A - Alice and Books
显然,一定会拿到最后一个,接下来只需要枚举另一组的最大编号即可。
// Problem: A. Alice and Books
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 953 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1978/problem/A
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){
cin >> a[i];
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n - 1; i ++){
ans = max(ans , a[i] + a[n - 1]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B - New Bakery
构建关于k的函数,发现是一个等差数列,因此直接贪心的取最大值即可。
// Problem: B. New Bakery
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 953 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1978/problem/B
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve()
{
int n , a , b;;
cin >> n >> a >> b;
int ans = a * n;
int pre = 0;
int k = b - a;
if(k > 0){
int l = k , r = k - n + 1;
r = max(0LL , r);
ans += ((l + r) * (l - r + 1)) / 2;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C - Manhattan Permutations
发现无论怎么变化,曼哈顿值一定是偶数,接下来考虑什么情况下最大:手操一下很快发现将整个排列降序一下后的曼哈顿值最大,接下来只要不大于这个的偶数就一定能被构造出来
// Problem: C. Manhattan Permutations
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 953 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1978/problem/C
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve()
{
int n , k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int>ans(n + 5 , 0);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
ans[i] = i;
}
if(k & 1){
cout << "No\n";
}
else{
int l = 1 , r = n;
while(k > 0 && l < r){
if(k > 2 * (r - l)){
swap(ans[l] , ans[r]);
k -= 2 * (r - l);
r--;
l++;
}
else{
while(k != 2 * (r - l)){
r--;
}
swap(ans[l] , ans[r]);
k = 0;
}
}
if(k > 0){
cout << "No\n";
}
else{
cout <<"Yes\n";
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D - Elections
思路:分类讨论,首先若后面的选举人存在比当前选举人票数多的情况,那么必然是将前面所有的人全部排除,然后再看票数是否大于后面最大的票,若还是小,则将后面票数最多的人也排除掉。
相反,若后面不存在比当前选举人票数多的情况,那么需要看前面是否存在票数比它多的,若前面存在票数比它多的,那么也必然需要将前面所有的人都排除。
接下来考虑前面后面都不存在比它多的,可以观察到:若第一个人加上c以后比当前选举人多了,那么这个人就必须被删掉,以此类推..直到区间内不存在比它票数还要多的人为止。因此对于第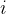
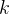

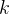
总上,我们需要统计的是,删去前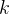

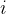
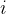
![[1,i-1]](/image/aHR0cHM6Ly9sYXRleC5jc2RuLm5ldC9lcT8lNUIxJTJDaS0xJTVE)
// Problem: D. Elections
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 953 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1978/problem/D
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m , k;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
//ST表
//倍增实现(求解区间最小值/最大值问题)
int Max[N][21];
int Min[N][21];
vector<int>val(N + 5 , 0);
struct ST{
void init(){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
Max[i][0] = val[i];
Min[i][0] = val[i];
}
}
void work(){
for(int j = 1;j <= 21;j++)
for(int i = 1;i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n ; i++){
Max[i][j] = max(Max[i][j - 1] , Max[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
Min[i][j] = min(Min[i][j - 1] , Min[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
int QueryMax(int l,int r)
{
int k = log2(r-l+1);
return max(Max[l][k],Max[r-(1<<k)+1][k]);//把拆出来的区间分别取最值
}
int QueryMin(int l , int r){
int k = log2(r-l+1);
return min(Min[l][k],Min[r-(1<<k)+1][k]);//把拆出来的区间分别取最值
}
};
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int>suf(n + 5 , 0);
vector<int>S(n + 5 , 0);
vector<int>pre(n + 5 , 0);
vector<int>pre_num(n + 5 , 0);
a[n + 1] = 0;
a[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i ++){
cin >> a[i];
S[i] = S[i - 1] + a[i];
pre[i] = max(pre[i - 1] , a[i - 1]);
if(pre[i] == pre[i - 1]){
pre_num[i] = pre_num[i - 1];
}
else{
pre_num[i] = i - 1;
}
}
for(int i = n ; i >= 1;i --){
suf[i] = max(suf[i + 1] , a[i + 1]);
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
val[i] = a[i] + k + S[i - 1];
}
ST st;
st.init();
st.work();
auto check =[&](int l , int r){
return st.QueryMin(l , r);
};
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
int nex = suf[i];
if(i == 1){
if(a[i] + k < suf[i]){
cout << 1 << " ";
}
else{
cout << 0 << " ";
}
continue;
}
if(nex > a[i]){
if(val[i] >= nex)
cout << (i - 1) << " ";
else
cout << 1 + (i - 1) << " ";
}
else{
int l = 1 , r = i - 1;
if(pre[i] >= a[i]){
cout << r << " ";
continue;
}
if(check(l , r) >= a[i]){
cout << i - 1 << " ";
}
else{
while(l < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(r - l <= 2){
for(int j = l ; j <= r ; j++){
if(val[j] < a[i]){
l = j;
r = j - 1;
break;
}
}
break;
}
if(check(l , mid) < a[i]){
r = mid;
}
else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
cout << l - 1 << " ";
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E - Computing Machine
思路:很经典的将区间操作转化成端点操作,首先考虑全部修改,然后可以发现对比于区间修改而言,只有区间最靠左的两个数跟区间最靠右的两个数可能会不一样,因此只需要关注区间的左右四个点即可,若区间长度小于4的我们直接特判。
// Problem: E. Computing Machine
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 953 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1978/problem/E
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
string s1 , s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
s1 = "#" + s1;
s2 = "#" + s2;
string tmp_s2 = s2;
string tmp_s1 = s1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n - 2 ; i ++){
if(s1[i] == s1[i + 2] && s1[i] == '0'){
tmp_s2[i + 1] = '1';
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n - 2 ; i ++){
if(tmp_s2[i] == tmp_s2[i + 2] && tmp_s2[i] == '1'){
tmp_s1[i + 1] = '1';
}
}
vector<int>pre(n + 5 , 0);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
pre[i] = pre[i - 1] + (tmp_s1[i] == '1');
}
int q;
cin >> q;
while(q--){
int l , r;
cin >> l >> r;
int ans = pre[r] - pre[l - 1];
if(r - l <= 6){
string ts1 = s1.substr(l , (r - l + 1));
string ts2 = s2.substr(l , (r - l + 1));
ans = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i <= r - l - 2 ; i ++){
if(ts1[i] == ts1[i + 2] && ts1[i] == '0'){
ts2[i + 1] = '1';
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i <= r - l - 2 ; i ++){
if(ts2[i] == ts2[i + 2] && ts2[i] == '1'){
ts1[i + 1] = '1';
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i <= r - l ; i ++){
if(ts1[i] == '1'){
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
continue;
}
//判断左边
if(l == 1){
}
else if(l == 2){
if(tmp_s1[l] == '1' && s1[l] == '0'){
ans--;
}
if(l + 1 <= n && tmp_s1[l + 1] == '1' && s1[l + 1] == '0' && s2[l] == '0'){
ans--;
}
}
else{
if(tmp_s1[l] == '1' && s1[l] == '0'){
ans--;
}
if(l + 1 <= n && tmp_s1[l + 1] == '1' && s1[l + 1] == '0' && s2[l] == '0'){
ans--;
}
}
if(r == n){
}
else if(r == n - 1){
if(tmp_s1[r] == '1' && s1[r] == '0'){
ans--;
}
if(r - 1 >= 1 && tmp_s1[r - 1] == '1' && s1[r - 1] == '0' && s2[r] == '0'){
ans--;
}
}
else{
if(tmp_s1[r] == '1' && s1[r] == '0'){
ans--;
}
if(r - 1 >= 1 && tmp_s1[r - 1] == '1' && s1[r - 1] == '0' && s2[r] == '0'){
ans--;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1978F - Large Graph
题意:
注意到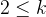
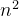
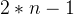
然后考虑每一列之间是否连通,由于只需要关心gcd是否大于1,所以我们只需要关注当前列有一个素因子与前面k列相同即可。于是我们只需要维护k列的素因子的情况,然后用并查集来维护连通块即可。特别的,由于只需要一条边即可连通,因此我们只需要记录每个素因子最后出现的位置即可。
// Problem: F. Large Graph
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 953 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1978/F
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 4000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 1e06+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
std::vector<int> minp, primes;
void sieve(int n) {
minp.assign(n + 1, 0);
primes.clear();
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (minp[i] == 0) {
minp[i] = i;
primes.push_back(i);
}
for (auto p : primes) {
if (i * p > n) {
break;
}
minp[i * p] = p;
if (p == minp[i]) {
break;
}
}
}
}
struct DSU {
std::vector<int> f, siz;
DSU() {}
DSU(int n) {
init(n);
}
void init(int n) {
f.resize(n);
std::iota(f.begin(), f.end(), 0);
siz.assign(n, 1);
}
int find(int x) {
while (x != f[x]) {
x = f[x] = f[f[x]];
}
return x;
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) {
return false;
}
siz[x] += siz[y];
f[y] = x;
return true;
}
int size(int x) {
return siz[find(x)];
}
};
vector<int>mp(N + 5 , 0);
void solve()
{
int n , k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int>pri[n + 5];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){
int x = a[i];
for(auto it : primes){
if(x % it == 0){
pri[i].pb(mp[it]);
while(x % it == 0){
x /= it;
}
}
if(x / it < it){
break;
}
}
if(x > 1){
pri[i].pb(mp[x]);
}
}
vector<int>tmp(2 * n + 5 , 0);
LL ans = 2 * n - 1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++){
tmp[i] = i + 1;
}
tmp[n - 1] = 0;
for(int i = n ; i < 2 * n - 1 ; i ++){
tmp[i] = i - n + 1;
}
DSU dsu(2 * n + 5);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 2 * n - 1 ; i ++){
if(a[tmp[i]] == 1){
if(i <= n - 1){
ans += i;
}
else{
ans += 2 * n - 2 - i;
}
continue;
}
}
vector<int>pos(90000 , -1);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 2 * n - 1 ; i ++){
if(i > k){
for(auto it : pri[tmp[i - k - 1]]){
if(pos[it] == i - k - 1){
pos[it] = -1;
}
}
}
if(a[tmp[i]] == 1){
continue;
}
for(auto it : pri[tmp[i]]){
if(pos[it] != -1){
if(!dsu.same(i , pos[it])) ans--;
dsu.merge(i , pos[it]);
}
pos[it] = i;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
sieve(N);
int idx = 1;
for(auto it : primes){
mp[it] = idx++;
}
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}