目录
1. 什么是策略模式
定义一系列算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法可独立于使用它的客户而变化。
2. 使用场景
策略模式是处理算法的不同变体的一种成熟模式,策略模式通过接口或抽象类封装算法的标识,即在接口中定义一个抽象方法,实现该接口的类将实现接口中的抽象方法。
在策略模式中,封装算法标识的接口称作策略,实现该接口的类称作具体策略。
3. 模式的结构与使用
策略模式的结构中包括三种角色:
- 策略(Strategy)
- 具体策略(ConcreteStrategy)
- 上下文(Context)
4. 简单例子
以下会使用三种打分方法计算最后得分. 使用算术平均值方案; 使用几何平均值方案; 使用(去掉最高、最底)算术平均值方案.
4.1 策略(Strategy)
定义一个接口来计算得分.
package indi.peter.designpattern.strategy;
public interface ComputableStrategy {
public abstract double computeScore(double[] a);
}
4.2 具体策略-使用算术平均值计算得分
package indi.peter.designpattern.strategy;
public class StrategyOne implements ComputableStrategy {
public double computeScore(double[] a) {
double score = 0, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
sum = sum + a[i];
}
score = sum / a.length;
return score;
}
}4.3 具体策略-使用几何平均值计算得分
package indi.peter.designpattern.strategy;
public class StrategyTwo implements ComputableStrategy {
public double computeScore(double[] a) {
double score = 0, multi = 1;
int n = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
multi = multi * a[i];
}
score = Math.pow(multi, 1.0 / n);
return score;
}
}4.4 具体策略-使用(去掉最高、最底)算术平均值计算得分
package indi.peter.designpattern.strategy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class StrategyThree implements ComputableStrategy {
public double computeScore(double[] a) {
if (a.length <= 2) {
return 0;
}
double score = 0, sum = 0;
Arrays.sort(a);
for (int i = 1; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
sum = sum + a[i];
}
score = sum / (a.length - 2);
return score;
}
}4.5 上下文
注入策略, 调用接口进行得分计算.
package indi.peter.designpattern.strategy;
public class GymnasticsGame {
ComputableStrategy strategy;
public void setStrategy(ComputableStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public double getPersonScore(double[] a) {
if (strategy != null) {
return strategy.computeScore(a);
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}4.6 应用
package indi.peter.designpattern.strategy;
public class Application {
public static void main(String args[]) {
GymnasticsGame game = new GymnasticsGame();
game.setStrategy(new StrategyOne());
Person zhang = new Person();
zhang.setName("张三");
double[] a = { 9.12, 9.25, 8.87, 9.99, 6.99, 7.88 };
Person li = new Person();
li.setName("李四");
double[] b = { 9.15, 9.26, 8.97, 9.89, 6.97, 7.89 };
zhang.setScore(game.getPersonScore(a));
li.setScore(game.getPersonScore(b));
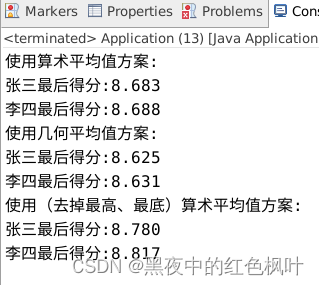
System.out.println("使用算术平均值方案:");
System.out.printf("%s最后得分:%5.3f%n", zhang.getName(), zhang.getScore());
System.out.printf("%s最后得分:%5.3f%n", li.getName(), li.getScore());
game.setStrategy(new StrategyTwo());
zhang.setScore(game.getPersonScore(a));
li.setScore(game.getPersonScore(b));
System.out.println("使用几何平均值方案:");
System.out.printf("%s最后得分:%5.3f%n", zhang.getName(), zhang.getScore());
System.out.printf("%s最后得分:%5.3f%n", li.getName(), li.getScore());
game.setStrategy(new StrategyThree());
zhang.setScore(game.getPersonScore(a));
li.setScore(game.getPersonScore(b));
System.out.println("使用(去掉最高、最底)算术平均值方案:");
System.out.printf("%s最后得分:%5.3f%n", zhang.getName(), zhang.getScore());
System.out.printf("%s最后得分:%5.3f%n", li.getName(), li.getScore());
}
}
class Person {
String name;
double score;
public void setScore(double t) {
score = t;
}
public void setName(String s) {
name = s;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
5. 模式应用的开源框架
Spring Boot 中使用的策略模式通常是通过注解的配置类中用@Bean注解来提供不同的策略实现。这样,你可以根据需要动态地注入不同的策略实现。以下是一个简单的策略模式的例子:
// 策略接口
public interface MyStrategy {
void execute();
}
// 策略实现
@Component
public class MyStrategyImpl1 implements MyStrategy {
@Override
public void execute() {
// 实现细节
System.out.println("Strategy 1 executed.");
}
}
// 另一个策略实现
@Component
public class MyStrategyImpl2 implements MyStrategy {
@Override
public void execute() {
// 实现细节
System.out.println("Strategy 2 executed.");
}
}
// 配置类
@Configuration
public class StrategyConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "strategy.type", havingValue = "impl1")
public MyStrategy myStrategyImpl1() {
return new MyStrategyImpl1();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "strategy.type", havingValue = "impl2")
public MyStrategy myStrategyImpl2() {
return new MyStrategyImpl2();
}
}
// 使用策略的服务
@Service
public class MyService {
@Autowired
private MyStrategy myStrategy;
public void executeStrategy() {
myStrategy.execute();
}
}6. 模式优点
上下文(Context)和具体策略(ConcreteStrategy)是松耦合关系。因此上下文只知道它要使用某一个实现Strategy接口类的实例,但不需要知道具体是哪一个类。
策略模式满足“开-闭原则”。当增加新的具体策略时,不需要修改上下文类的代码,上下文就可以引用新的具体策略的实例。
富贵必从勤苦得,男儿须读五车书。加油少年郎!!!