背景
在编写CarrierConfig的时候经常出现配置不生效的情况,比如运营商支持大范围的imsi,或者是测试人员写卡位数的问题等等,因此就需要模式匹配(包含但不限于正则表达式)。
基本概念:
- 模式匹配涉及定义一个“模式”,该模式可以是一个字符串、正则表达式或其他结构。系统将此模式应用于目标数据,找出符合该模式的部分。
应用场景:
- 字符串匹配: 查找特定字符序列或模式,例如在文本中查找单词或短语。
- 数据解析: 分析和提取数据,例如从 JSON 或 XML 文档中提取信息。
- 正则表达式: 使用正则表达式进行复杂的字符串匹配和替换操作。
- 逻辑匹配: 例如在函数式编程中,使用模式匹配来简化条件语句。
编程语言中的模式匹配实现:
很多编程语言都支持模式匹配的特性,例如:
- Haskell: 强大的模式匹配功能,可用于列表、元组等数据结构。
- Scala: 提供内置的模式匹配语法,用于匹配类型和结构。
- Java: 使用
Pattern和Matcher类进行正则表达式匹配。- Python: 使用
re模块进行正则表达式匹配。
解析逻辑
packages/apps/CarrierConfig/src/com/android/carrierconfig/DefaultCarrierConfigService.java
详细代码
参数解析:
xmlImsi: 这是从 XML 资源中获取的 IMSI 表达式,它可能是一个正则表达式。id: 这是一个CarrierIdentifier对象,提供了当前的 IMSI。获取当前 IMSI:
String currentImsi = id.getImsi();: 该行代码从CarrierIdentifier对象中获取当前的 IMSI 字符串。正则表达式匹配:
Pattern imsiPattern = Pattern.compile(xmlImsi, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);: 这行代码将 XML 中的 IMSI 表达式编译成正则表达式模式,并设置为不区分大小写(尽管在 IMSI 字符串中通常不涉及大小写问题)。Matcher matcher = imsiPattern.matcher(currentImsi);: 这行代码创建一个Matcher对象,用于比较当前 IMSI。执行匹配:
matchFound = matcher.matches();: 这个方法检查当前 IMSI 是否与正则表达式匹配。
参数检查
checkFilters检查的参数包含:
如下代码可见,支持正则匹配的只有imsi和sp。
/**
* Checks to see if an XML node matches carrier filters.
*
* <p>This iterates over the attributes of the current tag pointed to by {@code parser} and
* checks each one against {@code id} or {@link Build.DEVICE} or {@link R.string#sku_filter} or
* {@link Build.BOARD}. Attributes that are not specified in the node will not be checked, so a
* node with no attributes will always return true. The supported filter attributes are,
* <ul>
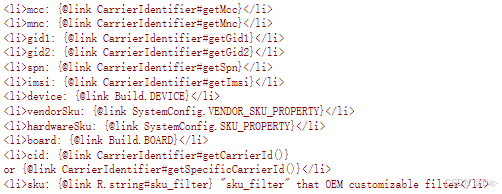
* <li>mcc: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getMcc}</li>
* <li>mnc: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getMnc}</li>
* <li>gid1: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getGid1}</li>
* <li>gid2: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getGid2}</li>
* <li>spn: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getSpn}</li>
* <li>imsi: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getImsi}</li>
* <li>device: {@link Build.DEVICE}</li>
* <li>vendorSku: {@link SystemConfig.VENDOR_SKU_PROPERTY}</li>
* <li>hardwareSku: {@link SystemConfig.SKU_PROPERTY}</li>
* <li>board: {@link Build.BOARD}</li>
* <li>cid: {@link CarrierIdentifier#getCarrierId()}
* or {@link CarrierIdentifier#getSpecificCarrierId()}</li>
* <li>sku: {@link R.string#sku_filter} "sku_filter" that OEM customizable filter</li>
* </ul>
* </p>
*
* <p>
* The attributes imsi and spn can be expressed as regexp to filter on patterns.
* The spn attribute can be set to the string "null" to allow matching against a SIM
* with no spn set.
* </p>
*
* @param parser an XmlPullParser pointing at a START_TAG with the attributes to check.
* @param id the carrier details to check against.
* @param sku a filter to be customizable.
* @return false if any XML attribute does not match the corresponding value.
*/
static boolean checkFilters(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable CarrierIdentifier id, String sku) {
String vendorSkuProperty = SystemProperties.get(
"ro.boot.product.vendor.sku", "");
String hardwareSkuProperty = SystemProperties.get(
"ro.boot.product.hardware.sku", "");
for (int i = 0; i < parser.getAttributeCount(); ++i) {
boolean result = true;
String attribute = parser.getAttributeName(i);
String value = parser.getAttributeValue(i);
switch (attribute) {
case "mcc":
result = (id == null) || value.equals(id.getMcc());
break;
case "mnc":
result = (id == null) || value.equals(id.getMnc());
break;
case "gid1":
result = (id == null) || value.equalsIgnoreCase(id.getGid1());
break;
case "gid2":
result = (id == null) || value.equalsIgnoreCase(id.getGid2());
break;
case "spn":
result = (id == null) || matchOnSP(value, id);
break;
case "imsi":
result = (id == null) || matchOnImsi(value, id);
break;
case "device":
result = value.equalsIgnoreCase(Build.DEVICE);
break;
case "vendorSku":
result = value.equalsIgnoreCase(vendorSkuProperty);
break;
case "hardwareSku":
result = value.equalsIgnoreCase(hardwareSkuProperty);
break;
case "board":
result = value.equalsIgnoreCase(Build.BOARD);
break;
case "cid":
result = (id == null) || (Integer.parseInt(value) == id.getCarrierId())
|| (Integer.parseInt(value) == id.getSpecificCarrierId());
break;
case "name":
// name is used together with cid for readability. ignore for filter.
break;
case "sku":
result = value.equalsIgnoreCase(sku);
break;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "Unknown attribute " + attribute + "=" + value);
result = false;
break;
}
if (!result) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}IMSI的匹配逻辑
参数解析:
xmlImsi: 这是从 XML 资源中获取的 IMSI 表达式,它可能是一个正则表达式。id: 这是一个CarrierIdentifier对象,提供了当前的 IMSI。获取当前 IMSI:
String currentImsi = id.getImsi();: 该行代码从CarrierIdentifier对象中获取当前的 IMSI 字符串。正则表达式匹配:
Pattern imsiPattern = Pattern.compile(xmlImsi, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);: 这行代码将 XML 中的 IMSI 表达式编译成正则表达式模式,并设置为不区分大小写(尽管在 IMSI 字符串中通常不涉及大小写问题)。Matcher matcher = imsiPattern.matcher(currentImsi);: 这行代码创建一个Matcher对象,用于比较当前 IMSI。执行匹配:
matchFound = matcher.matches();: 这个方法检查当前 IMSI 是否与正则表达式匹配。
/**
* Check to see if the IMSI expression from the XML matches the IMSI of the
* Carrier.
*
* @param xmlImsi IMSI expression fetched from the resource XML
* @param id Id of the evaluated CarrierIdentifier
* @return true if the XML IMSI matches the IMSI of CarrierIdentifier, false
* otherwise.
*/
static boolean matchOnImsi(String xmlImsi, CarrierIdentifier id) {
boolean matchFound = false;
String currentImsi = id.getImsi();
// If we were able to retrieve current IMSI, see if it matches.
if (currentImsi != null) {
//使用 Pattern 和 Matcher 接口,
//使用正则表达式来匹配 xmlImsi 与 currentImsi。
//这允许 xmlImsi 采用正则表达式的形式,从而支持更复杂的匹配逻辑,比如匹配特定模式的 IMSI 字符串。
Pattern imsiPattern = Pattern.compile(xmlImsi, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
Matcher matcher = imsiPattern.matcher(currentImsi);
matchFound = matcher.matches();
}
return matchFound;
}