文章目录
前言
Spring IoC容器的实现原理:工厂模式+解析XML+反射机制
一、手写spring框架之核心接口实现
参考之前已知写的测试类中的第一行代码:
ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("myspring.xml");
//以及getBean()方法
因此编写接口类ApplicationContext:
public interface ApplicationContext {
/**
* 根据bean的名称获取对应的bean对象
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
Object getBean(String beanName);
}
该接口类ApplicationContext对应的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:
主要功能是解析spring.xml文件,需要用到dom4j以及jaxen【需要导入对应的依赖文件】
关键代码如下:
//获取类路径当中的资源
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();//dom4j解析XML文件的核心对象
//获取一个输入流,指向配置文件 //只适合从类路径当中加载资源
InputStream in = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(configLocation);
//读文件
Document document = reader.read(in);
//获取文档里的所有bean标签
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//bean");
二、手写spring框架之实例化Bean
将所有的Bean对象先创建出来,也就是在Bean的三级缓存中提到的,先将Bean对象“曝光”。
在第一步解析xml文件的基础上,可以通过遍历bean标签拿到每个bean对应的id属性值、class属性值,再通过反射机制进行对象创建
关键代码:
//获取id属性它的值
String id = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取class属性的值
String className = beanElt.attributeValue("class");
//通过反射机制创建对象,将其放到Map集合中,提前“曝光”
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
//获取无参数构造方法
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor();//无参数构造方法
//调用无参数构造方法实例化Bean
Object bean = declaredConstructor.newInstance();//创建对象
//将Bean“曝光”,加入Map集合
singletonObjects.put(id,bean);
测试类:
public class MySpringTest {
@Test
public void testMySpring(){
ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("myspring.xml");
}
}
此时运行结果:
三个对象均创建成功,此时属性值为null
三、手写spring框架之获取所有set方法
创建对象之后,接下来的操作就是给对象的属性赋值。
需要在重新遍历一次Bean标签,获取id获取class以及需要获取该bean标签下的所有属性property标签(循环套循环)
重新遍历一遍bean标签:获取id获取class
遍历所有的属性标签时:获取属性名
获取属性类型
拼接set方法名
获取set方法
关键代码如下:
//再次把所有的Bean标签都遍历一遍 这次主要是给对象的属性赋值
nodes.forEach(node->{
try{
Element beanElt = (Element) node;
//获取id
String id = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取className
String className = beanElt.attributeValue("class");
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
//获取该bean标签下所有的属性propertry标签
List<Element> propertys = beanElt.elements("property");
//遍历所有的属性标签:
propertys.forEach(property->{
try{
//获取属性名
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");
//获取属性类型
Field field = aClass.getField(propertyName);
System.out.println("属性名:"+propertyName);
//拼接method方法
String setMethodName = "set"+propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0)+propertyName.substring(1);
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = aClass.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName,field.getType() );
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
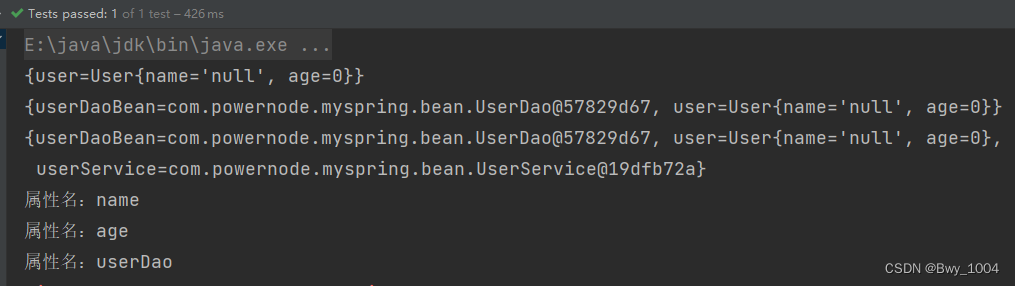
运行结果:
四、手写spring框架之给属性赋值
//获取具体的值
String value = property.attributeValue("value");
String ref = property.attributeValue("ref");
if (value!=null) {
//这个值是简单类型
}
if (ref!=null) {
//这个值是非简单类型
}
4.1 非简单类型属性赋值
在三获取到set方法的基础上,调用set方法==(调用set方法没有返回值)==
非简单类型与简单类型相比较为简单,
对象就是map集合中的value值,非简单类型同样也是map集合中的值,id就是ref的值
if (ref!=null) {
//这个值是非简单类型
//调用set方法
setMethod.invoke(singletonObjects.get(id),singletonObjects.get(ref));
}
4.2 简单类型属性赋值
简单类型较为复杂原因在于 获取到的value值始终都是String类型的,而简单类型不只有String,还有int等等其他类型,因此需要根据属性的类型再去赋值。
在手写的框架里只支持:byte short int long float double boolean char以及八种包装类型:Byte Short Integer Long Float Double Boolean Character还有String类型
Object actualValue = null;
if (value!=null) {
//这个值是简单类型
String propertyTypeSimpleName = field.getType().getSimpleName();
switch (propertyTypeSimpleName){
case "byte":
actualValue = Byte.parseByte(value);
break;
case "short":
actualValue = Short.parseShort(value);
break;
case "double":
actualValue = Double.parseDouble(value);
break;
case "boolean":
actualValue = Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
break;
case "int":
actualValue = Integer.parseInt(value);
break;
case "long":
actualValue = Long.parseLong(value);
break;
case "float":
actualValue = Float.parseFloat(value);
break;
case "char":
actualValue = value.charAt(0);
break;
case "Byte":
actualValue = Byte.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Short":
actualValue = Short.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Integer":
actualValue = Integer.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Long":
actualValue = Long.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Float":
actualValue = Float.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Double":
actualValue = Double.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Boolean":
actualValue = Boolean.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Character":
actualValue = Character.valueOf(value.charAt(0));
break;
case "String":
actualValue =value;
break;
}
//调用set方法
setMethod.invoke(singletonObjects.get(id),actualValue);
}
测试类:
public class MySpringTest {
@Test
public void testMySpring(){
ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("myspring.xml");
Object user = application.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
UserService userService = (UserService) application.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
}
}
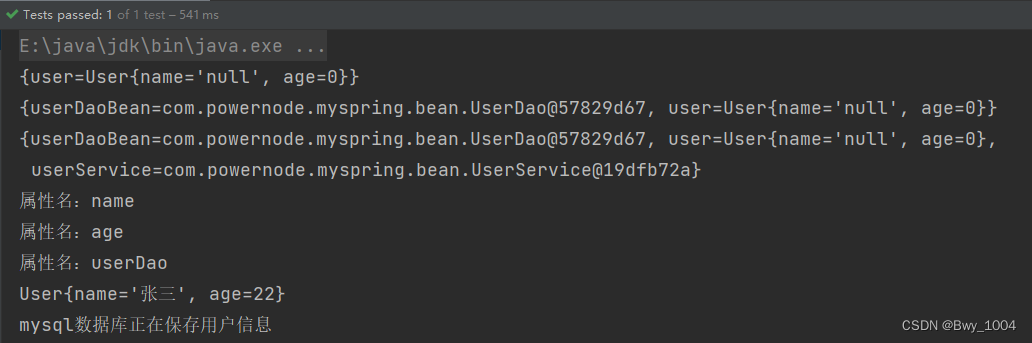
运行结果:
赋值成功。 可以将此框架打包发布【两个类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext以及ApplicationContext】
附:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的完整代码
package org.myspringframework;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.Node;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
private Map<String,Object> singletonObjects = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 解析mybatis的配置文件,然后初始化所有的Bean对象
* @param configLocation spring配置文件的路径
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation){
try{
//解析mybatis.xml文件,然后实例化bean,将Bean存放到singletonObjects集合当中
//获取类路径当中的资源
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();//dom4j解析XML文件的核心对象
//获取一个输入流,指向配置文件 //只适合从类路径当中加载资源
InputStream in = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(configLocation);
//读文件
Document document = reader.read(in);
//获取文档里的所有bean标签
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//bean");
//遍历bean标签
nodes.forEach(node->{
try{
//System.out.println(node);
//向下转型的目的是为了使用Element接口里更加丰富的方法
Element beanElt = (Element) node;
//获取id属性它的值
String id = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取class属性的值
String className = beanElt.attributeValue("class");
//通过反射机制创建对象,将其放到Map集合中,提前“曝光”
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
//获取无参数构造方法
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor();//无参数构造方法
//调用无参数构造方法实例化Bean
Object bean = declaredConstructor.newInstance();//创建对象
//将Bean“曝光”,加入Map集合
singletonObjects.put(id,bean);
System.out.println(singletonObjects.toString());
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
//再次把所有的Bean标签都遍历一遍 这次主要是给对象的属性赋值
nodes.forEach(node->{
try{
Element beanElt = (Element) node;
//获取id
String id = beanElt.attributeValue("id");
//获取className
String className = beanElt.attributeValue("class");
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
//获取该bean标签下所有的属性propertry标签
List<Element> propertys = beanElt.elements("property");
//遍历所有的属性标签:
propertys.forEach(property->{
try{
//获取属性名
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");
//获取属性类型
Field field = aClass.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
System.out.println("属性名:"+propertyName);
//拼接method方法
String setMethodName = "set"+propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0)+propertyName.substring(1);
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = aClass.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName,field.getType() );
//获取具体的值
String value = property.attributeValue("value");
String ref = property.attributeValue("ref");
Object actualValue = null;
if (value!=null) {
//这个值是简单类型
String propertyTypeSimpleName = field.getType().getSimpleName();
switch (propertyTypeSimpleName){
case "byte":
actualValue = Byte.parseByte(value);
break;
case "short":
actualValue = Short.parseShort(value);
break;
case "double":
actualValue = Double.parseDouble(value);
break;
case "boolean":
actualValue = Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
break;
case "int":
actualValue = Integer.parseInt(value);
break;
case "long":
actualValue = Long.parseLong(value);
break;
case "float":
actualValue = Float.parseFloat(value);
break;
case "char":
actualValue = value.charAt(0);
break;
case "Byte":
actualValue = Byte.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Short":
actualValue = Short.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Integer":
actualValue = Integer.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Long":
actualValue = Long.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Float":
actualValue = Float.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Double":
actualValue = Double.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Boolean":
actualValue = Boolean.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Character":
actualValue = Character.valueOf(value.charAt(0));
break;
case "String":
actualValue =value;
break;
}
//调用set方法
setMethod.invoke(singletonObjects.get(id),actualValue);
}
if (ref!=null) {
//这个值是非简单类型
//调用set方法
setMethod.invoke(singletonObjects.get(id),singletonObjects.get(ref));
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
return singletonObjects.get(beanName);
}
}