事务的本质
何为事务管理
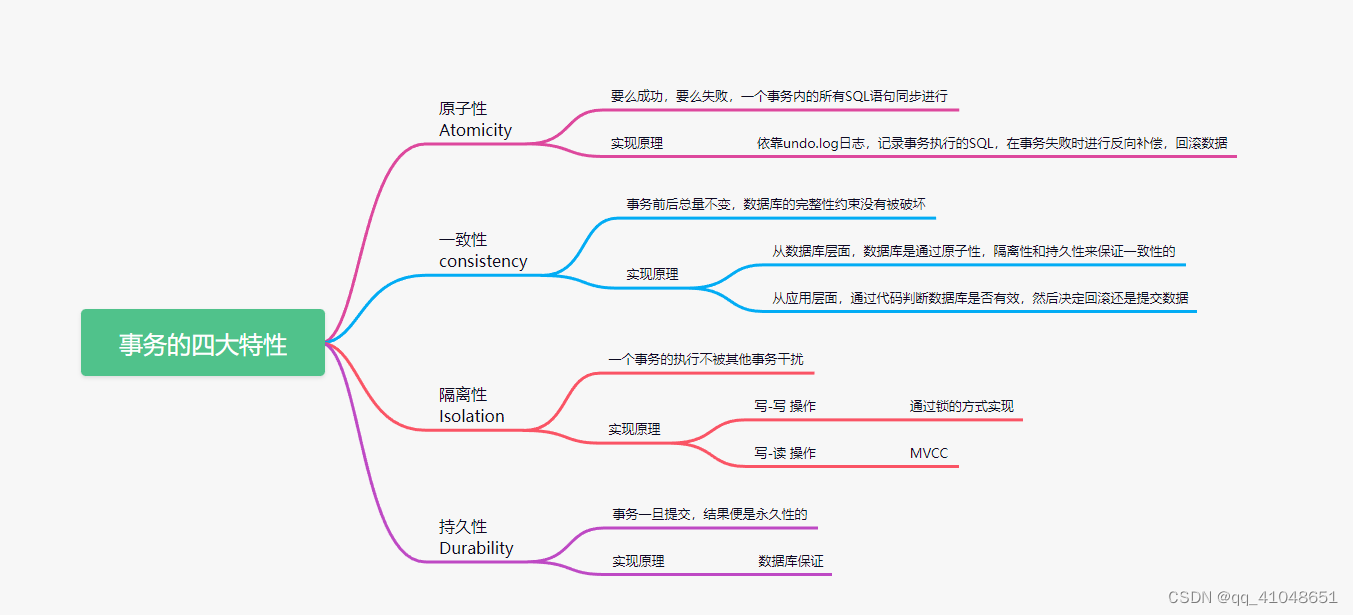
数据库事务(Database Transaction) ,是指作为单个逻辑工作单元执行的一系列操作,要么完全地执行,要么完全地不执行。
事务处理可以确保除非事务性单元内的所有操作都成功完成,否则不会永久更新面向数据的资源。通过将一组相关操作组合为一个要么全部成功要么全部失败的单元,可以简化错误恢复并使应用程序更加可靠。
一个逻辑工作单元要成为事务,必须满足所谓的 ACID(原子性、一致性、隔离性和持久性)属性。事务是数据库运行中的逻辑工作单位,由DBMS中的事务管理子系统负责事务的处理。
JDBC中的事务管理
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 注册 JDBC 驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 打开连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "123456");
// 执行查询
stmt = conn.createStatement();
conn.setAutoCommit(false); // 关闭自动提交
// 添加用户信息
String sql = "INSERT INTO T_USER(id,user_name)values(1,'管理员')";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
// 添加日志问题
sql = "INSET INTO t_log(id,log)values(1,'添加了用户:管理员')";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
conn.commit(); // 上面两个操作都没有问题就提交
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 出现问题就回滚
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
try {
if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException se2) {
}
try {
if (conn != null) conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
通过上面的代码我们发现关键的操作有这三个:
Spring中的事务管理
Spring中支持两种事务的使用方式
- 基于XML配置方式
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
<!-- 开启扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dpb.*"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="username" value="pms"/>
<property name="password" value="pms"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置JdbcTemplate -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--
Spring中,使用XML配置事务三大步骤:
1. 创建事务管理器
2. 配置事务方法
3. 配置AOP
-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="advice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="fun*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- aop配置 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))" id="tx"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="advice" pointcut-ref="tx"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 基于注解方式
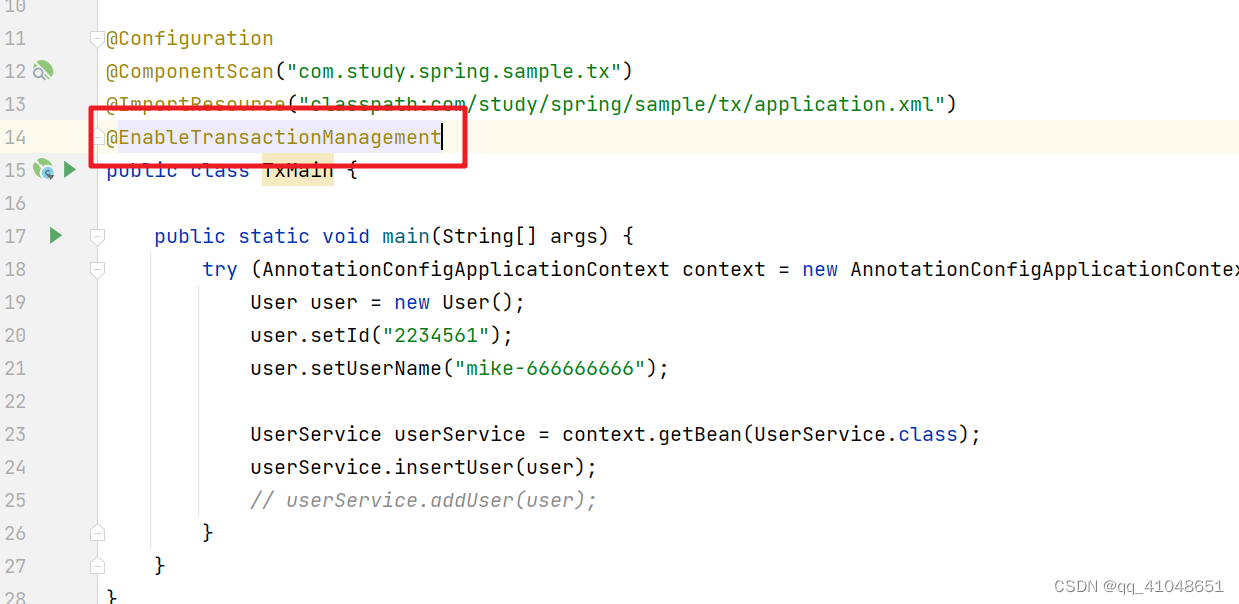
先开启事务注解
对应方法上添加@Transactional注解
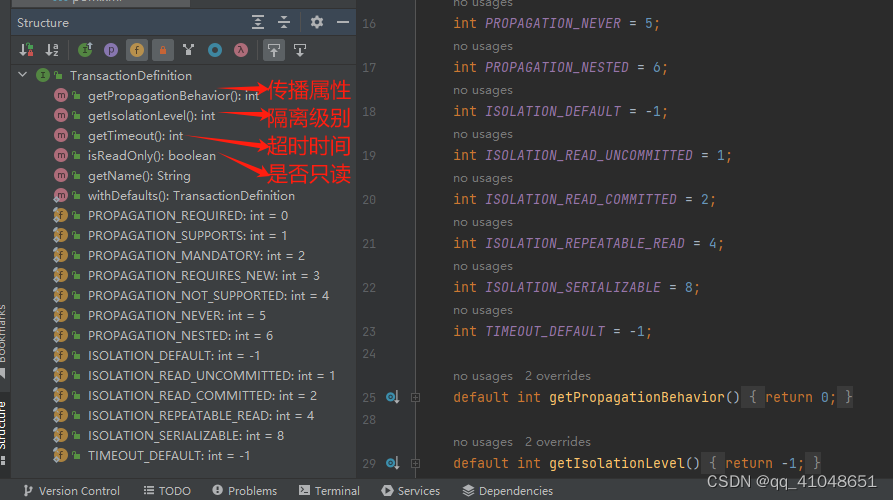
传播特性及隔离级别扩展知识
传播属性:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38526573/article/details/87898161
隔离级别:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38526573/article/details/87898730
Spring事务的源码设计
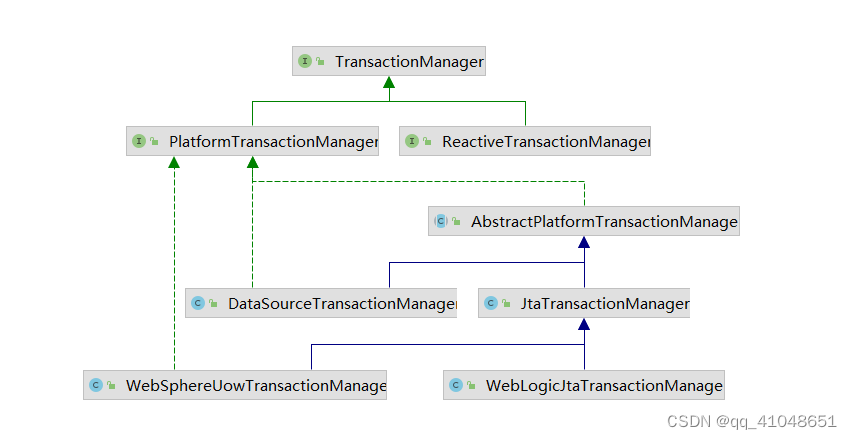
事务管理器
PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器
ReactiveTransactionManager:响应式编程的事务管理器
我们关注的重点是PlatformTransactionManager:
public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager {
/**
获取事务
*/
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException;
/**
提交数据
*/
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
回滚数据
*/
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
PlatformTransactionManager也是个接口,下面有两个比较重要的实现:
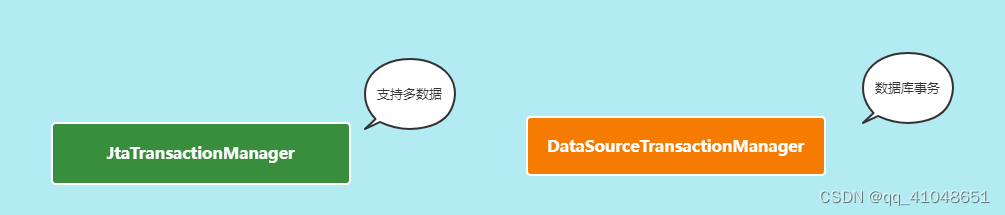
JtaTransactionManager:支持分布式事务【本身服务中的多数据源】
DataSourceTransactionManager:数据源事务管理器。在但数据源中的事务管理,这个是我们分析的重点。提供了相关的事务操作方法:doBegin、doCommit、doRollback等等。
事务定义
PlatformTransactoinManager中看到了 TransactionDefinition 这个对象,通过字面含义是 事务定义,里面定义了事务的传播属性和隔离级别。
事务的开启
在PlatformTransactionManager中通过getTransaction(transactionDefinition)开启事务,AbstractPlatformTransactionManager实现了PlatformTransactionManager接口,具体看AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中的getTransaction方法。
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
// 如果没有事务定义信息则使用默认的事务管理器定义信息
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取事务
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 判断当前线程是否存在事务,判断依据为当前线程记录的连接不为空且连接中的transactionActive属性不为空
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// 当前线程已经存在事务
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
// 事务超时设置验证
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
// 如果当前线程不存在事务,但是PropagationBehavior却被声明为PROPAGATION_MANDATORY抛出异常
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,PROPAGATION_NESTED都需要新建事务
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
//没有当前事务的话,REQUIRED,REQUIRES_NEW,NESTED挂起的是空事务,然后创建一个新事务
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// 恢复挂起的事务
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
// 创建一个空的事务
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
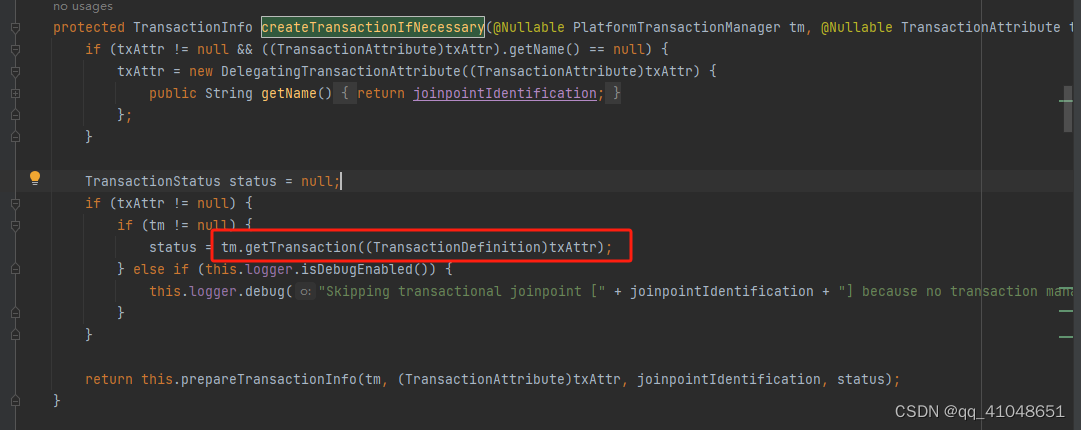
- 获取事务doGetTransaction()方法
/**
* 创建一个DataSourceTransactionObject当作事务,设置是否允许保存点,然后获取连接持有器ConnectionHolder
* 里面会存放JDBC的连接,设置给DataSourceTransactionObject,当然第一次是空的
*
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
// 创建一个数据源事务对象
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
// 是否允许当前事务设置保持点
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
/**
* TransactionSynchronizationManager 事务同步管理器对象(该类中都是局部线程变量)
* 用来保存当前事务的信息,我们第一次从这里去线程变量中获取 事务连接持有器对象 通过数据源为key去获取
* 由于第一次进来开始事务 我们的事务同步管理器中没有被存放.所以此时获取出来的conHolder为null
*/
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
// 非新创建连接则写false
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
// 返回事务对象
return txObject;
}
- 事务管理方法:handleExistingTransaction
主要争对事务的传播特性做一下操作 - startTransaction开启事务和连接
/**
* Start a new transaction.
*/
private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,
boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources) {
// 是否需要新同步
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
// 创建新的事务
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 开启事务和连接
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 新同步事务的设置,针对于当前线程的设置
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
doBegin方法开启和连接事务,主要是设置一些属性,关闭自动提交功能同时把连接绑定到本地线程中bindResource
Spring事务源码串联
编程式事务
结合上面的设计我们就可以来实现事务的处理了
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager txManager;
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
@Transactional
public void insertUser(User u) {
// 1、创建事务定义
DefaultTransactionDefinition definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 2、根据定义开启事务
TransactionStatus status = txManager.getTransaction(definition);
try {
this.userDao.insert(u);
Log log = new Log(System.currentTimeMillis() + "", System.currentTimeMillis() + "-" + u.getUserName());
// this.doAddUser(u);
this.logService.insertLog(log);
// 3、提交事务
txManager.commit(status);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 4、异常了,回滚事务
txManager.rollback(status);
throw e;
}
}
AOP声明式事务
我们从编程式事务可以看出开发人员每次编写代码在业务方法执行前后都要对事务进行操作,执行前创建事务定义、开启事务,执行后需要提交事务、回滚等操作。
我们都知道Spring的事务时根据SpringAOP来实现的,那基于什么来解决编程式事务带来的问题呢?
这里SpringAOP的环绕通知就派上用场了。
拦截器注入
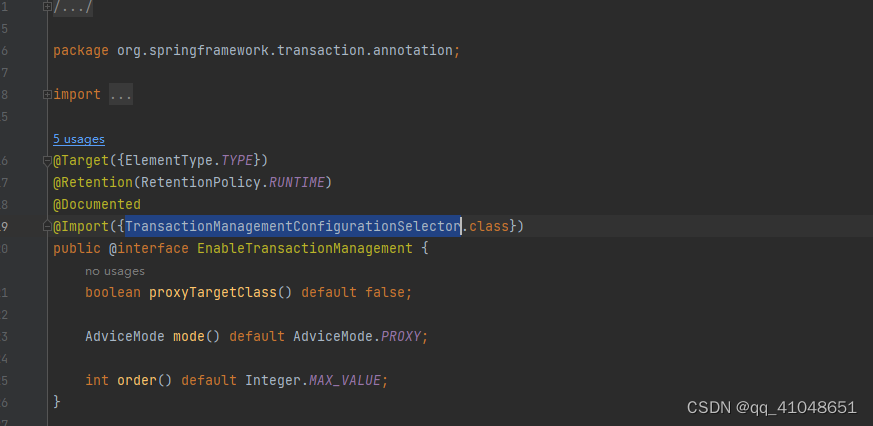
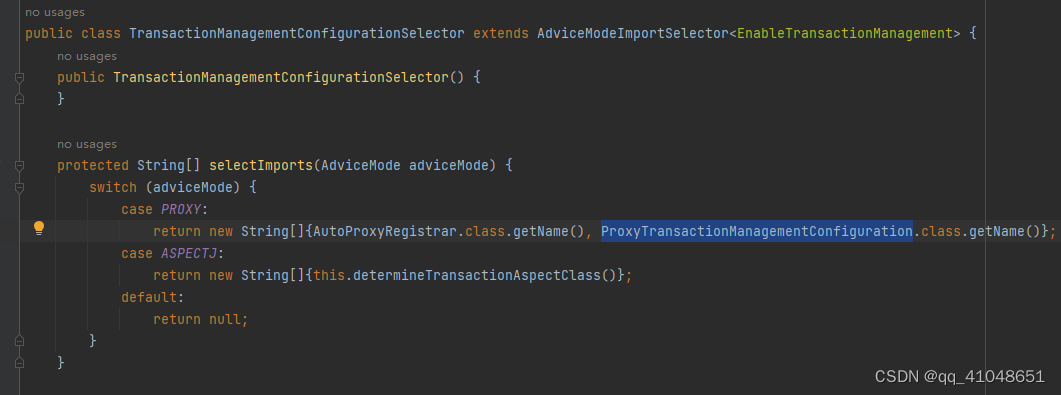
我们在开启事务时添加了EnableTransactionManagement注解,这个注解里使用了@Import注解导入了一个TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector
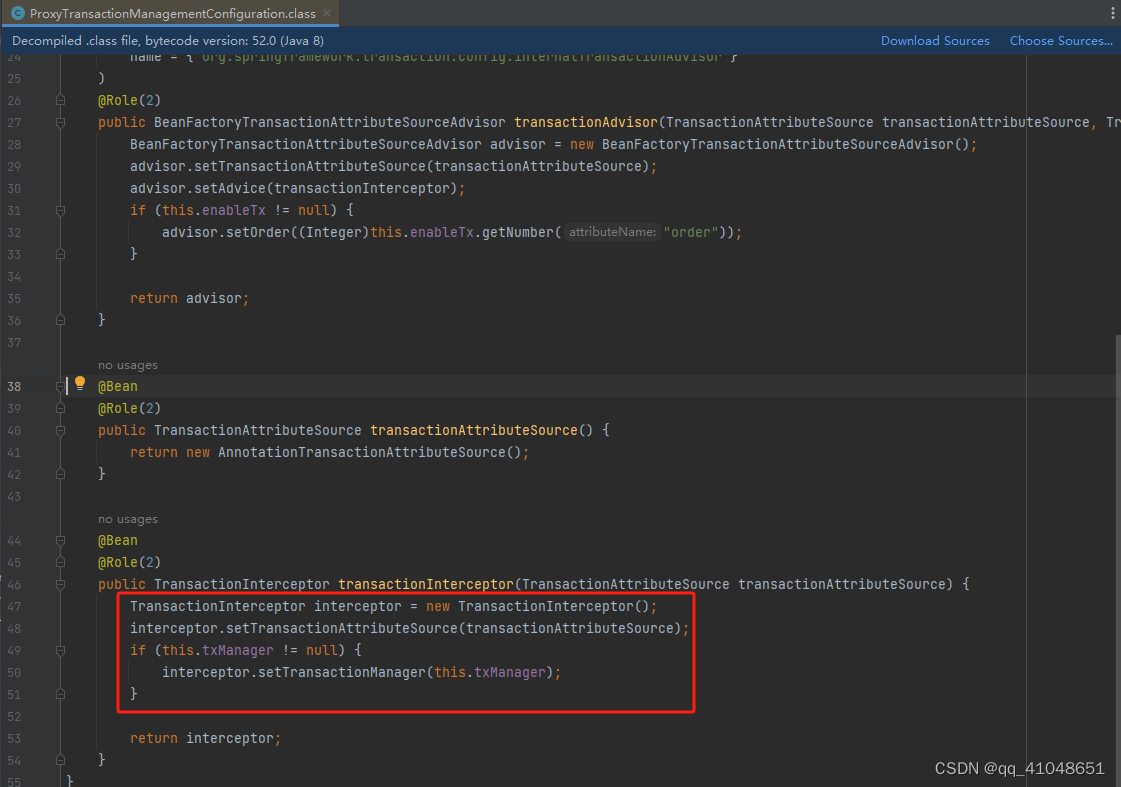
对拦截器的注入:
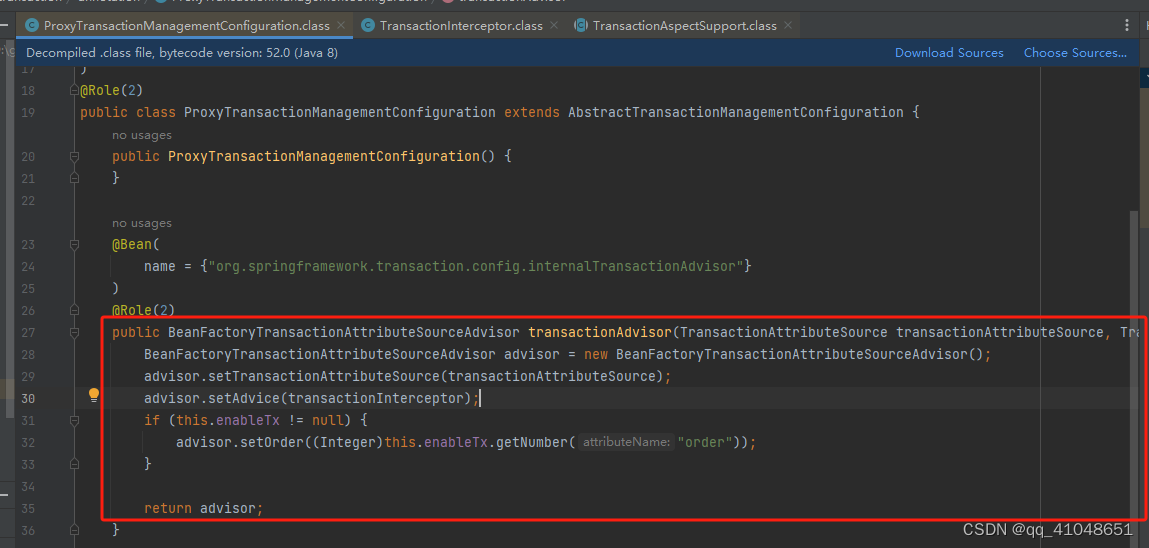
将拦截器关联到Advisor
事务的使用
从上面我们知道TransactionInterceptor就是我们的通知,我们来看看这个拦截器是怎么处理的。
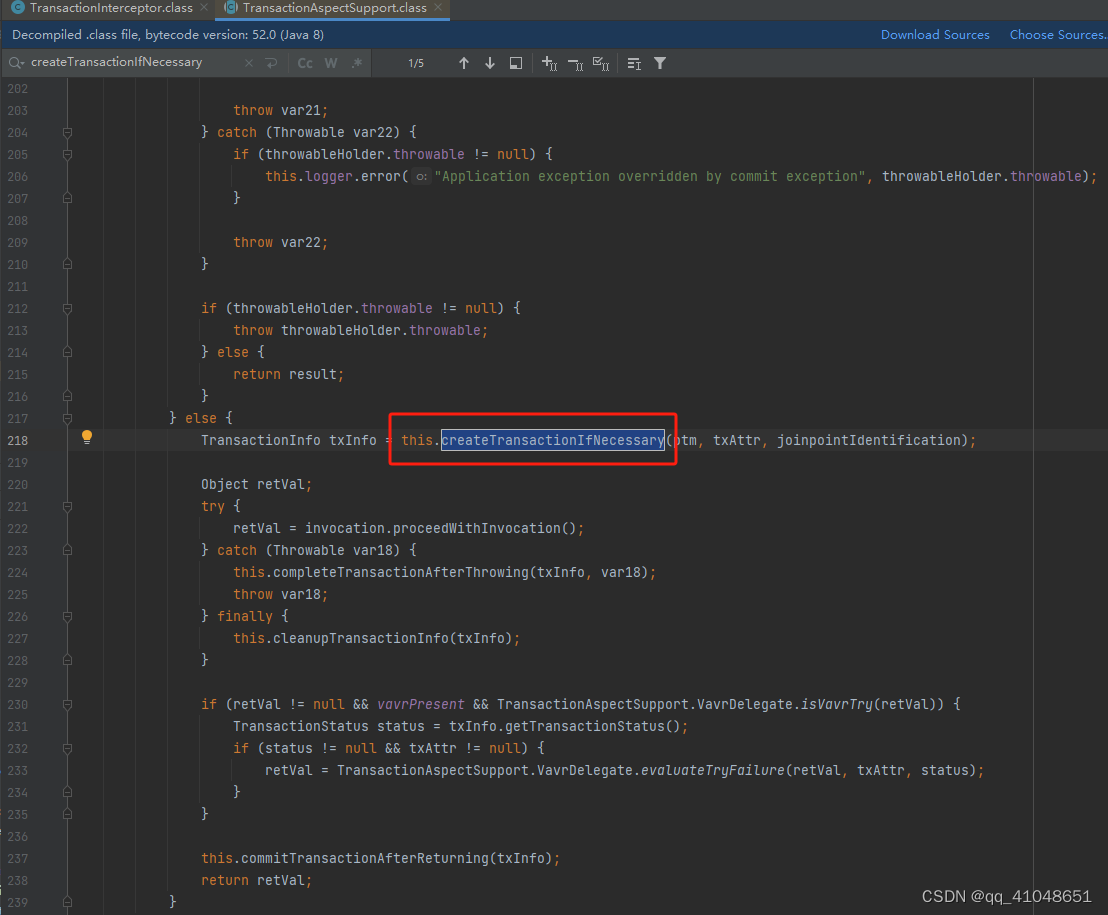
在需要开启事务的地方添加@Transactional开启注解,最终会走到TransactionInterceptor的invoke方法进入到invokeWithinTransaction方法中。
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
// 获取我们的事务属性源对象
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 通过事务属性源对象获取到当前方法的事务属性信息
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取我们配置的事务管理器对象
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {
throw new TransactionUsageException(
"Unsupported annotated transaction on suspending function detected: " + method +
". Use TransactionalOperator.transactional extensions instead.");
}
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(method.getReturnType());
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(
method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
// 获取连接点的唯一标识 类名+方法名
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 声明式事务处理
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 执行被增强方法,调用具体的处理逻辑
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 异常回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//清除事务信息,恢复线程私有的老的事务信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
//成功后提交,会进行资源储量,连接释放,恢复挂起事务等操作
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
// 编程式事务处理
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
创建事务、开启事务
然后就走到了之前讲过的PlatformTransactionManager里的getTransaction了