Easy Redis Java 客户端:Redisson
前言
Redission是一个基于Redis的Java框架。它提供了许多分布式的数据结构和功能,如分布式锁、Map、Queue和Topic等。Redission可以帮助简化并发编程的复杂性,并提供可重入锁、公平锁等常用的分布式锁,支持异步执行、锁的自动续期、锁的等待,等特性。
Redisson的宗旨是促进使用者对Redis的关注分离(Separation of Concern),从而让使用者能够将精力更集中地放在处理业务逻辑上。
你可能会有点蒙,Redisson和Jedis、Lettuce有什么区别?
总结下来,Jedis 把 Redis 命令封装的非常全面,Lettuce 则进一步丰富了 Api,支持 Redis 各种高级特性。
但是两者并没有进一步深化,只给了你操作 Redis 数据库的工具,而 Redisson 则是基于 Redis、Lua 和 Netty 建立起了一套的分布式解决方案,比如分布式锁的实现,分布式对象的操作等等。
引入官方依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.29.0</version>
</dependency>
SpringBoot提供的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.29.0</version>
</dependency>
配置文件
有多种方式来集成Redisson配置:编程式配置、声明式配置
声明式配置
- 通用配置
#redis地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
#redis端口
spring.redis.port=6379
#redis密码(非必须)
spring.redis.password=123456
使用通用的 Spring Boot 2.7.x 及以下设置:
spring:
redis:
database:
host:
port:
password:
ssl:
timeout:
connectTimeout:
clientName:
cluster:
nodes:
sentinel:
master:
nodes:
示例如下(yaml文件修改格式即可):
#数据库编码
spring.redis.database= 0
##是否开启ssl
spring.redis.ssl=false
# 读取超时
spring.redis.timeout=5000
# 连接超时
spring.redis.connect-timeout=10000
##客户端名称
spring.redis.client-name=myClientName
##集群部署 ip:port,...
spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.1.1:6379,192.168.1.2:6379,192.168.1.3:6379
##哨兵模式 主节点名称
#spring.redis.sentinel.master=mymaster
##哨兵模式 节点列表 ip:port,...
spring.redis.sentinel.nodes=192.168.1.1:7001,192.168.1.1:7002,192.168.1.1:7003
- Redisson引入文件
另外也可以使用 Redisson 配置文件,再application. properties添加
spring.redis.redisson.file=classpath:redisson.yml
resources目录下创建redisson.yml文件
# 单节点配置
singleServerConfig:
# 数据库编号
database: 0
# 节点地址
address: redis://127.0.0.1:6379
# 密码
password: 123456
- 使用竖杠符号
|
竖杠符号(|)是YAML语法中的一种特殊表示方式,称为"折叠文本块"标记。它用于指示多行文本块,在保留换行符的同时,将所有行连接成单个字符串。在这种情况下,文本块的缩进会被忽略,而每行的缩进将被认为是相对于最短缩进的偏移量。这在配置文件中特别有用,因为它允许你在不失去可读性的情况下编写多行文本。
可以直接再application. properties添加(注意|格式)
redis:
redisson:
config: |
singleServerConfig:
address: redis://127.0.0.1:6379
password: 123456
编程式配置
#redis地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
#redis端口
spring.redis.port=6379
#redis密码(非必须)
spring.redis.password=123456
对应Java配置如下:
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
config.useSingleServer().setPassword("123456");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
- 集群模式
单点故障问题主要是由于Redis是单机运行的,该机器出现故障后,会间接导致使用Redis的程序出现错误。因此我们可以使用集群模式来避免这个问题。
---
clusterServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
failedSlaveReconnectionInterval: 3000
failedSlaveNodeDetector: !<org.redisson.client.FailedConnectionDetector> {}
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: !<org.redisson.connection.balancer.RoundRobinLoadBalancer> {}
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
subscriptionMode: "SLAVE"
nodeAddresses:
- "redis://127.0.0.1:7004"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:7001"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:7000"
scanInterval: 1000
pingConnectionInterval: 30000
keepAlive: false
tcpNoDelay: true
threads: 16
nettyThreads: 32
codec: !<org.redisson.codec.Kryo5Codec> {}
transportMode: "NIO"
-
idleConnectionTimeout: 如果池连接一段时间未使用,并且当前连接数量大于最小空闲连接池大小,则将关闭并从池中删除。单位为毫秒,默认:10000。 -
connectTimeout: 连接到任何Redis服务器时超时,默认:10000。 -
timeout:Redis服务器响应超时。Redis命令发送成功后开始倒计时。单位为毫秒,默认:3000。 -
retryAttempts: 如果在retryAttempts之后Redis命令不能被发送到Redis服务器,将会抛出错误。但如果发送成功,则会启动超时。 -
retryInterval:在此时间间隔之后,将执行另一次发送Redis命令的尝试。单位为毫秒,默认:1500。 -
failedSlaveReconnectionInterval:Redis Slave重新连接尝试的时间间隔。单位为毫秒,默认:3000。 -
failedSlaveNodeDetector:定义失败的Redis Slave节点检测器对象。
(1)FailedConnectionDetector:如果Redis节点在定义的毫秒间隔内有持续的连接错误,则标记为失败。默认值是180000毫秒。
(2)FailedCommandsDetector:如果Redis节点有一定数量的命令执行错误,则将其标记为失败,该错误由定义的时间间隔定义,以毫秒为单位。
(3)FailedCommandsTimeoutDetector:如果Redis节点有一定数量的命令执行超时错误,则标记为失败,该错误由在定义的间隔中定义,以毫秒为单位。 -
password:Redis服务器鉴权密码。 -
subscriptionsPerConnection:每个订阅连接限制的订阅。 -
clientName:客户端连接名称。 -
loadBalancer:连接为多台Redis服务器的负载均衡器。 -
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize:订阅(发布/订阅)通道的最小空闲连接池大小。 -
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize:订阅(发布/订阅)通道的最大连接池大小。 -
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize:Redis 'slave’节点每个从节点的最小空闲连接数 -
slaveConnectionPoolSize:Redis 'slave’节点每个slave节点最大连接池大小。 -
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize:每个Redis主节点的最小空闲连接数。 -
masterConnectionPoolSize:Redis主节点最大连接池大小。 -
readMode:设置读操作使用的节点类型。可用值:
(1)SLAVE-从从节点读取,如果没有SLAVE可用,使用MASTER。
(2)MASTER-从主节点读取,
(3)MASTER_SLAVE-从主节点和从节点读取 -
subscriptionMode:设置订阅操作使用的节点类型。可用值:
(1)SLAVE-订阅从节点,
(2)MASTER-订阅主节点, -
nodeAddresses:格式中添加Redis节点地址。可以一次添加多个节点。应该定义所有节点(主节点和从节点)。 -
scanInterval:复制节点扫描间隔(毫秒)。 -
pingConnectionInterval:PING命令发送间隔每连接到Redis。以毫秒为单位定义。 -
keepAlive:使能TCP连接keepAlive。 -
tcpNoDelay:使能TCP noDelay连接。 -
threads:线程用于执行对象的侦听器逻辑、对象和任务的调用处理程序。 -
nettyThreads:reddisson使用的所有内部redis客户端之间共享的线程数。Netty线程用于Redis响应解码和命令发送。 -
codec:Redis数据编解码器。读写Redis数据时使用。 -
transportMode:传输方式
(1)TransportMode.NIO,
(2)TransportMode.EPOLL-需要classpathnetty-transport-native-epoll中的库
(3)TransportMode.KQUEUE- -需要classpathnetty-transport-native-kqueue中的库
转换为Java配置,部分示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.useClusterServers()
.setScanInterval(2000) // 集群状态扫描间隔(毫秒)
// 使用"rediss://"进行SSL连接
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7000", "redis://127.0.0.1:7001")
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7002");
config.useClusterServers().setIdleConnectionTimeout(50000);
config.useSingleServer().setConnectTimeout(10000);
config.useClusterServers().setTimeout(3000);
config.setThreads(16);
config.setNettyThreads(32);
config.setTransportMode(TransportMode.NIO);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
- 复制模式
在复制模式下,将轮询每个节点的角色,以确定是否发生了故障转移,从而产生了新的主节点。
---
replicatedServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
failedSlaveReconnectionInterval: 3000
failedSlaveNodeDetector: !<org.redisson.client.FailedConnectionDetector> {}
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: !<org.redisson.connection.balancer.RoundRobinLoadBalancer> {}
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
subscriptionMode: "SLAVE"
nodeAddresses:
- "redis://redishost1:2812"
- "redis://redishost2:2815"
- "redis://redishost3:2813"
scanInterval: 1000
monitorIPChanges: false
threads: 16
nettyThreads: 32
codec: !<org.redisson.codec.Kryo5Codec> {}
transportMode: "NIO"
monitorIPChanges:用于监控Redis节点的IP地址变化。
转换为Java配置,部分示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.useReplicatedServers()
.setScanInterval(2000) // 集群状态扫描间隔(毫秒)
// 使用"rediss://"进行SSL连接
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7000", "redis://127.0.0.1:7001")
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7002");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
return redisson;
}
}
- 单实例模式
所有的数据都存储在一个Redis实例中,不提供高可用性和故障转移机制。
---
singleServerConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
address: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379"
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
connectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
connectionPoolSize: 64
database: 0
dnsMonitoringInterval: 5000
threads: 16
nettyThreads: 32
codec: !<org.redisson.codec.Kryo5Codec> {}
transportMode: "NIO"
database:用于 Redis 连接的数据库索引dnsMonitoringInterval:以毫秒为单位的时间间隔检查终结点的 DNS。应用程序必须确保 JVM DNS 缓存 TTL 足够低以支持此功能。设置为禁用:-1。
转换为Java配置,部分示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
config.useSingleServer().setDatabase(0);
config.useSingleServer().setDnsMonitoringInterval(3000);
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
return redisson;
}
}
- 哨兵模式
当主节点出现故障时,由Redis Sentinel自动完成故障发现和转移,并通知应用方,实现高可用性。
---
sentinelServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
failedSlaveReconnectionInterval: 3000
failedSlaveNodeDetector: !<org.redisson.client.FailedConnectionDetector> {}
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: !<org.redisson.connection.balancer.RoundRobinLoadBalancer> {}
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
subscriptionMode: "SLAVE"
sentinelAddresses:
- "redis://127.0.0.1:26379"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:26389"
masterName: "mymaster"
database: 0
threads: 16
nettyThreads: 32
codec: !<org.redisson.codec.Kryo5Codec> {}
transportMode: "NIO"
sentinelAddresses:以host:port格式添加Redis Sentinel节点地址。一次可以添加多个节点。masterName:Redis Sentinel服务器和主变更监控任务使用的主服务器名称。
转换为Java配置,部分示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSentinelServers()
.setMasterName("myMasterName")
.setScanInterval(2000) //集群状态扫描间隔(毫秒)
//使用"rediss://"进行SSL连接
.addSentinelAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:26389", "redis://127.0.0.1:26379");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
return redisson;
}
}
- 主从模式
一主多从,一个主节点,多个从节点,其中主节点拥有读写操作权限,从节点只能拥有读权限,由此可以降低主节点的读取压力,降低损坏风险。
---
masterSlaveServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
failedSlaveReconnectionInterval: 3000
failedSlaveNodeDetector: !<org.redisson.client.FailedConnectionDetector> {}
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: !<org.redisson.connection.balancer.RoundRobinLoadBalancer> {}
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 24
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
subscriptionMode: "SLAVE"
slaveAddresses:
- "redis://127.0.0.1:6381"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:6380"
masterAddress: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379"
database: 0
threads: 16
nettyThreads: 32
codec: !<org.redisson.codec.Kryo5Codec> {}
transportMode: "NIO"
slaveAddresses:在host:portrediss://格式中添加Redis从节点地址。可以一次添加多个节点。使用SSL连接协议。masterAddress:在host:portrediss://格式的Redis主节点地址。使用SSL连接协议。
转换为Java配置,部分示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.useMasterSlaveServers()
//使用"rediss://"进行SSL连接
.setMasterAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379")
.addSlaveAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6389", "redis://127.0.0.1:6332", "redis://127.0.0.1:6419")
.addSlaveAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6399");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
return redisson;
}
}
基本使用
我们再以Redisson方式在代码中操作redis。
(1)查看所有key
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/fetch")
public void fetch(){
RKeys rKeys = redissonClient.getKeys();
rKeys.getKeysStream().forEach(System.out::println);
/** Output
* test
* x
*/
}
}
(2)判断key是否存在
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/fetch")
public void fetch(){
//检查提供的密钥是否存在,返回现有密钥的数量
long exists = redissonClient.getKeys().countExists("test");
System.out.println(exists);
/** Output
* 1
*/
}
}
(3)删除key
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/fetch")
public void fetch(){
//删除指定密钥,返回现有密钥的数量
long exists = redissonClient.getKeys().delete("x");
System.out.println(exists);
/** Output
* 1
*/
}
}
(4)设置key有效期
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//返回true表示设置成功,false则失败
boolean time = redissonClient.getKeys().expire("test",10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(time);
/** Output
* true
*/
}
}
(5)获取key有效期
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//时间单位为毫秒,如果密钥不存在,则为-2。-1表示密钥存在,但没有相关的过期时间
long time = redissonClient.getKeys().remainTimeToLive("test");
System.out.println(time);
/** Output
* 3784
*/
}
}
(6)查询key类型
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//一共5种类型:OBJECT(string), MAP, LIST, SET, ZSET
RType test = redissonClient.getKeys().getType("test");
System.out.println(test.name());
/** Output
* OBJECT
*/
}
}
(7)重命名key
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//返回true表示设置成功,false则失败
boolean test = redissonClient.getKeys().renamenx("test","test2");
System.out.println(test);
/** Output
* true
*/
}
}
(8)移除key存活时间
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//返回true表示设置清除成功,false则失败
boolean test = redissonClient.getKeys().clearExpire("test");
System.out.println(test);
/** Output
* true
*/
}
}
- string
(1)设置字符串值。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
RBucket<Object> test = redissonClient.getBucket("testStr");
//test.set("hello");
test.set("hello",1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
(2)获取值。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
Object test = redissonClient.getBucket("testStr").get();
System.out.println(test);
/** Output
* hello
*/
}
}
(3)获取字符串值的长度。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
RBucket<Object> testStr = redissonClient.getBucket("testStr");
System.out.println(testStr.size());
/** Output
* 5
*/
}
}
(4)自加、自减
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong("myAtomicLong");
//设置初始值
atomicLong.set(10);
//自增
long l = atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println(l);
//自减
long l1 = atomicLong.decrementAndGet();
System.out.println(l1);
/** Output
* 11
* 10
*/
}
}
- hash
(1)设置值,获取值。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//设置值
RMap<Object, Object> rMap = redissonClient.getMap("maps");
rMap.put("one",1);
rMap.put("two",2);
rMap.put("three",3);
//设置过期时间
rMap.expire(Duration.ofMinutes(1));
//获取值
RMap<Object, Object> maps = redissonClient.getMap("maps");
System.out.println(maps);
}
}
(2)获取所有keys和values。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
RMap<Object, Object> rMap = redissonClient.getMap("maps");
//所有key
Set<Object> objects = rMap.keySet();
objects.stream().forEach(item-> System.out.println(item));
Collection<Object> values = rMap.values();
//所有value
values.stream().forEach(item-> System.out.println(item));
}
}
很多方式和Map使用基本一致。
- list
(1)插入元素,获取元素,删除元素。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//插入元素
RList<Object> rList = redissonClient.getList("lists");
rList.add("one");
rList.add("two");
rList.add("three");
//获取元素
// List<Object> lists = redissonClient.getList("lists").range(0, -1);
List<Object> lists = redissonClient.getList("lists").readAll();
lists.stream().forEach(item-> System.out.println(item));
//删除元素
redissonClient.getList("lists").remove("one");//value删除
redissonClient.getList("lists").remove(1);//下标删除
}
}
很多方式和List使用基本一致。
- set
(1)插入元素,获取元素,删除元素。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//插入元素
RSet<Object> rSet = redissonClient.getSet("sets");
rSet.add("one");
rSet.add("two");
rSet.add("three");
//获取元素
Set<Object> objects = redissonClient.getSet("sets").readAll();
objects.stream().forEach(item-> System.out.println(item));
//删除元素
redissonClient.getSet("sets").remove("one");
}
}
很多方式和Set使用基本一致。
- zset
(1)添加元素,获取元素,删除元素。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
//插入元素
RScoredSortedSet<Object> zsets = redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet("zsets");
zsets.add(2,"two");
zsets.add(3,"three");
zsets.add(1,"one");
//获取元素
Collection<ScoredEntry<Object>> zsets1 = redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet("zsets").entryRange(0, -1);
zsets1.stream().forEach(item-> System.out.println(item.getValue()));//正序
Collection<ScoredEntry<Object>> zsets2 = redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet("zsets").entryRangeReversed(0, -1);
zsets2.stream().forEach(item-> System.out.println(item.getValue()));//倒序
//删除元素
redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet("zsets").remove("one");
}
}
- 队列
在Redisson中,提供了RBlockingQueue, RDeque先进先出的队列结构。
(1)RDeque双端队列
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
RQueue<Object> queue = redissonClient.getQueue("test");
//插入队列
queue.add("one");
queue.add("two");
queue.add("three");
//获取队列并删除
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
//删除指定队列
queue.remove("three");
}
}
(2)RBlockingQueue阻塞队列
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RBlockingQueue<Object> queue = redissonClient.getBlockingQueue("test");
//放入元素,如果队列满,当前线程将会被阻塞
queue.put("one");
queue.put("two");
queue.put("three");
//获取队列,队列中没有元素将阻塞
System.out.println(queue.take());
}
}
- 布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。它的优点是空间效率和查询时间都比一般的算法要好的多,缺点是有一定的误识别率和删除困难。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
RBloomFilter rBloomFilter = redissonClient.getBloomFilter("blooms");
// 初始化预期插入的数据量为10000和期望误差率为0.01
rBloomFilter.tryInit(10000, 0.01);
// 插入部分数据
rBloomFilter.add("100");
rBloomFilter.add("200");
rBloomFilter.add("300");
//设置过期时间
rBloomFilter.expire(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 判断是否存在
System.out.println(rBloomFilter.contains("300"));
System.out.println(rBloomFilter.contains("200"));
System.out.println(rBloomFilter.contains("999"));
}
}
除了这些,还有集群模式、主从复制、哨兵模式等等,以后有空再单独发布文章。
分布式锁
Redisson 提供了多种分布式锁的实现,其中包括可重入锁、公平锁、读写锁等,这些锁都是基于 Redis 实现的,具有高性能和可靠性。
可重入锁
可重入锁(Reentrant Lock)是一种同步机制,它允许线程在持有锁的情况下可以再次获取该锁,而不会造成死锁。具体来说,可重入锁允许一个线程在执行期间多次获得同一个锁,而不会被自己持有的锁所阻塞( Java 的内置锁(如 synchronized 和 ReentrantLock)都是支持重入的)。
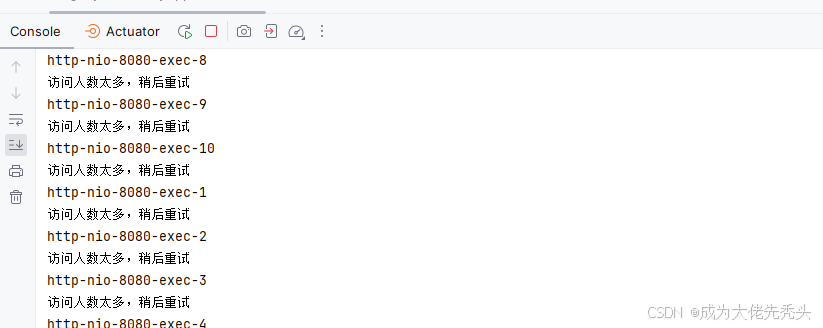
如果用以前的jedis,会导致第二次直接获取不到锁,示例代码如下:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
String lockKey = "request_key";
String clientId = "pod_1";
try {
if (!tryLock(lockKey,clientId)){
System.out.println("访问人数太多,稍后重试");
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
reLock(lockKey,clientId);
} finally {
unLock(lockKey);
}
}
/**
* 测试锁的重入
*/
private void reLock(String lockKey,String clientId) {
try {
if (!tryLock(lockKey,clientId)){
System.out.println("访问人数太多,稍后重试");
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} finally {
unLock(lockKey);
}
}
public boolean tryLock(String key, Object value) {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value);
}
public Object unLock(String key) {
return redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
执行结果如图:
如果要解决这个问题,就需要进行更多的操作,比如:lua脚本或者存储获取锁的次数,来达到可重入锁的效果。
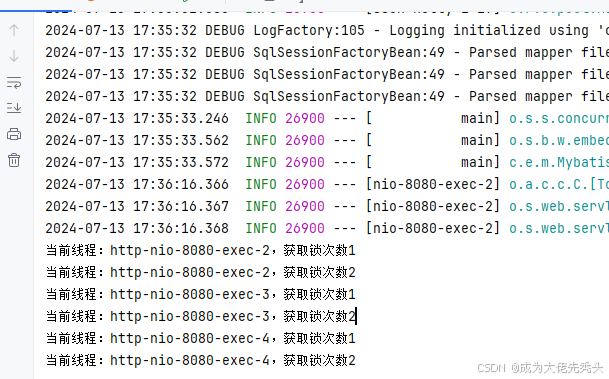
Redisson可重入锁实现了java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock接口,示例代码如下:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
try {
if (!lock.tryLock()){
System.out.println("访问人数太多,稍后重试");
return;
}
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取锁次数"+lock.getHoldCount());
reLock();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 测试锁的重入
*/
private void reLock() {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
try {
if (!lock.tryLock()){
System.out.println("访问人数太多,稍后重试");
return;
}
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",获取锁次数"+lock.getHoldCount());
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
执行结果如图:
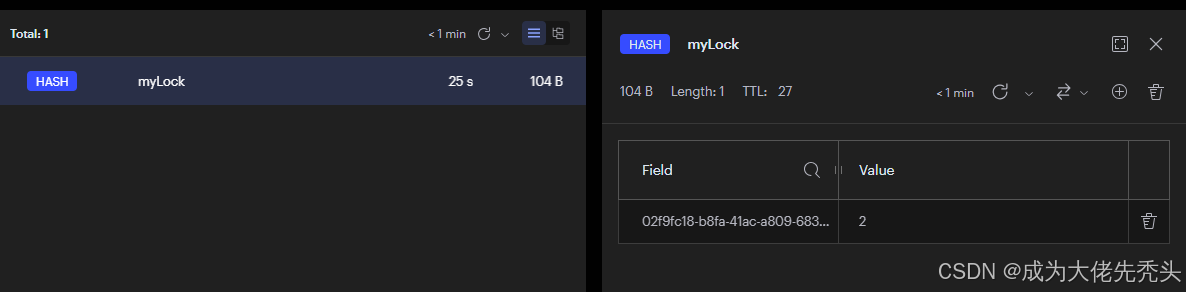
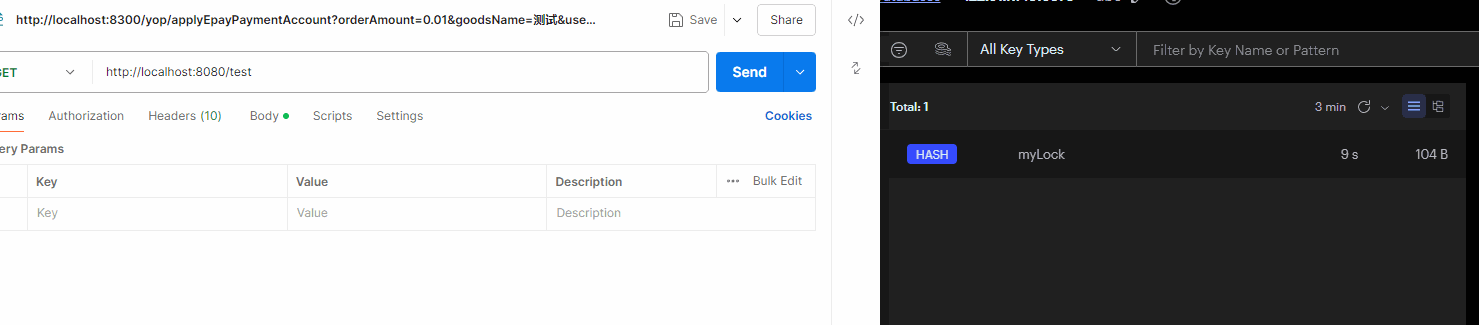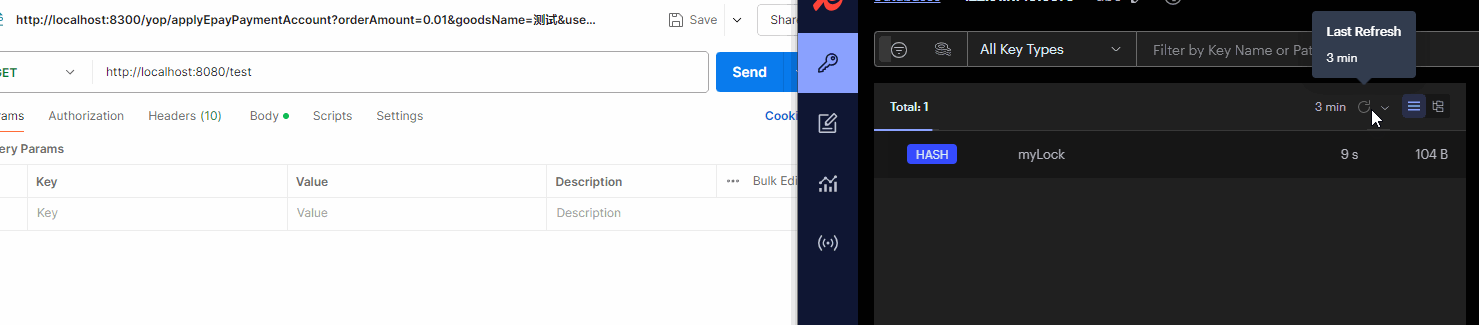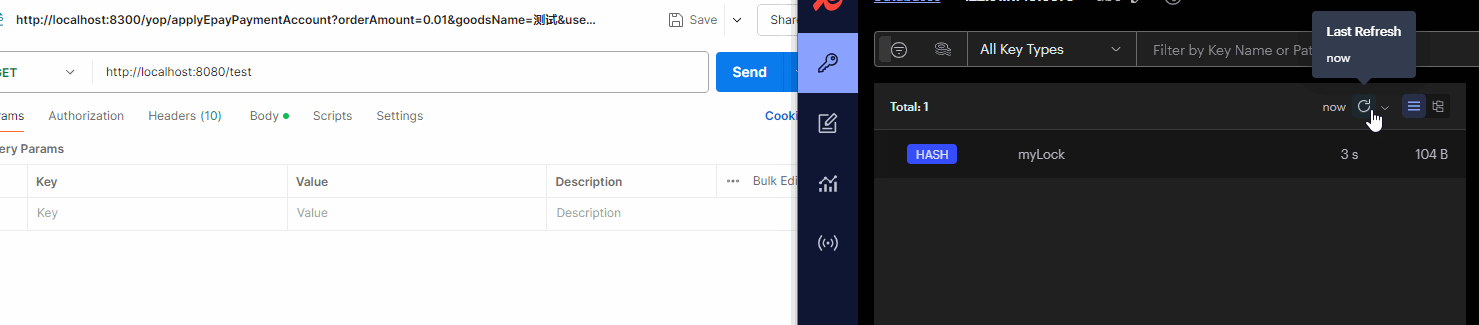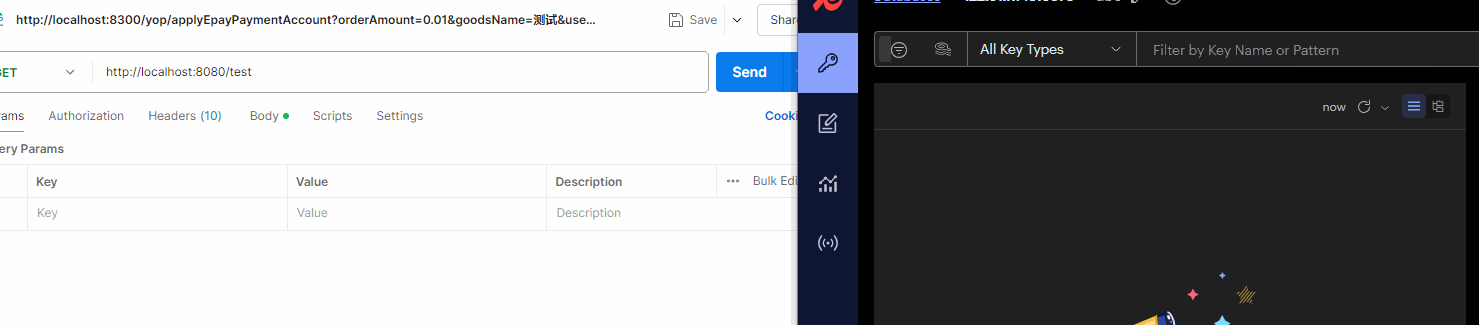
Redis中是通过HASH来存储锁,可重入锁的实现通常会使用Value值来跟踪锁的持有次数。每次成功获取锁时,Value值会递增;每次释放锁时,Value值递减。这样设计可以确保同一个线程可以多次获取锁,而不会引发死锁或其他同步问题。
Redisson提供了多种方法获取锁,除了tryLock()方法,下面简单来介绍他们的用法:
lock()方法:和tryLock()方法一样,属于Lock类。无参方法,默认30秒有效期,10秒种进行续期,会阻塞。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
lock.lock();
}
}
执行结果如图:
tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit)方法:属于Lock类。有参方法,设置获取锁的时间,超过时间自动释放,返回false。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
//设置获取锁的等待时间5秒
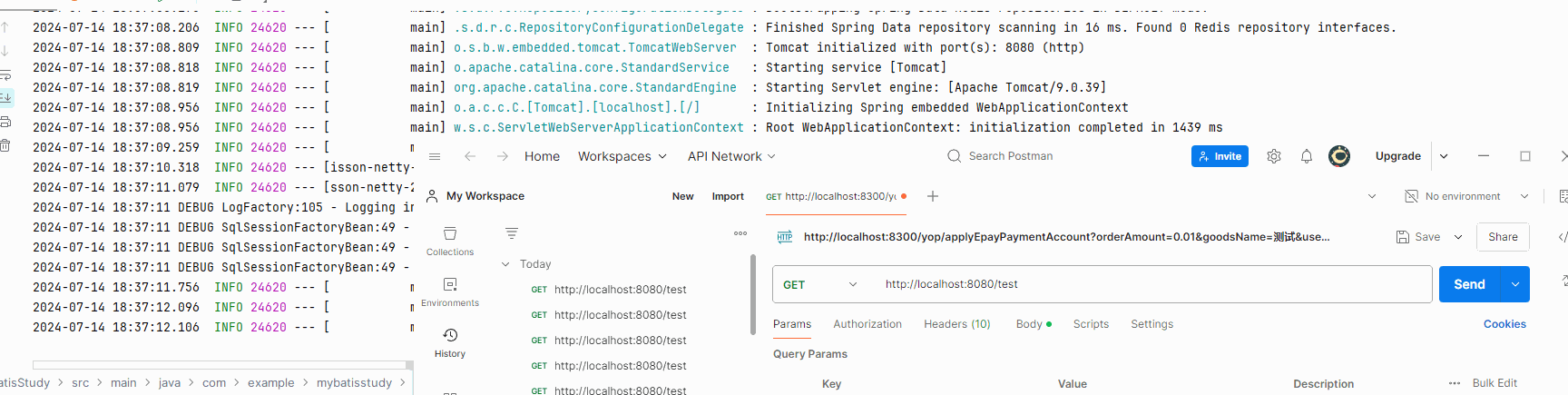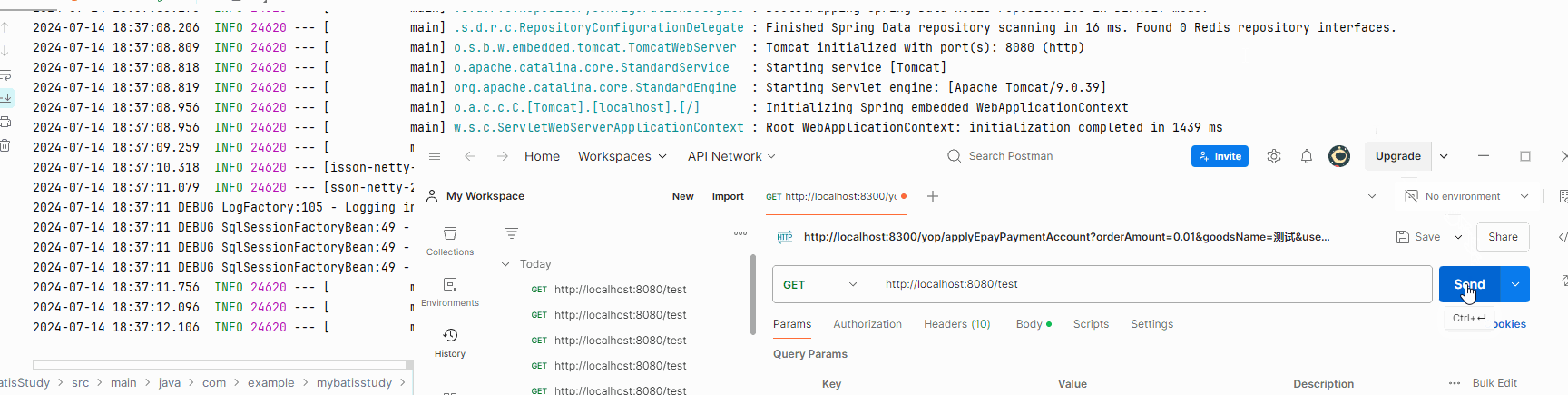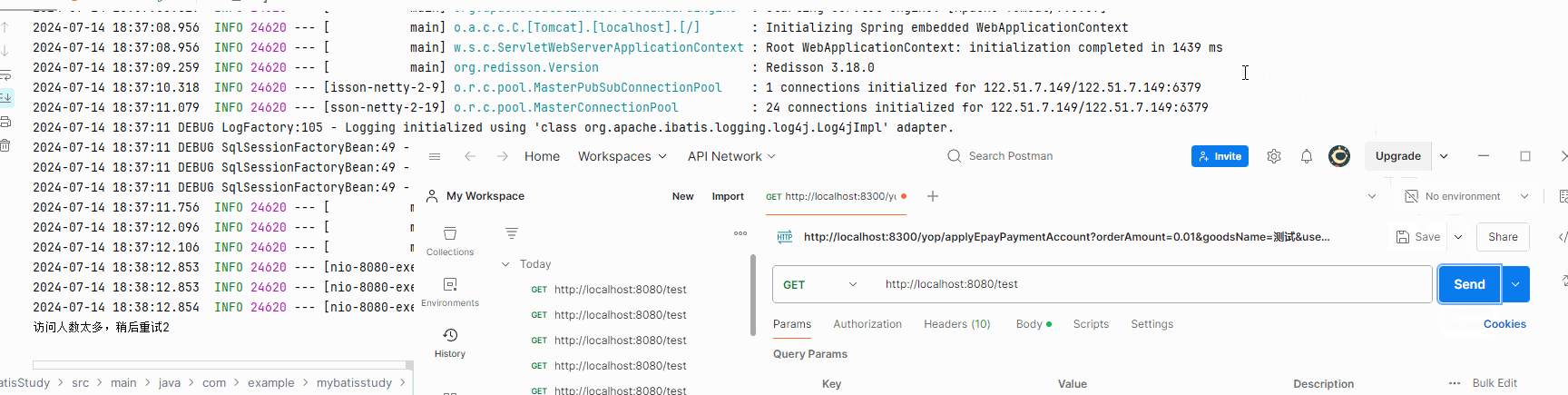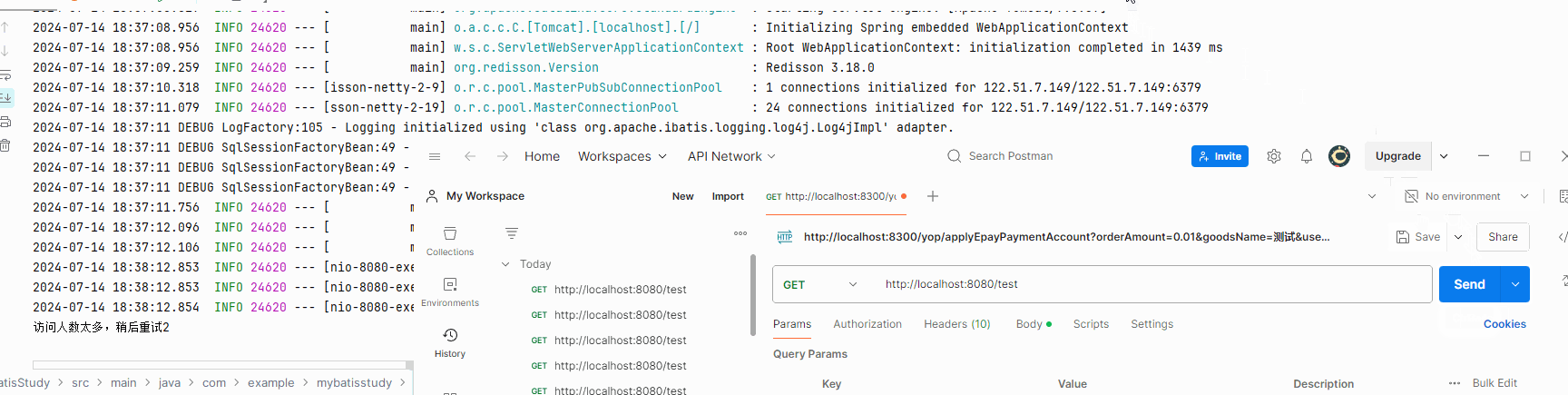
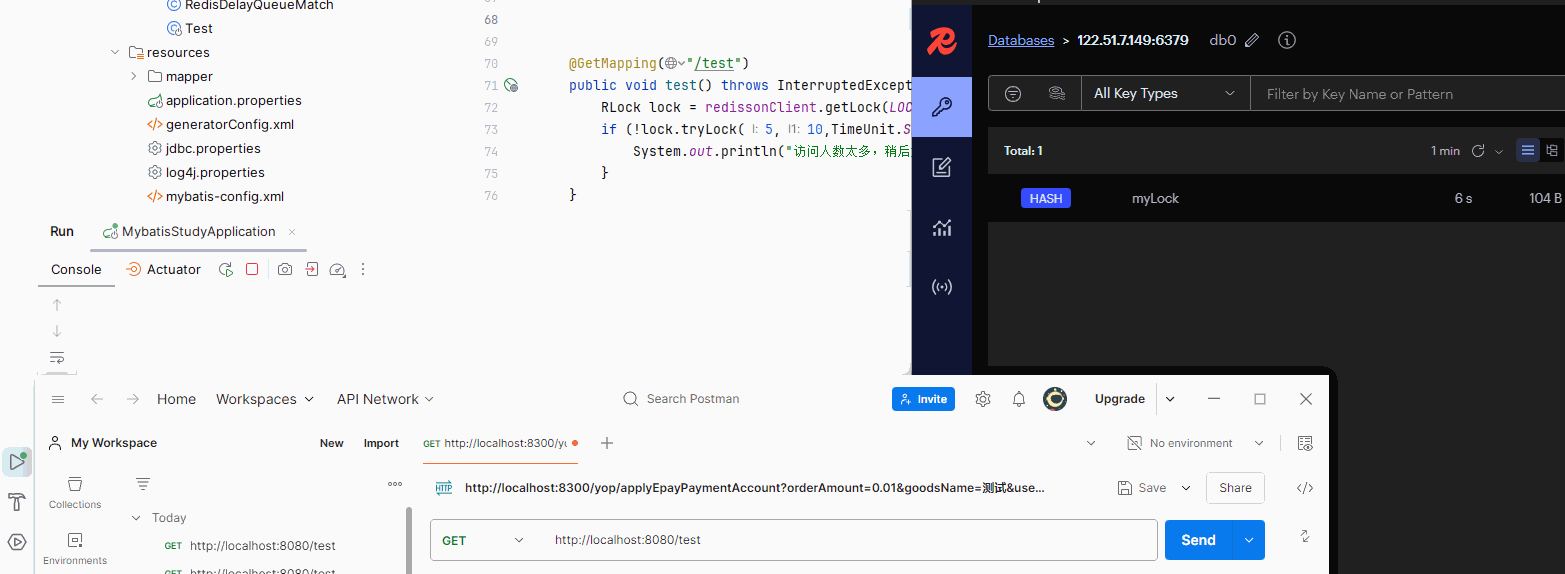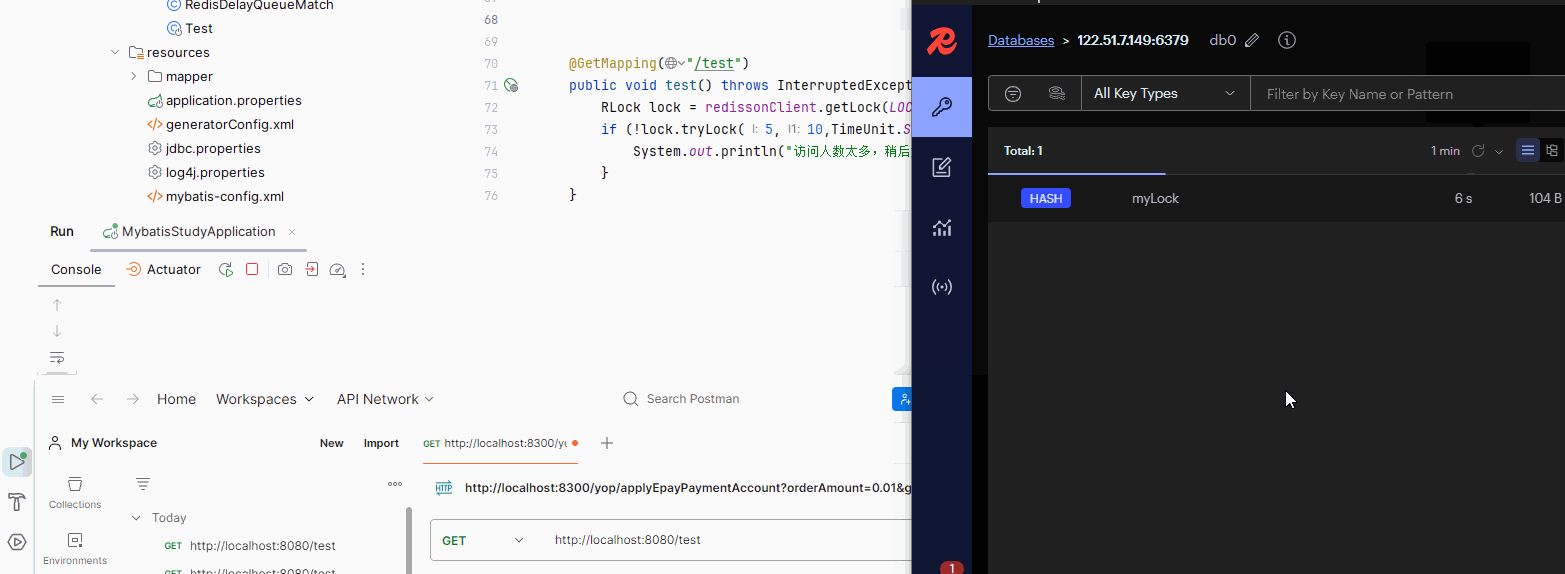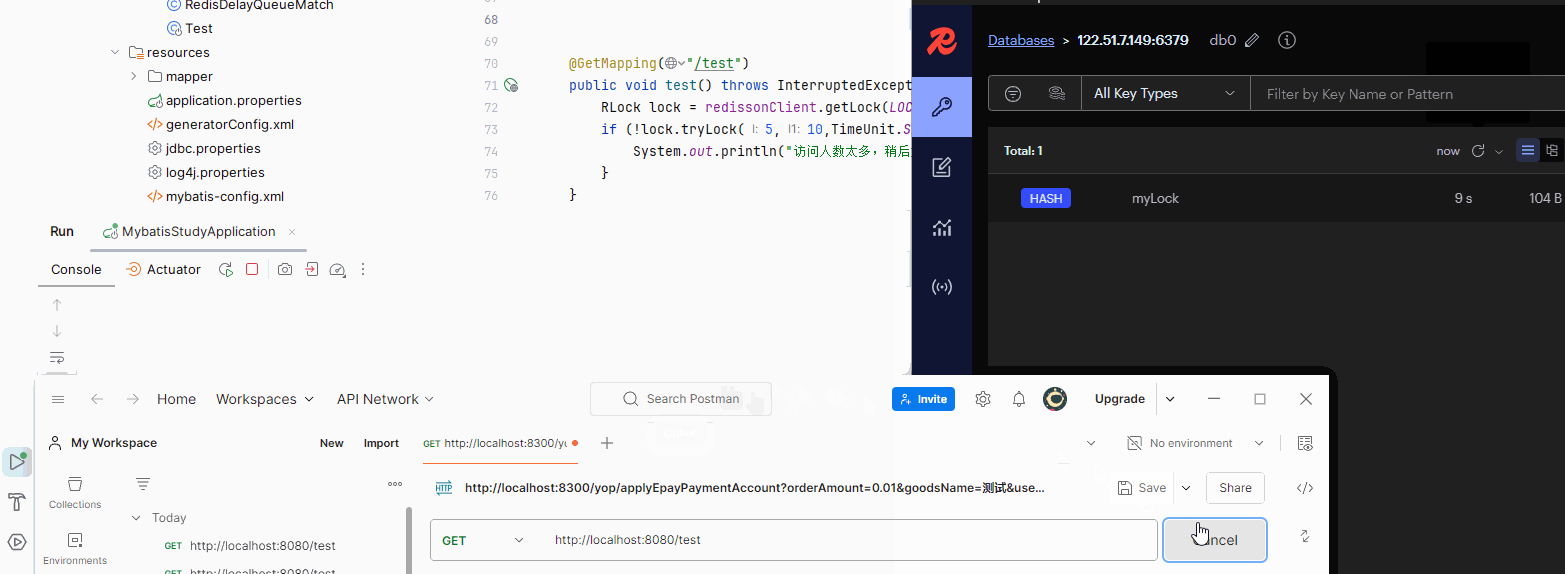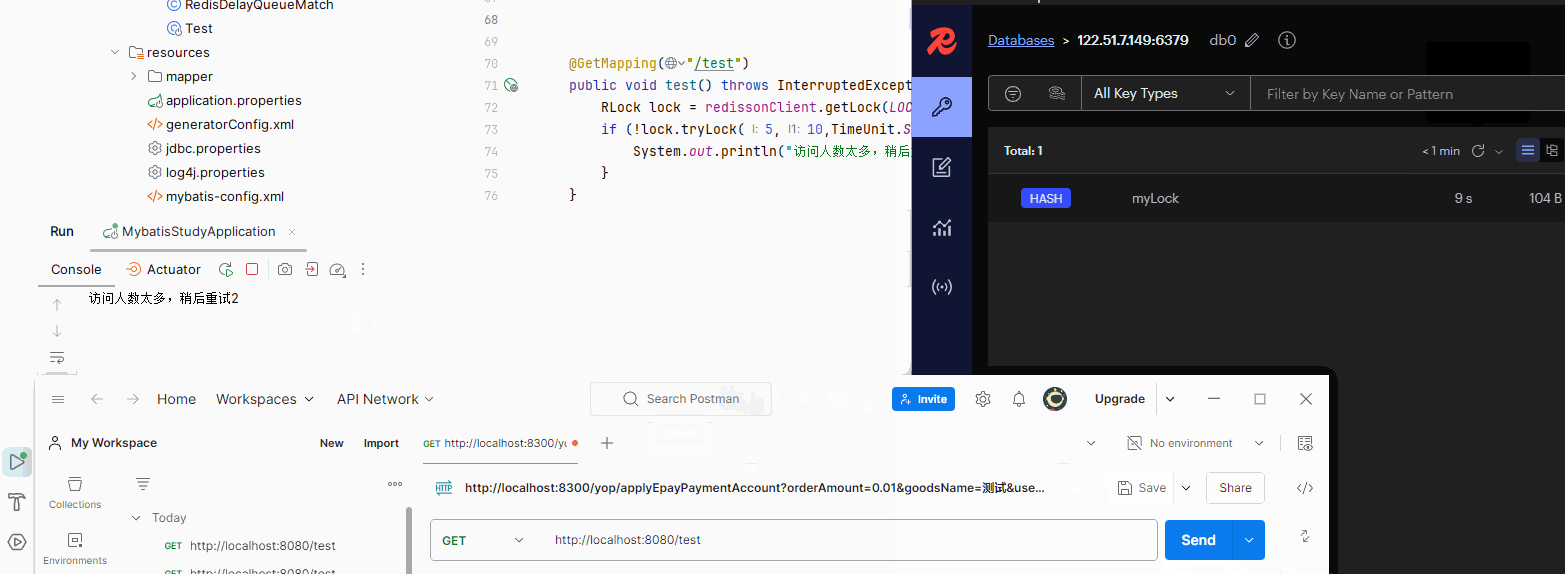
if (!lock.tryLock(5,TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
System.out.println("访问人数太多,稍后重试2");
}
}
}
执行结果如图:
tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)方法:属于RLock类。有参方法,设置获取锁的时间,锁的释放时间,未获取锁超过时间自动释放,获取锁后在指定时间内释放。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
//设置获取锁的等待时间5秒,锁的过期时间10秒
if (!lock.tryLock(5,10,TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
System.out.println("访问人数太多,稍后重试2");
}
}
}
执行结果如图:
lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)方法:属于RLock类。有参方法,设置锁的释放时间,超过时间自动释放。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
//10秒后自动释放锁
lock.lock(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
执行结果如图:
公平锁
可重入锁是非公平锁。公平锁是一种按照请求顺序获取锁的机制,即先到先得,能够避免饥饿现象。在 Redisson 中,公平锁的实现是基于 Redis 的原子操作和监听机制来实现的。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getFairLock(LOCK_KEY);
lock.lock();
}
}
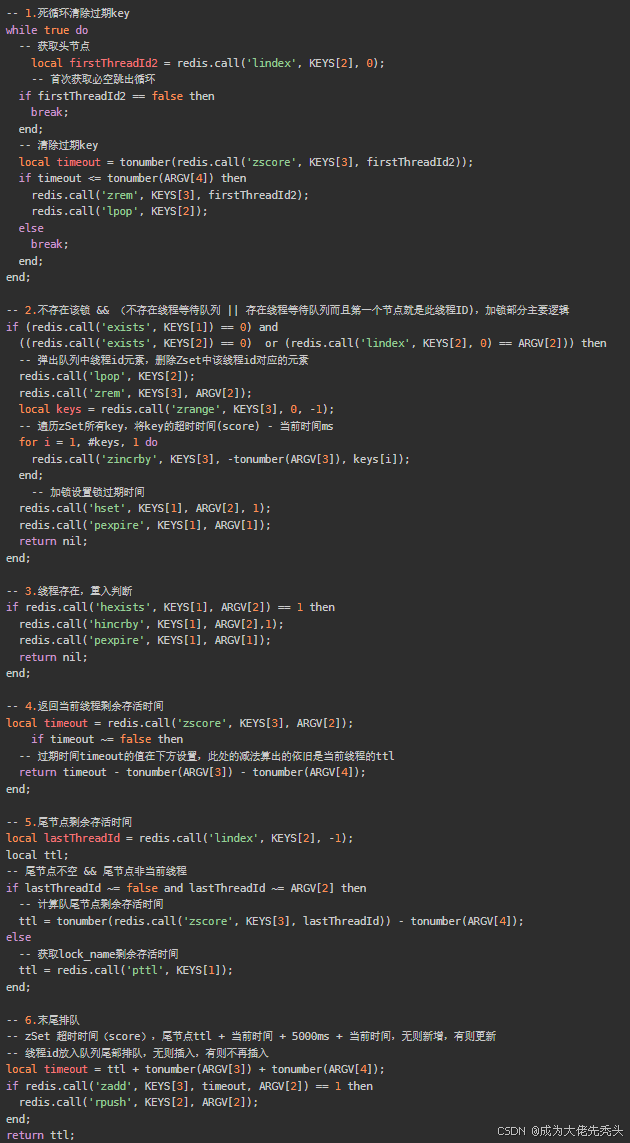
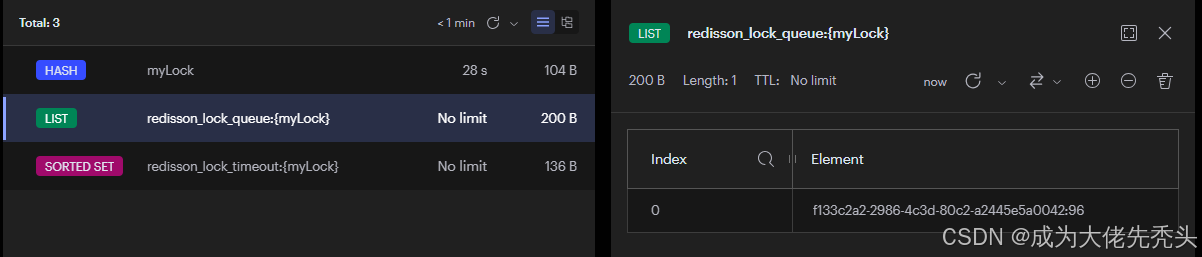
在Redisson中通过List和zSet去实现公平锁,把lua脚本复制出来整理,如图:
其中List维护了一个等待的线程队列redisson_lock_queue:[xxx},zSet维护了一个线程超时情况的有序集合redisson_lock_timeout:{xxx},在List存放等待线程ID,zSet中存放线程ID所对应的过期时间,通过排序来确认他们的优先级,每当上个线程执行完毕后释放锁,通知下一个线程。
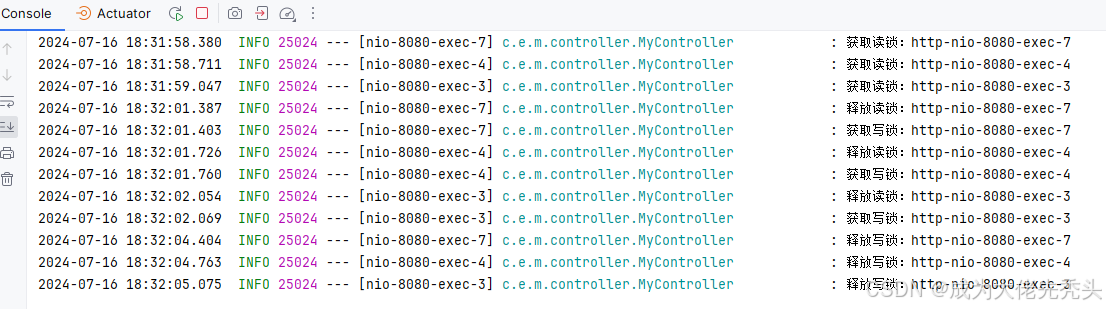
读写锁
在Redisson中,读写锁是一种支持读写分离的锁机制,可以实现多个线程对数据的并发读取,以及写操作的互斥访问。
- 读锁(共享锁):多个线程可以同时获取读锁,用于并发读取共享资源,不阻塞其他读线程,但会阻塞写线程。
- 写锁(排它锁):写锁是互斥的,即同一时刻只允许一个线程获取写锁进行写操作,阻塞其他读写线程。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
RReadWriteLock lock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock(LOCK_KEY);
//读锁
RLock rLock = lock.readLock();
try {
logger.info("获取读锁:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
logger.info("释放读锁:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
rLock.unlock();
//写锁
rLock = lock.writeLock();
try {
logger.info("获取写锁:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
logger.info("释放写锁:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
rLock.unlock();
}
}
执行结果如图:
信号量
信号量允许定义一个计数器,该计数器表示当前可用的许可证数量。线程或客户端可以通过获取许可证来访问受信号量保护的资源,当许可证数量为0时,请求许可证的线程将被阻塞,直到有许可证可用。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
RSemaphore lock = redissonClient.getSemaphore(LOCK_KEY);
//设置初始许可证数量为10
lock.trySetPermits(10);
try {
//获取一个信号量
lock.acquire();
// lock.tryAcquire();
// lock.tryAcquireAsync();
// lock.tryAcquire(23, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// lock.tryAcquireAsync(23, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放一个信号量
// lock.release();
// lock.release(10);
// lock.releaseAsync();
// lock.releaseAsync(10);
}
}
}
如果不释放信号量,则会导致阻塞,执行结果如图:
联锁
Redisson的联锁(RedLock)是一种基于Redis实现的分布式锁方案,专门用于处理多节点、多实例环境下的分布式锁管理需求。它通过在多个独立的Redis实例上进行协调,确保在分布式系统中的不同节点上能够安全地获取和释放锁。
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379").setPassword("123456");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient2(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6380").setPassword("123456");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient3(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6381").setPassword("123456");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient2;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient3;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
RLock lock1 = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
RLock lock2 = redissonClient2.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
RLock lock3 = redissonClient3.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
RLock lock = redissonClient.getMultiLock(lock1,lock2,lock3);
try {
//同时加锁:lock1 lock2 lock3, 联锁通过在多个节点上加锁,需要大多数节点(超过半数)成功加锁才算整体加锁成功。
lock.tryLock();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
红锁
Redisson的红锁(RedLock)是一种分布式锁方案,旨在提供跨多个Redis节点的高可用性和安全性。它是基于Redis实现的一种锁机制,特别适用于需要高可用性和分布式环境下的锁管理需求。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient2;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient3;
private final static String LOCK_KEY = "myLock";
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
RLock lock1 = redissonClient.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
RLock lock2 = redissonClient2.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
RLock lock3 = redissonClient3.getLock(LOCK_KEY);
RLock lock = redissonClient.getRedLock(lock1,lock2,lock3);
try {
// 同时加锁:lock1 lock2 lock3, 需要大部分(大多数)的锁节点成功加锁才能认为获取锁成功。例如,如果有5个Redis节点,需要至少3个节点成功加锁才算成功。
lock.tryLock();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
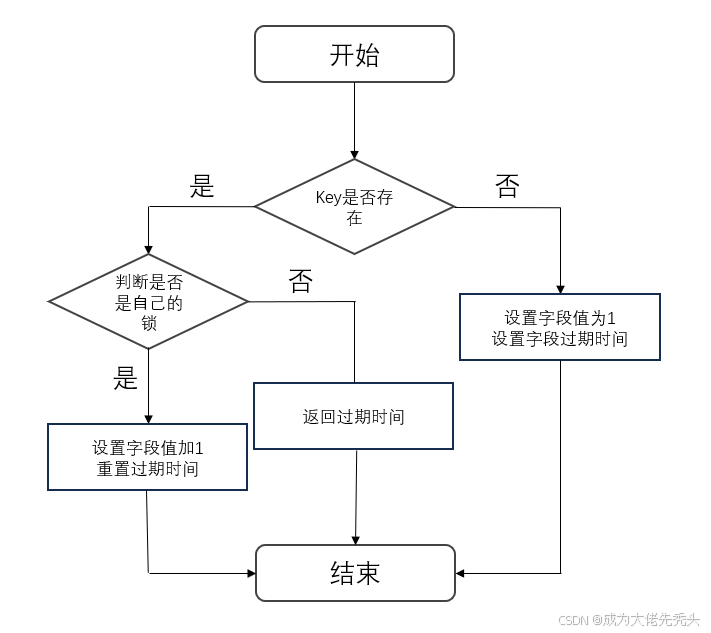
加锁机制
通过HASH来存储锁,key表示锁的名称,field表示持有者的线程ID,value重入次数。
基本流程如下:
底层是lua脚本,示例代码如下:
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) " +//锁是否存在,O 表示不存在。
"then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +//唯一标识的值+1
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +//设置超时时间
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) " +//判断hash结构中 fieldKey与客户端的唯一标识是否相等。相等表示当前加锁请求是锁重入。
"then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", //唯一标识不匹配,返回剩余过期时间
Collections.singletonList(this.getRawName()), new Object[]{unit.toMillis(leaseTime), this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
KEYS[1]:锁的名称。ARGV[1]:锁的有效时间(单位毫秒)。ARGV[2]:客户端唯一标识,线程ID。
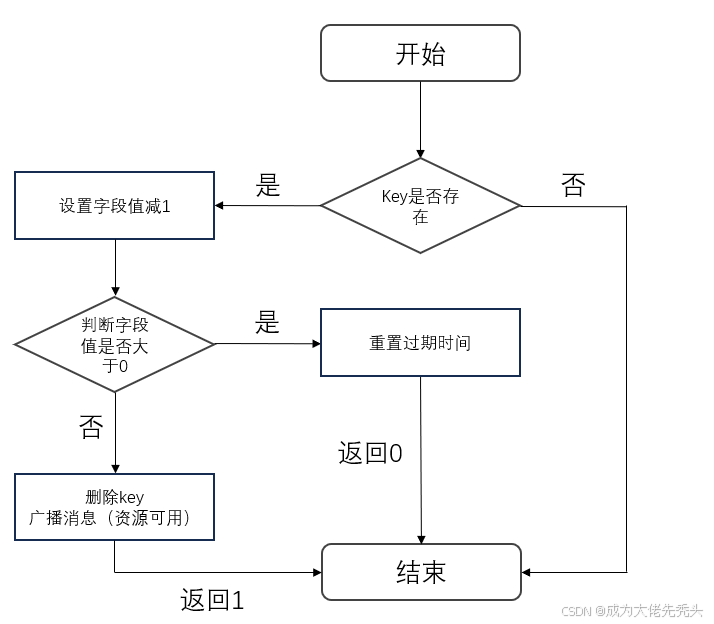
释放锁机制
释放锁的时候要确保锁的重入次数为0,并且还需要保证不能删除别人的锁。
基本流程如下:
底层是lua脚本,示例代码如下:
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) " +//判断key是否存在,0表示不存在
"then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +//字段值-1
"if (counter > 0) " +//判断字段值-1,后大于0
"then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +//设置过期时间
"return 0;" +
" else " +//判断字段值-1后,小于等于0
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +//删除key
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +//发布通知
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return nil;", Arrays.asList(this.getRawName(), this.getChannelName()), new Object[]{LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
KEYS[1]:锁的名称。KEYS[2]:消息发布的目标频道。ARGV[1]:发布到频道的消息内容。ARGV[2]:锁的有效时间(单位毫秒)。ARGV[3]:客户端唯一标识,线程ID。
看门狗
Redisson中有一个WatchDog机制,也就是看门狗机制,主要用于给锁续期,在上面的可重入锁的执行结果中有介绍过,每10秒钟判断锁是否释放,如果没有释放则续期30秒钟。
一般用于解决业务执行时间大于锁的过期时间,导致锁被释放的情况。
一般是通过估算业务执行时间,设置锁的过期时间,但是会有很多意想不到的情况,并不可靠;另一种方法就是开辟一个线程去监听锁释是否被释放,也就是WatchDog机制,给锁续期。
一般在不设置过期时间,也就是leaseTiem为-1的情况下,才有WatchDog机制。
进入tryAcquireAsync()方法,判断是否设置了过期时间,没设置过期时间则leaseTime 为-1,进入else代码块。
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
RFuture ttlRemainingFuture;
//如果指定了加锁时间,会直接去加锁
if (leaseTime > 0L) {
ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {//没有设置过期时间,默认
ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, this.internalLockLeaseTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
//异步操作
CompletionStage<Long> f = ttlRemainingFuture.thenApply((ttlRemaining) -> {
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
if (leaseTime > 0L) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
//锁续期操作
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
return ttlRemaining;
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper(f);
}
往下走进入scheduleExpirationRenewal()方法,第一次进来ExpirationEntry(Map结构存放,记录获取锁的次数)中为null,进入else代码块,添加线程id,然后执行renewExpiration()方法,实现刷新。
protected void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();
ExpirationEntry oldEntry = (ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
//记录锁次数
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
try {
//实现刷新
this.renewExpiration();
} finally {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
this.cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
}
public static class ExpirationEntry {
private final Map<Long, Integer> threadIds = new LinkedHashMap();
private volatile Timeout timeout;
public ExpirationEntry() {
}
public synchronized void addThreadId(long threadId) {
this.threadIds.compute(threadId, (t, counter) -> {
counter = (Integer)Optional.ofNullable(counter).orElse(0);
counter = counter + 1;
return counter;
});
}
}
进入renewExpiration()方法,创建任务,延迟时间是过期时间的三分之一,也就是说,30/3=10s,每10秒钟刷新过期时间
private void renewExpiration() {
ExpirationEntry ee = (ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName());
if (ee != null) {
//创建延时任务
Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = (ExpirationEntry)RedissonBaseLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonBaseLock.this.getEntryName());
if (ent != null) {
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId != null) {
//具体续期脚本
CompletionStage<Boolean> future = RedissonBaseLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.whenComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
RedissonBaseLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonBaseLock.this.getRawName() + " expiration", e);
RedissonBaseLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(RedissonBaseLock.this.getEntryName());
} else {
if (res) {//重新续期
RedissonBaseLock.this.renewExpiration();
} else {
RedissonBaseLock.this.cancelExpirationRenewal((Long)null);
}
}
});
}
}
}
//internalLockLeaseTime 的1/3时间去执行续期任务
}, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
}
通过lua脚本,重新设置有效期
protected CompletionStage<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) " +
"then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1;" +
" end;" +
" return 0;", Collections.singletonList(this.getRawName()), this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId));
}
KEYS[1]:锁的名称。ARGV[1]:锁的有效时间(单位毫秒)。ARGV[2]:客户端唯一标识,线程ID。
释放锁的时候,同时移除锁的续期任务
protected void cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId) {
//获取锁对象
ExpirationEntry task = (ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName());
if (task != null) {
if (threadId != null) {
task.removeThreadId(threadId);//移除任务
}
if (threadId == null || task.hasNoThreads()) {
Timeout timeout = task.getTimeout();
if (timeout != null) {
timeout.cancel();//关闭时间
}
//删除实例
EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(this.getEntryName());
}
}
}
项目案例
延迟队列
如果你的项目不想过于集成太多中间件,又想实现定期通知的效果,比如:生日祝福、未支付的订单失效、异步处理等,项目也不是过于复杂,那么使用Redisson进行延迟任务是一个不错的选择。
@RestController
public class MyController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyController.class);
@Autowired
RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
RBlockingQueue<Object> queue = redissonClient.getBlockingQueue("test");
RDelayedQueue<Object> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getDelayedQueue(queue);
delayedQueue.offer("hello world",5,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
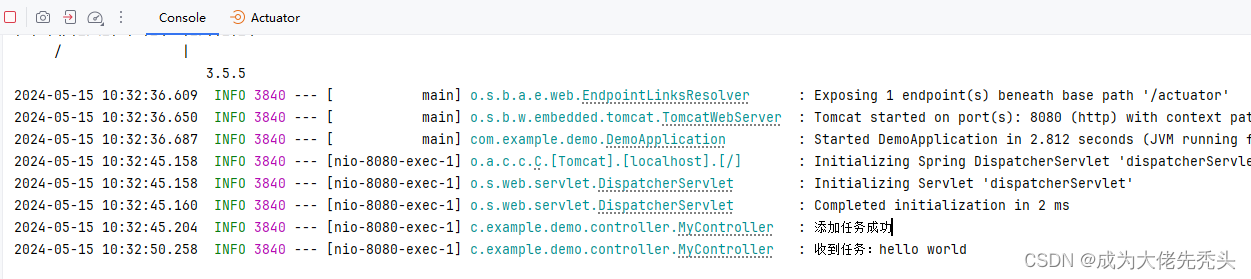
log.info("添加任务成功");
while (true){
Object take = queue.take();
log.info("收到任务:{}",take);
}
}
}
执行结果如下
然后我们将代码封装一下,示例代码如下:
封装工具类
@Component
public class RedisDelayQueueUtil {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisDelayQueueUtil.class);
/**
* 添加延迟队列
*
* @param value 队列值
* @param delay 延迟时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
* @param queueCode 队列键
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> boolean addDelayQueue(@NonNull T value, @NonNull long delay, @NonNull TimeUnit timeUnit, @NonNull String queueCode) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(queueCode) || Objects.isNull(value)) {
return false;
}
try {
RBlockingDeque<Object> blockingDeque = redissonClient.getBlockingDeque(queueCode);
RDelayedQueue<Object> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getDelayedQueue(blockingDeque);
delayedQueue.offer(value, delay, timeUnit);
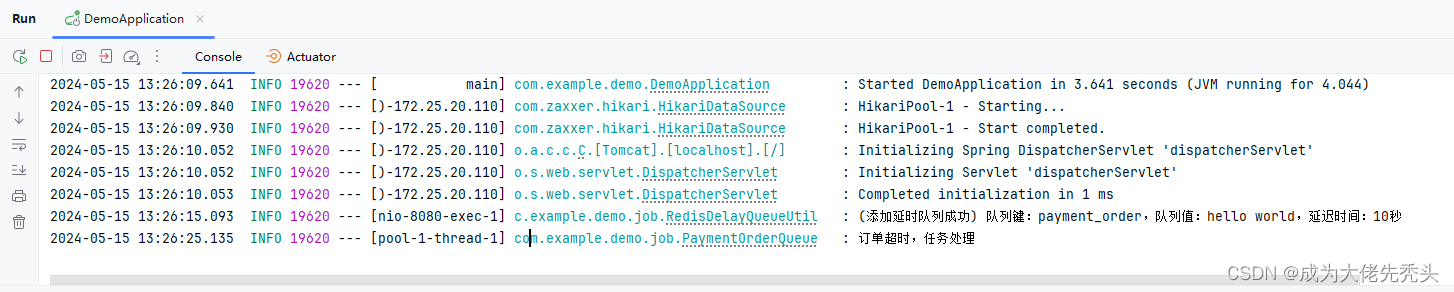
log.info("(添加延时队列成功) 队列键:{},队列值:{},延迟时间:{}", queueCode, value, timeUnit.toSeconds(delay) + "秒");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("(添加延时队列失败) {}", e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException("(添加延时队列失败)");
}
return true;
}
/**
* 获取延迟队列
*
* @param queueCode
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> T getDelayQueue(@NonNull String queueCode) throws InterruptedException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(queueCode)) {
return null;
}
RBlockingDeque<Map> blockingDeque = redissonClient.getBlockingDeque(queueCode);
T value = (T) blockingDeque.take();
return value;
}
/**
* 删除指定队列中的消息
*
* @param o 指定删除的消息对象队列值(同队列需保证唯一性)
* @param queueCode 指定队列键
*/
public boolean removeDelayedQueue(@NonNull Object o, @NonNull String queueCode) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(queueCode) || Objects.isNull(o)) {
return false;
}
RBlockingDeque<Object> blockingDeque = redissonClient.getBlockingDeque(queueCode);
RDelayedQueue<Object> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getDelayedQueue(blockingDeque);
boolean flag = delayedQueue.remove(o);
//delayedQueue.destroy();
return flag;
}
}
监听类
public class DelayJob {
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
@Component
public class RedisDelayQueueMatch implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private List<RedisDelayQueueHandle> list;
private static final Map<String,RedisDelayQueueHandle> maps = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
list.stream().forEach(item ->{
maps.put(item.code(),item);
});
}
public RedisDelayQueueHandle match(String code){
if(code == null){
return null;
}
return maps.get(code);
}
}
@Component
public class FileRedisDelayQueueRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FileRedisDelayQueueRunner.class);
@Autowired
private RedisDelayQueueUtil redisDelayQueueUtil;
@Autowired
private RedisDelayQueueMatch redisDelayQueueMatch;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
executorService.execute(() -> {
while (true) {
for (RedisDelayQueueEnum redisDelayQueueEnum : RedisDelayQueueEnum.values()) {
try {
Object delayQueue = redisDelayQueueUtil.getDelayQueue(redisDelayQueueEnum.getCode());
if (delayQueue != null) {
//通过code匹配出具体实现类
RedisDelayQueueHandle match = redisDelayQueueMatch.match(redisDelayQueueEnum.getCode());
DelayJob delayJob = new DelayJob();
delayJob.setMessage(delayJob.toString());
match.execute(delayJob);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
}
}
控制层代码
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
RedisDelayQueueUtil redisDelayQueueUtil;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
redisDelayQueueUtil.addDelayQueue("hello world",10,TimeUnit.SECONDS, RedisDelayQueueEnum.payment_order.getCode());
}
}
//处理类
public interface RedisDelayQueueHandle {
void execute(DelayJob delayJob);
String code();
}
//订单超时的具体处理类
@Component
public class PaymentOrderQueue implements RedisDelayQueueHandle{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PaymentOrderQueue.class);
@Override
public void execute(DelayJob delayJob) {
log.info("订单超时,任务处理");
//todo
}
@Override
public String code() {
return RedisDelayQueueEnum.payment_order.getCode();
}
}
执行结果如图
发布订阅
Redisson提供了RTopic接口来实现发布/订阅模式。以下是一个使用Redisson进行发布订阅的简单示例:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
MyPublisher myPublisher;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/publish")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
//向频道发布消息
myPublisher.publish("sendMessage","hello world");
}
}
@Component
public class MyPublisher {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyPublisher.class);
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
public void publish(String name,String msg) {
RTopic topic = redissonClient.getTopic(name);
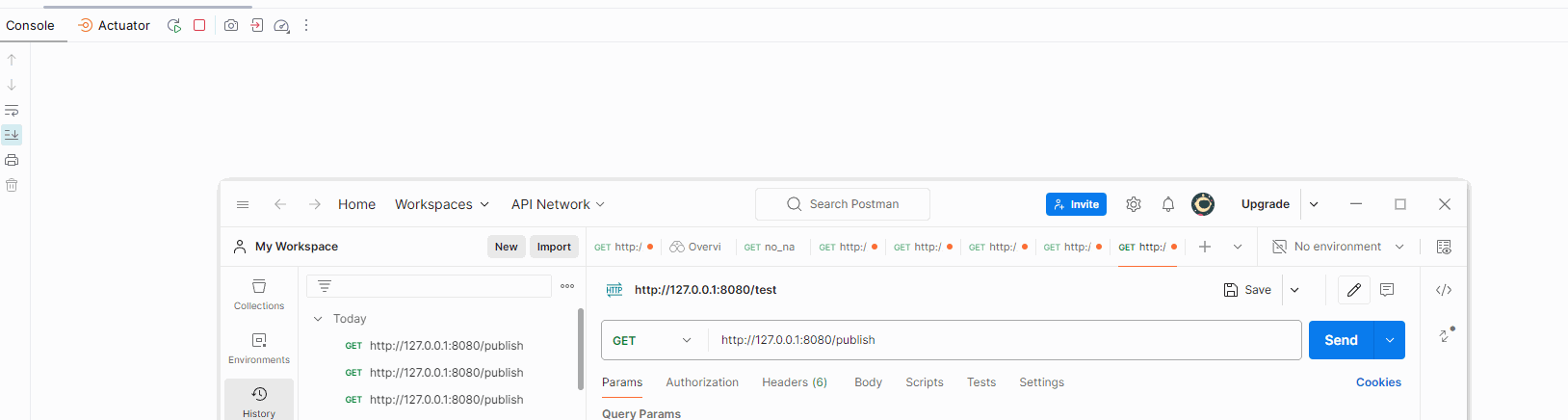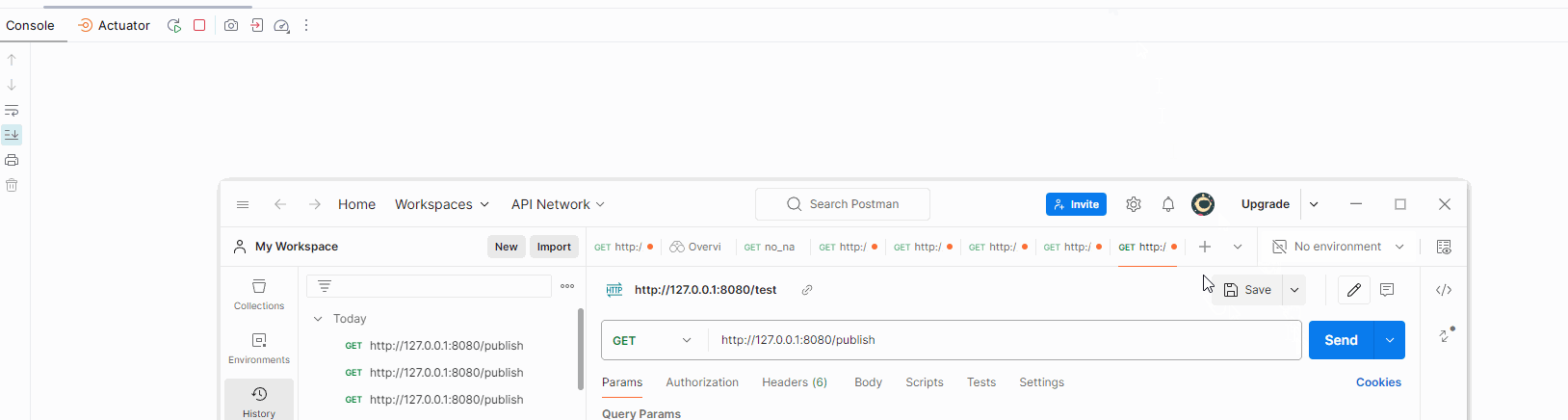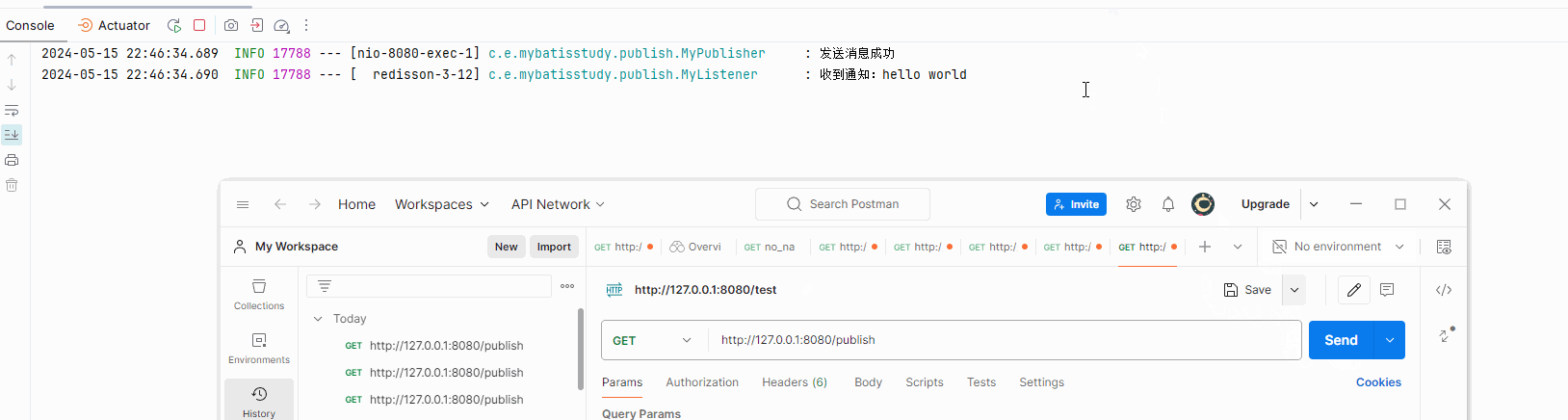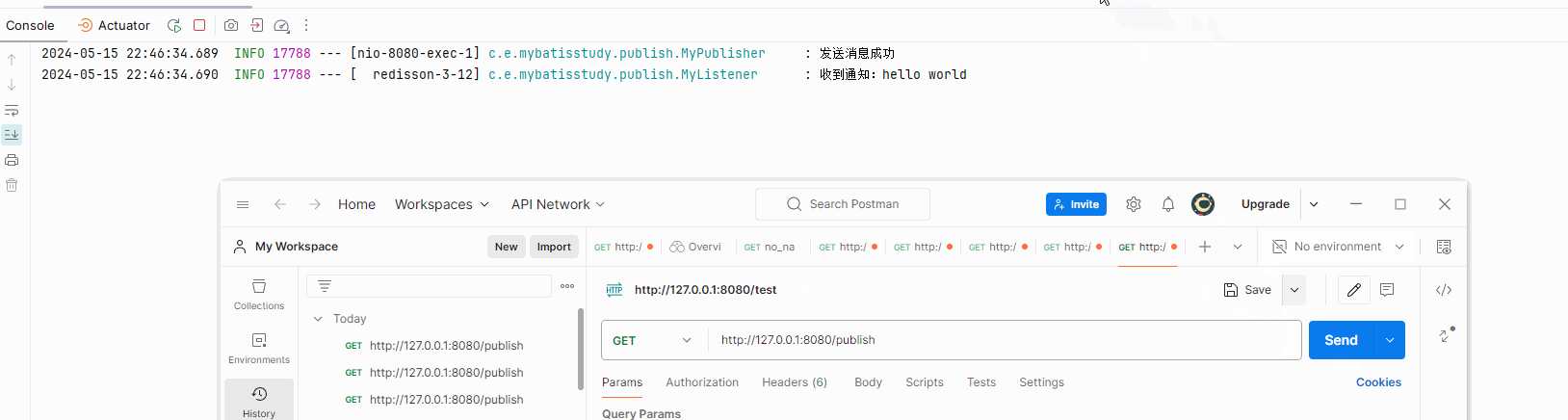
topic.publish(msg);
logger.info("发送消息成功");
}
}
@Component
public class MyListener implements MessageListener<String> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyListener.class);
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
//开启监听
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
//确保监听器已经准备好接收消息
RTopic topic = redissonClient.getTopic("sendMessage");
topic.addListener(String.class,this::onMessage);
}
@Override
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, String msg) {
log.info("收到通知:{}",msg);
}
}
执行结果如图
限流
Redisson使用RateLimiter进行限流操作,底层使用lua脚本,限流器每秒会产生X个令牌放入令牌桶,调用接口需要去令牌桶里面拿令牌。如果令牌被其它请求拿完了,那么自然而然,当前请求就调用不到指定的接口。
示例代码如下:
@RestController
public class MyController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyController.class);
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
// 2. 获取RRateLimiter对象
RRateLimiter rateLimiter = redissonClient.getRateLimiter("myRateLimiter");
// 3. 设置限流策略,例如每2分钟产生3个令牌
rateLimiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 3, 2, RateIntervalUnit.MINUTES);
long l = rateLimiter.availablePermits();
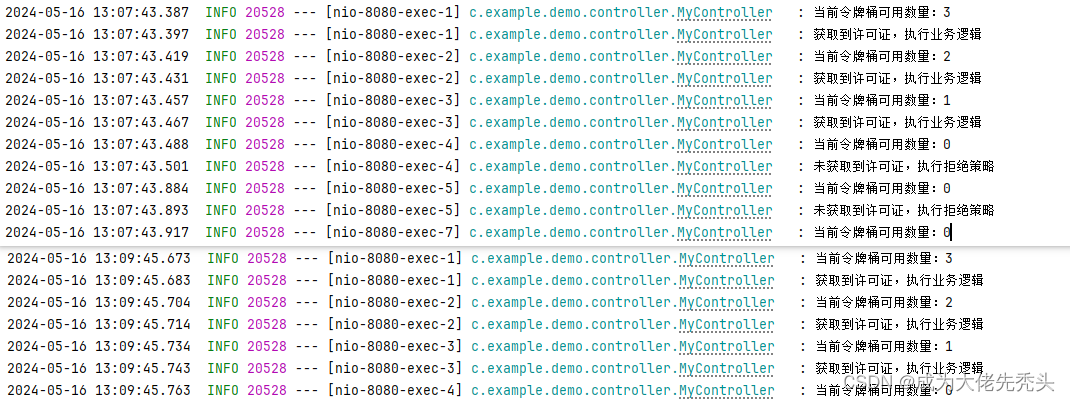
log.info("当前令牌桶可用数量:{}", l);
// 4. 尝试获取许可证
// rateLimiter.tryAcquire(1,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)等待许可证的最长时间10毫秒,获取1个许可证
if (rateLimiter.tryAcquire(1)) {
// 如果获取到许可证,执行业务逻辑
log.info("获取到许可证,执行业务逻辑");
} else {
// 如果未获取到许可证,执行拒绝策略
log.info("未获取到许可证,执行拒绝策略");
}
}
}
我们可以看到第一次请求完成后,再请求获取不到令牌,进入拒绝策略,间隔两分钟后生产了3个令牌,再次请求,执行结果如图
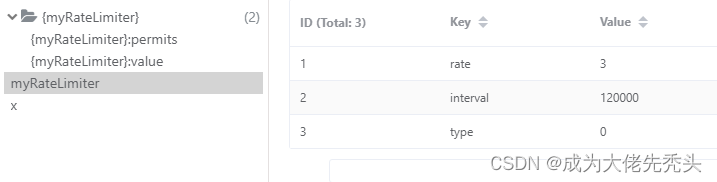
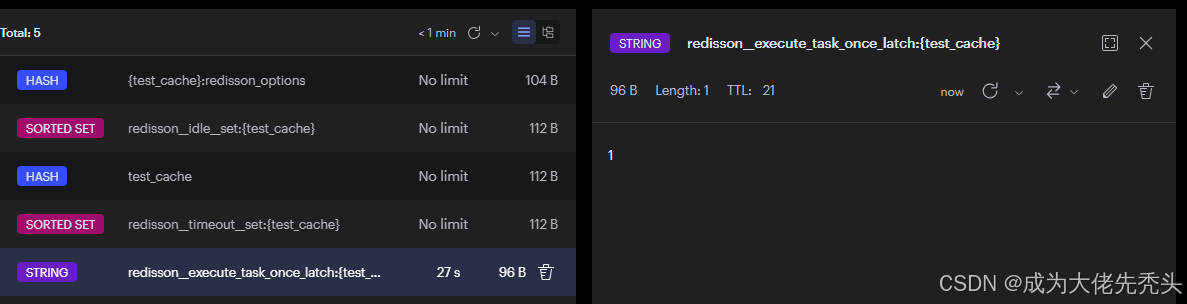
我们可以打开Redis客户端查看是如何管理的:rate令牌数,interval生产令牌桶间隔时间,type单机还是集群,示例如图所示:
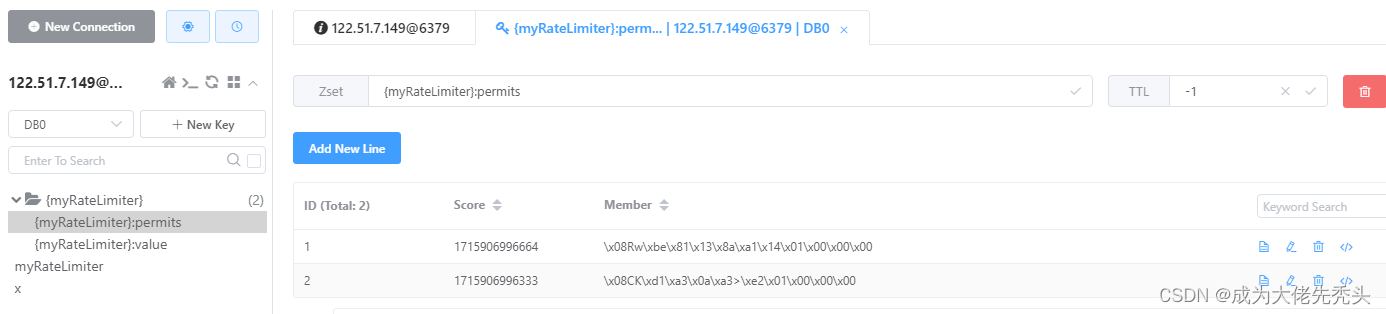
{yourname}:permits使用zset存储,记录获取令牌的数据,示例如图所示:
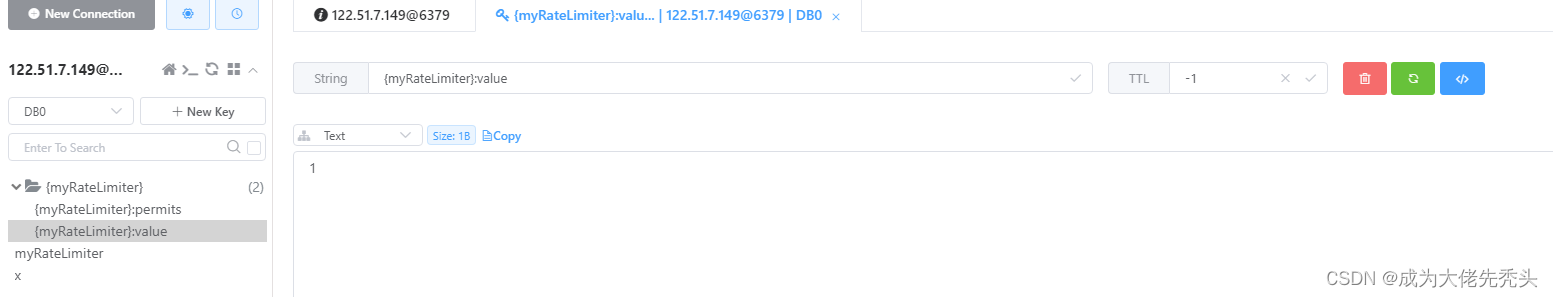
{yourname}:value使用string存储,可以查看令牌数量,示例如图所示:
我们可以将他封装成一个注解,方便多业务场景的限流通用。示例代码如下:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface GlobalRateLimiter {
String key();
long rate() default 5L;
long rateInterval() default 1L;
RateIntervalUnit rateIntervalUnit() default RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS;
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class GlobalRateLimiterAspect {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.example.mybatisstudy.annotation.GlobalRateLimiter)")
public void pointcut(){
}
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
GlobalRateLimiter annotation = method.getAnnotation(GlobalRateLimiter.class);
String key = annotation.key();
long rate = annotation.rate();
long rateInterval = annotation.rateInterval();
RateIntervalUnit rateIntervalUnit = annotation.rateIntervalUnit();
RRateLimiter rateLimiter = redissonClient.getRateLimiter(key);
if (!rateLimiter.isExists()){
rateLimiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL,rate,rateInterval,rateIntervalUnit);
//todo 可以设置一个过期时间
}
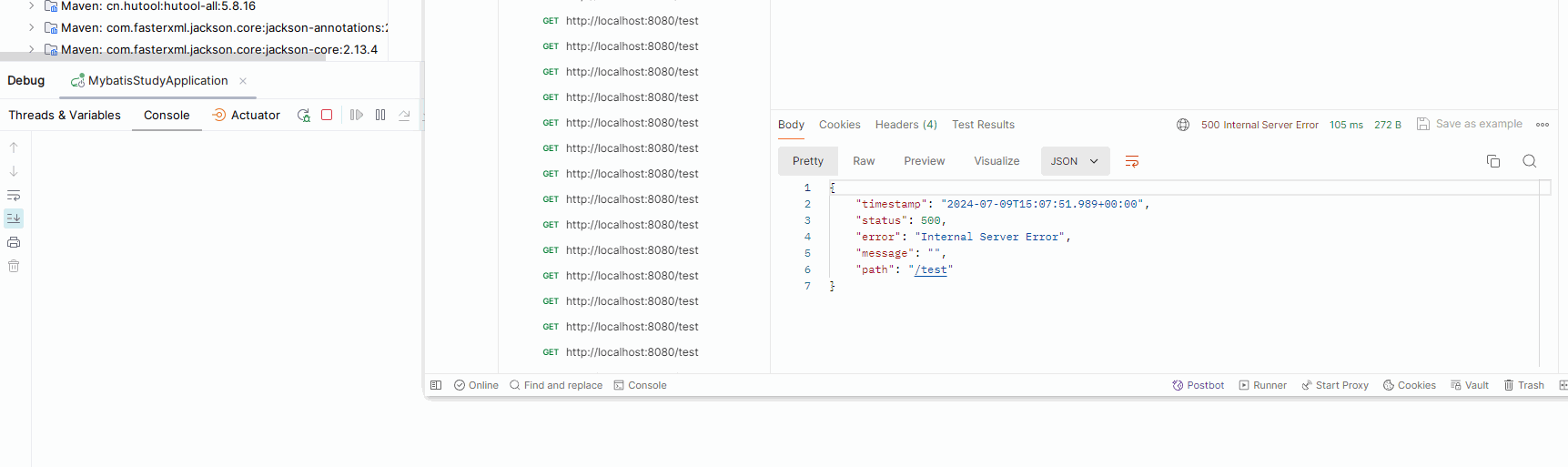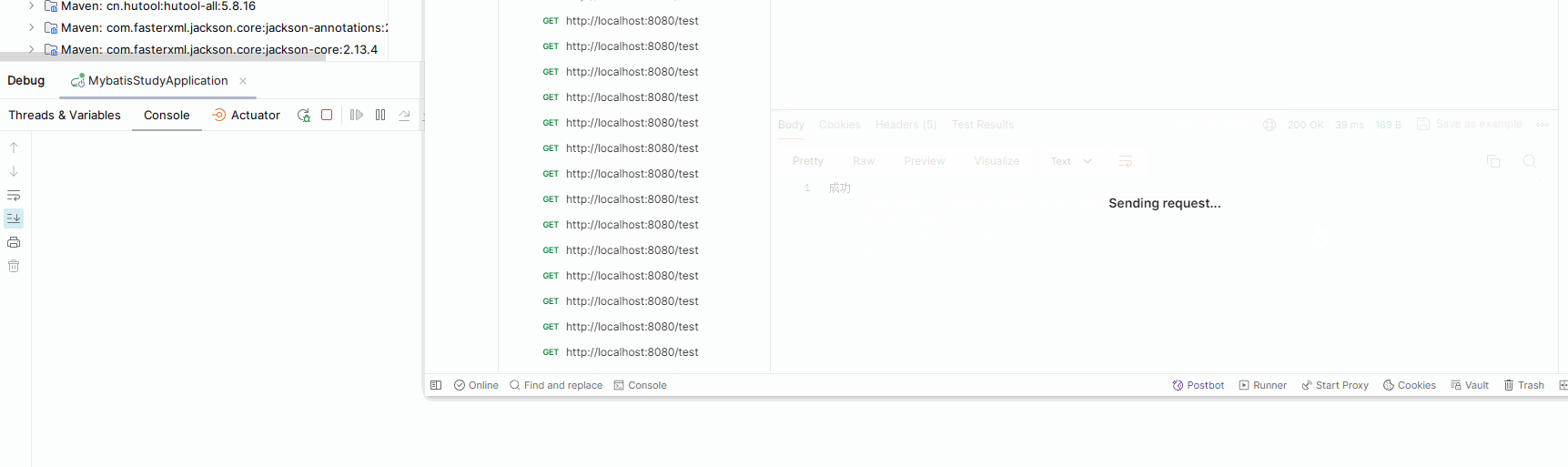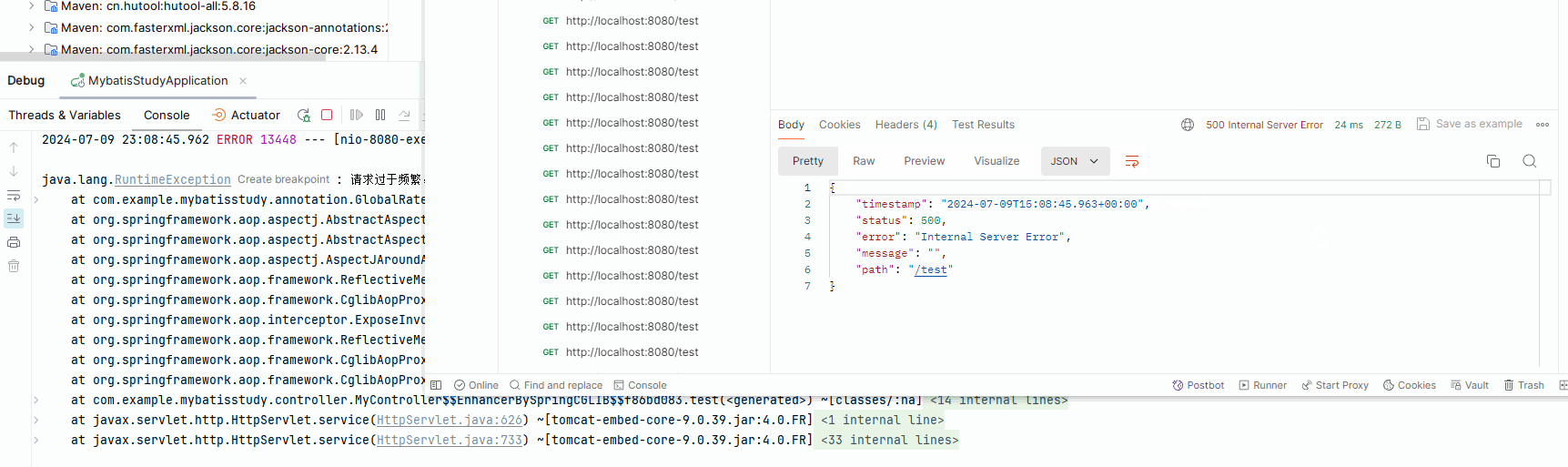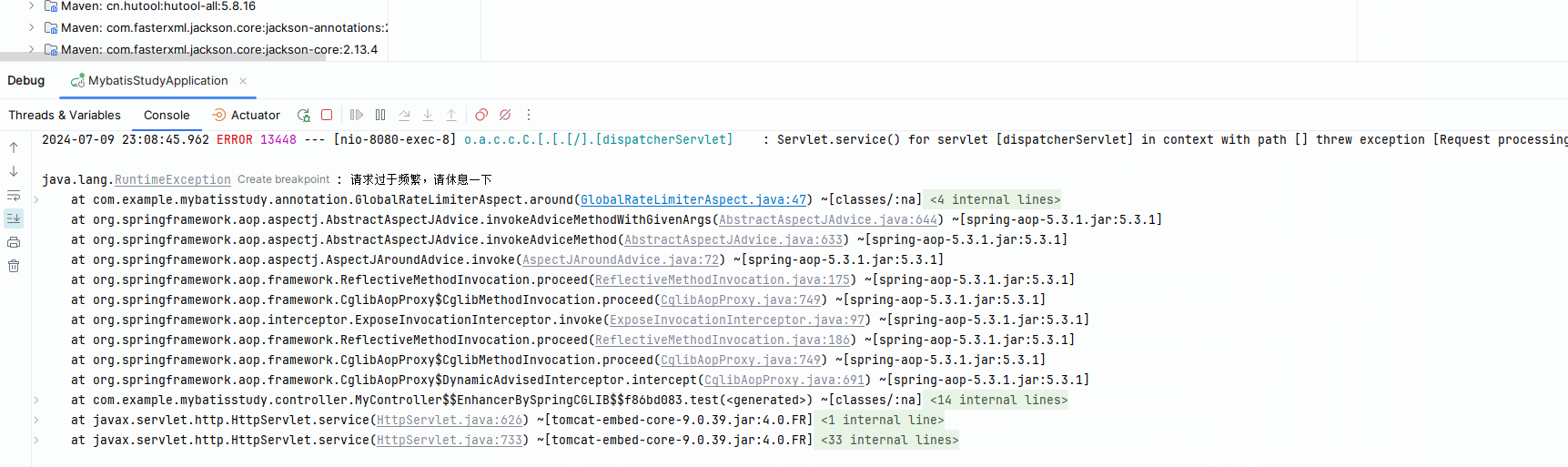
if(!rateLimiter.tryAcquire(1)){
throw new RuntimeException("请求过于频繁,请休息一下");
}
return point.proceed();
}
}
@RestController
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/test")
@GlobalRateLimiter(key = "test",rate = 2,rateInterval = 60)
public ResponseEntity test() {
return ResponseEntity.ok("成功");
}
}
执行结果如图
分布式自增ID
分布式系统中生成自增ID是一个常见的需求,特别是在需要保证全局唯一性和并发性的场景下。Redis可以作为生成分布式自增ID的工具,我们可以通过计数器的实现方式:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
System.out.println(id("memberId"));
System.out.println(seqNo("memberNo"));
/** OutPut:
* 1721645124953002
* 20240722184524000000000000000002
*/
}
/**
* 生成16位的自增id
* String.format("%0"+len+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet())用于格式化整型,补零到指定长度
* 比如:
* String.format("%0" + 3 + "d", id); 将生成字符串 "045"。
* @param idName 唯一key值
* @return 时间戳+补零自增
*/
private String id(String idName){
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(idName);
return System.currentTimeMillis() + String.format("%0"+3+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet());
}
/**
* 生成32位的自增no,
* String.format("%0"+len+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet())用于格式化整型,补零到指定长度
* 比如:
* String.format("%0" + 20 + "d", id); 将生成字符串 "000000000000000012345"。
* @param seqName 唯一key值
* @return 日期格式++补零自增
*/
private String seqNo(String seqName){
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(seqName);
//转换日期格式
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatters = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
String localDateStr = LocalDateTime.now().format(dateTimeFormatters);
//计算剩余补零长度
int len = 32-localDateStr.length();
return localDateStr + String.format("%0"+len+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet());
}
}
封装
Spring提供了CacheManager接口,用于管理应用程序中的缓存。主要负责创建、配置、管理和销毁缓存对象。
Cache 是实际存储数据的对象或接口,它负责存储和检索缓存的数据。它是CacheManager的一部分,用于实际存储缓存项并提供相关的操作接口。
我们可以基于Spring提供这两个类,封装成自己的代码(以前公司这样用的,感觉很优雅),示例代码如下:
先创建一个CacheManager 的Bean。
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient){
RedissonSpringCacheManager redissonSpringCacheManager = new RedissonSpringCacheManager(redissonClient);
return redissonSpringCacheManager;
}
}
然后定义一个接口,实现它,编写基本功能操作
public interface CacheManage {
Cache getCache(String name);
String id16(String idName);
String seqNo32(String seqName);
RLock getLock(String key);
}
@Component
public class RedisCacheManage implements CacheManage {
private CacheManager cacheManager;
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
public RedisCacheManage(CacheManager cacheManager, RedissonClient redissonClient) {
this.cacheManager = cacheManager;
this.redissonClient = redissonClient;
}
@Override
public Cache getCache(String name) {
return cacheManager.getCache(name);
}
/**
* 生成16位的自增id
* String.format("%0"+len+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet())用于格式化整型,补零到指定长度
* 比如:
* String.format("%0" + 3 + "d", id); 将生成字符串 "045"。
* @param idName 唯一key值
* @return 时间戳+补零自增
*/
public String id16(String idName){
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(idName);
return System.currentTimeMillis() + String.format("%0"+3+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet());
}
/**
* 生成32位的自增no,
* String.format("%0"+len+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet())用于格式化整型,补零到指定长度
* 比如:
* String.format("%0" + 20 + "d", id); 将生成字符串 "000000000000000012345"。
* @param seqName 唯一key值
* @return 日期格式++补零自增
*/
public String seqNo32(String seqName){
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redissonClient.getAtomicLong(seqName);
//转换日期格式
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatters = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
String localDateStr = LocalDateTime.now().format(dateTimeFormatters);
//计算剩余补零长度
int len = 32-localDateStr.length();
return localDateStr + String.format("%0"+len+"d",atomicLong.incrementAndGet());
}
@Override
public RLock getLock(String key) {
return redissonClient.getLock(key);
}
}
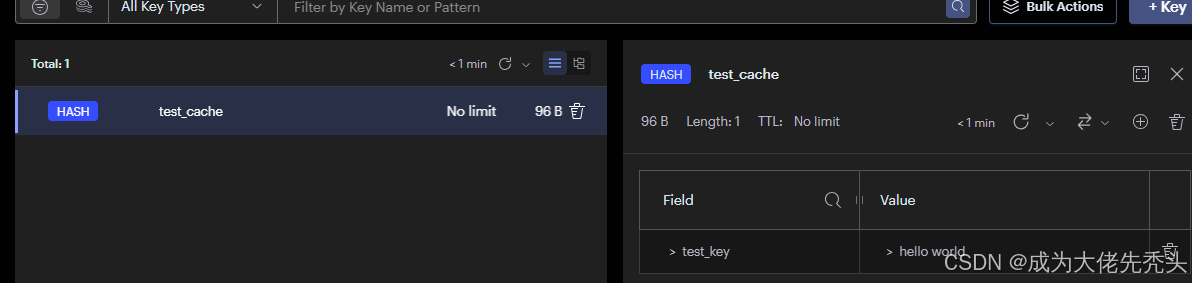
我们在Spring初始化的时候获取Cache,并定义为全局变量,往后都基于此Map进行put()和get()操作,便于管理,我们可以看下底层是如何存储的,如图所示,存储在Map结构中。
测试用例如下:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
CacheManage cacheManage;
Cache cache;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
cache = cacheManage.getCache("test_cache");
}
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
cache.put("test_key","hello world");
String s = cache.get("test_key", String.class);
System.out.println(s);
/** Output:
* hello world
*/
}
}
执行结果如图
有一些场景可能需要设置缓存过期时间,防止长时间占用,浪费内存。
我们可以自定义一个CacheManage,然后继承RedissonSpringCacheManager,示例代码如下:
public class MyRedisCacheManage extends RedissonSpringCacheManager {
public MyRedisCacheManage(RedissonClient redisson) {
super(redisson);
}
@Override
protected CacheConfig createDefaultConfig() {
//设置默认缓存过期时间,ttl过期时间为30分钟、最大空闲时间为5分钟
return new CacheConfig(30 * 60 * 1000,5 * 60 * 1000);
}
}
然后配置Bean的时候更换为自定义的类
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient){
MyRedisCacheManage redissonSpringCacheManager = new MyRedisCacheManage(redissonClient);
return redissonSpringCacheManager;
}
}
然后开启一个线程倒计时,如果达到空闲时间就会清除,否则ttl过期清除(经过测试hash里面过期清除的是最先插入的key值,不会全部清除)。
可能有些时候,你需要单独设置不同的过期时间,你可以这样处理
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient){
MyRedisCacheManage redissonSpringCacheManager = new MyRedisCacheManage(redissonClient);
//单独设置缓存过期时间
Map<String,CacheConfig> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("mycache1",new CacheConfig(5 * 60 * 1000,2 * 60 * 1000));
map.put("mycache2",new CacheConfig(15 * 60 * 1000,7 * 60 * 1000));
redissonSpringCacheManager.setConfig(map);
return redissonSpringCacheManager;
}
}
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
CacheManage cacheManage;
Cache cache;
Cache cache1;
Cache cache2;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
cache = cacheManage.getCache("test_cache");
cache1 = cacheManage.getCache("mycache1");
cache2 = cacheManage.getCache("mycache2");
}
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test() {
cache.put("test_key","hello world");
cache1.put("mycache1","hello world1");
cache2.put("mycache2","hello world2");
}
}