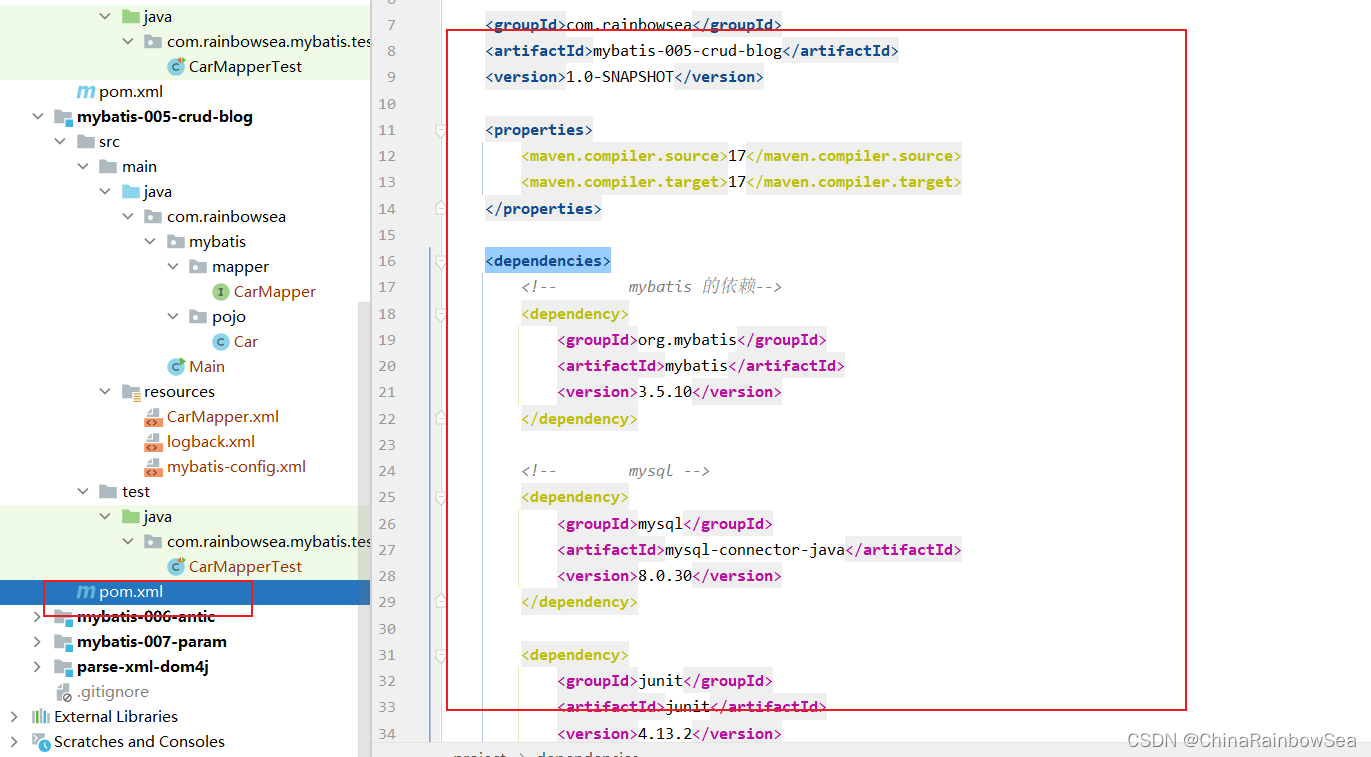
在pom.xml 文件当中配置相关的依赖的 jar 包如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.rainbowsea</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-005-crud-blog</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- mybatis 的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 logback的依赖,这个日志框架实现了slf4j 规范-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
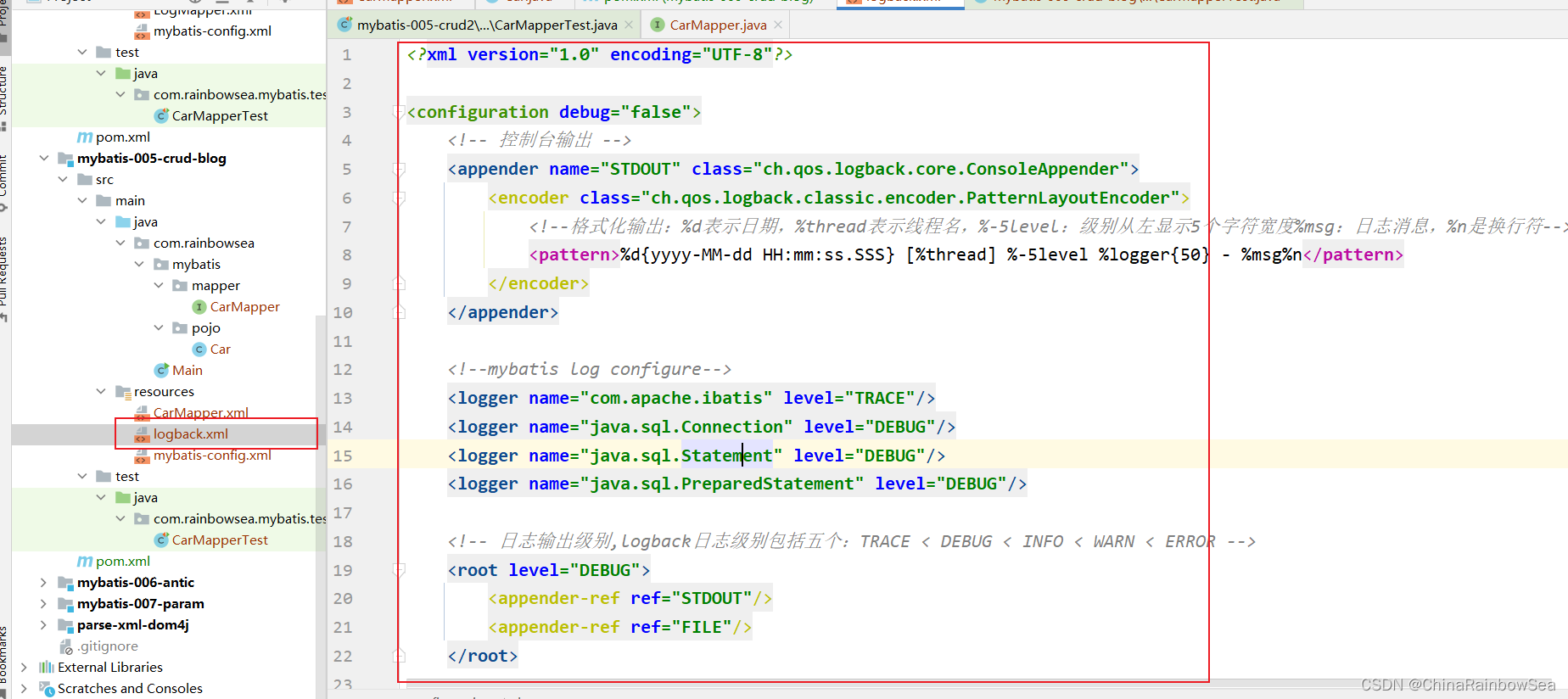
配置 logback 的配置文件,用于打印显示,我们的日志信息,方便我们查看我们的运行过程,效果。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="false">
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--mybatis log configure-->
<logger name="com.apache.ibatis" level="TRACE"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/>
<!-- 日志输出级别,logback日志级别包括五个:TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
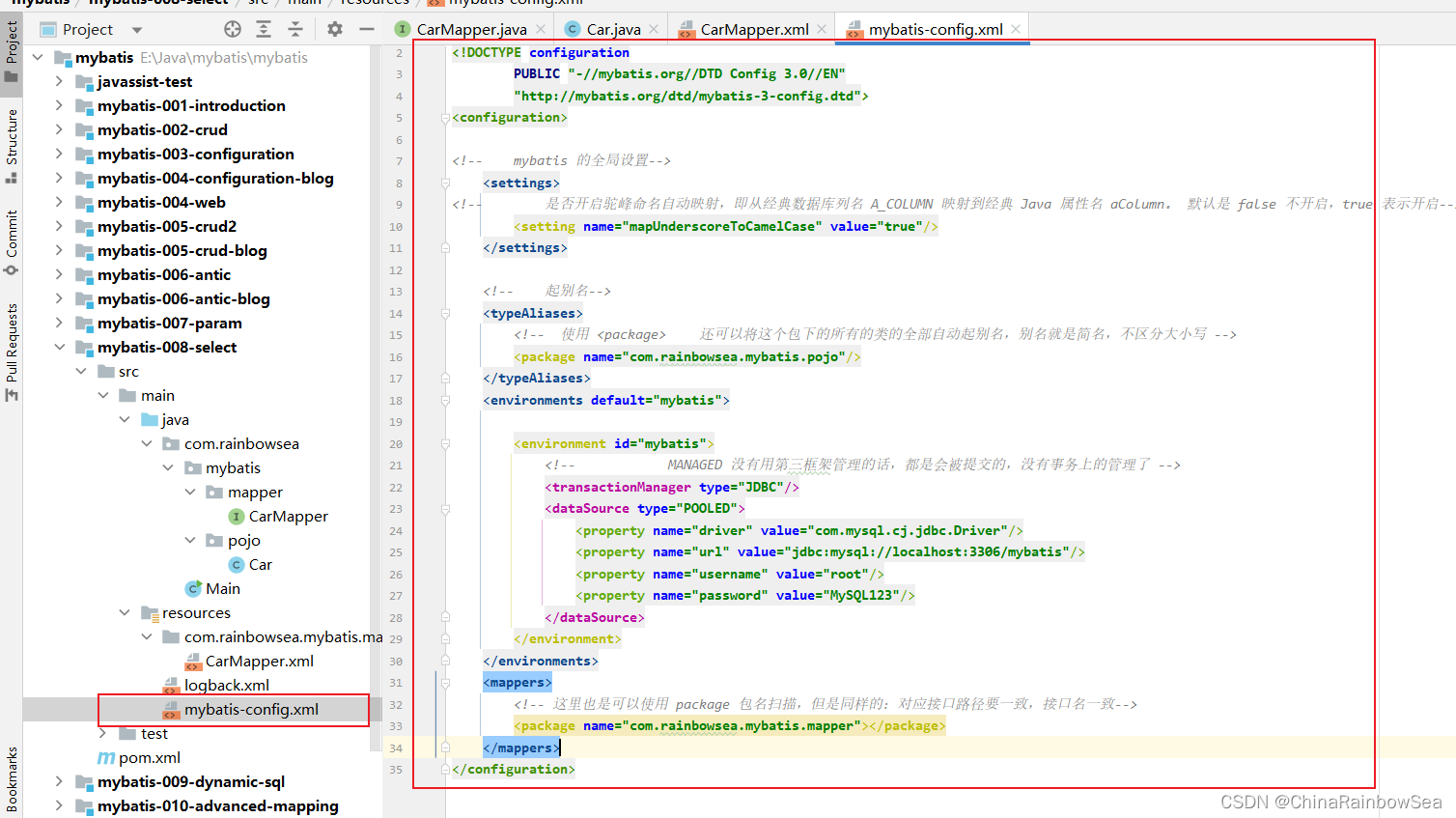
配置 MyBatis 的核心配置文件,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 使用 <package> 还可以将这个包下的所有的类的全部自动起别名,别名就是简名,不区分大小写 -->
<package name="com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="mybatis">
<environment id="mybatis">
<!-- MANAGED 没有用第三框架管理的话,都是会被提交的,没有事务上的管理了 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="MySQL123"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- 这里也是可以使用 package 包名扫描,但是同样的:对应接口路径要一致,接口名一致-->
<package name="com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper"></package>
</mappers>
</configuration>
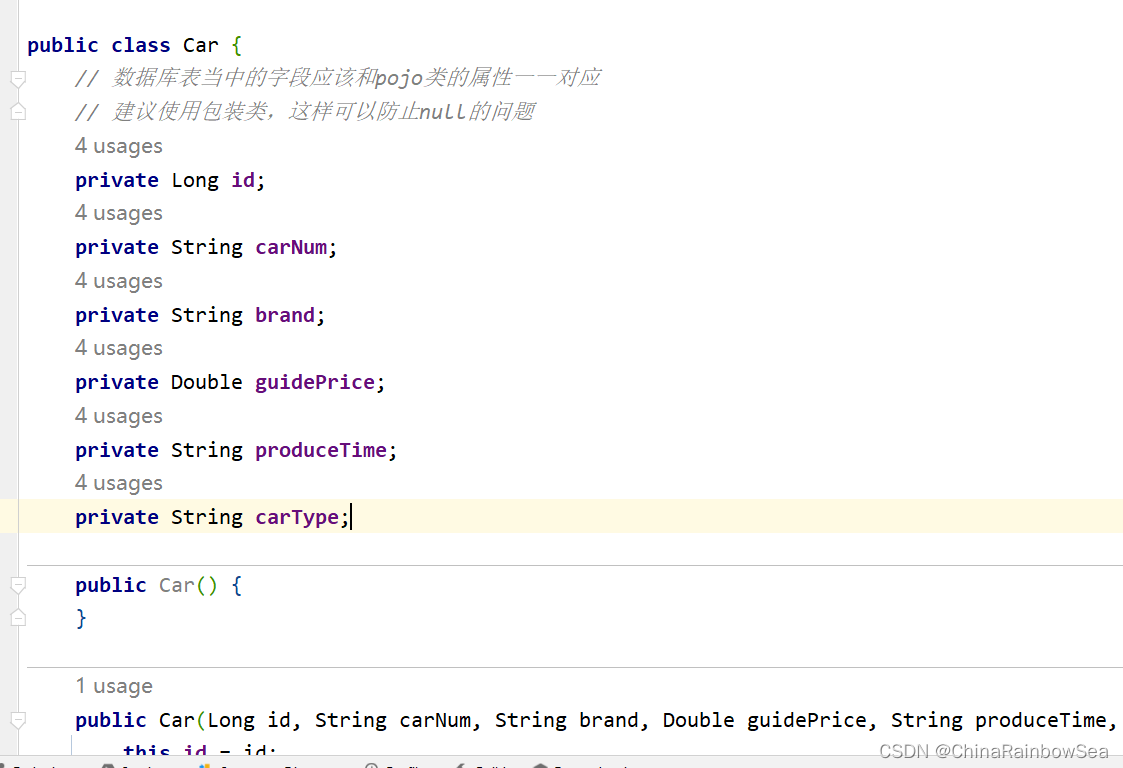
对照 t_car 创建的ORM 映射的 Car 类
注意:在MyBatis 当中对应的ORM ,一般在框架里对应的 Bean实体类,一定要实现该 set 和 get 方法以及无参数构造方法,无法框架无法使用反射机制,进行操作 。
建议用包装类,这样可以防止 Null的问题,因为(简单类型 int num = null ,是不可以赋值为 null)的编译无法通过
package com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo;
public class Car {
// 数据库表当中的字段应该和pojo类的属性一一对应
// 建议使用包装类,这样可以防止null的问题
private Long id;
private String carNum;
private String brand;
private Double guidePrice;
private String produceTime;
private String carType;
public Car() {
}
public Car(Long id, String carNum, String brand, Double guidePrice, String produceTime, String carType) {
this.id = id;
this.carNum = carNum;
this.brand = brand;
this.guidePrice = guidePrice;
this.produceTime = produceTime;
this.carType = carType;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"id=" + id +
", carNum='" + carNum + '\'' +
", brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", guidePrice=" + guidePrice +
", produceTime='" + produceTime + '\'' +
", catType='" + carType + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCarNum() {
return carNum;
}
public void setCarNum(String carNum) {
this.carNum = carNum;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Double getGuidePrice() {
return guidePrice;
}
public void setGuidePrice(Double guidePrice) {
this.guidePrice = guidePrice;
}
public String getProduceTime() {
return produceTime;
}
public void setProduceTime(String produceTime) {
this.produceTime = produceTime;
}
public String getcarType() {
return carType;
}
public void setcarType(String catType) {
this.carType = catType;
}
}
3. MyBatis 的一级缓存
一级缓存默认是开启的。不需要做任何配置。
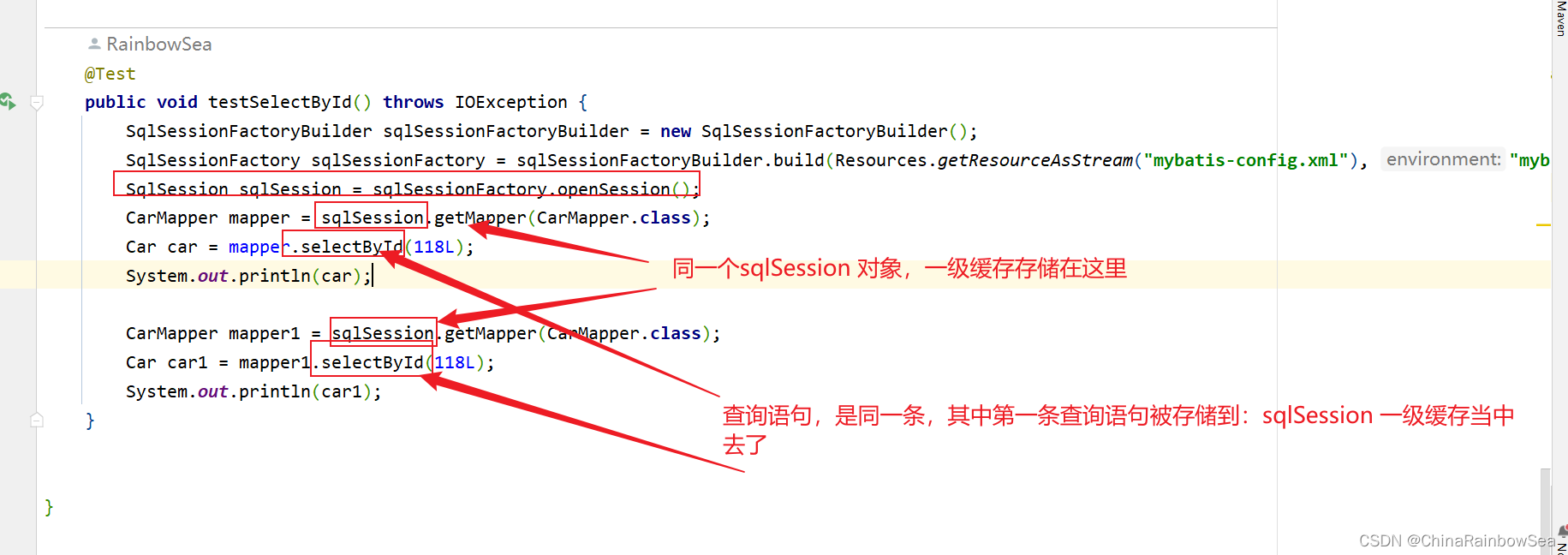
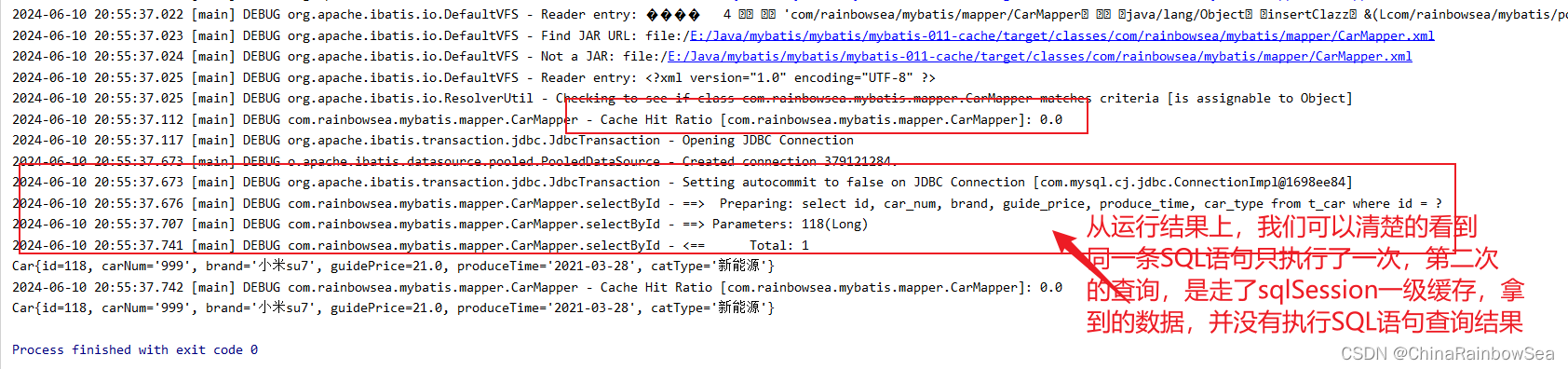
原理:只要使用同一个SqlSession对象执行同一条SQL语句,就会走缓存。
一级缓存的内容是:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSession 当中的。注意:其缓存的作用域
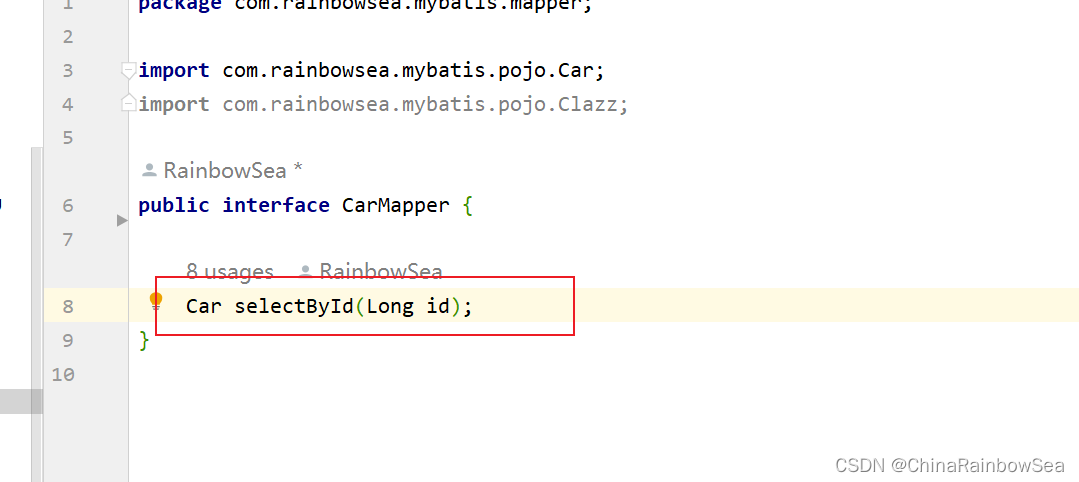
package com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Clazz;
public interface CarMapper {
Car selectById(Long id);
}
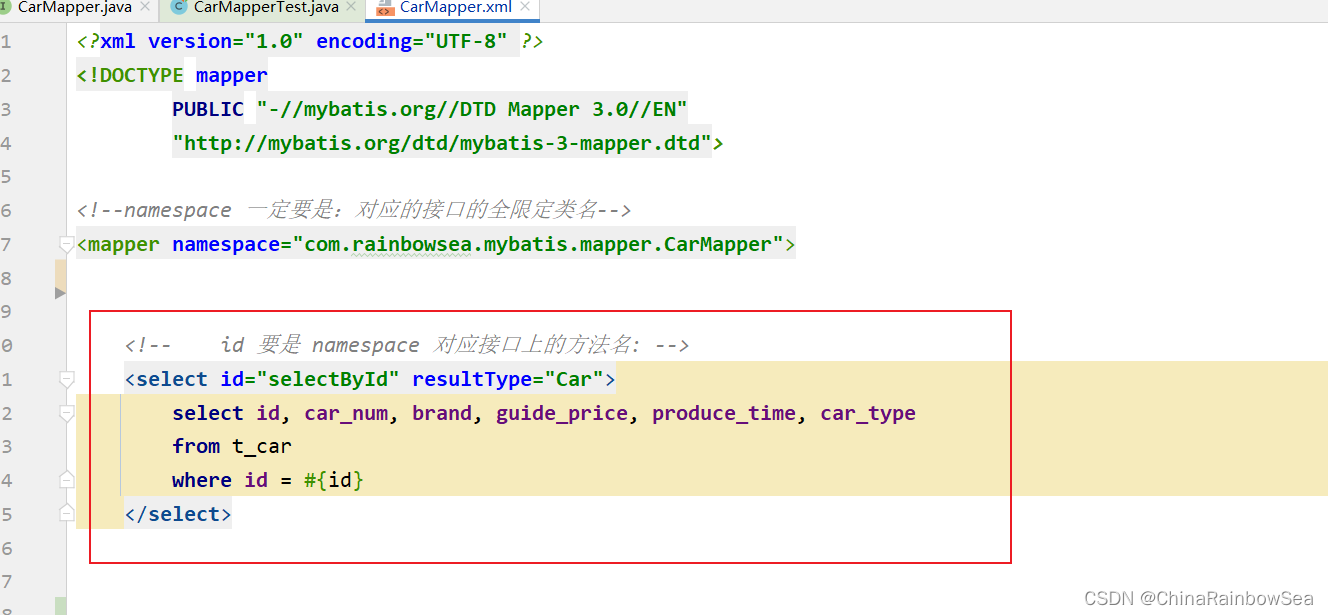
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
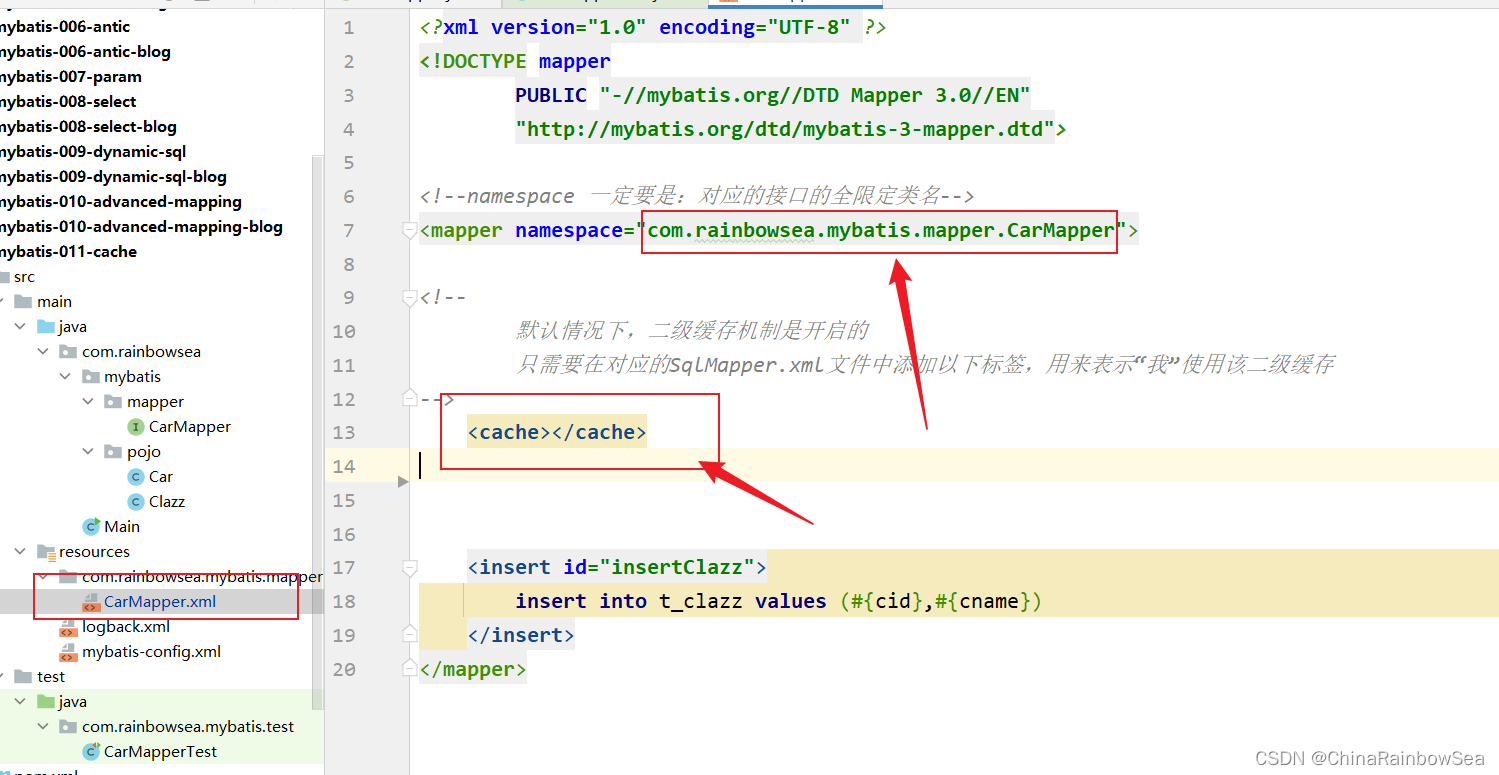
<!--namespace 一定要是:对应的接口的全限定类名-->
<mapper namespace="com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
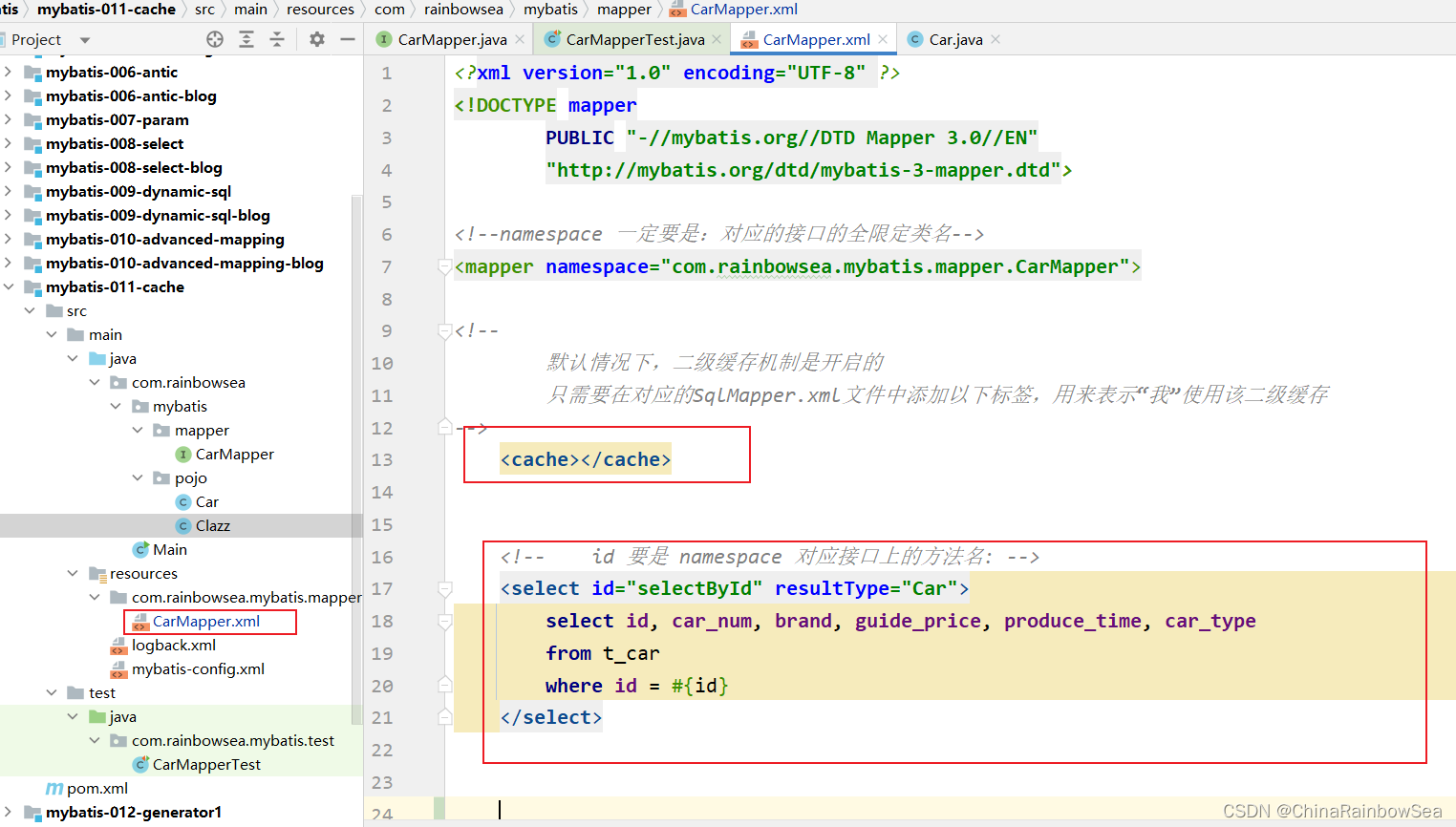
<!-- id 要是 namespace 对应接口上的方法名: -->
<select id="selectById" resultType="Car">
select id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type
from t_car
where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
运行测试:
@Test
public void testSelectById() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"), "mybatis");
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car);
CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car1 = mapper1.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car1);
}
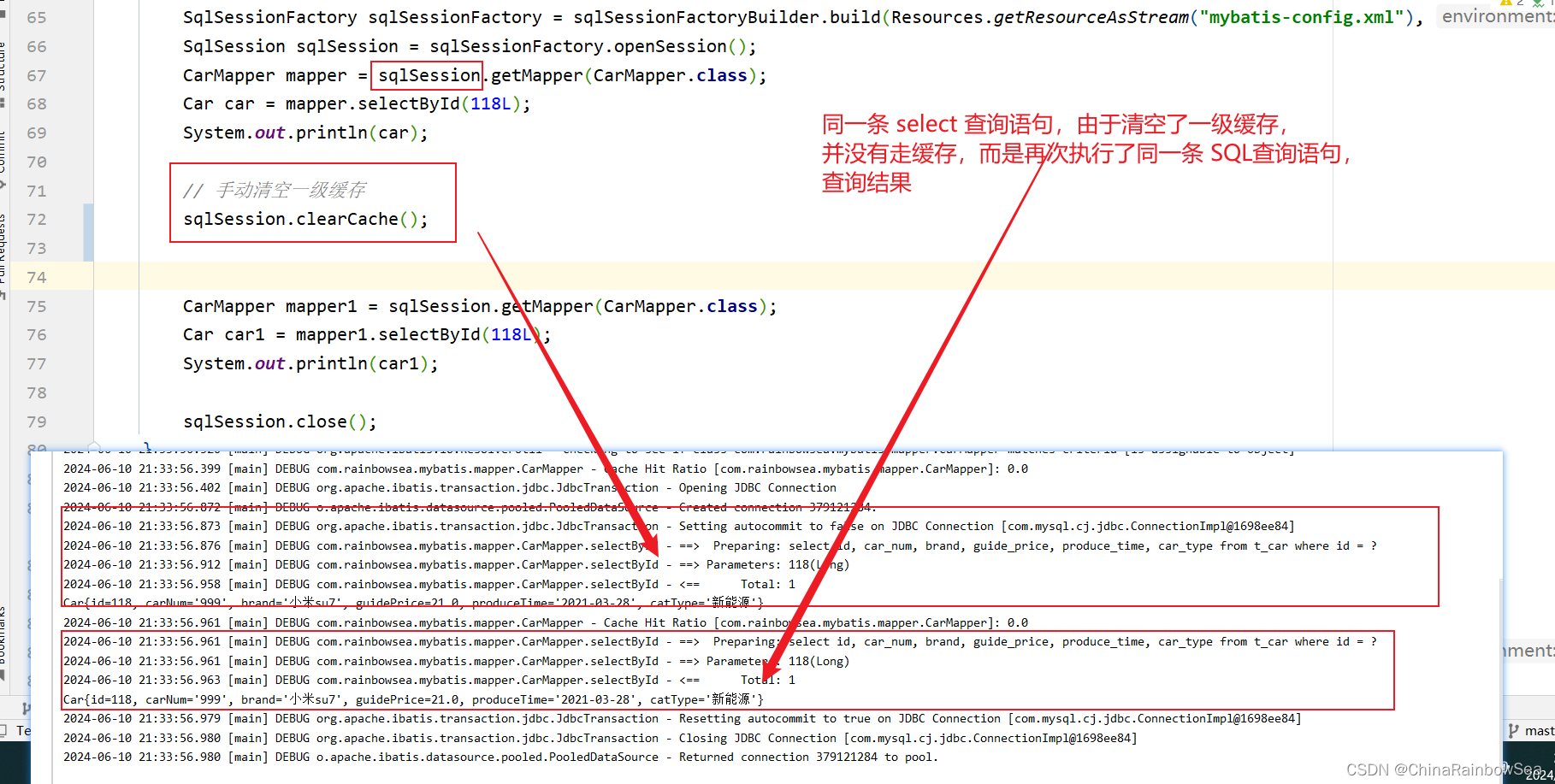
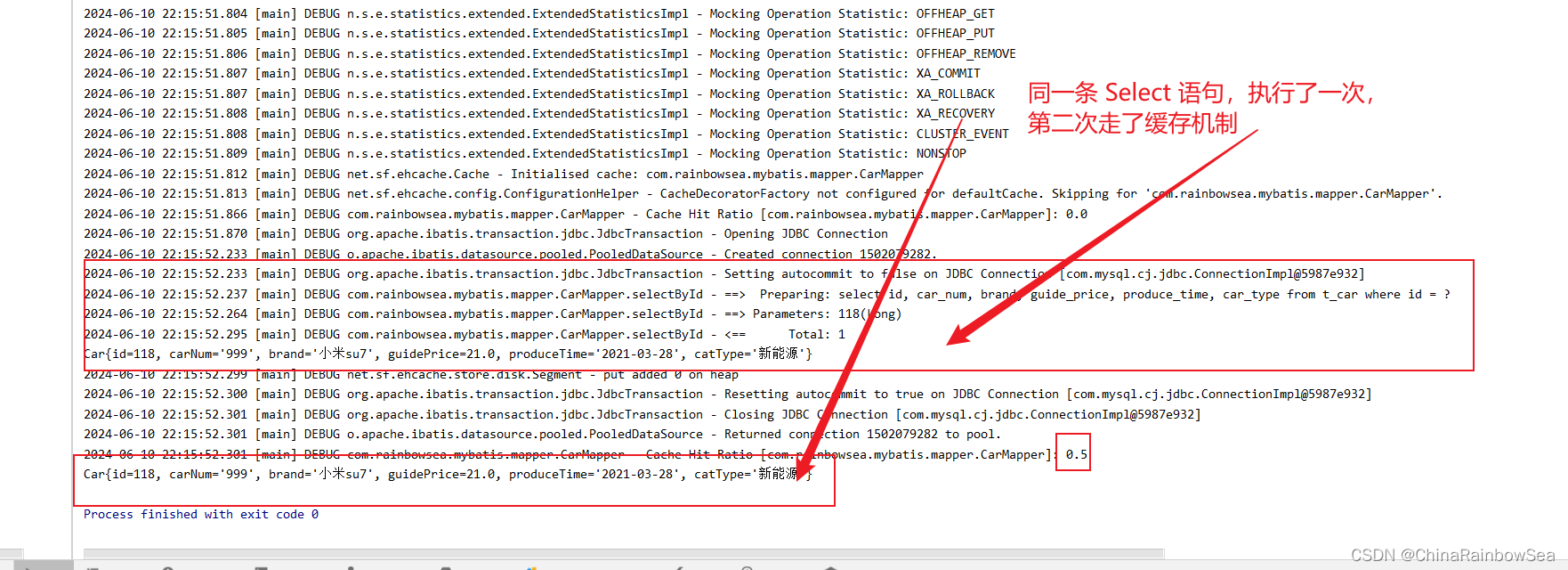
执行 Select 查询语句的时候,首先从对应的这个 Select 语句的 SqlSession 对象(一级缓存)当中查询是否有对应该Select 查询语句的缓存有的话,就不执行该 查询的 SQL 语句了,而是直接从一级缓存当中取出这个 Select 查询语句的数据结果。第一次执行 Select 语句(因为MyBatis 一级缓存默认是开启的)就会将存入到 sqlSession 对象(一级缓存)当中,方便后续的查询。
3.1 一级缓存失效情况/条件
一级缓存失效了,二级缓存同样也是失效的了,所以一级缓存失效的条件也是二级缓存失效的条件,他们的条件都是一样的。
思考:什么时候不走缓存?
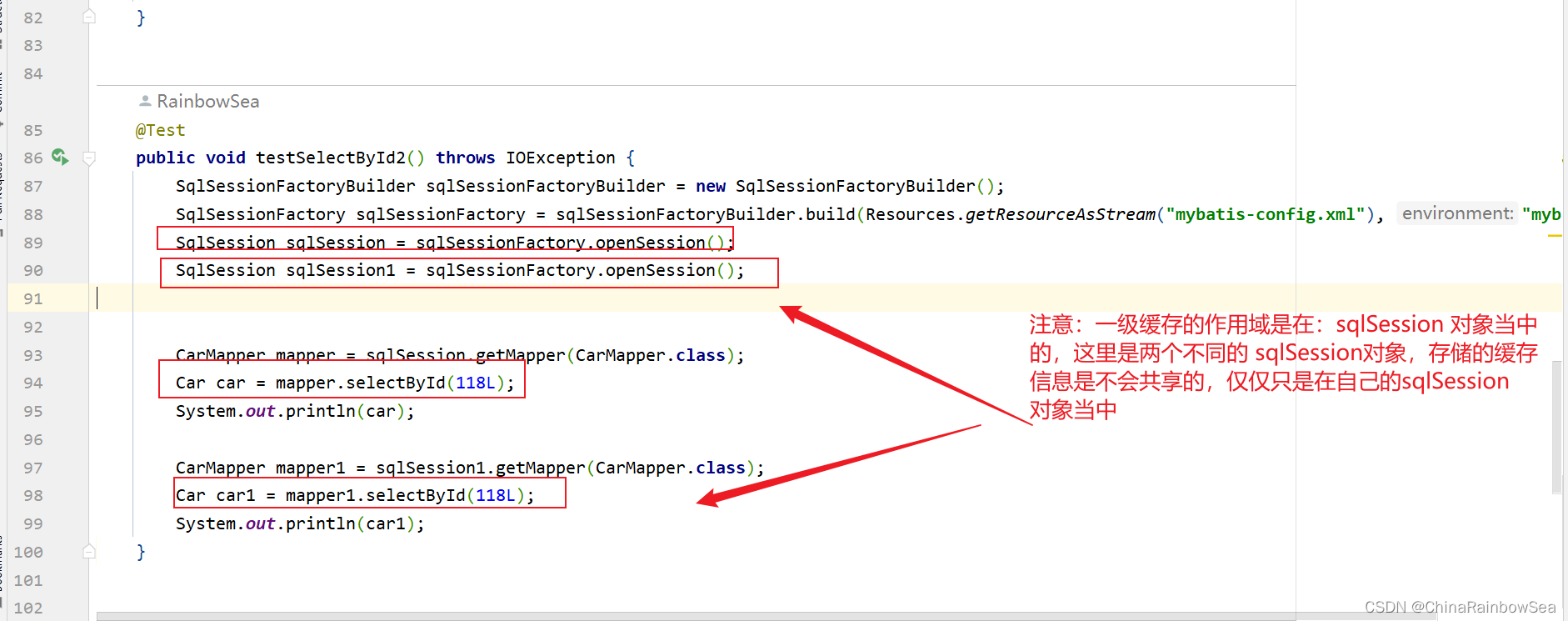
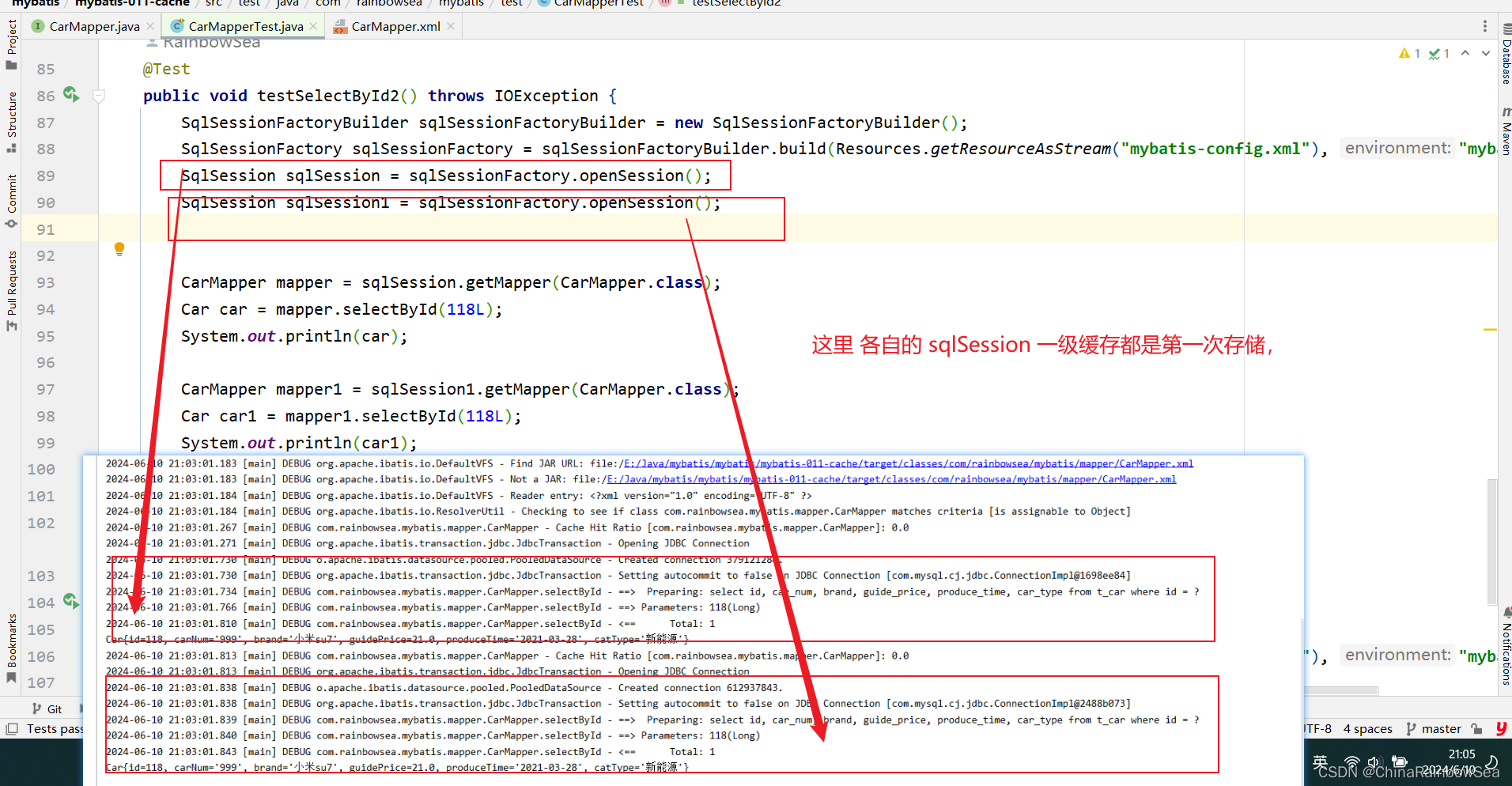
- sqlSession 对象不是同一个,肯定不走缓存。
- 查询条件不一样,肯定不走缓存。
一级缓存失效情况包括两种:
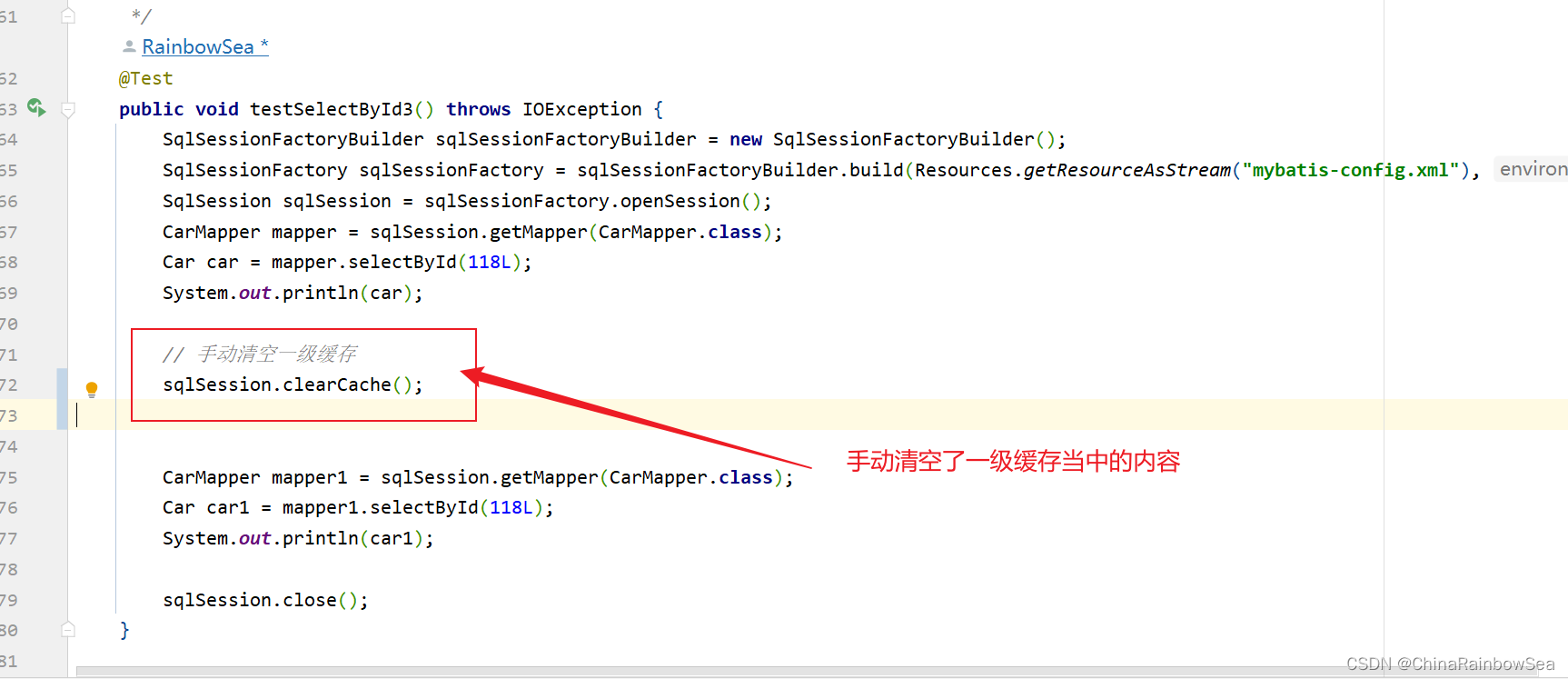
- 第一种:第一次查询和第二次查询之间,手动清空了一级缓存。执行:执行了 sqlSession.clearCache()方法,这是手动情况缓存。
- 第二种:执行了INSERT 或 DELETE 或UPDATE语句,不管你是操作任意一张表,都会清空一级缓存。
无论你是,你做了以上两件事的任意一种,都会让一级缓存清空 。
第一种:第一次查询和第二次查询之间,手动清空了一级缓存。执行:执行了 sqlSession.clearCache()方法,这是手动情况缓存。
测试:
package com.rainbowsea.mybatis.test;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Clazz;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CarMapperTest {
/**
* 思考:什么时候不走缓存?
* sqlsession 对象不是同一个,肯定不走缓存
* 查询条件不一样,肯定不走缓存
* <p>
* 思考什么时候一级缓存失败?
* 第一次DQL和第二次DQL之间你做了一下两件事的任意一种,都会让一级缓存清空
* 1. 执行了 sqlSession.clearCache()方法,这是手动情况缓存
* 2. 执行了INSERT 或 DELETE 或UPDATE语句,不管你是操作那张表,都会清空一级缓存
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testSelectById3() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"), "mybatis");
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car);
// 手动清空一级缓存
sqlSession.clearCache();
CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car1 = mapper1.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car1);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
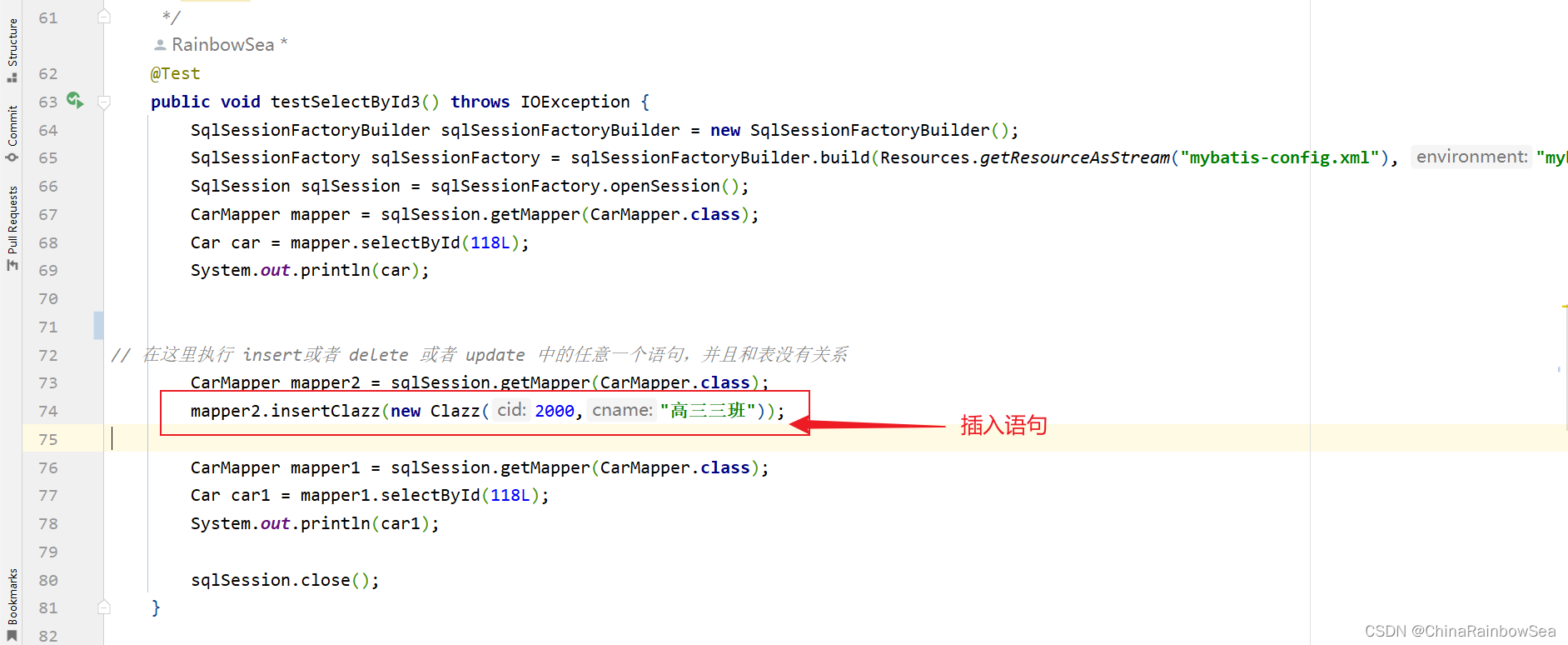
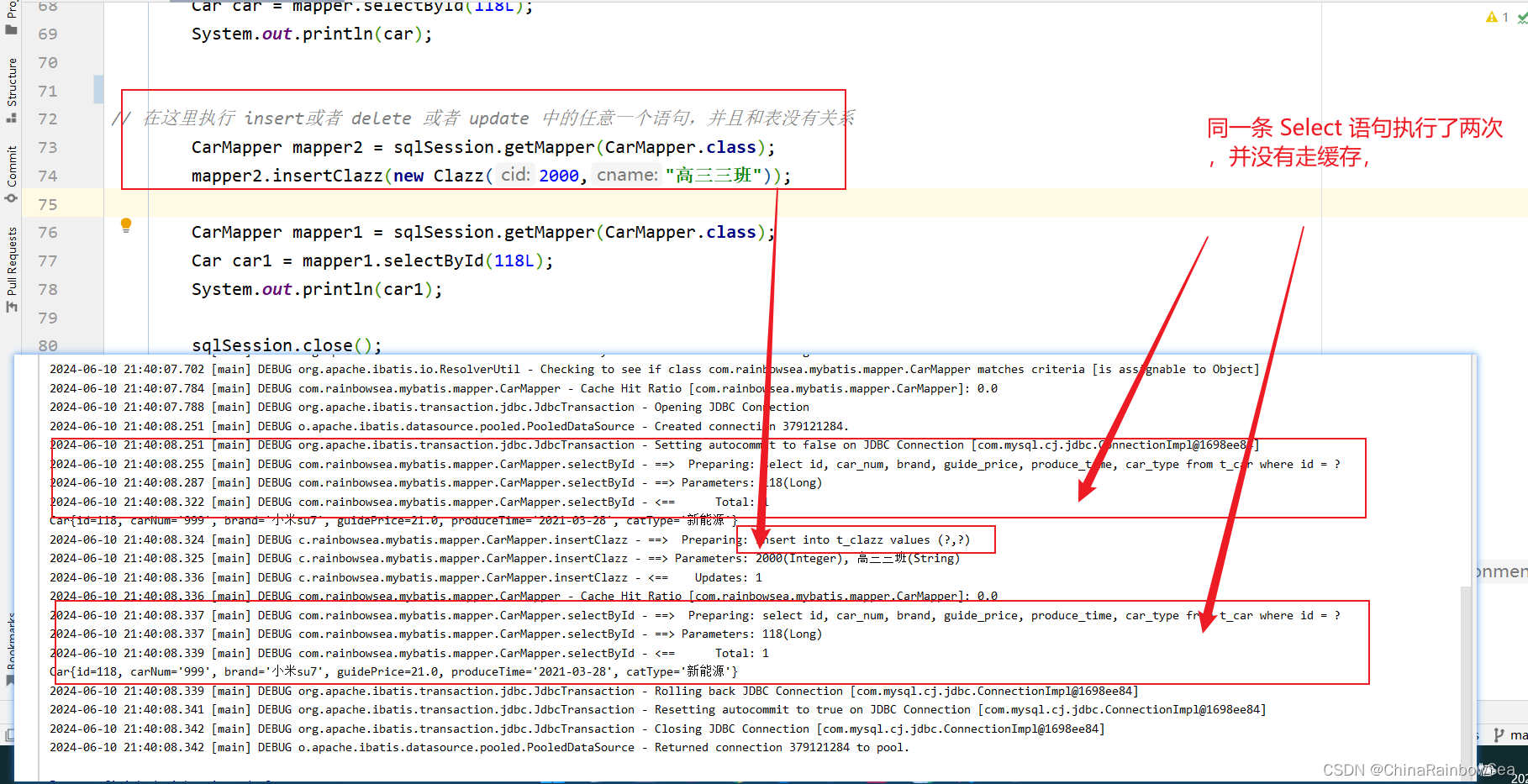
- 第二种:第一次查询和第二次查询之间,执行了增删改操作。【这个增删改和哪张表没有关系,只要有insert delete update操作,一级缓存就失效。】
@Test
public void testSelectById3() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"), "mybatis");
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car);
// 在这里执行 insert或者 delete 或者 update 中的任意一个语句,并且和表没有关系
CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
mapper2.insertClazz(new Clazz(2000,"高三三班"));
CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car1 = mapper1.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car1);
sqlSession.close();
}
4. MyBatis 的二级缓存
二级缓存的范围是SqlSessionFactory。
二级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSessionFactory 中,范围比一级缓存中更大一些。
使用二级缓存步骤/条件 :
- 要在 MyBatis 的核心配置文件当中,设置<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"> 全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。默认就是true,无需设置 。
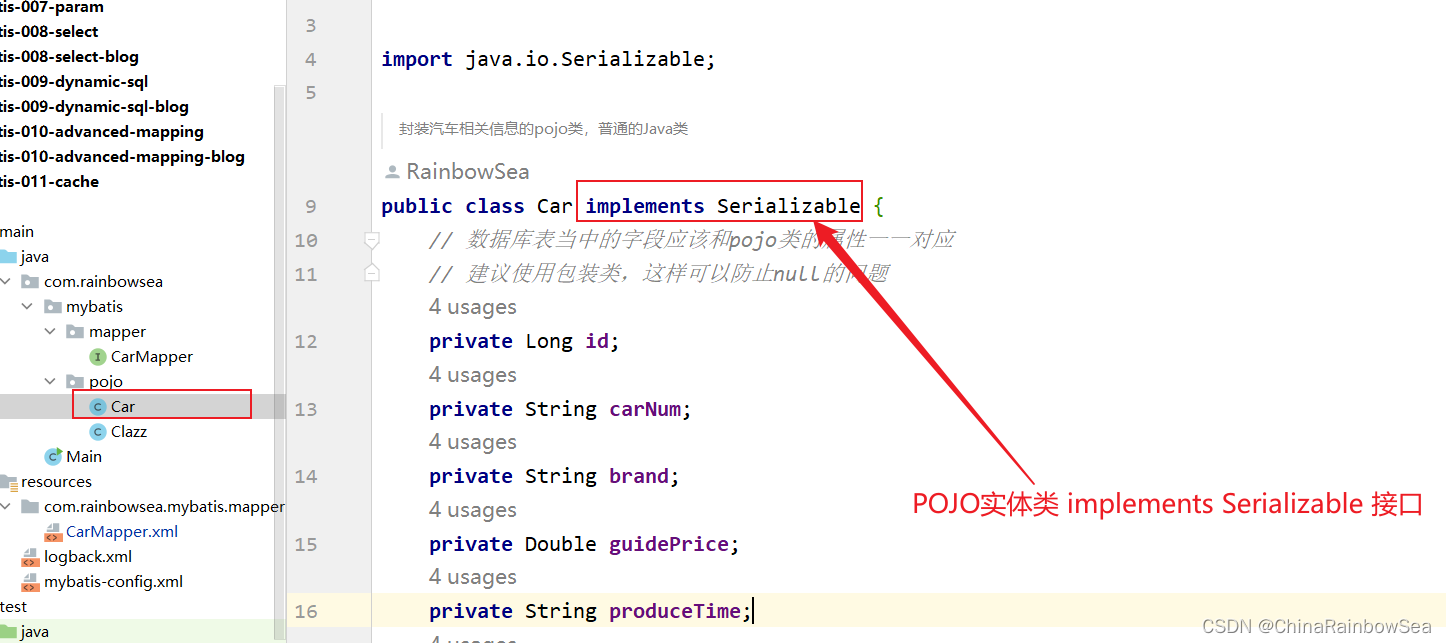
- 在需要使用二级缓存的 对应的
SqlMapper.xml文件中添加配置:- 使用二级缓存的实体类对象必须是可序列化的,也就是对应的POJO实体类,必须实现java.io.Serializable 接口
- 只有 当 SqlSession对象关闭或提交之后,一级缓存中的数据才会被写入到二级缓存当中。此时二级缓存才可用,不然没有提交/关闭,二级缓存是没有存储到数据信息的,是无效的。
第一步: 要在 MyBatis 的核心配置文件当中,设置<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"> 全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。默认就是true,无需设置 。
第二步: 在需要使用二级缓存的 对应的 SqlMapper.xml 文件中添加配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace 一定要是:对应的接口的全限定类名-->
<mapper namespace="com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
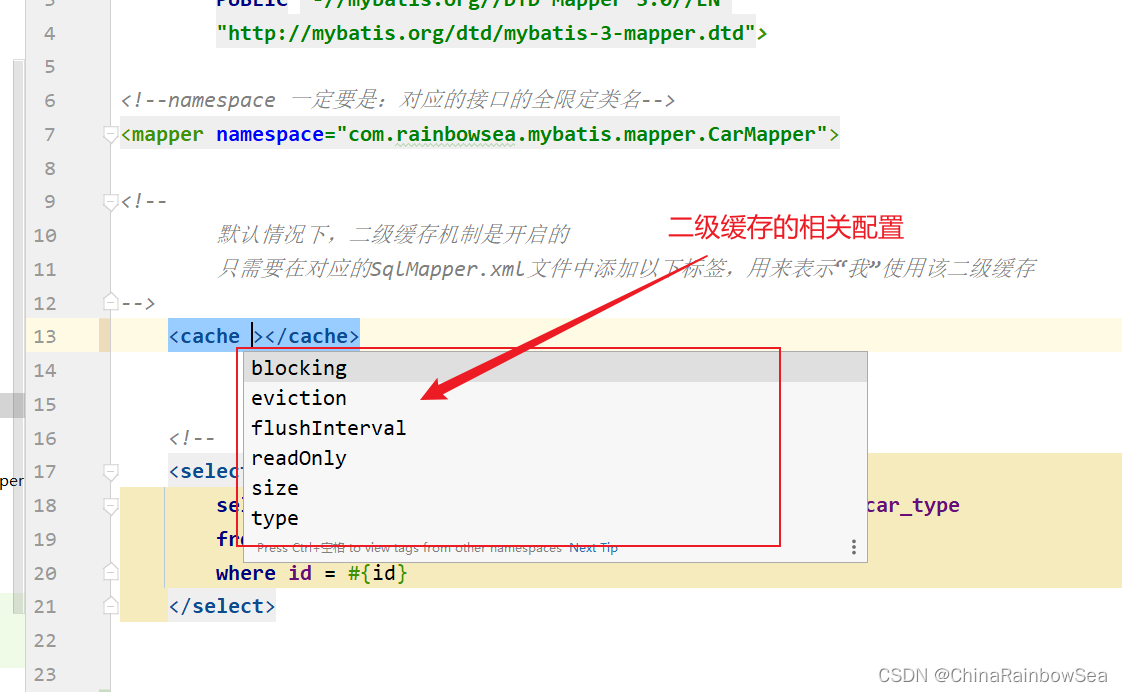
<!--
默认情况下,二级缓存机制是开启的
只需要在对应的SqlMapper.xml文件中添加以下标签,用来表示“我”使用该二级缓存
-->
<cache></cache>
<insert id="insertClazz">
insert into t_clazz values (#{cid},#{cname})
</insert>
</mapper>
第三步: 使用二级缓存的实体类对象必须是可序列化的,也就是对应的POJO实体类,必须实现java.io.Serializable 接口
第四步: 只有 当 SqlSession对象关闭或提交之后,一级缓存中的数据才会被写入到二级缓存当中。此时二级缓存才可用,不然没有提交/关闭,二级缓存是没有存储到数据信息的,是无效的。
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Clazz;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testSelectById4() throws IOException {
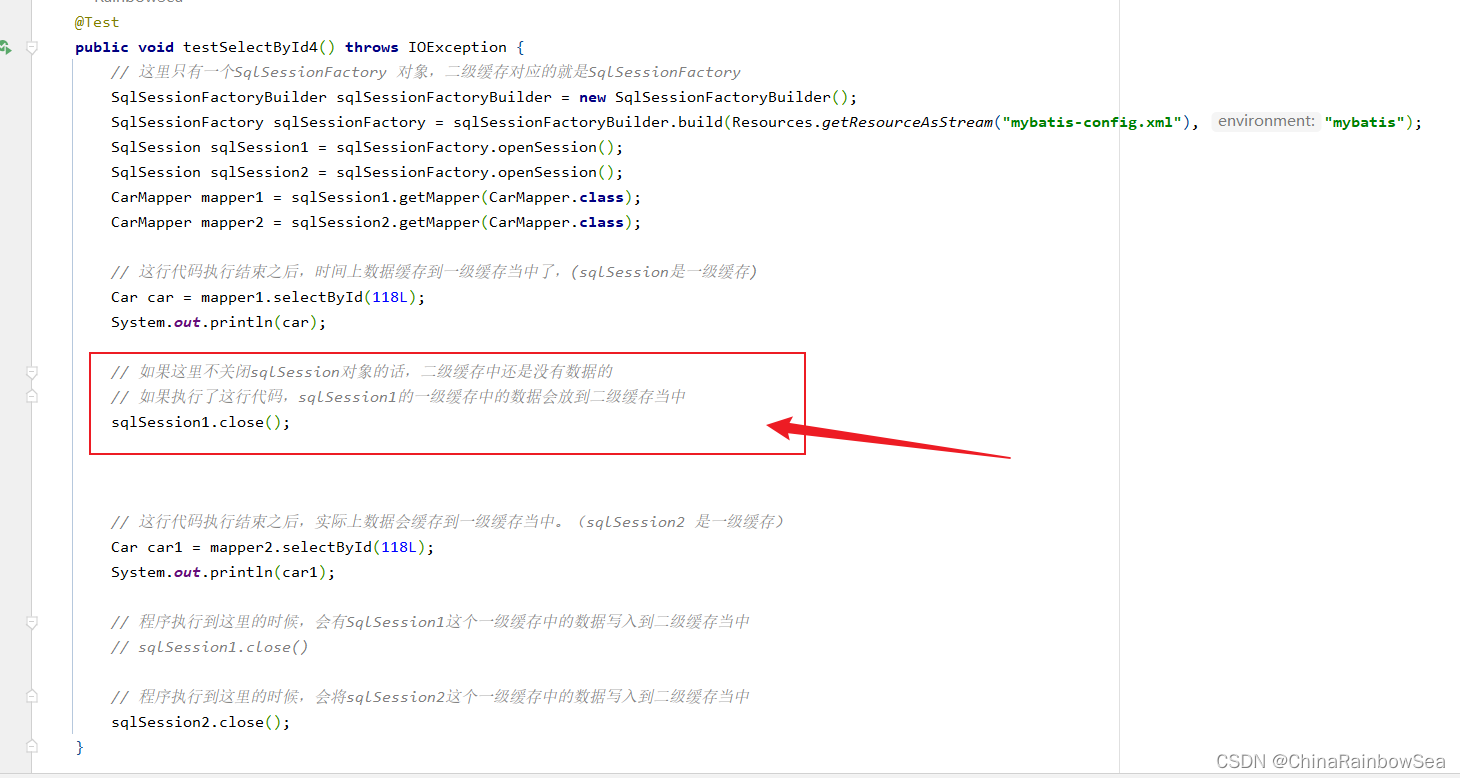
// 这里只有一个SqlSessionFactory 对象,二级缓存对应的就是SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"), "mybatis");
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
// 这行代码执行结束之后,时间上数据缓存到一级缓存当中了,(sqlSession是一级缓存)
Car car = mapper1.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car);
// 如果这里不关闭sqlSession对象的话,二级缓存中还是没有数据的
// 如果执行了这行代码,sqlSession1的一级缓存中的数据会放到二级缓存当中
sqlSession1.close();
// 这行代码执行结束之后,实际上数据会缓存到一级缓存当中。(sqlSession2 是一级缓存)
Car car1 = mapper2.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car1);
// 程序执行到这里的时候,会有SqlSession1这个一级缓存中的数据写入到二级缓存当中
// sqlSession1.close()
// 程序执行到这里的时候,会将sqlSession2这个一级缓存中的数据写入到二级缓存当中
sqlSession2.close();
}
}
运行测试:
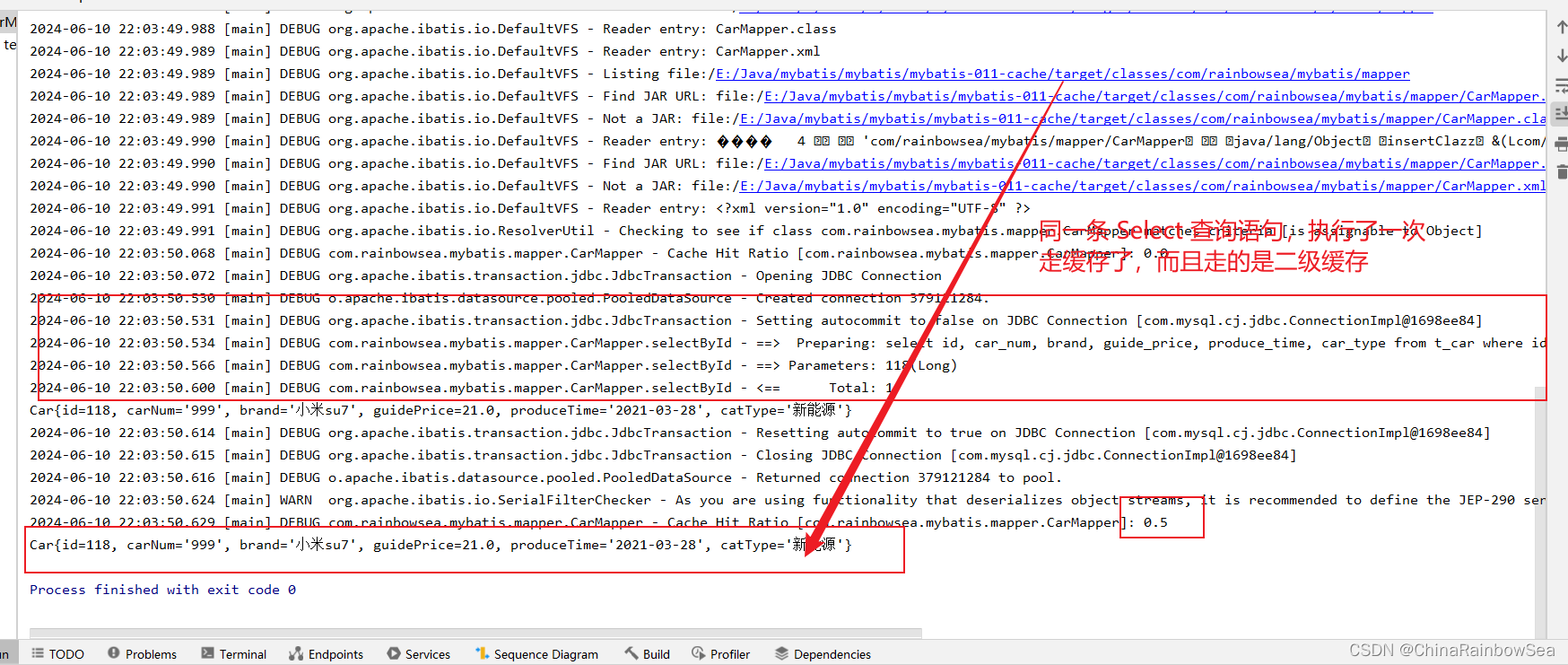
二级缓存的失效:只要两次查询之间出现了增删改操作。二级缓存就会失效。【一级缓存也会失效】
二级缓存的相关配置:
-
eviction :指定从缓存中移除某个对象的淘汰算法。默认采用LRU策略。
-
- LRU:Least Recently Used。最近最少使用。优先淘汰在间隔时间内使用频率最低的对象。(其实还有一种淘汰算法LFU,最不常用。)
- FIFO:First In First Out。一种先进先出的数据缓存器。先进入二级缓存的对象最先被淘汰。
- SOFT:软引用。淘汰软引用指向的对象。具体算法和JVM的垃圾回收算法有关。
- WEAK:弱引用。淘汰弱引用指向的对象。具体算法和JVM的垃圾回收算法有关。
-
flushInterval :
-
- 二级缓存的刷新时间间隔。单位毫秒。如果没有设置。就代表不刷新缓存,只要内存足够大,一直会向二级缓存中缓存数据。除非执行了增删改。
-
readOnly :
-
- true:多条相同的sql语句执行之后返回的对象是共享的同一个。性能好。但是多线程并发可能会存在安全问题。
- false:多条相同的sql语句执行之后返回的对象是副本,调用了clone方法。性能一般。但安全。
-
size :
-
- 设置二级缓存中最多可存储的java对象数量。默认值1024。
5. MyBatis 集成 EhCache 第三方缓存
集成EhCache是为了代替mybatis自带的二级缓存。一级缓存是无法替代的。
mybatis对外提供了接口,也可以集成第三方的缓存组件。比如EhCache、Memcache等。都可以。
EhCache是Java写的。Memcache是C语言写的。所以mybatis集成EhCache较为常见,按照以下步骤操作,就可以完成集成:
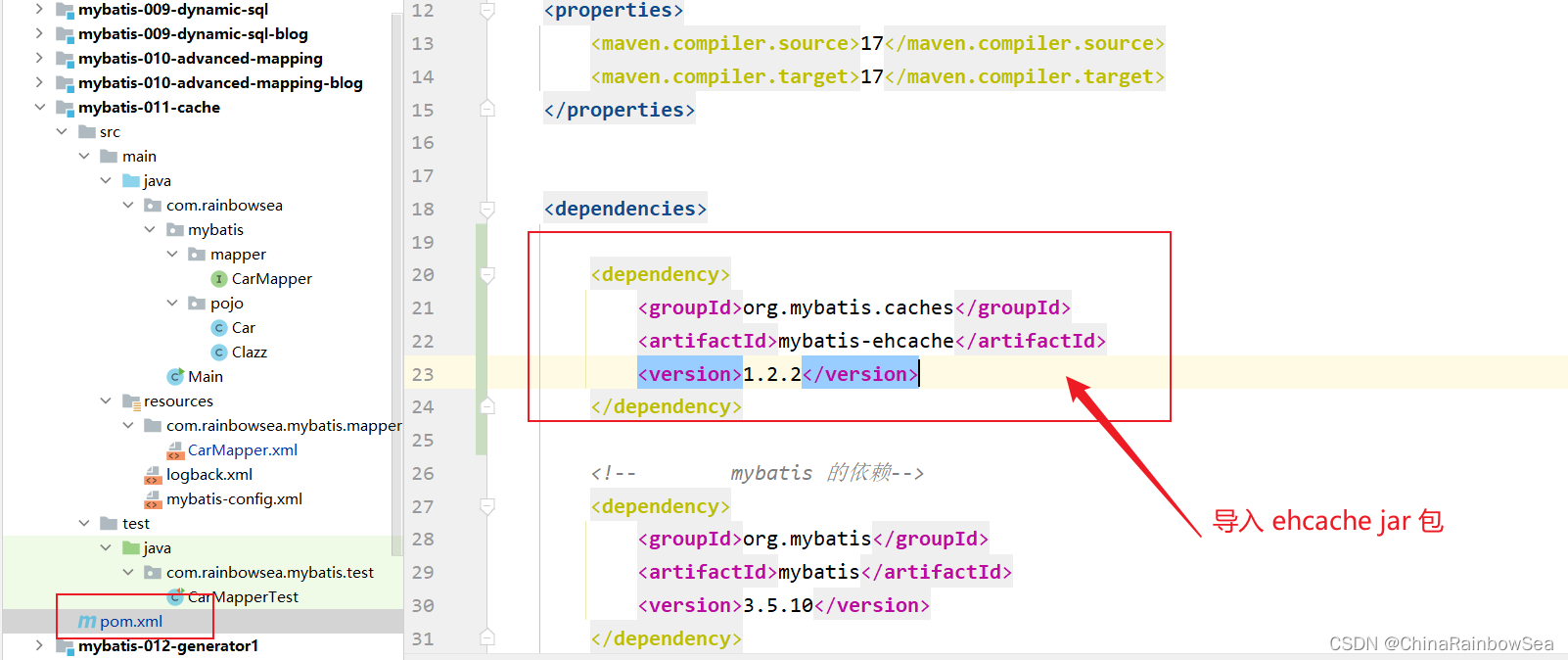
第一步: 引入mybatis 整合 ehcache 的依赖。
<!--mybatis集成ehcache的组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version>
</dependency>
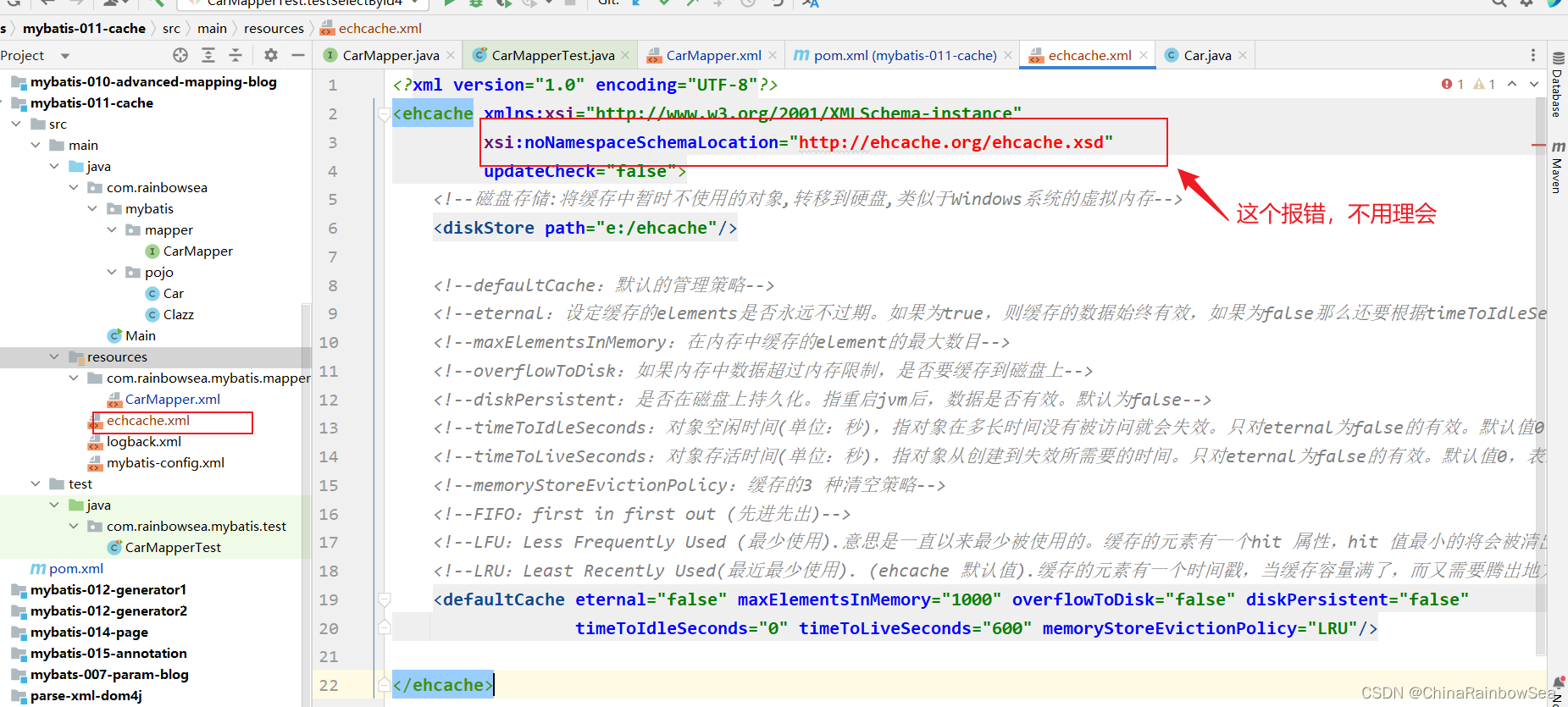
第二步: 在类的根路径下新建 echcache.xml (文件名必须是:echcache.xml 不可以修改)文件,并提供以下配置信息。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<!--磁盘存储:将缓存中暂时不使用的对象,转移到硬盘,类似于Windows系统的虚拟内存-->
<diskStore path="e:/ehcache"/>
<!--defaultCache:默认的管理策略-->
<!--eternal:设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断-->
<!--maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目-->
<!--overflowToDisk:如果内存中数据超过内存限制,是否要缓存到磁盘上-->
<!--diskPersistent:是否在磁盘上持久化。指重启jvm后,数据是否有效。默认为false-->
<!--timeToIdleSeconds:对象空闲时间(单位:秒),指对象在多长时间没有被访问就会失效。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--timeToLiveSeconds:对象存活时间(单位:秒),指对象从创建到失效所需要的时间。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问-->
<!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存的3 种清空策略-->
<!--FIFO:first in first out (先进先出)-->
<!--LFU:Less Frequently Used (最少使用).意思是一直以来最少被使用的。缓存的元素有一个hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存-->
<!--LRU:Least Recently Used(最近最少使用). (ehcache 默认值).缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存-->
<defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>
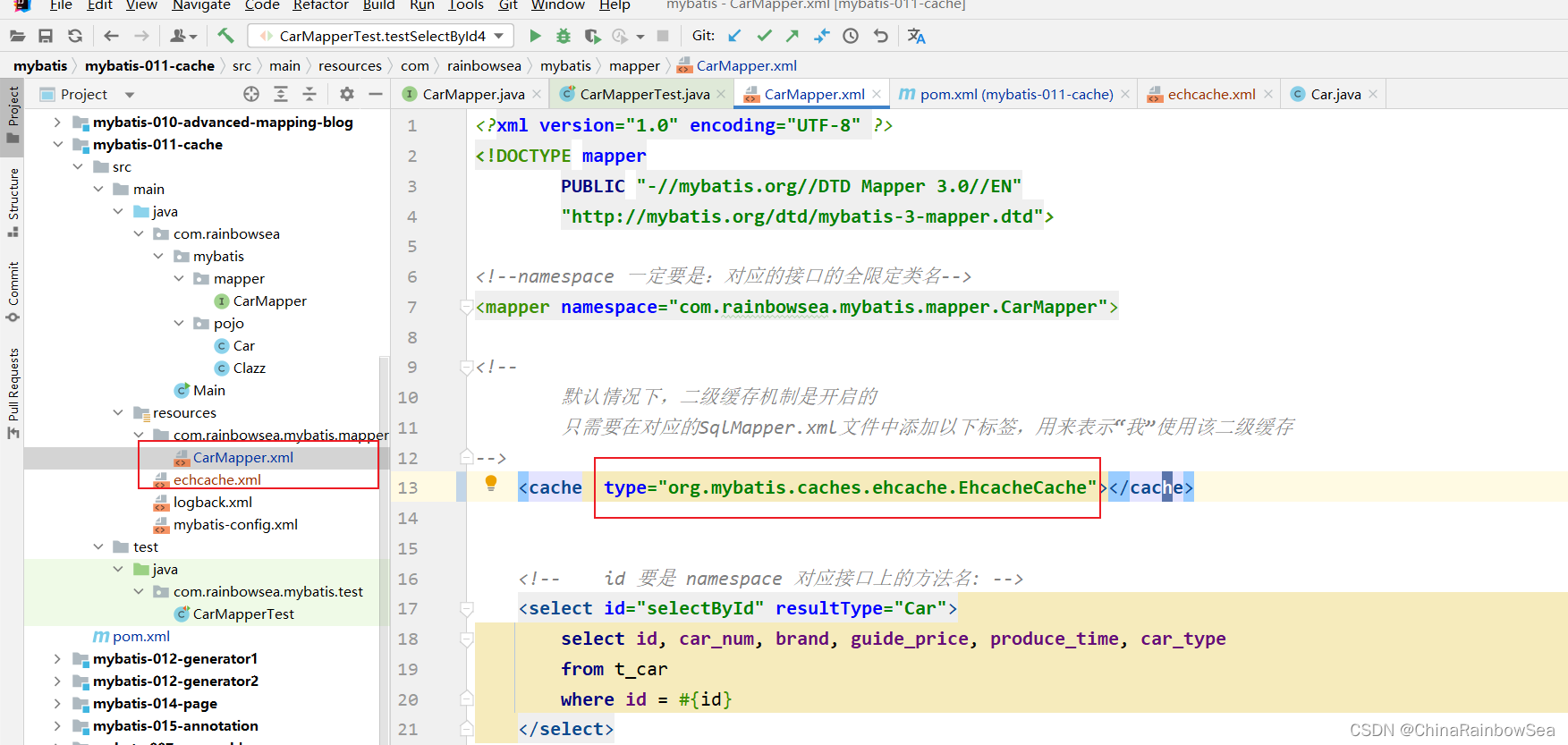
第三步: 修改对应的 SqlMapper.xml文件中的标签,添加type属性。
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace 一定要是:对应的接口的全限定类名-->
<mapper namespace="com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
<!--
默认情况下,二级缓存机制是开启的
只需要在对应的SqlMapper.xml文件中添加以下标签,用来表示“我”使用该二级缓存
-->
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache>
<!-- id 要是 namespace 对应接口上的方法名: -->
<select id="selectById" resultType="Car">
select id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type
from t_car
where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
第四步:编写测试程序使用。
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.rainbowsea.mybatis.pojo.Clazz;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CarMapperTest {
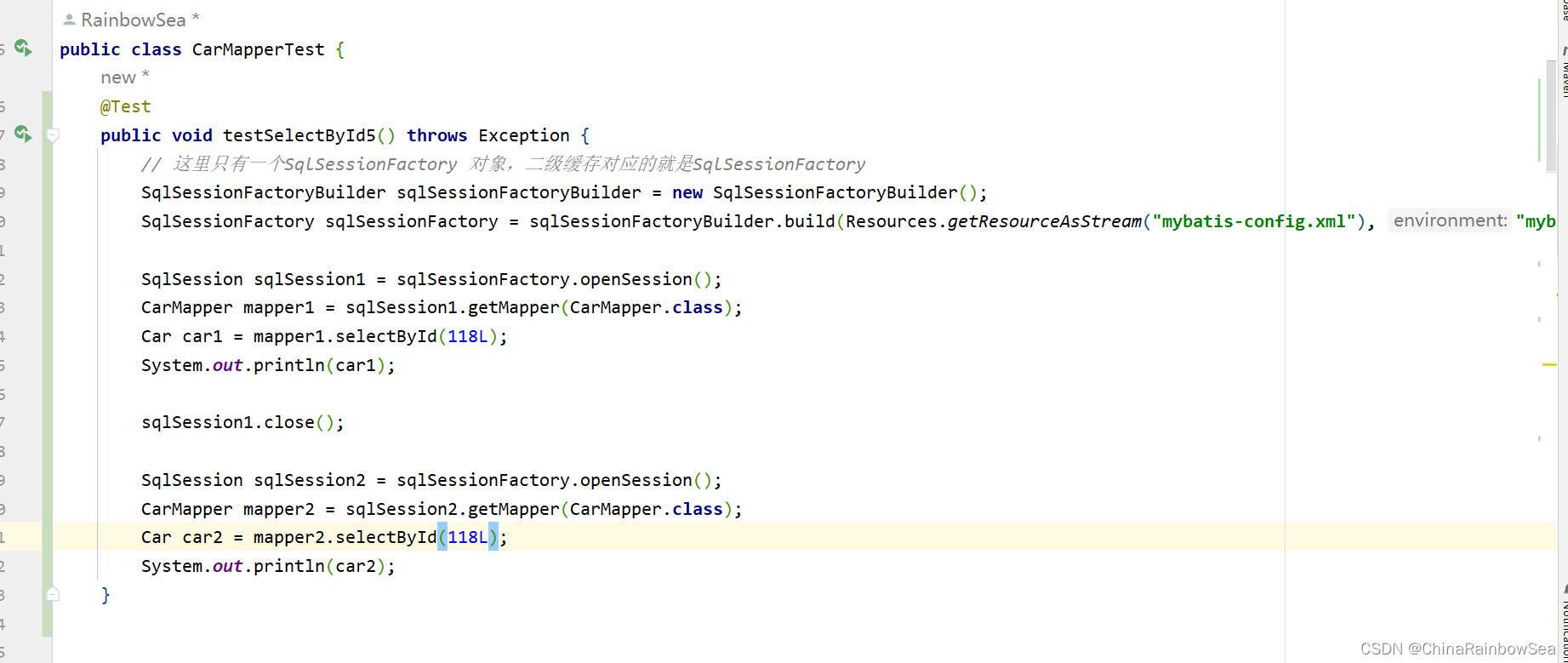
@Test
public void testSelectById5() throws Exception {
// 这里只有一个SqlSessionFactory 对象,二级缓存对应的就是SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"), "mybatis");
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car1 = mapper1.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car1);
sqlSession1.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car2 = mapper2.selectById(118L);
System.out.println(car2);
sqlSession2.close();
}
}
6. 总结:
- MyBatis 缓存包括:
- 一级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSession 中
- 二级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSessionFactory 中
- 或者是集成其它第三方的缓存:比如 EhCache(Java语言开发的),Memcache(C语言开发的)等。
- 注意:缓存只针对于 DQL(查询)语句,也就是说缓存机制只对应 Select 语句。
- 一级缓存默认是开启的
- 一级缓存失效情况包括两种:
- 第一种:第一次查询和第二次查询之间,手动清空了一级缓存。执行:执行了 sqlSession.clearCache()方法,这是手动情况缓存。
- 第二种:执行了INSERT 或 DELETE 或UPDATE语句,不管你是操作任意一张表,都会清空一级缓存。
- 一级缓存失效了,二级缓存也是失效了,二级缓存是通过将一级缓存的缓存存储到二级缓存当中的,所以一级失效,二级也是失效的
- 二级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到 SqlSessionFactory 中,范围比一级缓存中更大一些。