前言
OpenCV4.1.2 feature2d模块 ——
学习使用OpenCV Contrib modules的SIFT、SURF特征检测,
学习暴力匹配与FLANN匹配。
特征检测
特征检测实际上包含两个步骤:检测和描述。
检测是指将特征点的位置、方向等信息检测出来,描述指的是将这些特征点信息加以描述,形成128维或64维的特征描述子,以用于后续匹配。
OpenCV实现的特征检测接口包括detect()、compute()和detectAndCompute()函数,分别实现特征检测、特征描述,以及检测并描述一步到位。
SIFT和SURF特征检测步骤也大致相似,首先将图像转化为灰度图,然后创建一个对象,接着调用特征检测函数。使用drawKeyPoint()函数可以将检测到的特征点画出来。
SIFT
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, "{@input | box.png | input image}");
Mat src = imread(samples::findFile(parser.get<String>("@input")), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (src.empty())
{
cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl;
cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <Input image>" << endl;
return -1;
}
//-- SIFT检测与描述
Ptr<SIFT> detector = SIFT::create();
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
Mat descriptors;
detector->detectAndCompute(src, noArray(), keypoints, descriptors);
cout << keypoints.size() << endl;
cout << descriptors.size() << endl;
//-- 画出特征点
Mat img_keypoints;
drawKeypoints(src, keypoints, img_keypoints);
//-- Show detected (drawn) keypoints
imshow("SIFT Keypoints", img_keypoints);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatured contrib module to be run." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
keypoints和descriptors的大小:
603
[128 x 603]
SURF
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, "{@input | box.png | input image}");
Mat src = imread(samples::findFile(parser.get<String>("@input")), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (src.empty())
{
cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl;
cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <Input image>" << endl;
return -1;
}
//-- SURF检测与描述,设置hessianThreshold为400
int minHessian = 400;
Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create(minHessian);
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
Mat descriptors;
detector->detectAndCompute(src, noArray(), keypoints, descriptors);
cout << keypoints.size() << endl;
cout << descriptors.size() << endl;
//-- 画出特征点
Mat img_keypoints;
drawKeypoints(src, keypoints, img_keypoints);
//-- Show detected (drawn) keypoints
imshow("SURF Keypoints", img_keypoints);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatured contrib module to be run." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
keypoints和descriptors的大小:
786
[64 x 786]
特征匹配
特征匹配有暴力匹配和FLANN匹配,其使用步骤大致相同:
- 首先使用SIFT或SURF对两幅图像进行特征检测
- 然后使用cv::DescriptorMatcher进行匹配
// 创建一个暴力匹配器
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::BRUTEFORCE);
// 创建一个FLANN BASED匹配器
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::FLANNBASED);
- 使用cv::drawMatches画出匹配连线
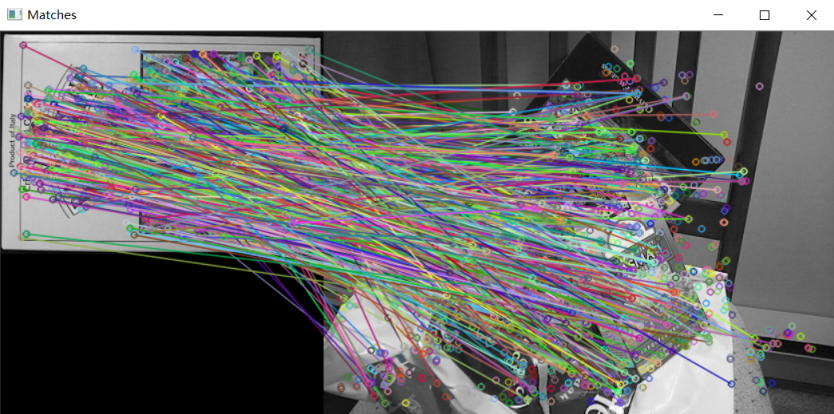
暴力匹配
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
const char* keys =
"{ help h | | Print help message. }"
"{ input1 | box.png | Path to input image 1. }"
"{ input2 | box_in_scene.png | Path to input image 2. }";
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys);
Mat img1 = imread(samples::findFile(parser.get<String>("input1")), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat img2 = imread(samples::findFile(parser.get<String>("input2")), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (img1.empty() || img2.empty())
{
cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl;
parser.printMessage();
return -1;
}
//-- 步骤1: 使用SURF检测关键点
int minHessian = 400;
Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create(minHessian);
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
detector->detectAndCompute(img1, noArray(), keypoints1, descriptors1);
detector->detectAndCompute(img2, noArray(), keypoints2, descriptors2);
//-- 步骤2: 使用暴力匹配器匹配描述子向量
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::BRUTEFORCE);
std::vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher->match(descriptors1, descriptors2, matches);
//-- 画出匹配
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches(img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, matches, img_matches);
//-- Show detected matches
imshow("Matches", img_matches);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatured contrib module to be run." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
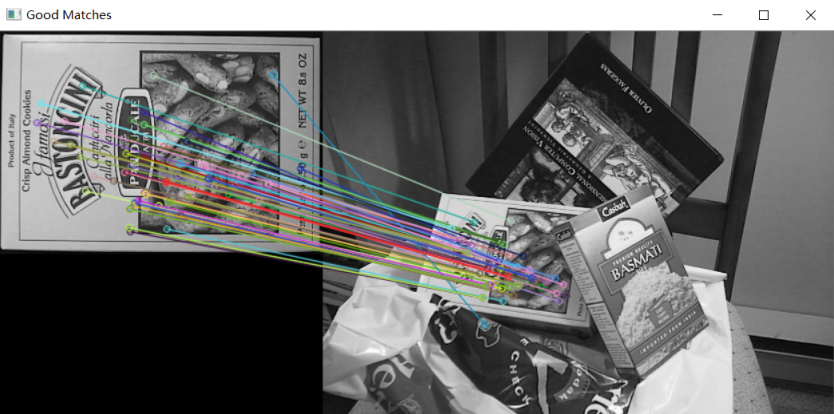
FLANN匹配
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
const char* keys =
"{ help h | | Print help message. }"
"{ input1 | box.png | Path to input image 1. }"
"{ input2 | box_in_scene.png | Path to input image 2. }";
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys);
Mat img1 = imread(samples::findFile(parser.get<String>("input1")), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat img2 = imread(samples::findFile(parser.get<String>("input2")), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (img1.empty() || img2.empty())
{
cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl;
parser.printMessage();
return -1;
}
//-- 步骤1: 使用SURF检测关键点
int minHessian = 400;
Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create(minHessian);
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
detector->detectAndCompute(img1, noArray(), keypoints1, descriptors1);
detector->detectAndCompute(img2, noArray(), keypoints2, descriptors2);
//-- 步骤2: 使用FLANN匹配器匹配描述子向量
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::FLANNBASED);
std::vector< std::vector<DMatch> > knn_matches;
matcher->knnMatch(descriptors1, descriptors2, knn_matches, 2);
//-- Filter matches using the Lowe's ratio test
const float ratio_thresh = 0.7f;
std::vector<DMatch> good_matches;
for (size_t i = 0; i < knn_matches.size(); i++)
{
if (knn_matches[i][0].distance < ratio_thresh * knn_matches[i][1].distance)
{
good_matches.push_back(knn_matches[i][0]);
}
}
//-- Draw matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches(img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1),
Scalar::all(-1), std::vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
//-- Show detected matches
imshow("Good Matches", img_matches);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatured contrib module to be run." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
参考
https://docs.opencv.org/4.1.2/d7/d66/tutorial_feature_detection.html.
https://docs.opencv.org/4.1.2/d5/dde/tutorial_feature_description.html.
https://docs.opencv.org/4.1.2/d5/d6f/tutorial_feature_flann_matcher.html.