对于http请求,无外乎都是get、post、put、delete。常用的也就那么几个。但刚学java的我还是记下他们的写法吧。虽然在工作中经常会用上,但也给初学的兄弟们更快上手吧。
get
//@PathVariable 注解就是在地址中/参数,在post put del 中一样通用。下面就不做讲解了
//String name , int age 就是 ? 后面的参数了
@GetMapping("/testObjFun/{id}/{code}")
public String testObjFun(String name , int age , @PathVariable String id , @PathVariable String code){
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(code);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "a";
}
post
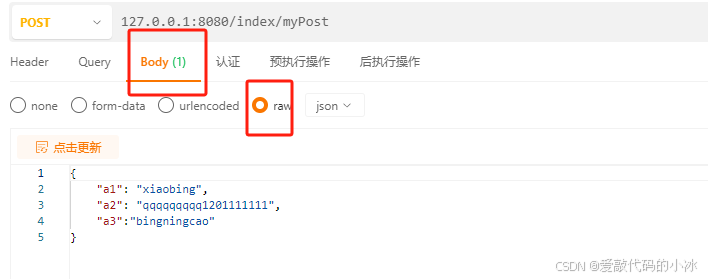
其实,在post中,是有两种方式的,一种是表单提交,另一种是截荷提交。
表单提交就是我们正常 form提交,而截何提交,则是 formdata的提交。
截荷提交
//截荷提交
//TestObject 是实体类,是需要另外定义的,如下所示
@PostMapping("/myPost")
public String myPost(@RequestBody TestObject testObject){
System.out.println(testObject);
String a1 = testObject.getA1();
String a2 = testObject.getA2();
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println(a2);
return "aa";
}
//实体类,就像我们定义数据表类一样的意思
package com.bnc.s12.common;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Configurable;
@Configurable
public class TestObject {
private String a1;
public String a2;
private String a3;
public String getA1() {
return a1;
}
public String getA2() {
return a2;
}
public String getA3() {
return a3;
}
public void setA1(String a1) {
this.a1 = a1;
}
public void setA2(String a2) {
this.a2 = a2;
}
public void setA3(String a3) {
this.a3 = a3;
}
}
在前端的代码大概是如下这样的
//这儿我只是写个例子,字段是需要跟实体类的字段要一致的
let data = new FormData();
data.addend("name" , "xiaobing");
data.append("age" , 15)
表单提交
@PostMapping("/myPost")
public String myPost(@RequestParam String name , @RequestParam String id , @RequestParam String code){
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(code);
System.out.println(name);
return "aa";
}
put 和 delete 都是一个意思,这儿我就不写了。获取前端的数据,无非就是把数据拿过来。也就是这么几种