文章目录
LSTM 时间序列预测
股票预测案例
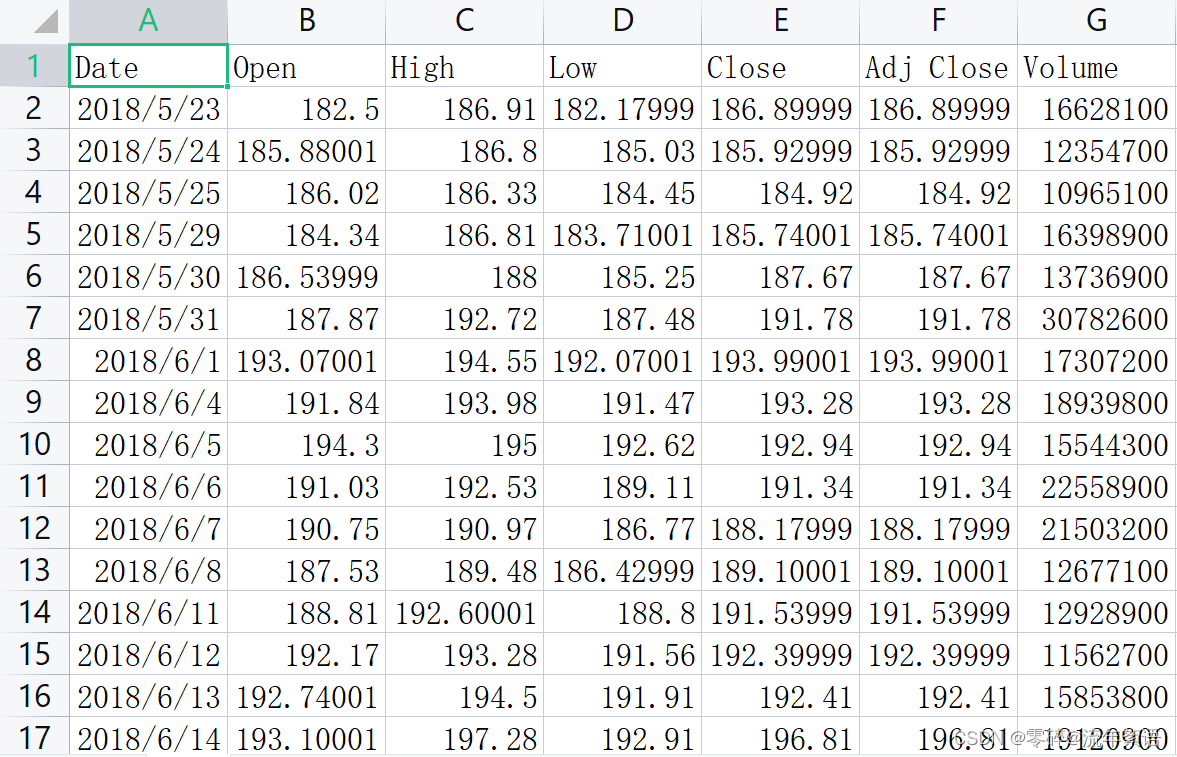
数据特征
- Date:日期
- Open:开盘价
- High:最高价
- Low:最低价
- Close:收盘价
- Adj Close:调整后的收盘价
- Volume:交易量
数据链接:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1rX_S3Jaz4zJVMKPW2BLdLA?pwd=hi55 提取码: hi55
对收盘价(Close)单特征进行预测
利用前n天的数据预测第n+1天的数据。
1. 导入数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
filepath = 'D:/pythonProjects/LSTM/data/rlData.csv'
data = pd.read_csv(filepath)
# 将数据按照日期进行排序,确保时间序列递增
data = data.sort_values('Date')
# 打印前几条数据
print(data.head())
# 打印维度
print(data.shape)
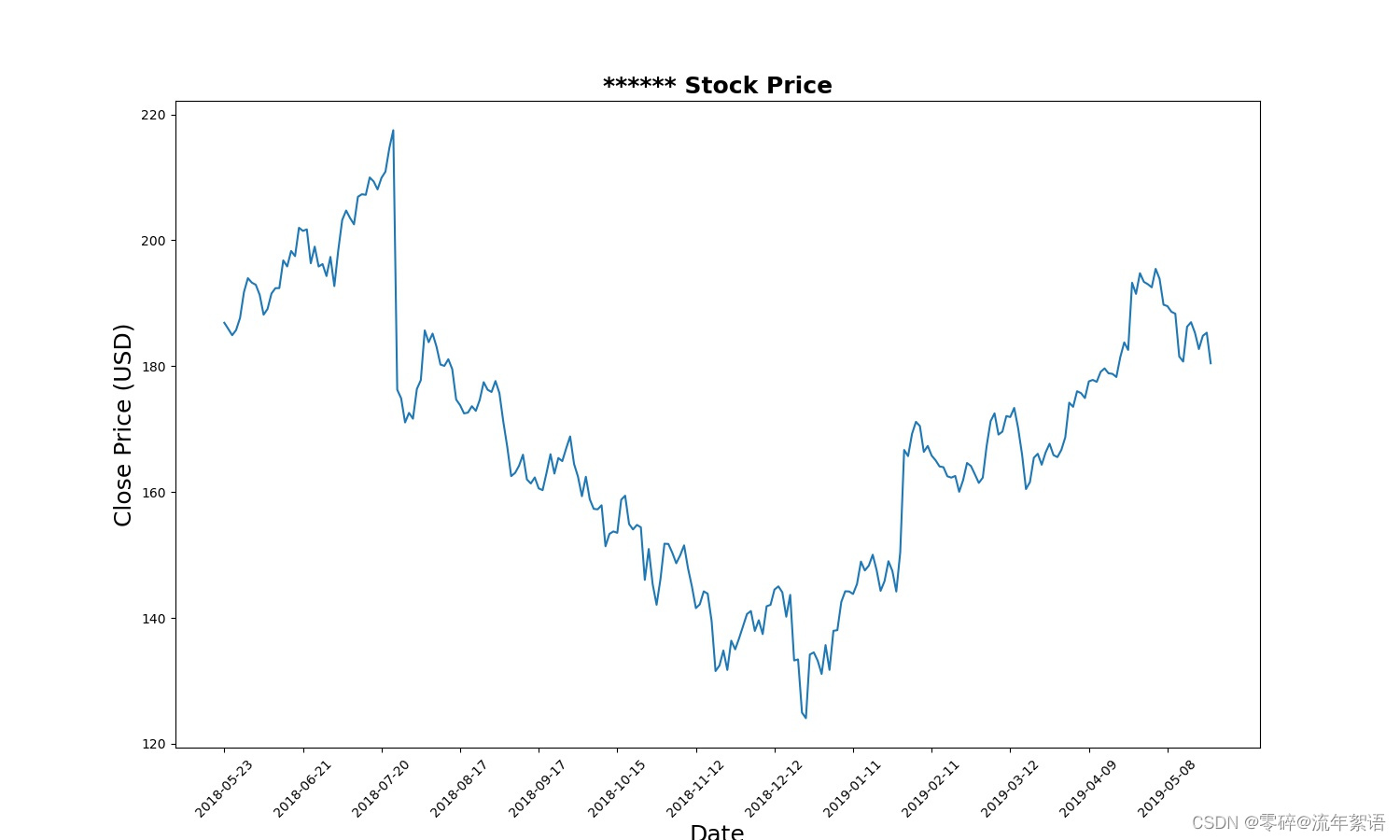
2. 将股票数据收盘价(Close)进行可视化展示
# 设置画布大小
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 9))
plt.plot(data[['Close']])
plt.xticks(range(0, data.shape[0], 20), data['Date'].loc[::20], rotation=45)
plt.title("****** Stock Price", fontsize=18, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Date', fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel('Close Price (USD)', fontsize=18)
plt.savefig('StockPrice.jpg')
plt.show()
3. 特征工程
# 选取Close作为特征
price = data[['Close']]
# 打印相关信息
print(price.info())
打印结果如下:
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 252 entries, 0 to 251
Data columns (total 1 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Close 252 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1)
memory usage: 3.9 KB
None
可以看出:price为DataFrame对象,以及其的结构和占用内存等信息
# 进行不同的数据缩放,将数据缩放到-1和1之间,归一化操作
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))
price['Close'] = scaler.fit_transform(price['Close'].values.reshape(-1, 1))
print(price['Close'].shape)
打印结果如下:
0 0.345034
1 0.324272
2 0.302654
3 0.320206
4 0.361515
...
247 0.310788
248 0.255565
249 0.300514
250 0.311216
251 0.207192
Name: Close, Length: 252, dtype: float64
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
Int64Index: 252 entries, 0 to 251
Series name: Close
Non-Null Count Dtype
-------------- -----
252 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1)
memory usage: 3.9 KB
None
(252,)
可以看出:price['Close']的值,price['Close']为Series结构,price['Close']的结构为(252,)
4. 数据集制作
# 今天的收盘价预测明天的收盘价
# lookback表示观察的跨度
def split_data(stock, lookback):
# 将stock转化为ndarray类型
data_raw = stock.to_numpy()
data = []
# you can free play(seq_length)
# 将data按lookback分组,data为长度为lookback的list
for index in range(len(data_raw) - lookback):
data.append(data_raw[index: index + lookback])
data = np.array(data);
print(type(data)) # (232, 20, 1)
# 按照8:2进行训练集、测试集划分
test_set_size = int(np.round(0.2 * data.shape[0]))
train_set_size = data.shape[0] - (test_set_size)
x_train = data[:train_set_size, :-1, :]
y_train = data[:train_set_size, -1, :]
x_test = data[train_set_size:, :-1]
y_test = data[train_set_size:, -1, :]
return [x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test]
lookback = 20
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = split_data(price, lookback)
print('x_train.shape = ', x_train.shape)
print('y_train.shape = ', y_train.shape)
print('x_test.shape = ', x_test.shape)
print('y_test.shape = ', y_test.shape)
打印结果如下:
x_train.shape = (186, 19, 1)
y_train.shape = (186, 1)
x_test.shape = (46, 19, 1)
y_test.shape = (46, 1)
5. 模型构建
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train).type(torch.Tensor)
x_test = torch.from_numpy(x_test).type(torch.Tensor)
# 真实的数据
y_train_lstm = torch.from_numpy(y_train).type(torch.Tensor)
y_test_lstm = torch.from_numpy(y_test).type(torch.Tensor)
y_train_gru = torch.from_numpy(y_train).type(torch.Tensor)
y_test_gru = torch.from_numpy(y_test).type(torch.Tensor)
# 输入的维度为1,只有Close收盘价
input_dim = 1
# 隐藏层特征的维度
hidden_dim = 32
# 循环的layers
num_layers = 2
# 预测后一天的收盘价
output_dim = 1
num_epochs = 100
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, output_dim):
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()
c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()
out, (hn, cn) = self.lstm(x, (h0.detach(), c0.detach()))
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out
model = LSTM(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_dim=hidden_dim, output_dim=output_dim, num_layers=num_layers)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
6. 模型训练
import time
hist = np.zeros(num_epochs)
start_time = time.time()
lstm = []
for t in range(num_epochs):
y_train_pred = model(x_train)
loss = criterion(y_train_pred, y_train_lstm)
print("Epoch ", t, "MSE: ", loss.item())
hist[t] = loss.item()
optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimiser.step()
training_time = time.time() - start_time
print("Training time: {}".format(training_time))
predict = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy()))
print(predict) # 预测值
original = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_lstm.detach().numpy()))
print(original) # 真实值
打印结果如下:其中预测值每次运行可能会有一定的差距,但不影响最后的结果。
torch.Size([186, 1])
Epoch 0 MSE: 0.19840142130851746
torch.Size([186, 1])
Epoch 1 MSE: 0.17595666646957397
torch.Size([186, 1])
Epoch 2 MSE: 0.1369851976633072
torch.Size([186, 1])
.. ...
Epoch 96 MSE: 0.008701297454535961
torch.Size([186, 1])
Epoch 97 MSE: 0.008698086254298687
torch.Size([186, 1])
Epoch 98 MSE: 0.008688708767294884
torch.Size([186, 1])
Epoch 99 MSE: 0.008677813224494457
Training time: 3.884610414505005
0
0 196.654999
1 201.095291
2 200.198563
3 200.494003
4 195.120148
.. ...
181 171.398987
182 171.508194
183 172.992401
184 169.850494
185 165.566605
[186 rows x 1 columns]
0
0 201.999985
1 201.500015
2 201.740005
3 196.350006
4 198.999985
.. ...
181 171.919998
182 173.369995
183 170.169998
184 165.979996
185 160.470001
[186 rows x 1 columns]
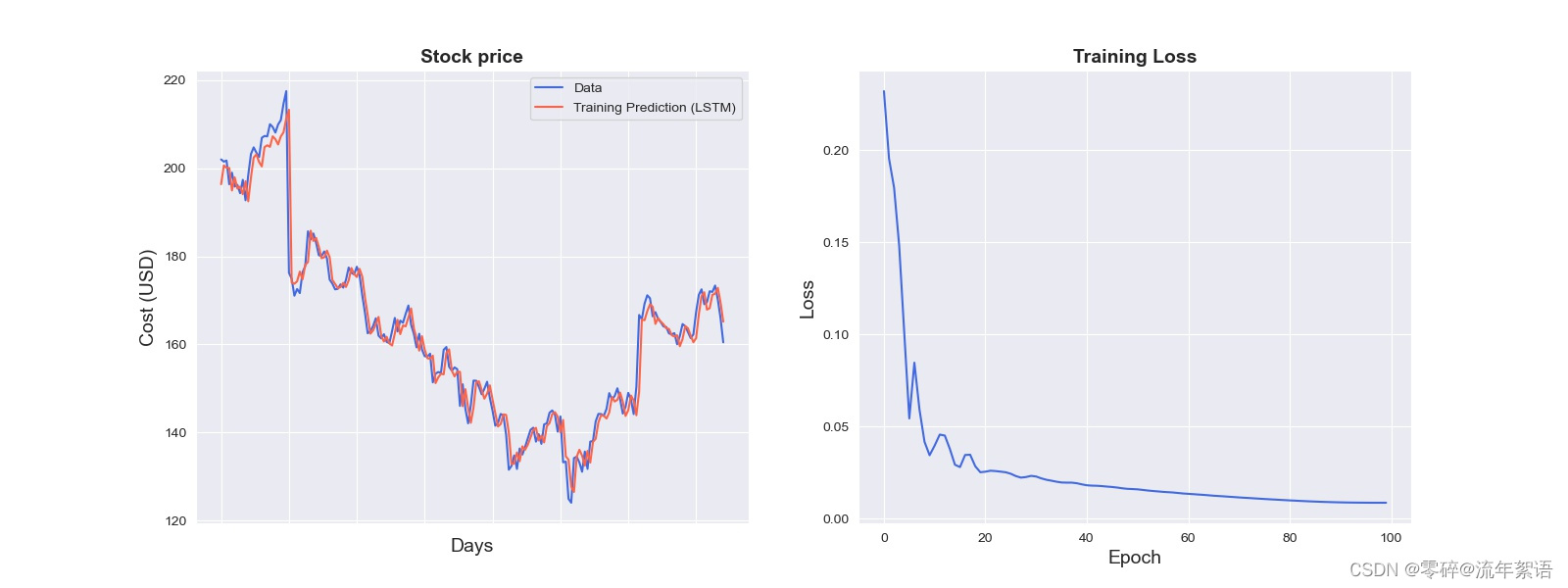
7. 模型结果可视化
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax = sns.lineplot(x = original.index, y = original[0], label="Data", color='royalblue')
ax = sns.lineplot(x = predict.index, y = predict[0], label="Training Prediction (LSTM)", color='tomato')
print(predict.index)
print("aaaa")
print(predict[0])
ax.set_title('Stock price', size = 14, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel("Days", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Cost (USD)", size = 14)
ax.set_xticklabels('', size=10)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax = sns.lineplot(data=hist, color='royalblue')
ax.set_xlabel("Epoch", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Loss", size = 14)
ax.set_title("Training Loss", size = 14, fontweight='bold')
fig.set_figheight(6)
fig.set_figwidth(16)
plt.show()
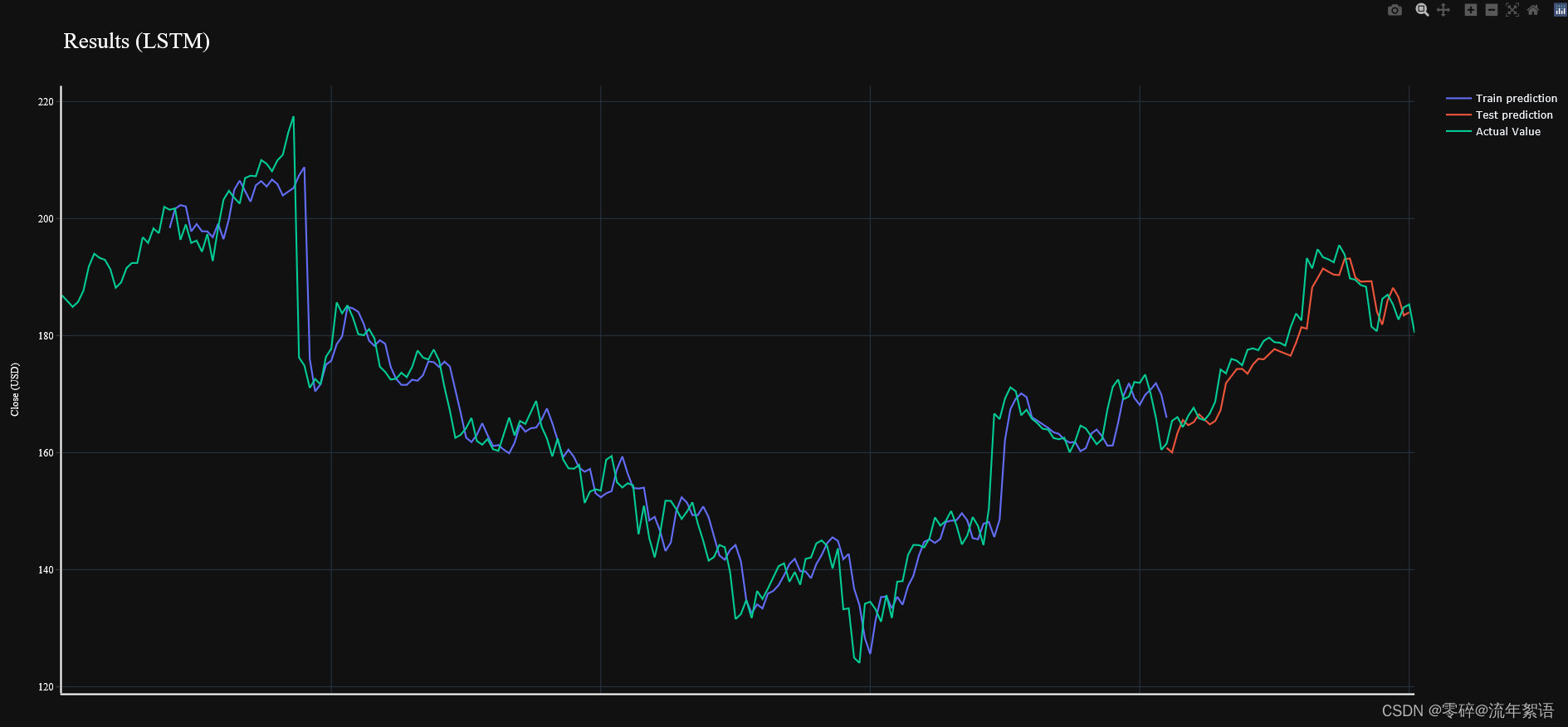
8. 模型验证
实际上是对结果的总结及进一步说明。
import math, time
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# make predictions
y_test_pred = model(x_test)
# invert predictions
y_train_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy())
y_train = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_lstm.detach().numpy())
y_test_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test_pred.detach().numpy())
y_test = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test_lstm.detach().numpy())
# calculate root mean squared error
trainScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train[:,0], y_train_pred[:,0]))
print('Train Score: %.2f RMSE' % (trainScore))
testScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test[:,0], y_test_pred[:,0]))
print('Test Score: %.2f RMSE' % (testScore))
lstm.append(trainScore)
lstm.append(testScore)
lstm.append(training_time)
# shift train predictions for plotting
trainPredictPlot = np.empty_like(price)
trainPredictPlot[:, :] = np.nan
trainPredictPlot[lookback:len(y_train_pred)+lookback, :] = y_train_pred
# shift test predictions for plotting
testPredictPlot = np.empty_like(price)
testPredictPlot[:, :] = np.nan
testPredictPlot[len(y_train_pred)+lookback-1:len(price)-1, :] = y_test_pred
original = scaler.inverse_transform(price['Close'].values.reshape(-1,1))
predictions = np.append(trainPredictPlot, testPredictPlot, axis=1)
predictions = np.append(predictions, original, axis=1)
result = pd.DataFrame(predictions)
import plotly.express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(go.Scatter(x=result.index, y=result[0],
mode='lines',
name='Train prediction')))
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=result.index, y=result[1],
mode='lines',
name='Test prediction'))
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(go.Scatter(x=result.index, y=result[2],
mode='lines',
name='Actual Value')))
fig.update_layout(
xaxis=dict(
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=False,
linecolor='white',
linewidth=2
),
yaxis=dict(
title_text='Close (USD)',
titlefont=dict(
family='Rockwell',
size=12,
color='white',
),
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='white',
linewidth=2,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Rockwell',
size=12,
color='white',
),
),
showlegend=True,
template = 'plotly_dark'
)
annotations = []
annotations.append(dict(xref='paper', yref='paper', x=0.0, y=1.05,
xanchor='left', yanchor='bottom',
text='Results (LSTM)',
font=dict(family='Rockwell',
size=26,
color='white'),
showarrow=False))
fig.update_layout(annotations=annotations)
fig.show()
完整代码
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
filepath = 'D:/pythonProjects/LSTM/data/rlData.csv'
data = pd.read_csv(filepath)
data = data.sort_values('Date')
print(data.head())
print(data.shape)
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 9))
plt.plot(data[['Close']])
plt.xticks(range(0, data.shape[0], 20), data['Date'].loc[::20], rotation=45)
plt.title("****** Stock Price", fontsize=18, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Date', fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel('Close Price (USD)', fontsize=18)
plt.show()
# 1.特征工程
# 选取Close作为特征
price = data[['Close']]
print(price.info())
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
# 进行不同的数据缩放,将数据缩放到-1和1之间
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))
price['Close'] = scaler.fit_transform(price['Close'].values.reshape(-1, 1))
print(price['Close'].shape)
# 2.数据集制作
# 今天的收盘价预测明天的收盘价
# lookback表示观察的跨度
def split_data(stock, lookback):
data_raw = stock.to_numpy()
data = []
# print(data)
# you can free play(seq_length)
for index in range(len(data_raw) - lookback):
data.append(data_raw[index: index + lookback])
data = np.array(data);
test_set_size = int(np.round(0.2 * data.shape[0]))
train_set_size = data.shape[0] - (test_set_size)
x_train = data[:train_set_size, :-1, :]
y_train = data[:train_set_size, -1, :]
x_test = data[train_set_size:, :-1]
y_test = data[train_set_size:, -1, :]
return [x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test]
lookback = 20
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = split_data(price, lookback)
print('x_train.shape = ', x_train.shape)
print('y_train.shape = ', y_train.shape)
print('x_test.shape = ', x_test.shape)
print('y_test.shape = ', y_test.shape)
# 注意:pytorch的nn.LSTM input shape=(seq_length, batch_size, input_size)
# 3.模型构建 —— LSTM
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train).type(torch.Tensor)
x_test = torch.from_numpy(x_test).type(torch.Tensor)
y_train_lstm = torch.from_numpy(y_train).type(torch.Tensor)
y_test_lstm = torch.from_numpy(y_test).type(torch.Tensor)
y_train_gru = torch.from_numpy(y_train).type(torch.Tensor)
y_test_gru = torch.from_numpy(y_test).type(torch.Tensor)
# 输入的维度为1,只有Close收盘价
input_dim = 1
# 隐藏层特征的维度
hidden_dim = 32
# 循环的layers
num_layers = 2
# 预测后一天的收盘价
output_dim = 1
num_epochs = 100
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, output_dim):
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()
c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()
out, (hn, cn) = self.lstm(x, (h0.detach(), c0.detach()))
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out
model = LSTM(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_dim=hidden_dim, output_dim=output_dim, num_layers=num_layers)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# 4.模型训练
import time
hist = np.zeros(num_epochs)
start_time = time.time()
lstm = []
for t in range(num_epochs):
y_train_pred = model(x_train)
loss = criterion(y_train_pred, y_train_lstm)
print("Epoch ", t, "MSE: ", loss.item())
hist[t] = loss.item()
optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimiser.step()
training_time = time.time() - start_time
print("Training time: {}".format(training_time))
# 5.模型结果可视化
predict = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy()))
original = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_lstm.detach().numpy()))
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax = sns.lineplot(x = original.index, y = original[0], label="Data", color='royalblue')
ax = sns.lineplot(x = predict.index, y = predict[0], label="Training Prediction (LSTM)", color='tomato')
# print(predict.index)
# print(predict[0])
ax.set_title('Stock price', size = 14, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel("Days", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Cost (USD)", size = 14)
ax.set_xticklabels('', size=10)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax = sns.lineplot(data=hist, color='royalblue')
ax.set_xlabel("Epoch", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Loss", size = 14)
ax.set_title("Training Loss", size = 14, fontweight='bold')
fig.set_figheight(6)
fig.set_figwidth(16)
plt.show()
# 6.模型验证
# print(x_test[-1])
import math, time
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# make predictions
y_test_pred = model(x_test)
# invert predictions
y_train_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy())
y_train = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_lstm.detach().numpy())
y_test_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test_pred.detach().numpy())
y_test = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test_lstm.detach().numpy())
# calculate root mean squared error
trainScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train[:,0], y_train_pred[:,0]))
print('Train Score: %.2f RMSE' % (trainScore))
testScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test[:,0], y_test_pred[:,0]))
print('Test Score: %.2f RMSE' % (testScore))
lstm.append(trainScore)
lstm.append(testScore)
lstm.append(training_time)
# In[40]:
# shift train predictions for plotting
trainPredictPlot = np.empty_like(price)
trainPredictPlot[:, :] = np.nan
trainPredictPlot[lookback:len(y_train_pred)+lookback, :] = y_train_pred
# shift test predictions for plotting
testPredictPlot = np.empty_like(price)
testPredictPlot[:, :] = np.nan
testPredictPlot[len(y_train_pred)+lookback-1:len(price)-1, :] = y_test_pred
original = scaler.inverse_transform(price['Close'].values.reshape(-1,1))
predictions = np.append(trainPredictPlot, testPredictPlot, axis=1)
predictions = np.append(predictions, original, axis=1)
result = pd.DataFrame(predictions)
import plotly.express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(go.Scatter(x=result.index, y=result[0],
mode='lines',
name='Train prediction')))
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=result.index, y=result[1],
mode='lines',
name='Test prediction'))
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(go.Scatter(x=result.index, y=result[2],
mode='lines',
name='Actual Value')))
fig.update_layout(
xaxis=dict(
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=False,
linecolor='white',
linewidth=2
),
yaxis=dict(
title_text='Close (USD)',
titlefont=dict(
family='Rockwell',
size=12,
color='white',
),
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='white',
linewidth=2,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Rockwell',
size=12,
color='white',
),
),
showlegend=True,
template = 'plotly_dark'
)
annotations = []
annotations.append(dict(xref='paper', yref='paper', x=0.0, y=1.05,
xanchor='left', yanchor='bottom',
text='Results (LSTM)',
font=dict(family='Rockwell',
size=26,
color='white'),
showarrow=False))
fig.update_layout(annotations=annotations)
fig.show()