在计算机视觉领域,目标检测一直是一个重要的研究方向。近年来,YOLO(You Only Look Once)系列模型凭借其高效的实时检测能力,成为了业界的标杆。最新发布的YOLOv11在前几代模型的基础上进行了多项改进。而单头自注意力 (SHSA)作为一种高效的注意力机制,也在视觉任务中展现了其独特的优势。其通过在输入通道的一部分上应用单头注意力来减少计算冗余,同时保留全局和局部信息的结合,从而提高了效率和准确性。接下来,本文先介绍SHSA基本原理,然后探讨如何将SHSA与YOLOv11结合,以进一步提升目标检测的效率和准确性。
1. 单头自注意力Single-Head Self-Attention(SHSA)结构介绍
SHSA通过仅对部分输入通道应用单头注意力,减少了计算冗余和内存访问成本。其主要特点包括:
1. 部分通道处理:仅对部分输入通道(默认比例为1/4.67)应用注意力层,其余通道保持不变。
2. 全通道投影:最终的投影应用于所有通道,确保注意力特征有效传播到所有通道。
3. 简化操作:减少内存绑定操作,提高了计算效率。
2. YOLOv11与SHSA的结合
将SHSA集成到YOLOv11的C2PSA模块模块中,形成C2PSA_SHSA模块,减少了计算冗余和内存访问成本,进一步提升模型的效率和性能。
3. 单头自注意力SHSA代码部分
import torch
from .conv import Conv
import torch.nn as nn
from .block import PSABlock,C2PSA
class GroupNorm(torch.nn.GroupNorm):
"""
Group Normalization with 1 group.
Input: tensor in shape [B, C, H, W]
"""
def __init__(self, num_channels, **kwargs):
super().__init__(1, num_channels, **kwargs)
class Conv2d_BN(torch.nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, a, b, ks=1, stride=1, pad=0, dilation=1,
groups=1, bn_weight_init=1):
super().__init__()
self.add_module('c', torch.nn.Conv2d(
a, b, ks, stride, pad, dilation, groups, bias=False))
self.add_module('bn', torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(b))
torch.nn.init.constant_(self.bn.weight, bn_weight_init)
torch.nn.init.constant_(self.bn.bias, 0)
@torch.no_grad()
def fuse(self):
c, bn = self._modules.values()
w = bn.weight / (bn.running_var + bn.eps)**0.5
w = c.weight * w[:, None, None, None]
b = bn.bias - bn.running_mean * bn.weight / \
(bn.running_var + bn.eps)**0.5
m = torch.nn.Conv2d(w.size(1) * self.c.groups, w.size(
0), w.shape[2:], stride=self.c.stride, padding=self.c.padding, dilation=self.c.dilation, groups=self.c.groups,
device=c.weight.device)
m.weight.data.copy_(w)
m.bias.data.copy_(b)
return m
class SHSA_BLOCK(torch.nn.Module):
"""Single-Head Self-Attention"""
def __init__(self, dim, qk_dim=16, pdim=32):
super().__init__()
self.scale = qk_dim ** -0.5
self.qk_dim = qk_dim
self.dim = dim
self.pdim = pdim
self.pre_norm = GroupNorm(pdim)
self.qkv = Conv2d_BN(pdim, qk_dim * 2 + pdim)
self.proj = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.ReLU(), Conv2d_BN(
dim, dim, bn_weight_init = 0))
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
x1, x2 = torch.split(x, [self.pdim, self.dim - self.pdim], dim = 1)
x1 = self.pre_norm(x1)
qkv = self.qkv(x1)
q, k, v = qkv.split([self.qk_dim, self.qk_dim, self.pdim], dim = 1)
q, k, v = q.flatten(2), k.flatten(2), v.flatten(2)
attn = (q.transpose(-2, -1) @ k) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim = -1)
x1 = (v @ attn.transpose(-2, -1)).reshape(B, self.pdim, H, W)
x = self.proj(torch.cat([x1, x2], dim = 1))
return x
class PSABlock_SHSA(PSABlock):
def __init__(self, c, qk_dim =16 , pdim=32, shortcut=True) -> None:
"""Initializes the PSABlock with attention and feed-forward layers for enhanced feature extraction."""
super().__init__( c)
self.attn = SHSA_BLOCK(c, qk_dim, pdim)
class C2PSA_SHSA(C2PSA):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, e=0.5):
"""Initializes the C2PSA module with specified input/output channels, number of layers, and expansion ratio."""
super().__init__(c1, c2)
assert c1 == c2
self.c = int(c1 * e)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(PSABlock_SHSA(self.c, qk_dim =16 , pdim=32) for _ in range(n)))
if __name__ =='__main__':
IDC = SHSA_BLOCK(256, 16, 32)
#创建一个输入张量
batch_size = 8
input_tensor=torch.randn(batch_size, 256, 64, 64 )
#运行模型并打印输入和输出的形状
output_tensor =IDC(input_tensor)
print("Input shape:",input_tensor.shape)
print("0utput shape:",output_tensor.shape)4. 将单头自注意力SHSA引入到YOLOv11中
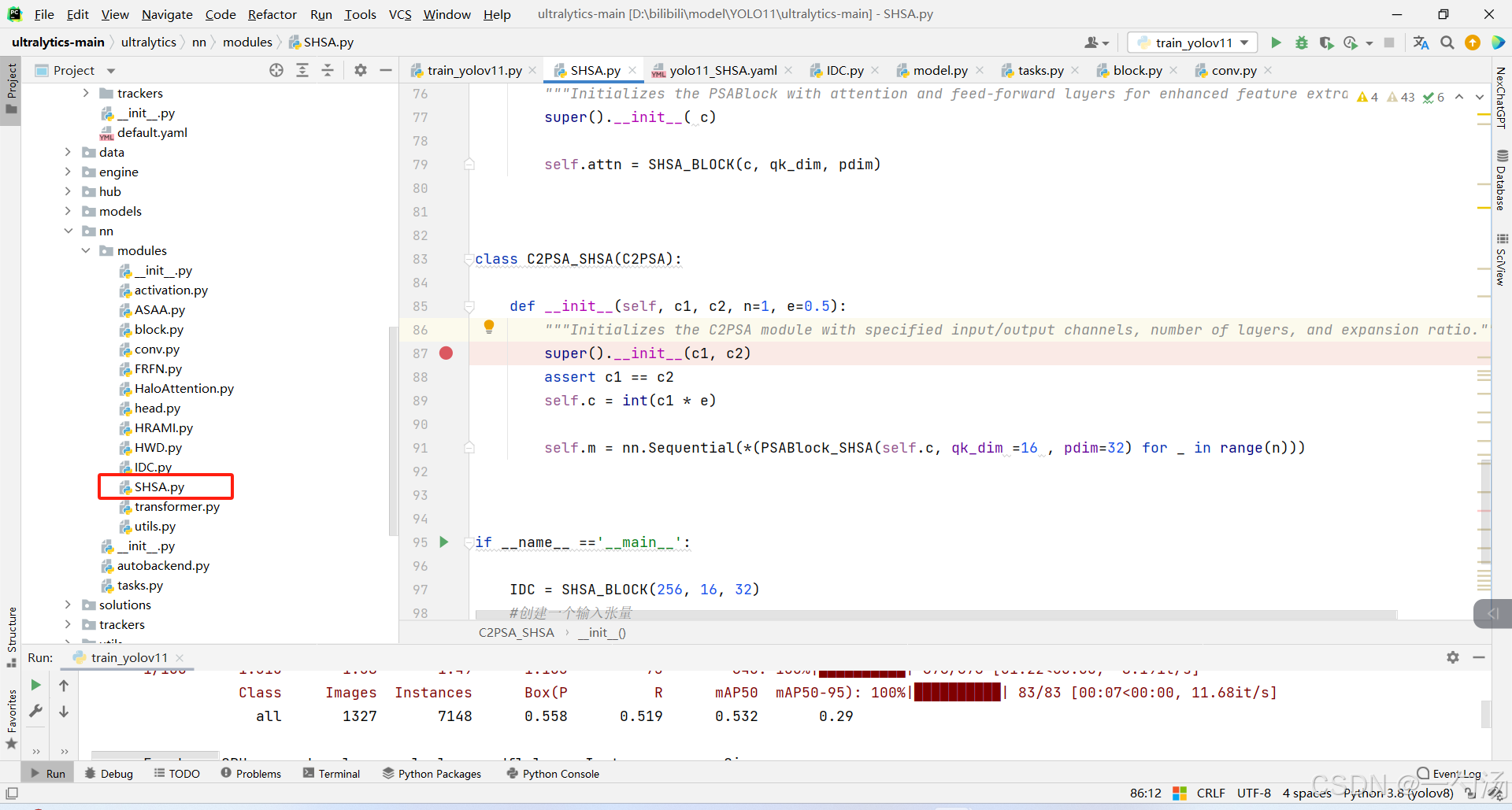
第一: 将下面的核心代码复制到D:\bilibili\model\YOLO11\ultralytics-main\ultralytics\nn路径下,如下图所示。
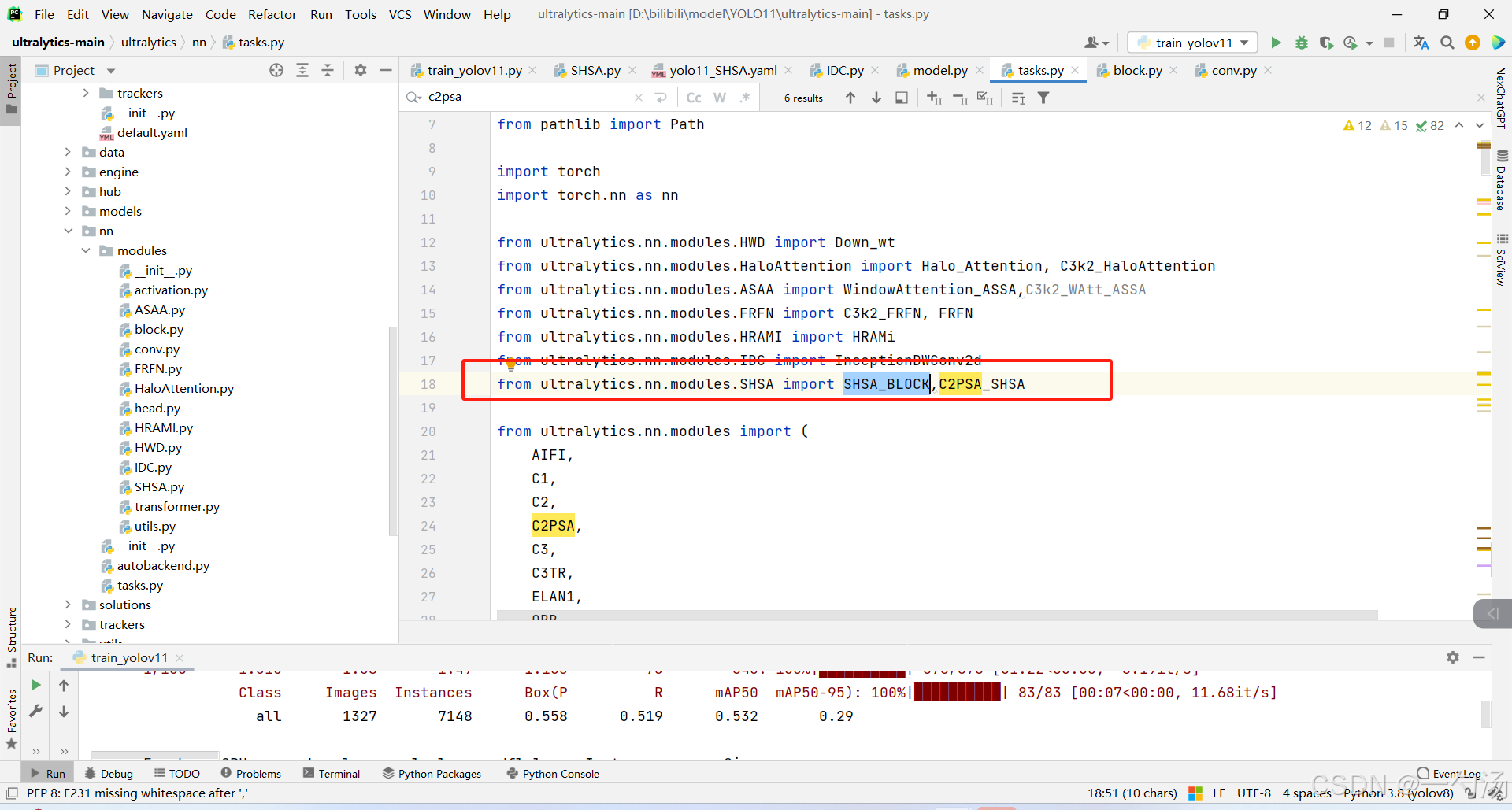
第二:在task.py中导入SHSA包
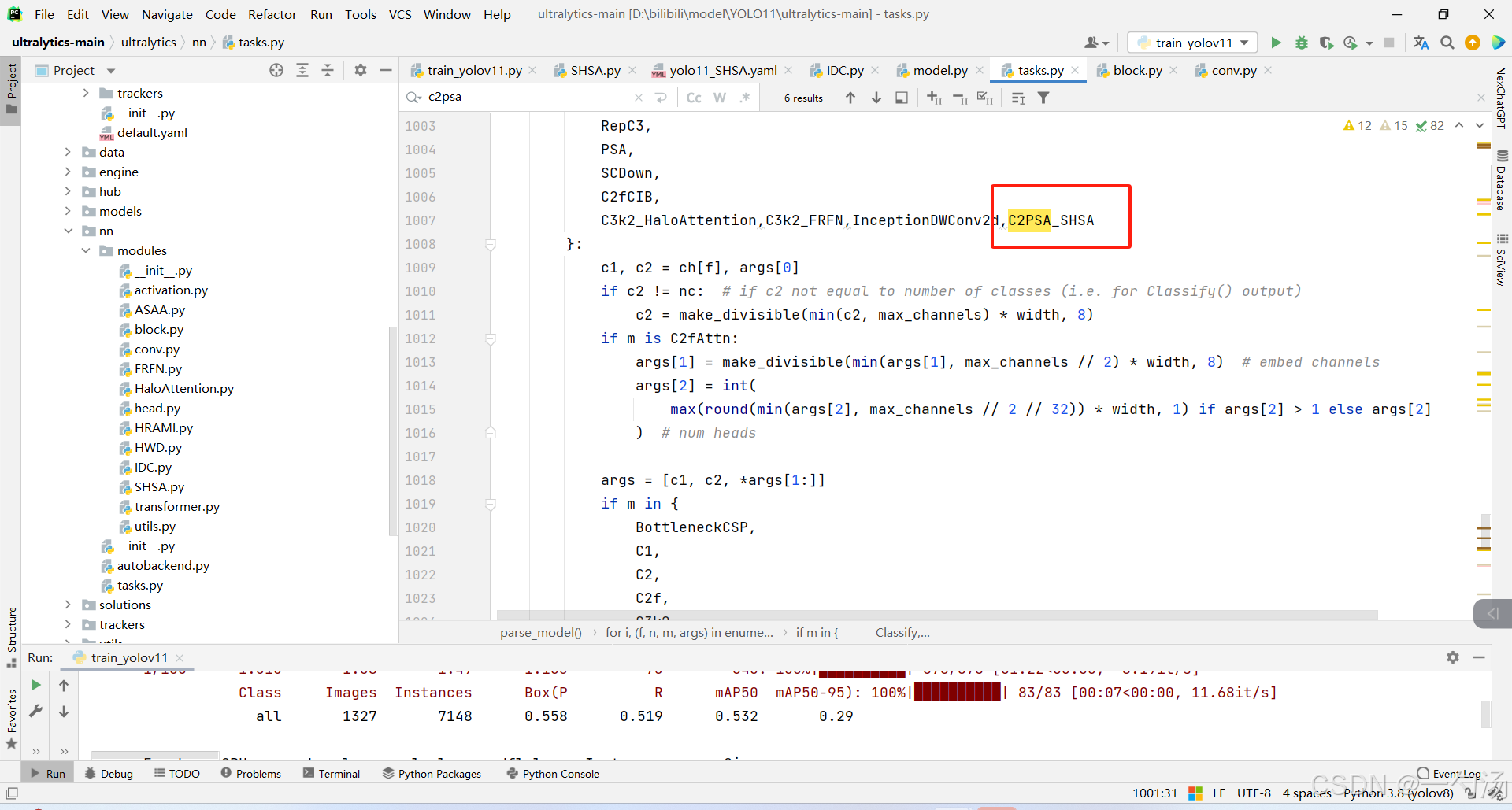
第三:在task.py中的模型配置部分下面代码
第四:将模型配置文件复制到YOLOV11.YAMY文件中
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
# YOLO11n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
- [-1, 2, C2PSA_SHSA, [1024]] # 10
# YOLO11n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
第五:运行成功
from ultralytics.models import NAS, RTDETR, SAM, YOLO, FastSAM, YOLOWorld
if __name__=="__main__":
# 使用自己的YOLOv11.yamy文件搭建模型并加载预训练权重训练模型
model = YOLO(r"D:\bilibili\model\YOLO11\ultralytics-main\ultralytics\cfg\models\11\yolo11_SHSA.yaml")\
.load(r'D:\bilibili\model\YOLO11\ultralytics-main\yolo11n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights
results = model.train(data=r'D:\bilibili\model\ultralytics-main\ultralytics\cfg\datasets\VOC_my.yaml',
epochs=100, imgsz=640, batch=8)